[botany lec] spores and cones
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Sporophylls
Modified leaves that produce sporangia (which become spores)
Homosporous plants
Most ferns and its relatives (except Selaginella)
Heterosporous plants
All seed plants (angiosperm and gymnosperms) and some seedless plants.
Spores
something that is present in bryophytes (Moss, liverworts, hornworts) and ferns and its relatives
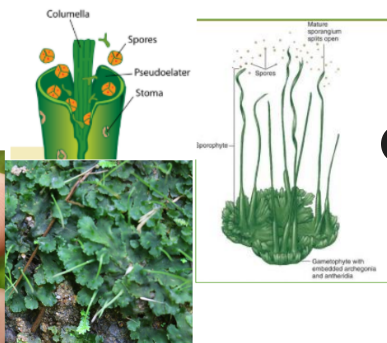
Calyptra
a maternal structure that protects the sporophyte offspring from dehydration, and positively impacts sporophyte survival and fitness in mosses.
Capsule
part of the moss that stores the spores
Operculum
part of the moss that is a cap-like covering that detaches to release spores
Leafy and Thalloid liverworts
two basic groups of liverworts
leafy liverworts
Group of liverworts that resemble a moss; its gametophyte consists of thin blades on a slender stipe
Thalloid liverworts
In this group of liverwort, gametophyte is flat and ribbon-like or heart-shaped and bilaterally symmetrical - this shape is called a thallus
Gemmae cups
small, intact, complete pieces of plant that are produced in a cup on the surface of the thallus and develop into gametophytes through asexual reproduction
Pseudoelaters
surround the spores and help propel them further in the environment
Columella
small column of tissue
Ferns
mostly homosporous, reproduce using spores contained in sori (sorus), Lightweight and easily disperse by water and wind. Protected inside a sporangium
Sori
clustered/aggregate sporangia, contains and produce spores
Indusium
thin membranous covering a sorus
Sporangium
an enclosure in which spores are formed.
Sporophylls
sporangium-bearing leaves
Strobili
terminal cone-like structures which bears the sporangium containing sporocytes
Cones
this is found in most species of gymnosperms
Microspores (male gametophytes) and megaspores (female gametophytes)
Kinds of spores produced by gymnosperms
Pollen cones (male strobili)
consists of papery or membranous scales called microsporophylls, arranged in spiral or whorls.
Microsporangia
develop in pairs towards the bases of the scales; it -houses the microsporocytes which undergo meiosis to produce microspores which eventually develop into pollen
Pollen grain
immature male gametophyte; produces pollen tube which slowly grows to the nucellus where the archegonia develop
Megaspores
are produced in megasporangia located within ovules at the bases of the seed cone scales, called megasporophylls.
Megasporangium
Each ovule has within it a ________ containing the nucellus and a single megasporocyte
Integument
thick layers surrounding the ovule, one of which becomes the seed coat
Micropyle
tubular channel or pore
Nucellus
food source of the growing gametophyte
hornwort
what kind of liverwort is this?