Lecture 13: Language And Referential Communication
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is referential communication?
Vocalization that refer to an object or event in the world that is external to the signaler
When an animal uses a specific signal (like a sound or movement) to refer to something in the environment, like food or a predator. The signal gives information that helps others respond appropriately
Referential vocalizations can be thought of as having meaning
What is the alternative of referential communication?
The alternative to referential vocalizations would be a vocalization that communicates the signalers internal state rather than referring to the external world (e.g. a sigh is not referential, but the word sigh is referential because it refers to sound produced by the act of sighing)
Why do animals make alarm calls?
Many animals produce vocalizations in the presence of predators. These have been dubbed alarm calls because other individuals react to them and will take evasive action to avoid a predator
What do vervet calls have?
They have semantic meaning
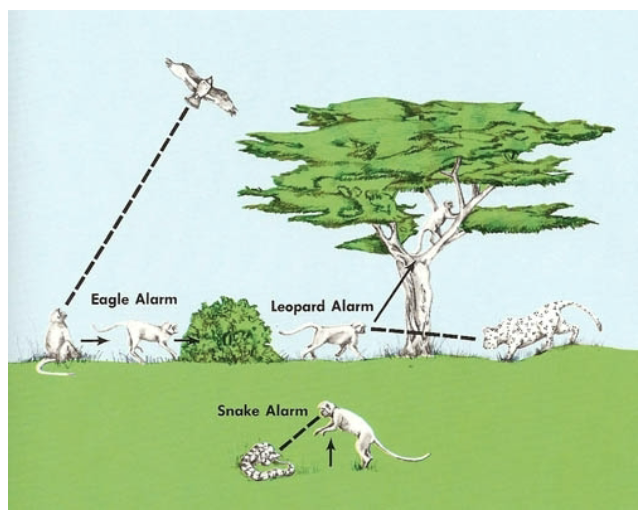
Three different calls for three different scenarios.
The calls elicit appropriate behavior for each predator
Eagle → hide in bush
Leopard → high branches of tree
Snake → Standard and look
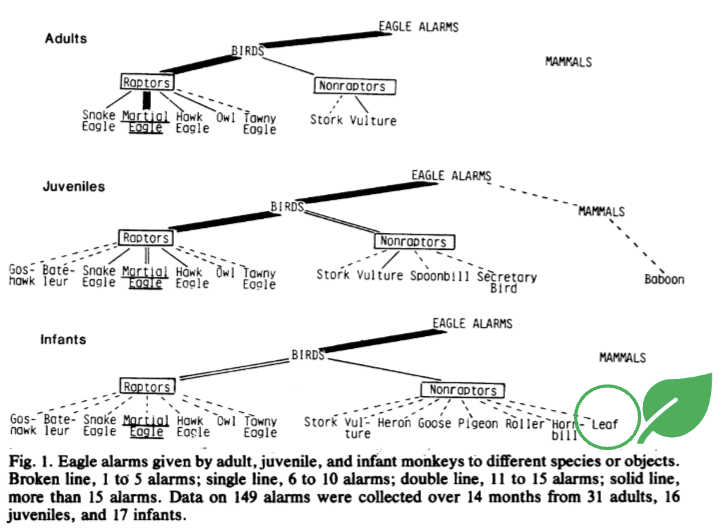
In regards to vervet calls, what happens as they develop?
This data shows how over development, vervets become much more specific to call to just the main predator. Infants ‘get’ that it is for a flying object, but take time to be good eagle-spotters
What does alarm call production show?
Alarm calls production shows elements of innate production and learning the context of use
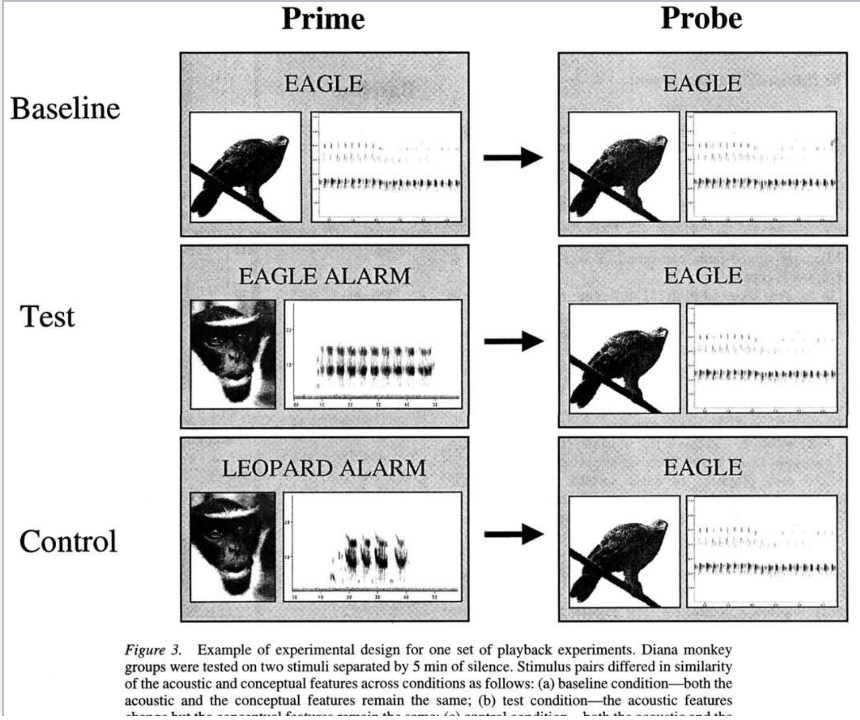
Describe the study design in order to determine if animals respond based on the sound or the meaning for Diana monkeys
Prime with one sound, which is played repeatedly (animals habituate)
Test with the probe sound – do they respond?
Baseline: Monkeys hear an eagle call repeatedly, then are tested with the same eagle call.
Test: Monkeys hear an eagle alarm call from another monkey and then are tested with an eagle call. If they already associate the alarm call with eagles, they might not react much to the eagle call.
Control: Monkeys hear a leopard alarm call and then are tested with an eagle call. Since leopards and eagles are different threats, if monkeys react strongly to the eagle call, it suggests they weren't expecting it based on the previous sound.
What were the results with Diana monkeys?
No responses to same sound a second time
No response when alarm and sound are for same animal
Increased response when new threat
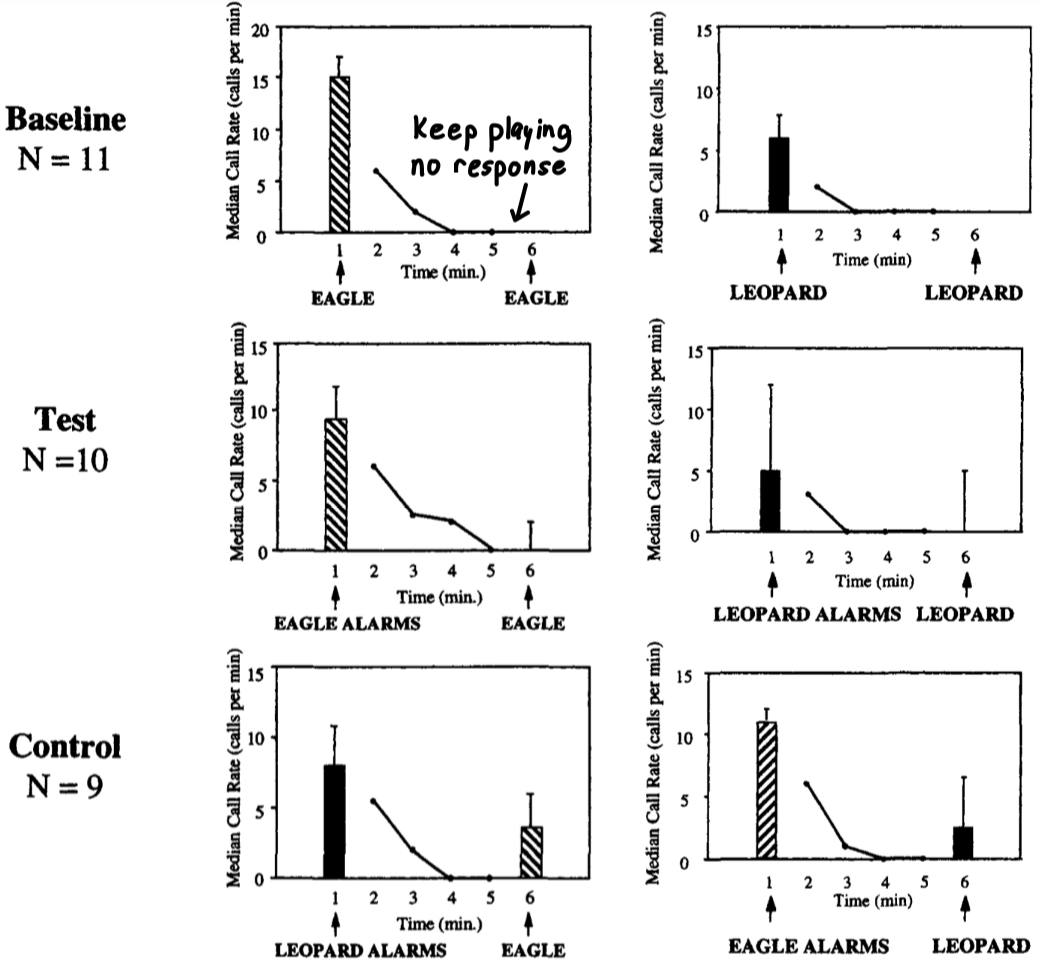
What was the experiment with Diana monkeys called?
This type of experiment is called habituation-dishabituation
What do young Diana monkeys learn to do to predators?
Young monkeys learn to categorize predators based on social learning and alarm calls
Young monkeys are exposed to a novel ambiguous predator
They are “told” it is either a snake or leopard based on hearing an alarm call
How do they categorize it in a future experience – treat as a snake or leopard?
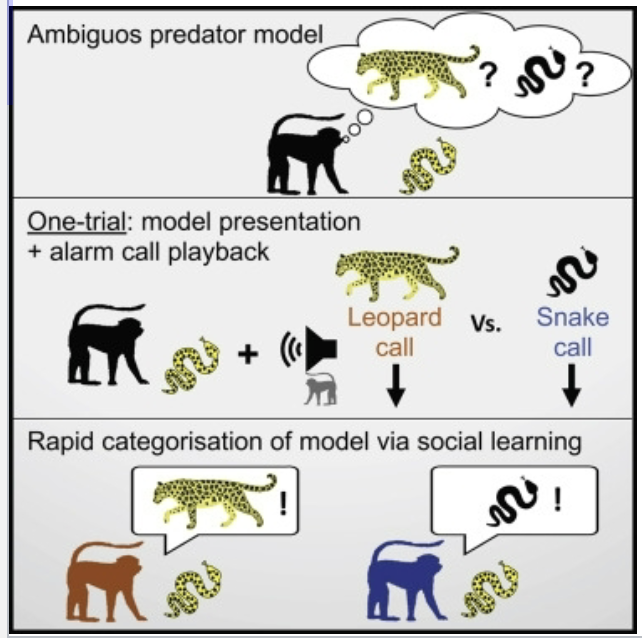
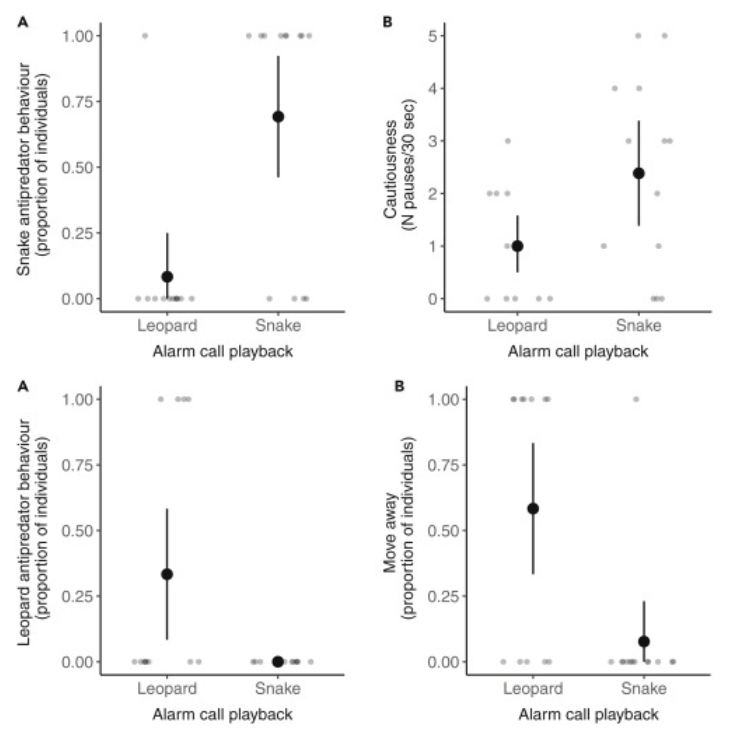
What were the results of using an ambiguous predator with Diana monkeys?
Monkeys learned it was either a snake or leopard
Top row: snake antipredatory behavior based on their initial experience
Bottom row: leopard antipredatory behavior base on their initial experience
What is special about Meerkat communication?
They have calls that tell if a predator is moving (i.e., “be on alert”)
They have calls that describe the level of threat – low to high
If monkeys have “nouns”, one could argue meerkats have a rudimentary form of verbs and adjectives too
What can honeybees communicate?
The location of food using a dance rather than a vocalization
If we record a honeybee’s waggle dances, what can we understand?
By recording waggle dances we can understand where bees are foraging without having to actually track them. Its like having their flight plans provided
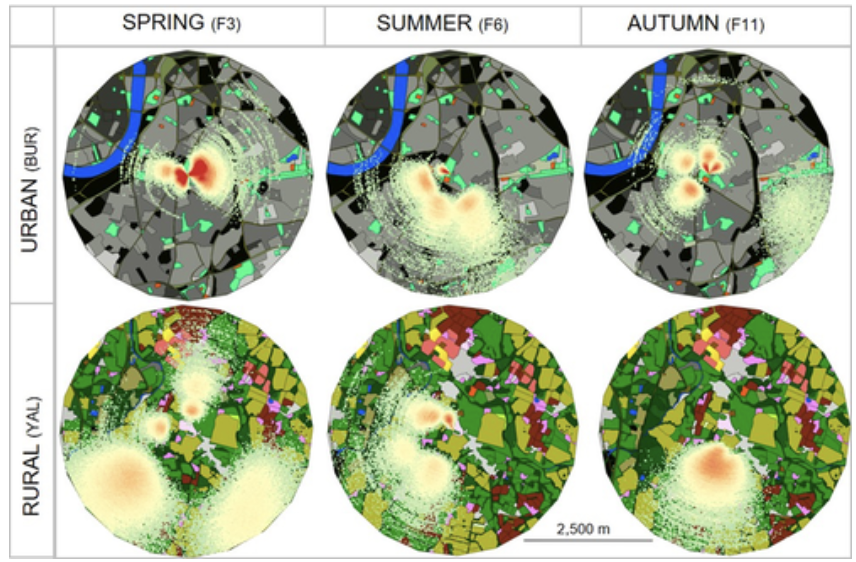
What was discovered between food searching in urban vs rural bees?
Compared dances in 20 colonies in London and rural areas near in the same general region. The goal is to compare foraging behavior of bees in different locations
Hive is at the center of the radial plots
Redder spots are where bees danced to the most
Foraging is closer and more concentrated in urban areas
What happens if a honeybee does a bad dance location?
Conditions may change while the dancer is advertising. Of particular concern is predation
Buzz runs tell others to stop
What does bee cognition outstrip?
Their communication
Bees understand color and flavor, but they don’t communicate about what flowers are in bloom
Bees can understand abstract concepts such as same v. different, but such sophisticated ideas are not in their ‘language’
What are the hypothesis for whether non-human animals can use language?
Humans are unique in language capacity
Other species can use language if reared in the right environment
What are the two major differences between humans and other species?
We grow up in an environment in which others are using language
We have a vocal apparatus that allows for the production of human language sounds
What did ape language projects involve?
Multiple apes have been raised by humans and attempted to be taught versions of sign language or pictographic communication