Week 1 - recap
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what data is categorical?
nominal data
what data is discrete/continuous
ordinal, interval, ratio
nominal data
numbers or names as labels, no numerical relationship between values e.g. gender, religion
ordinal data
organised by rank → values represent true numerical relationships, but intervals between values may not be equal → e.g. race position, likert scale ratings
interval data
true numerical relationships and intervals between values are equal → NO true 0 point e.g. temperature
ratio data
true numerical relationships, equal intervals and true 0 point e.g. height or distance
when would you use a mean?
discrete or continuous data which is normally distributed
when would you use a median
discrete or continuous data which is not normally distributed
when would you use a mode
categorical data
what test of difference would you use for 1 IV with 2 levels (between & within pps)
between pps → independent t-test
within pps → paired t-test
what test of difference would you use for 1 IV with >2 levels (between and within)
between pps → 1-way ANOVA
within pps → 1-way repeated measures ANOVA
what test of difference would you use for 2IVs, between, within and mixed design
between pps → 2-way independent ANOVA
within pps → 2-way repeated measures ANOVA
mixed design → 2-way mixed ANOVA
True-experimental IVs
IVs are actively manipulated
random allocation is possible → can make claims about causality
Quasi-experimental IVs
IV reflects fixed characteristics
random allocation is not possible (so must be cautious about implying causality)
e.g. handedness (2 levels; left and right)
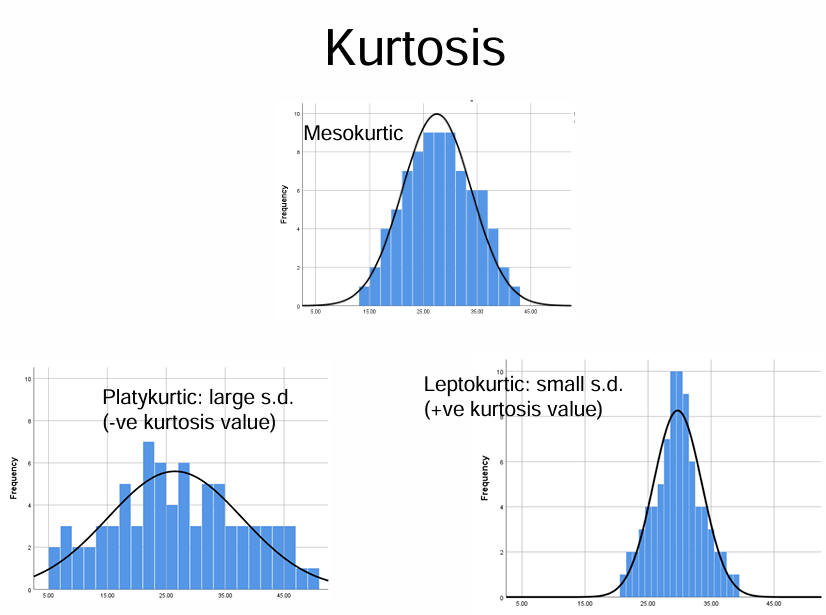
what does kurtosis represent - mesokurtic, platykurtuc, leptokurtic
kurtosis is the spread of standard deviation:
mesokurtic → standard s.d.
Platykurtic → large s.d., less concentrated, -ve kurtosis value
Leptokurtic → small s.d., more concentrated, positive kurtosis value
what is sampling error?
degree to which sample statistics differ from underlying population parameters
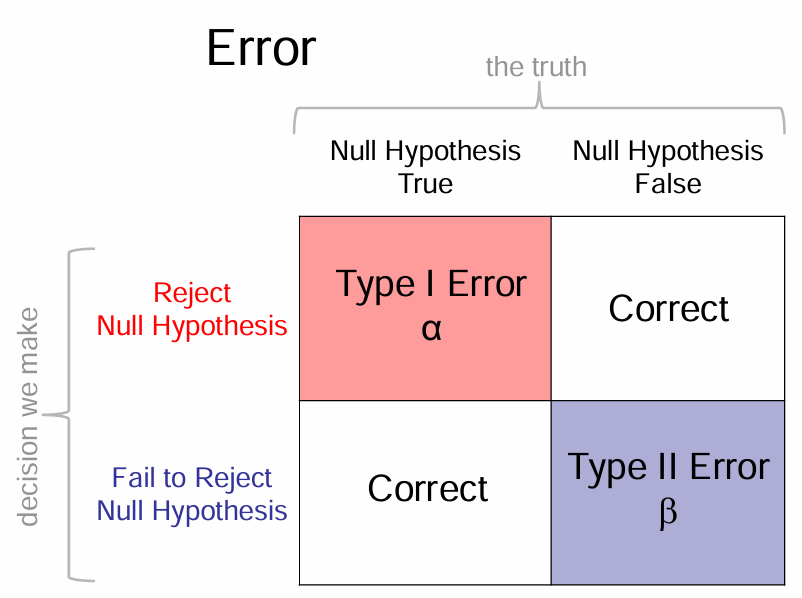
what is a type 1 and type 2 error?
type 1 = reject null when the null is true
type 2 = fail to reject the null when null is false