Alcohols (Basics)
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Alcohols (FG, shape, classification & physical properties)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Name the functional group that alcohols contain
Hydroxyl (-OH) group
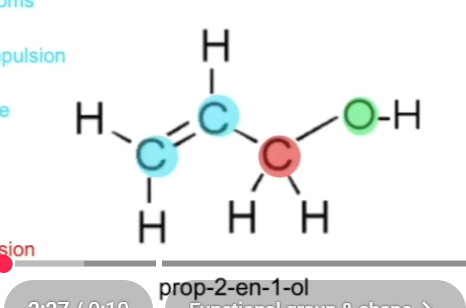
What is the bond angle and shape in alcohols? (Take prop-2-en-1-ol as an example)
3 electron regions around Carbon atoms in double bond (trigonal planar 120 deg)
4 electron regions around C atoms with single bond (Tetrahedral 109.5 deg)
4 electron regions around O atom with unequal repulsion (Non linear 104.5)
How can we classify alcohols?
Primary (1 deg), Secondary (2 deg) and Tertiary (3 deg)
What determines the classification (primary, secondary...) of an alcohol?
The number of carbon atoms or alkyl groups that are bonded directly to the -OH carbon.
Why do alcohols have higher boiling points than their corresponding alkanes?
Due to the presence of H-bonds between the OH groups
More energy is needed to overcome the intermolecular forces (Hydrogen bonding and Induced dipole forces)
How does the influence of hydrogen bonding in alcohol boiling point get less significant as the carbon chain gets longer in alkanes?
As carbon chain gets longer in alkanes, the number of electrons in the molecule increase
So induced dipole dipole forces get stronger
This narrows the gap in boiling point.
What has be the case for an alcohol to dissolve in water?
The energy released when H-bonds form between the alcohol and water
Has to overcome the intermolecular forces between the alcohol molecules
Difference in solubility in water between small and larger alcohols?
Small alcohols: infinitely soluble in water
Larger alcohols: Become less and less soluble due to strengthening induced dipole dipole forces between alcohol molecules