Lab F: Oral cavity Diagrams & digestion physiology
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
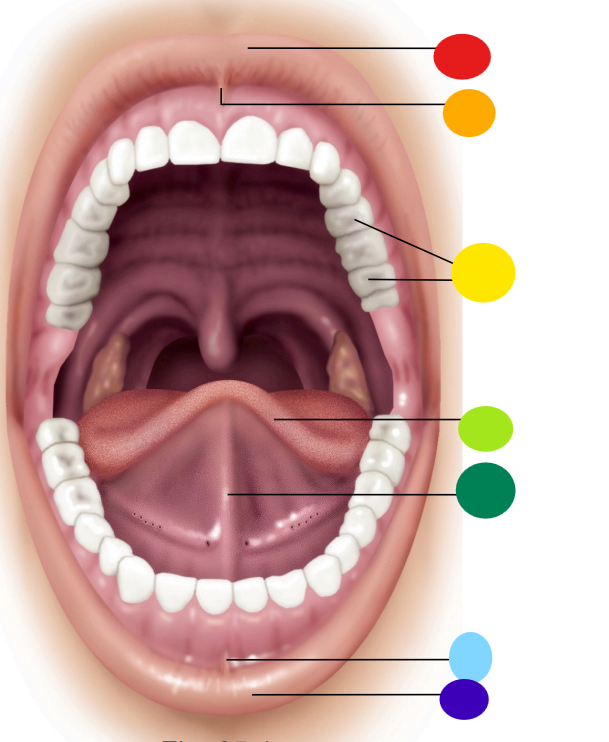
red
upper lip / labium
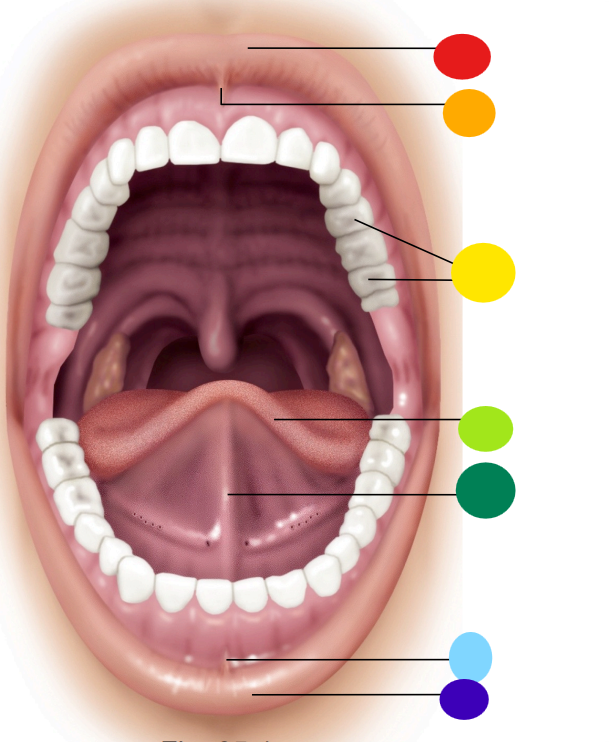
orange
superior labial frenulum
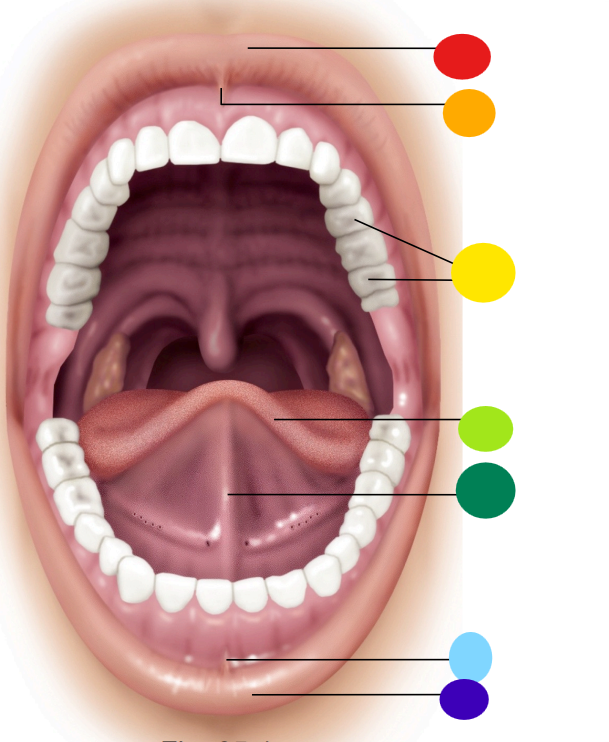
yellow
teeth
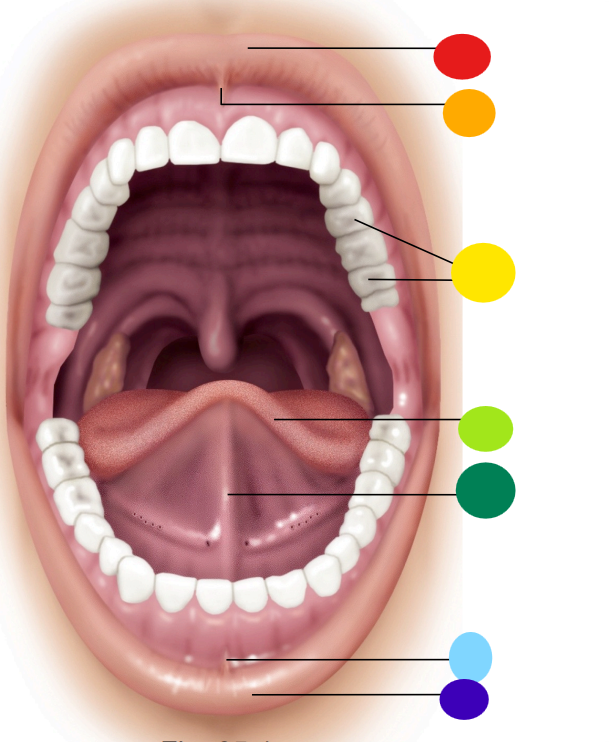
light green
tongue
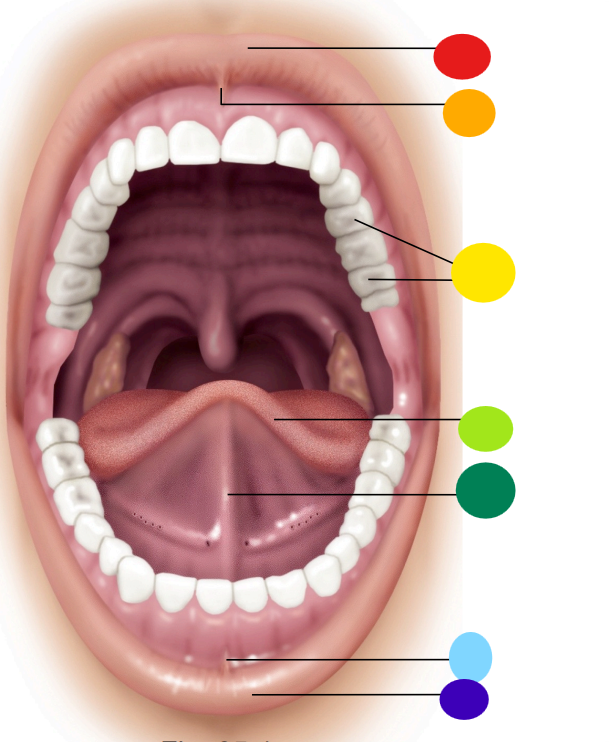
dark green
lingual frenulum
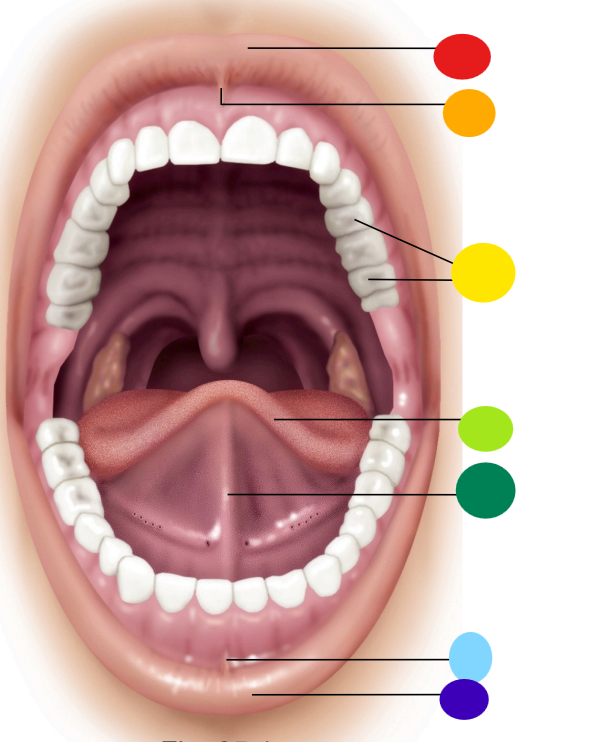
light blue
inferior labial frenulum
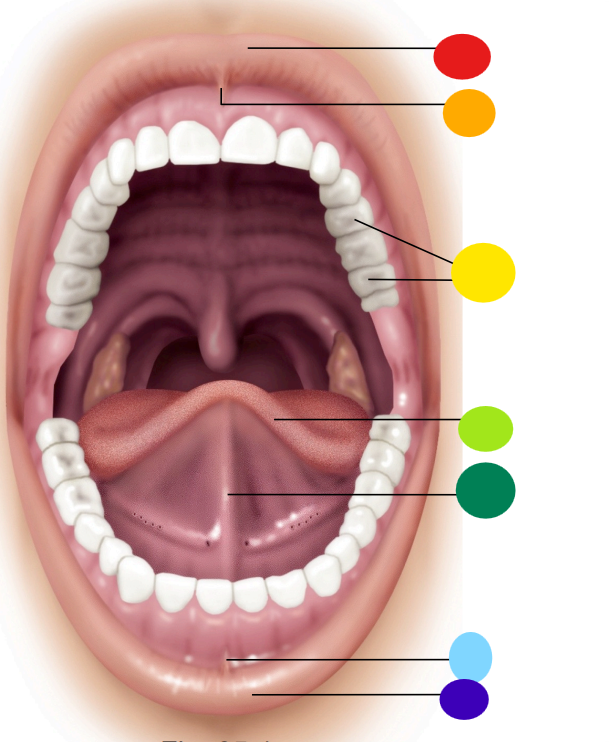
dark blue
lower lip / labium
what tissue type is the oral cavity lined with?
stratified squamous epithelium
What portions of the oral cavity are keratinized?
gingiva, dorsum of tongue, hard palate
What is the technical term for chewing?
mastication
What is the function of the frenula?
membranous folds of mucosa that stabilize the lips and tongue
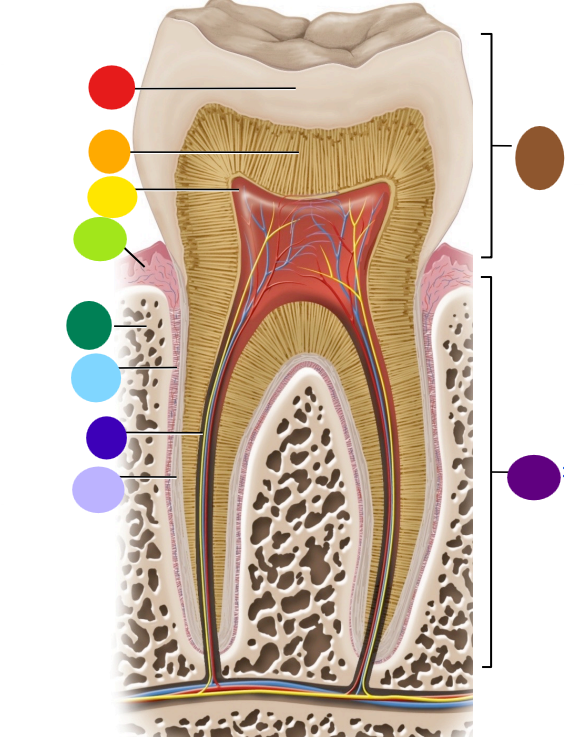
red
enamel
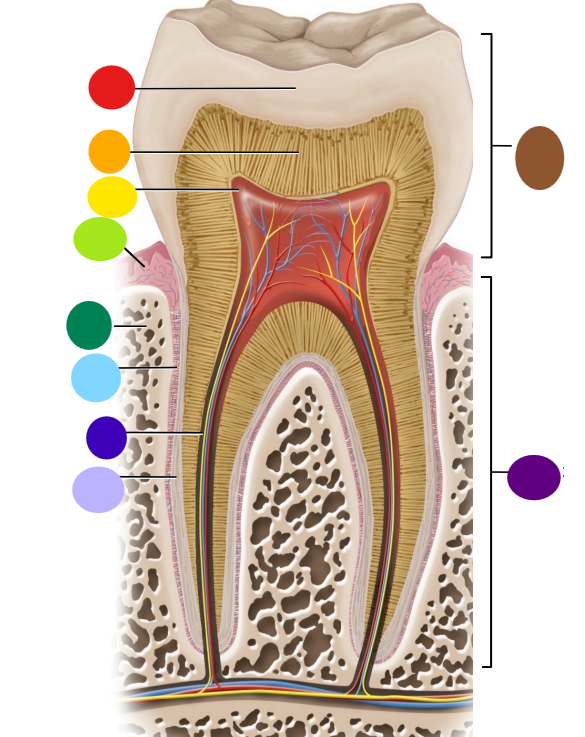
orange
dentin
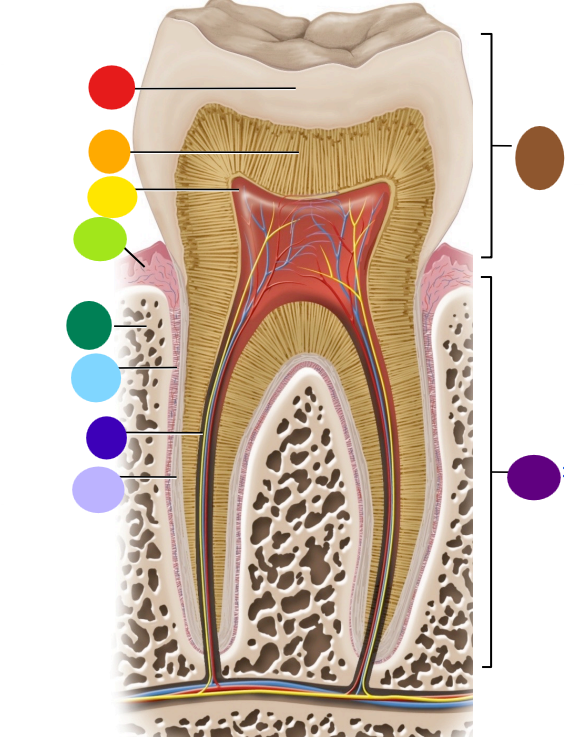
yellow
pulp cavity
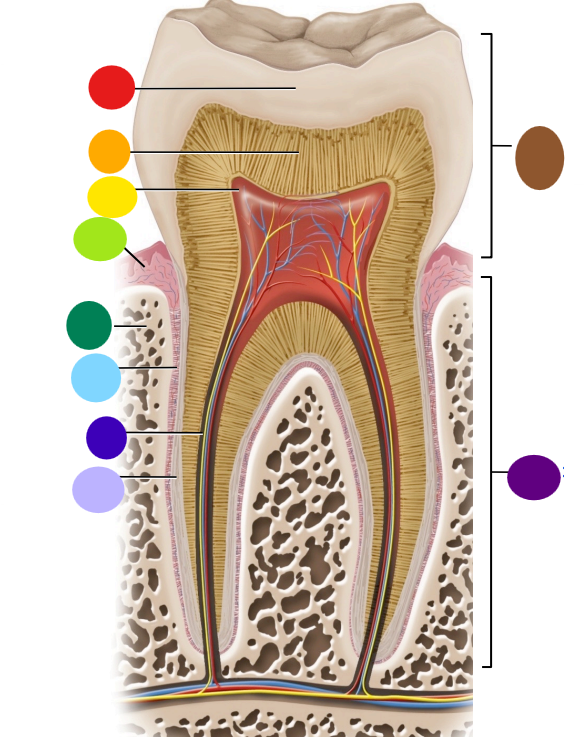
light green
gingiva
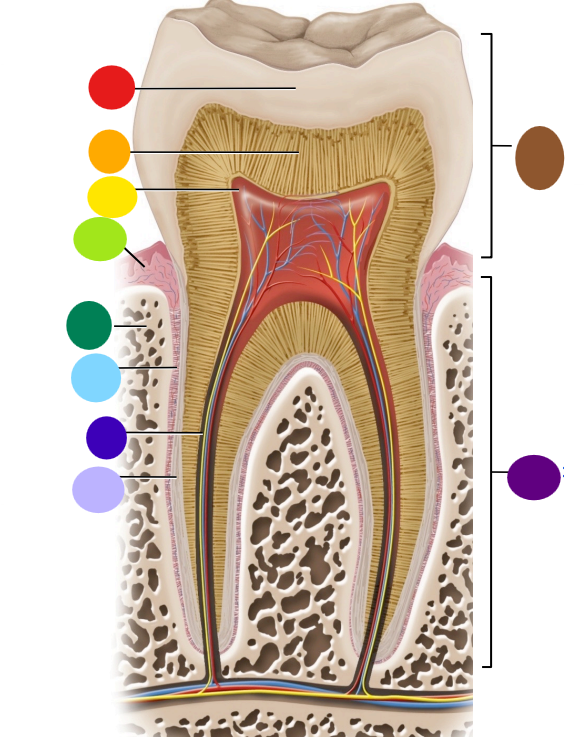
dark green
bone
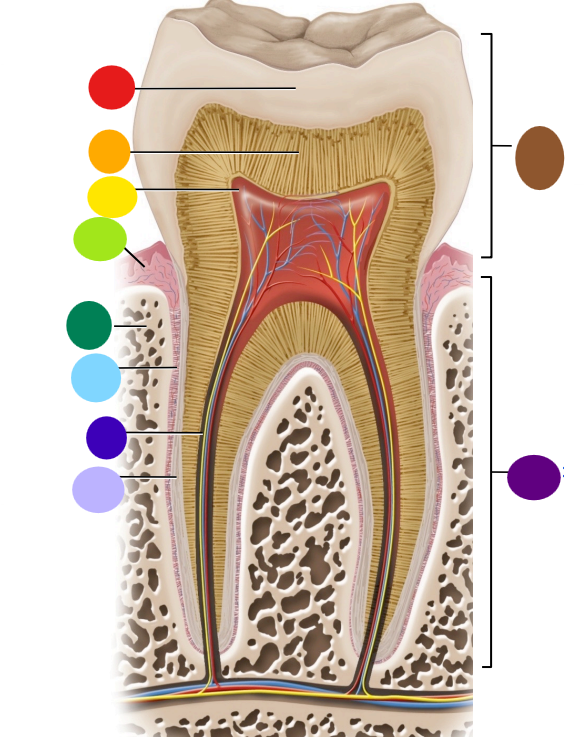
light blue
peridontal ligament
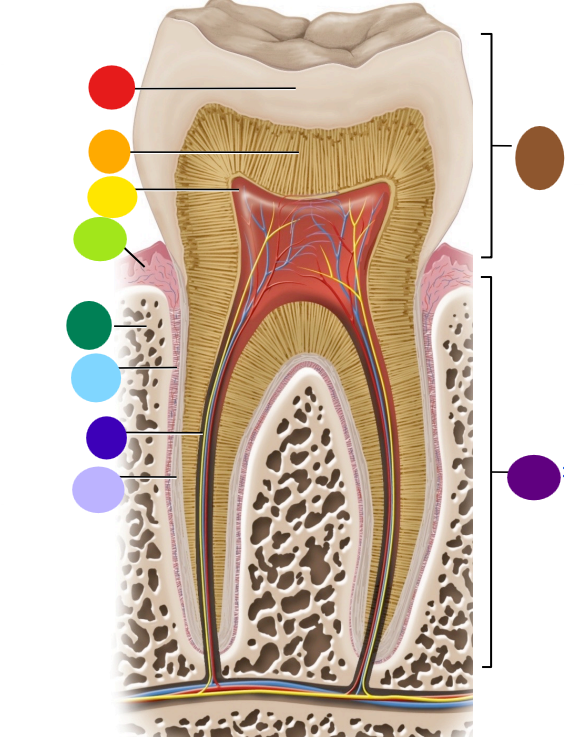
dark blue
root canal
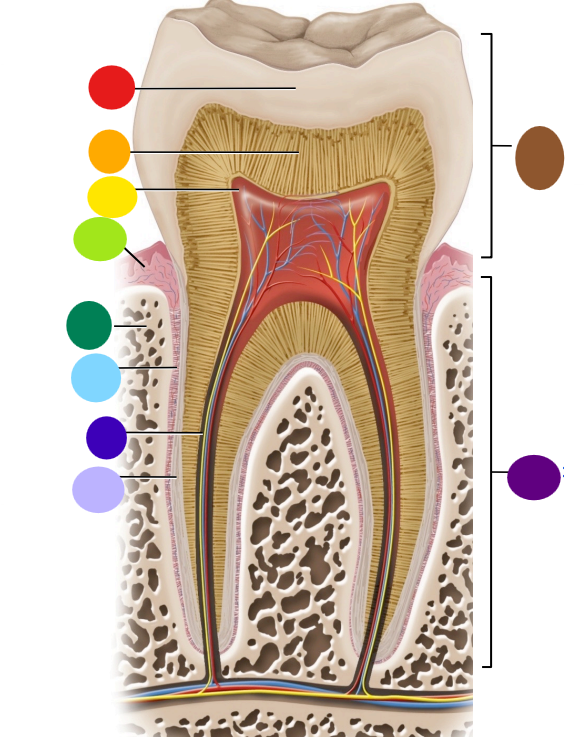
light purple
cementum
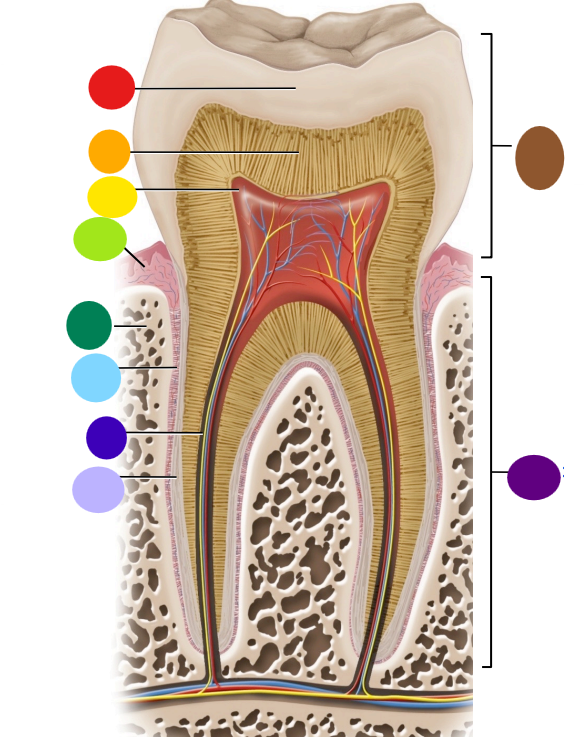
dark purple
root

brown
crown
Where is the root of the tooth embedded?
maxilla or mandible
What is the articulation between the root and bone called?
gomphosis the type of fibrous joint
What anchors the root of a tooth to the bone
periodontal ligament and cementum secreted by cementocytes
What cells secrete dentin?
odontoblasts
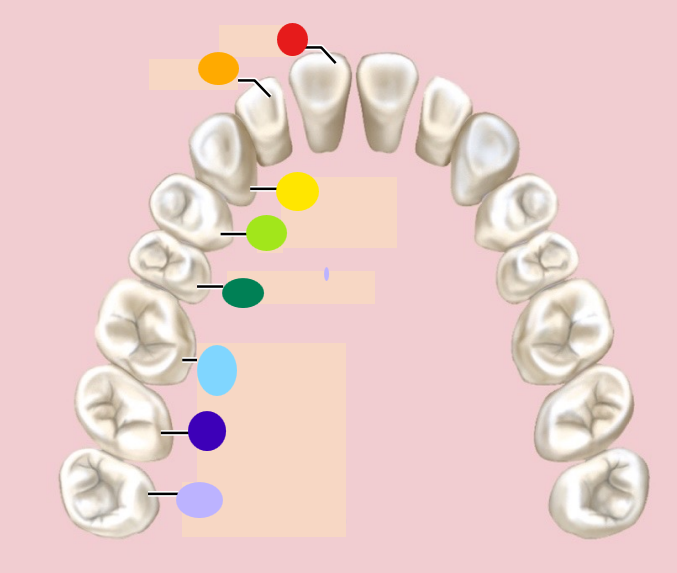
red
incisor
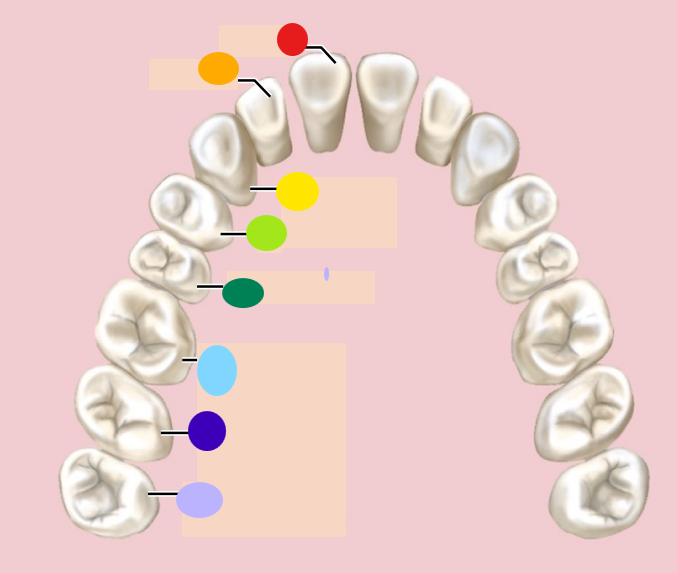
orange
incisor
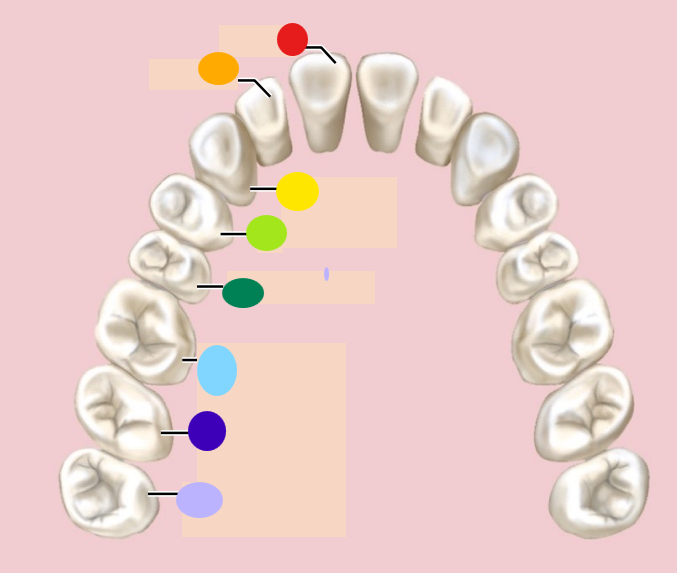
light green
1st premolar
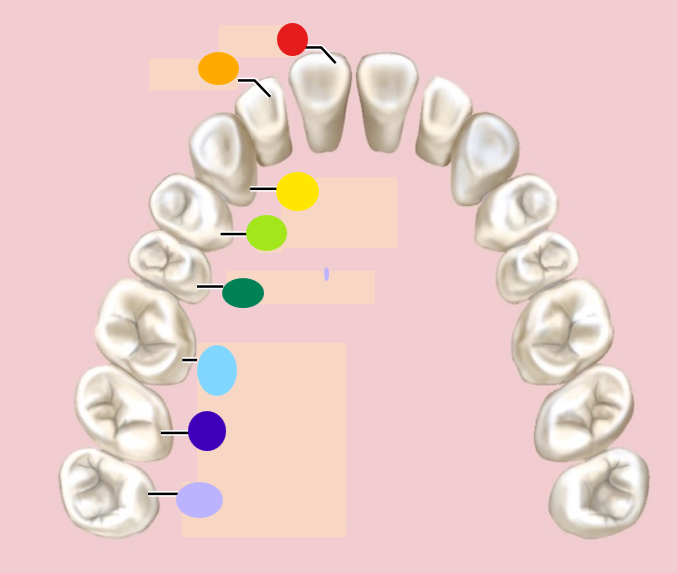
light green
1st premolar
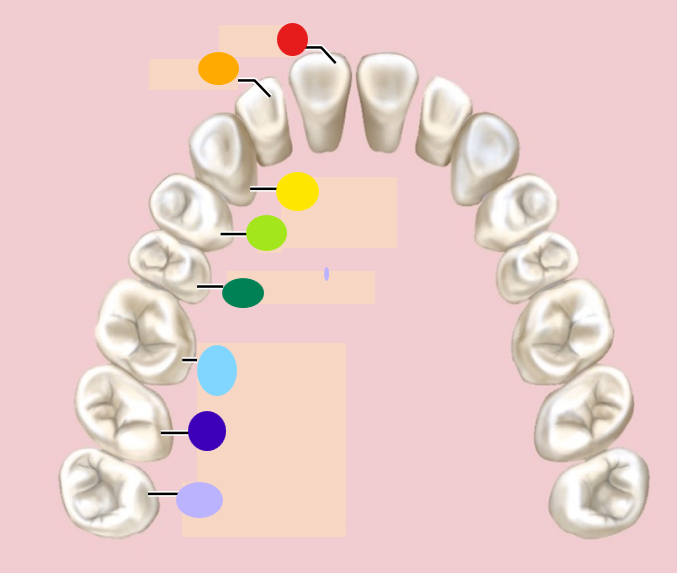
dark green
2nd premolar
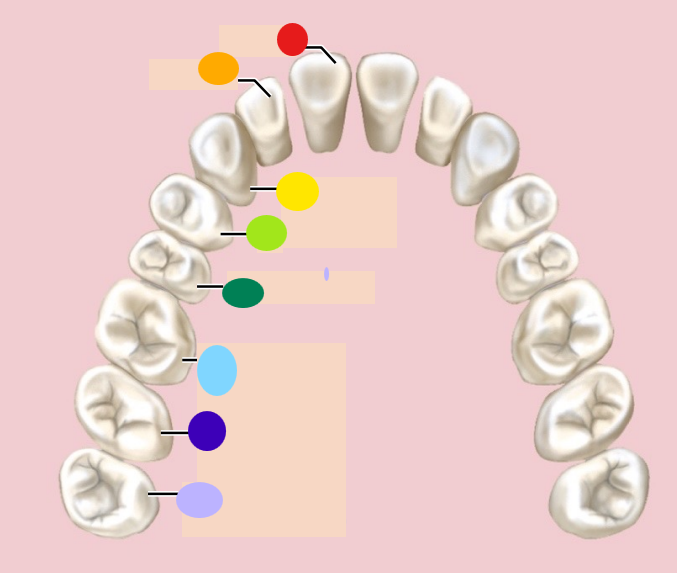
light blue
1st molar
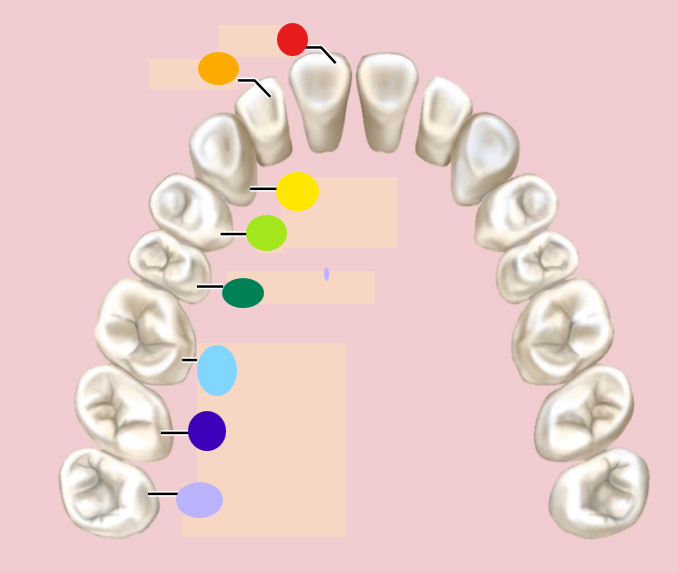
dark blue
2nd molar
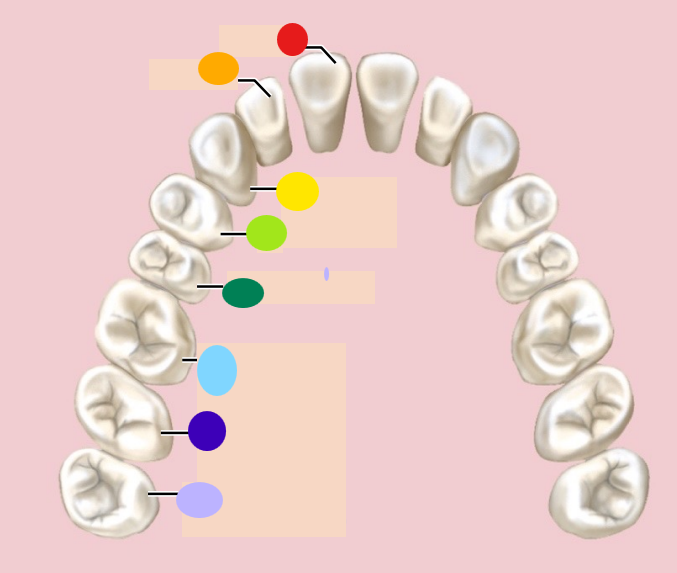
light purple
3rd molar / wisdom teeth
How many incisors do we have and what do they do
8, cutting
How many canines do we have and what do they do
4, puncturing and shredding
How many premolars do we have and what do they do
8, crushing and grinding
How many molars do we have and what do they do
12, crushing and grinding
what is the dental formula?
2,1,2,3 - number of each type of tooth on one side of the top or bottom
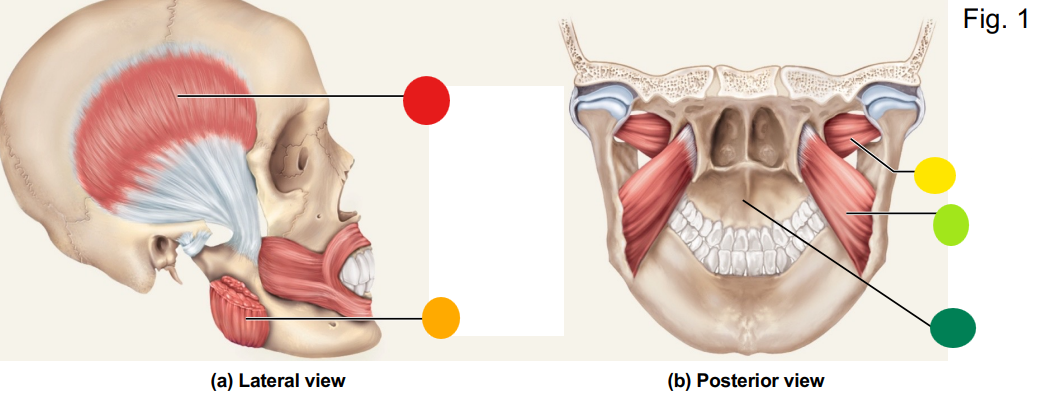
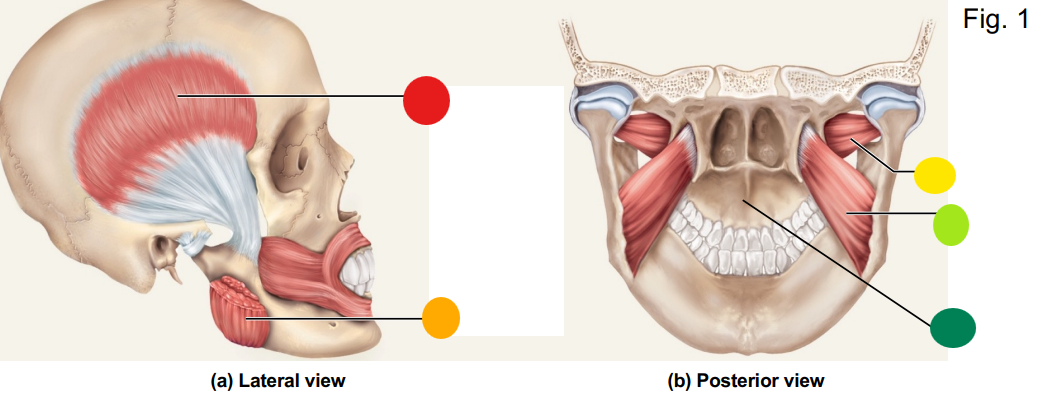
red
temporalis
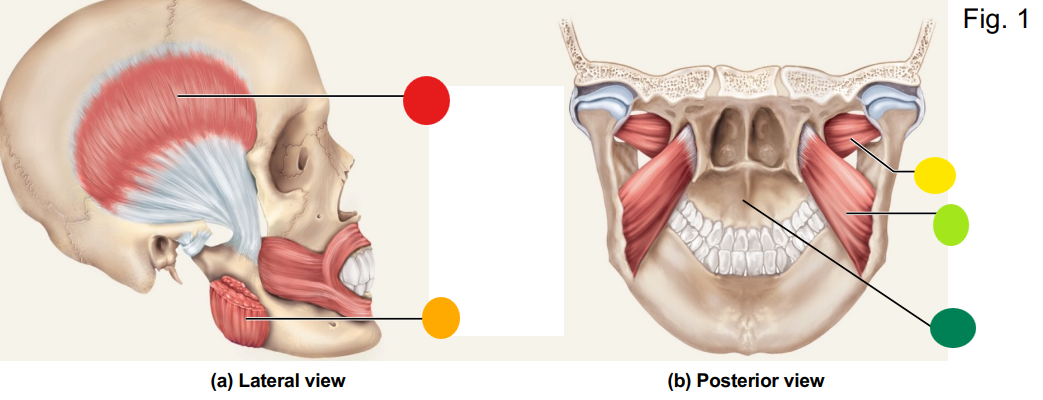
orange
masseter
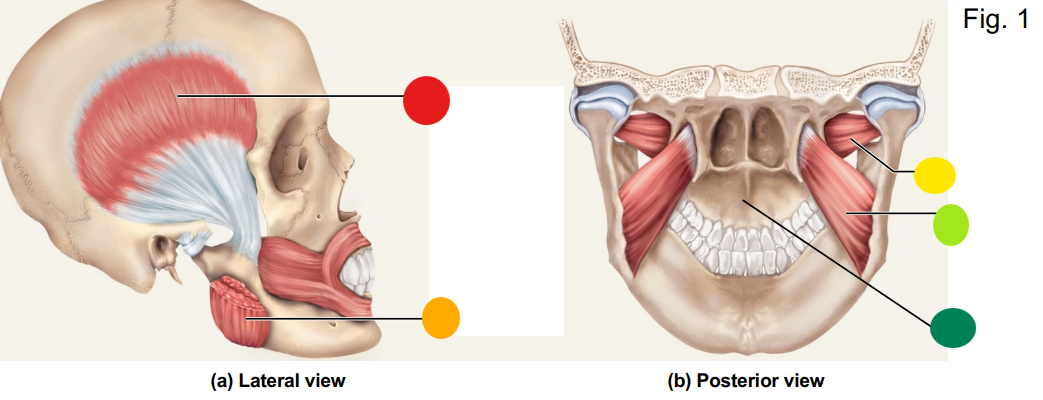
yellow
lateral pterygoid
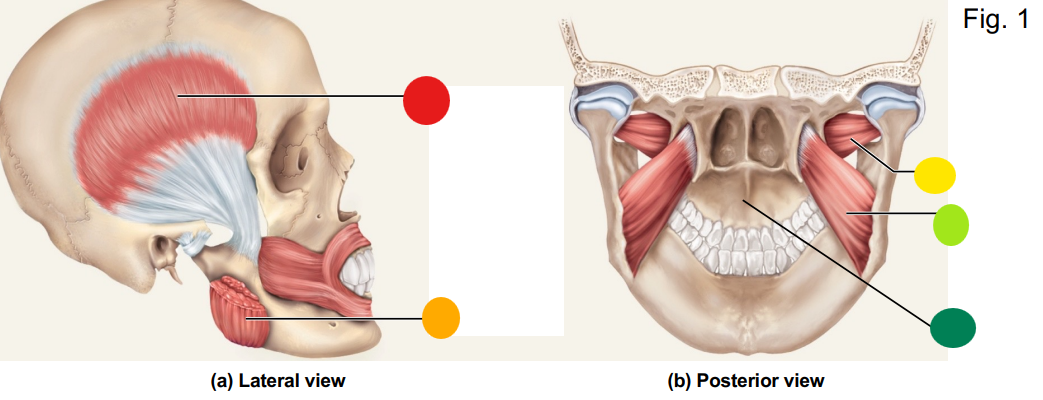
light green
medial pterygoid
dark green
interior of oral cavity
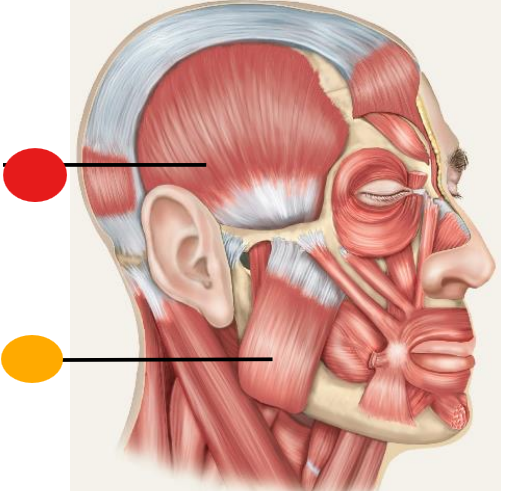
red
temporalis
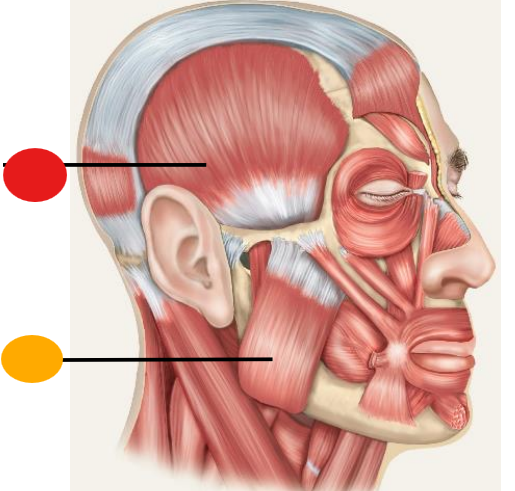
orange
masseter
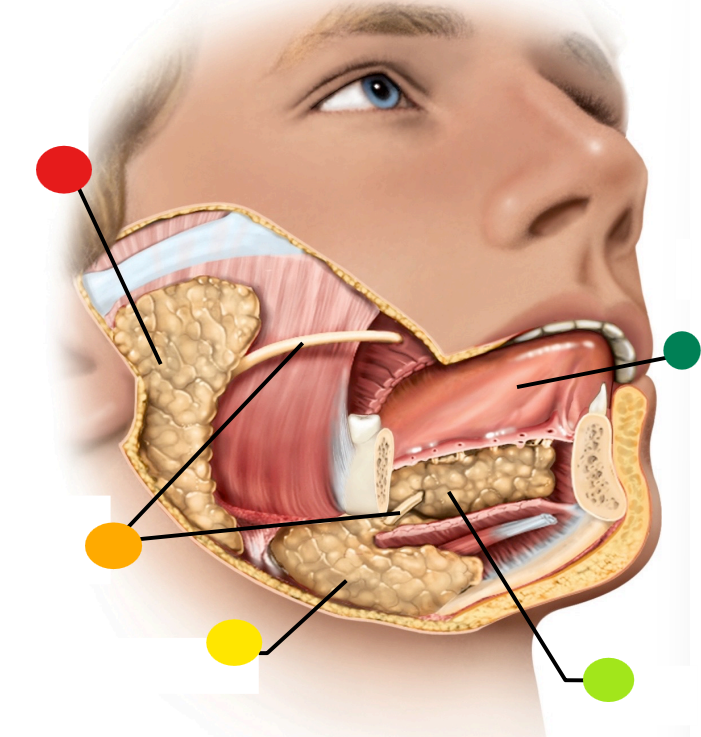
red
parotid gland
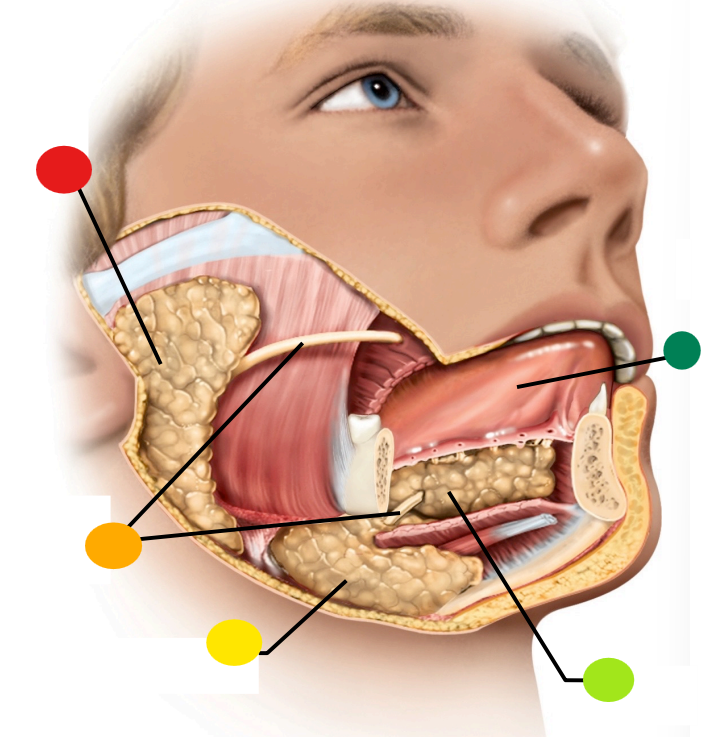
orange
salivary ducts
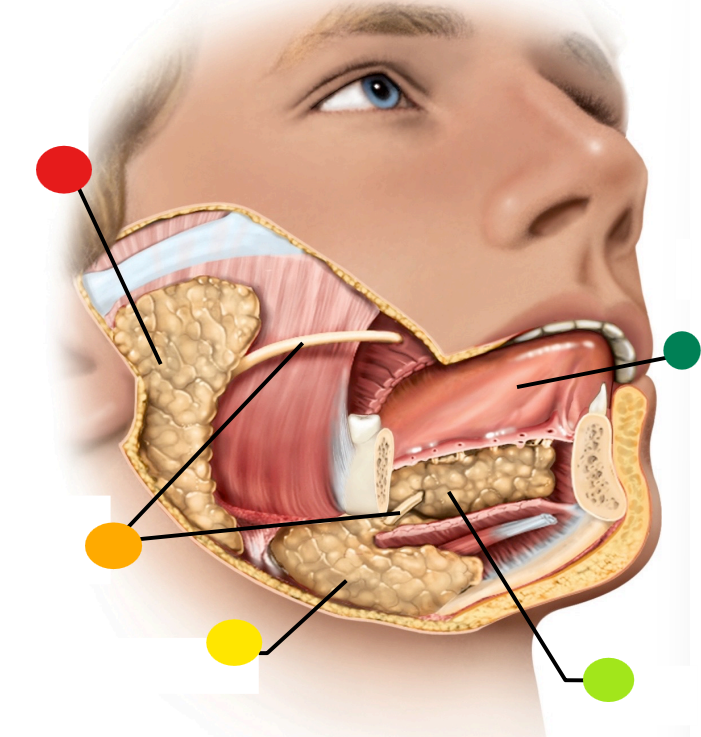
yellow
submandibular gland
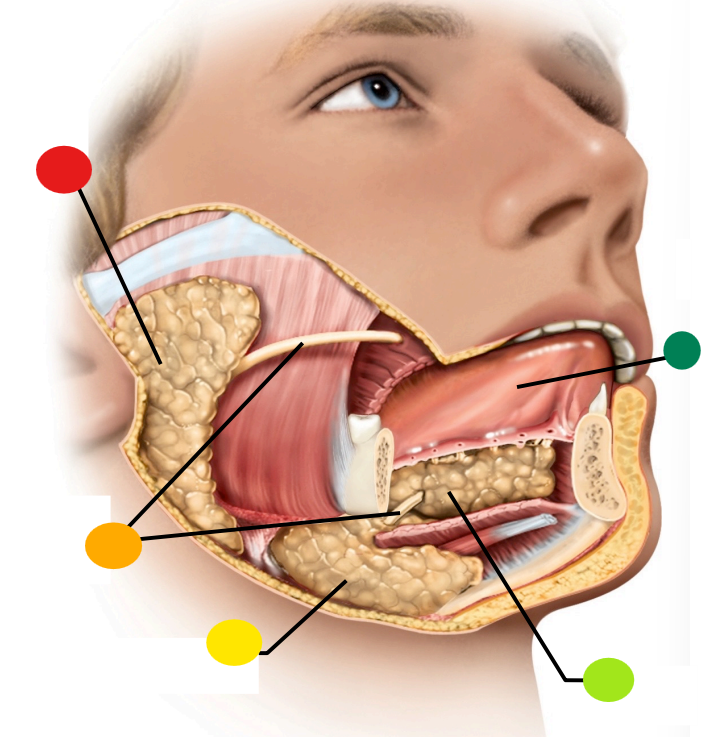
light green
sublingual gland
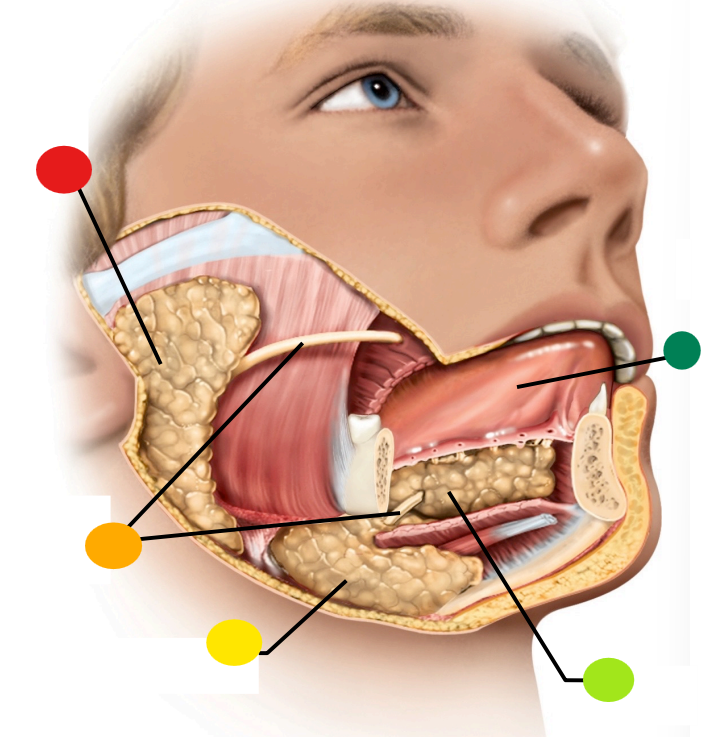
dark green
tongue
what type of gland is the salivary gland
seromucous exocrine gland
What is the function of the salivary duct?
carry saliva to the free surface within the mouth
What is saliva?
A watery hypotonic serous secretion that includes digestive enzymes
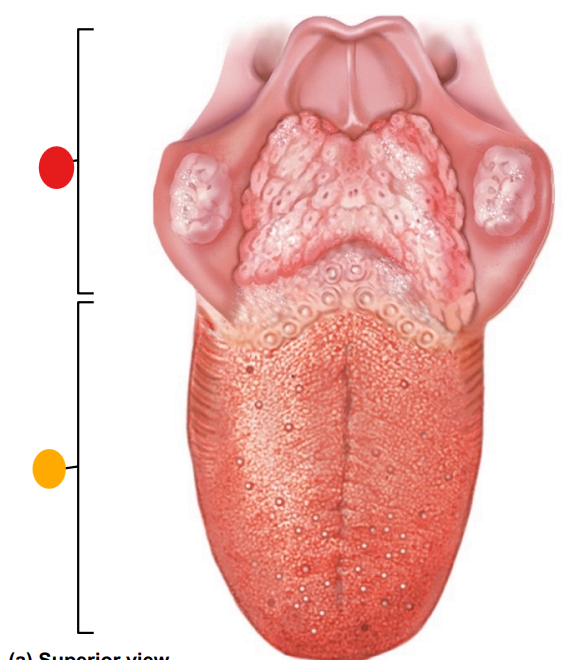
red
root of the tongue
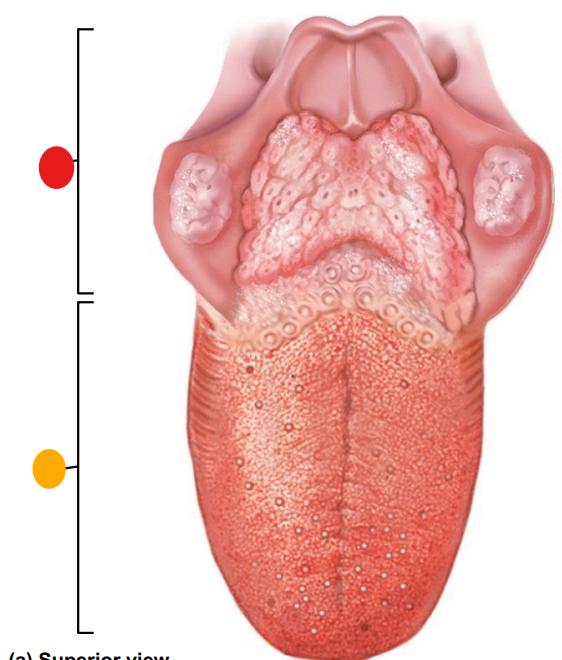
orange
body of the tongue
what tissue type is the tongue?
skeletal muscle
what is the function of the tongue?
sensory functions including touch, temperature, pain, taste via taste buds, assist with mastictation, phonation and deglutition
what is the major function of filiform papillae and where are they concentrated?
manipulation of food and perception of texture, tip of the tongue
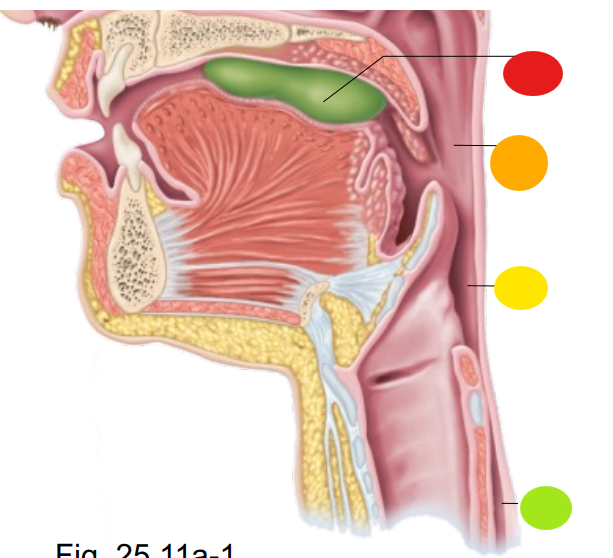
red
bolus of food
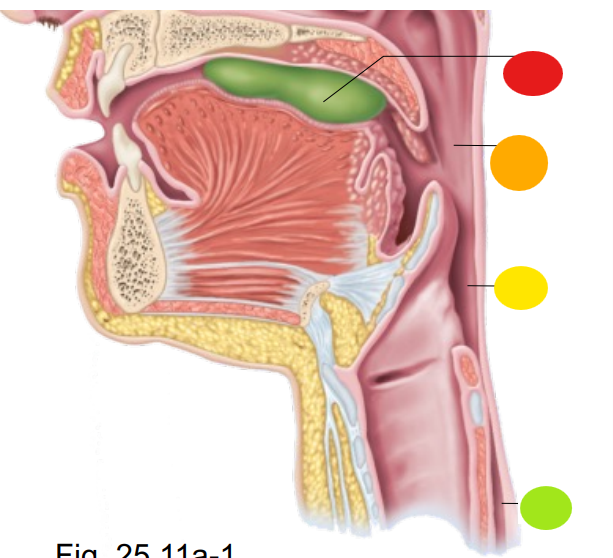
orange
oropharynx
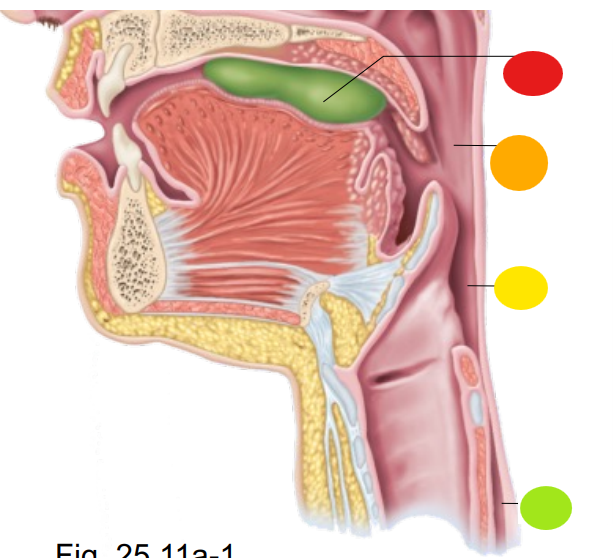
yellow
laryngopharynx
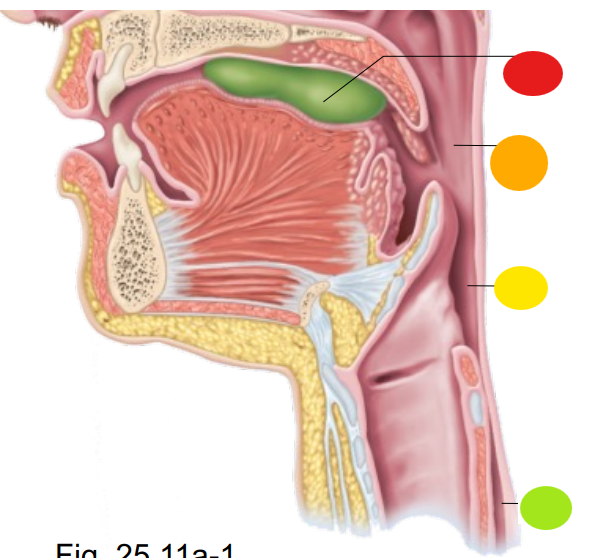
light green
esophagus
what is the technical term for swallowing?
deglutition
What is the optimal pH and temperature for gastric lipase?
4-5, 37 degrees C
What is the optimal pH and temperature for pancreatic lipase?
8, 37 degrees C
What is the optimal pH and temperature for salivary enzymes?
7, 37 degrees C
What is the function of amylase?
digests starches, such as amylose into maltose, a disaccharide
Where is amylase secreted?
from salivary glands into the mouth and pancreas into the small intestine
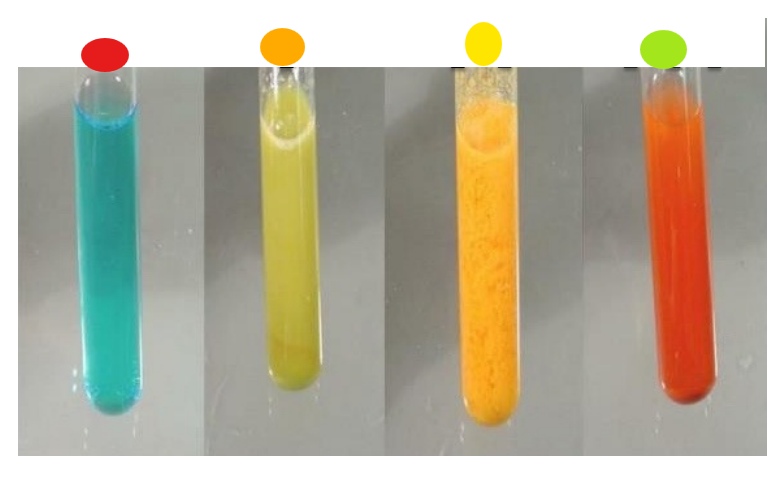
What test is this?
Benedict’s assay, shows presence of maltose
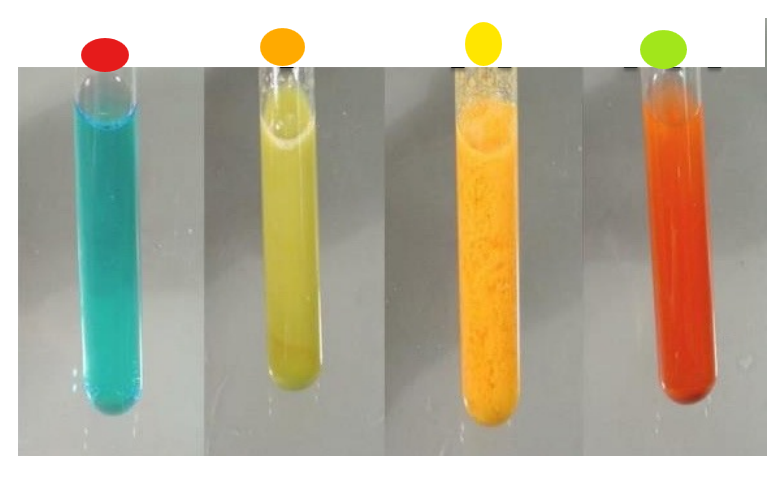
red
negative benedict’s assay
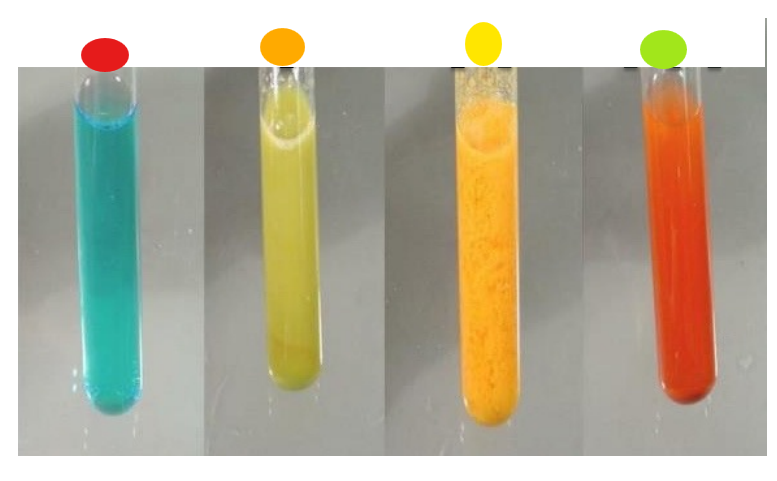
orange
+ benedict’s assay
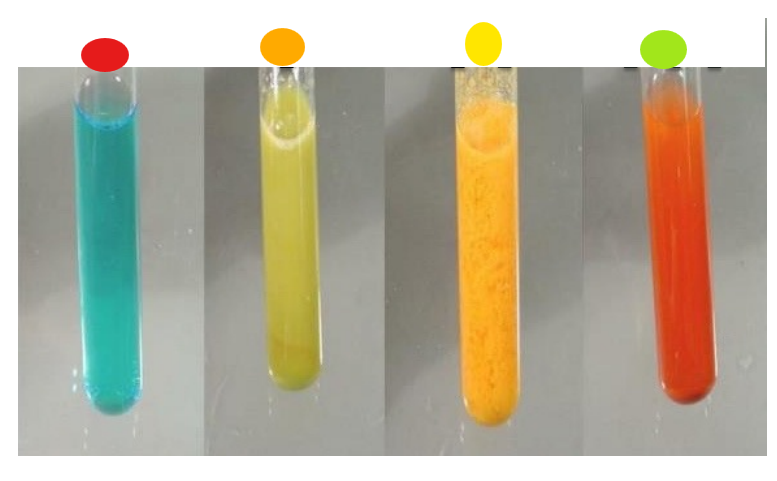
yellow
++ benedict’s assay
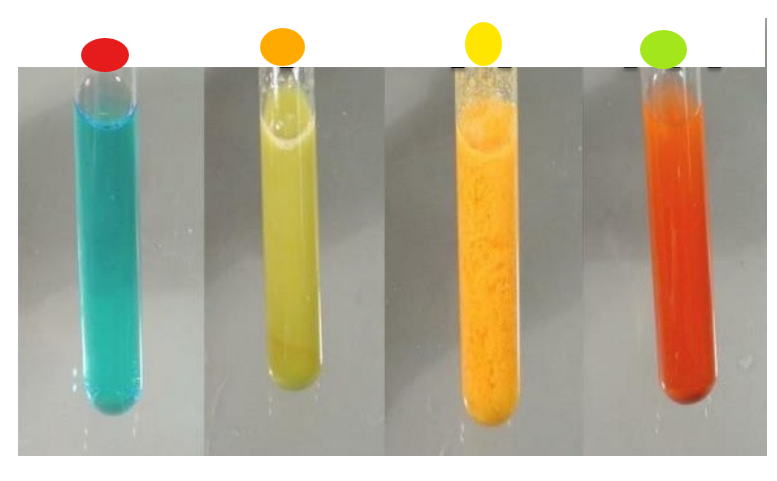
light green
+++ benedict’s assay
What is emulsification of fat and what aids in this during digestion?
Fat globule is broken down into smaller droplets to increase surface area, bile acids/salts have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region so are able to bind to fat droplets and interact with water and prevent it from clumping up
Where is bile secreted?
Bile is produced in the liver, stored in the gallbladder and enters the duodenum via the hepatopancreatic sphincter
What is the function of pancreatic lipase and by what mechanism?
breaks down triglycerides by hydrolysis into 1 monoglycerides and 2 free fatty acids
Where is lipase secreted?
salivary glands, stomach and from pancreas to duodenum
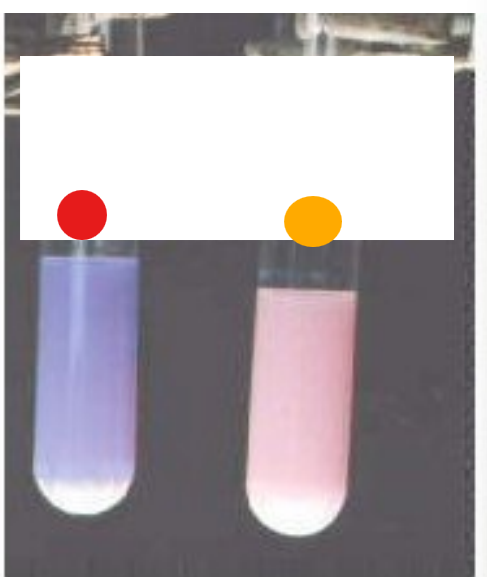

What test is this?
Litmus assay, indicates if fatty acids are present due to triglyceride digestion via a pH indicator
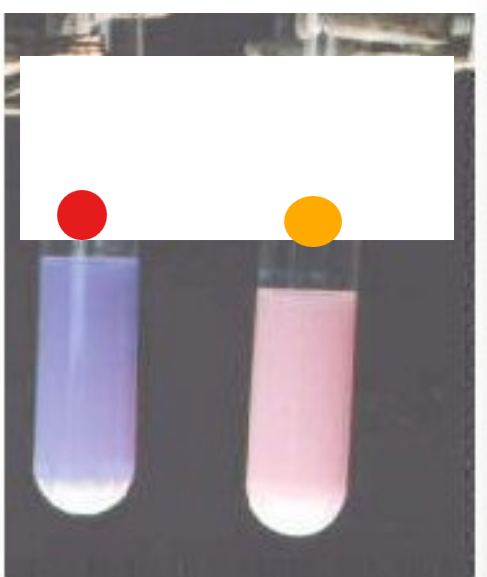

red
negative litmus assay
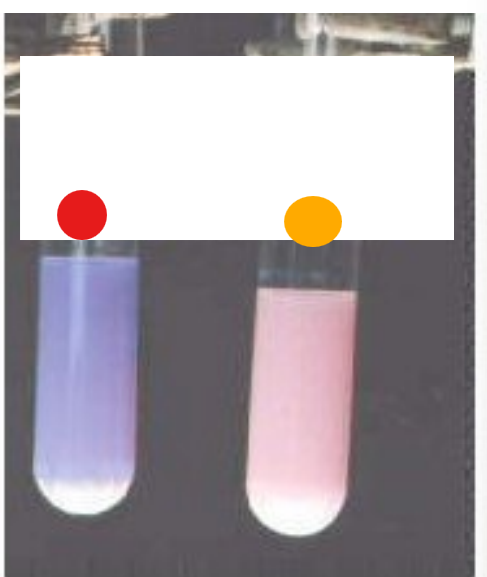

orange
+++ litmus assay
What is a protease?
enzymes that break down proteins
What is trypsin and where is it secretes?
A protease produced by the pancreas and is secreted through the hepatopancreatic sphincter to the duodenum
what is pepsin and where is it secreted?
A protease secreted by the stomach
What is a carboxypeptidase?
a protease that removes one amino acid at a time from the carboxyl end
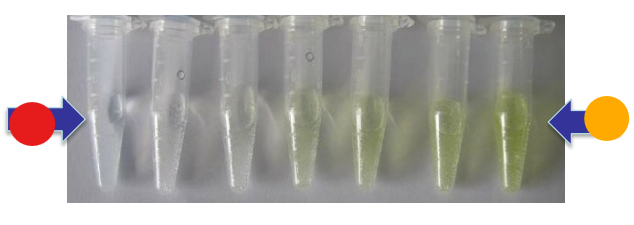
What test is this?
BAPNA protein assay, BPNA is a synthetic protein that is colorless, when trypsin binds to BAPNA, it cleaves it with a product of p-nitroaniline that is yellow and concentration is determined by spectrophotometer
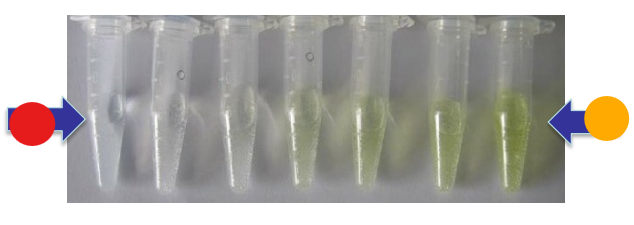
red
low trypsin activity
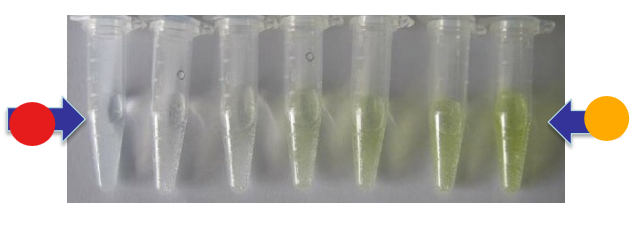
orange
high trypsin activity