Physics Definitions (Leaving Cert)
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
Self luminous object
An object that gives out it's own light
Non luminous object
An object that does not give out it's own light.
laws of Reflection
(1)The incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray are all in the same plane. (2) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
Second Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. I.e i = r
First Law of Refraction
The incident ray, the normal and the refracted ray are all on the same plane.
Diffuse Reflection
If the surface on which the light shines is rough, the reflected light is scattered in all directions.
Regular Reflection
Is the bouncing of light off an object that is silvered and polished, called a mirror, or a shiny flat surface.
Refractive Index
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction.
Real Image
An image formed by rays which actually pass through the image. Such an image would form on a screen.
Virtual Image
An image formed by the apparent intersection of rays (they do not actually pass through the image; they only appear to do so This image cannot be formed on a screen
Refraction
The bending of a light ray (or a wave) which occurs when it passes from one medium to another of different density or refractive index.
Critical Angle
When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, the angle of incidence whose corresponding angle of refraction is 90° is called the critical angle for those two media.
Total Internal Reflection
The reflection of all light, incident at a surface, back into the denser medium due to the critical angle being exceeded.
Optical Fibre
A fibre consisting of a very fine solid strand of high quality glass coated with a film of another glass of lower refractive index. Light is transmitted along it with no loss through the walls, due to total internal reflection occurring at the walls.
Power of Accommodation
The ability of the eye to change the focal length of its lens to form a sharp image on the retina.. This can be represented mathematically as p = 1 / f , where p is power and f is the focal length.
Short Sightedness
A defect in which the sufferer can see close objects clearly but not distant objects. The light rays fall short of the back of the eye. Fixed by using a concave lens.
Long Sightedness
A defect of vision in which the sufferer can successfully see distant objects but not ones close by. The light rays meet too far behind the eye. Fixed with a convex lens
Speed
Is the rate of change of distance with respect to time.
Displacement
Is distance in a given direction. ( Vector)
Velocity
Is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. (Vector)
Constant Velocity
Is when an object moves in a straight line and does not speed up or slow down.
Acceleration
Is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
Scalar Quantity
A quantity that has magnitude only and has no direction in space.
Vector Quantity
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction in space.
Force
Is anything that causes or tends to cause the velocity of an object to change.
Mass
Of a body is a measure of how difficult it is to accelerate that body.
Weight
The weight of an object is the force of the Earth's gravity acting on it. i.e. W =mg
Momentum
Mass x Velocity
Newton's First Law of Motion
States that every body will remain in a state of rest or traveling with constant velocity unless an unbalanced external force acts on it.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
States that when an unbalanced force acts on a body the rate of change of the body's momentum is directly proportional to the force and takes place in the direction of the force.
Newton's Third Law of Motion
States that if body A exerts a force on body B, the body B exerts an equal but opposite force on body A.
The principle/Law of conservation of momentum
In any reaction between bodies in a closed system, the total momentum before the interaction is equal to the total momentum after the interaction.
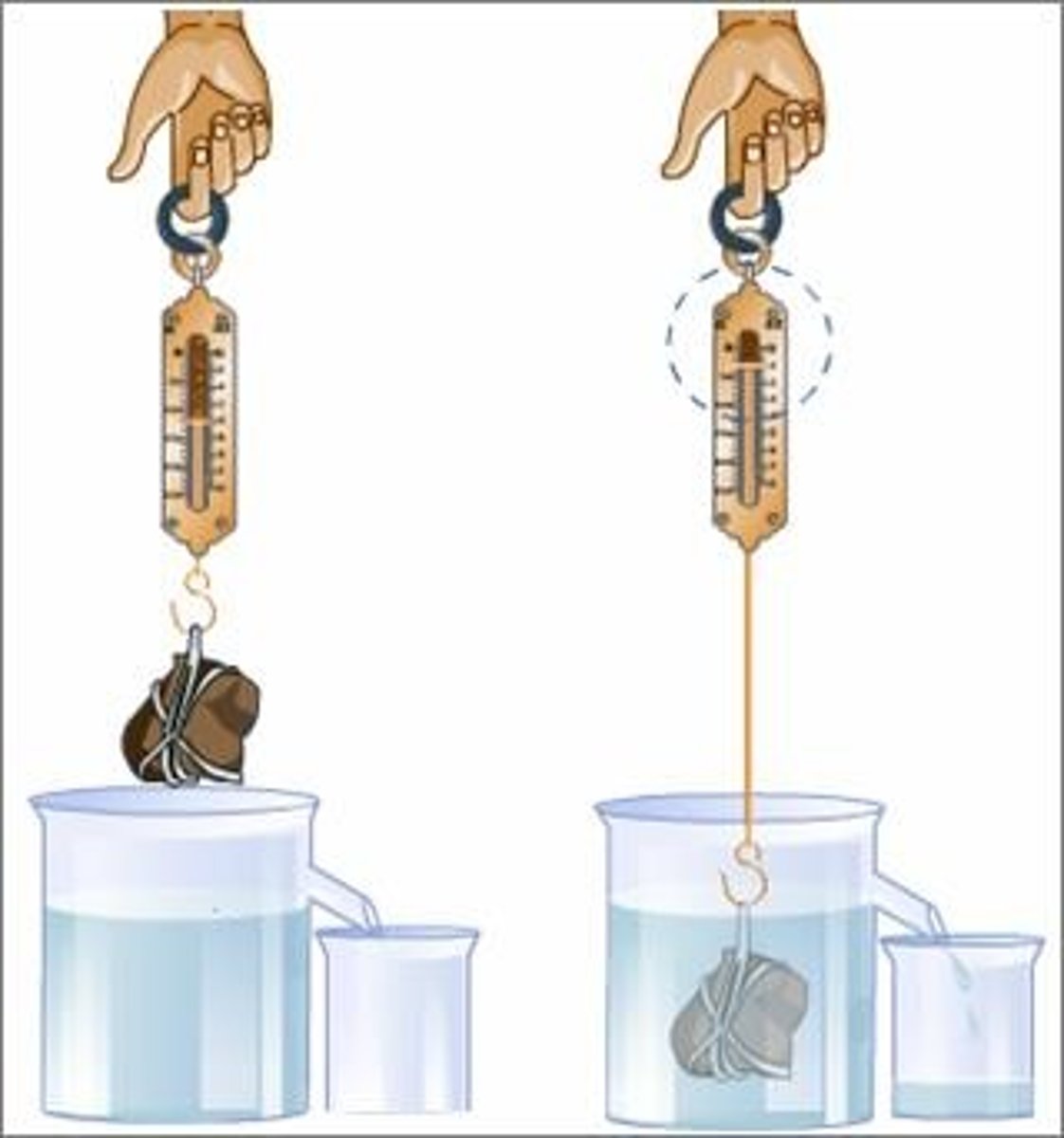
Archimedes' principle
When an object is immersed in a fluid, the upthrust it experiences is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid.
Pressure
Force per unit area.
Force / Area
Unit of pressure
The pressure is one pascal if a force of 1 N acts over an area of 1 m^2
Archimedes' Principle
When a body is partially of completely immersed in fluid, the upthrust is equal in magnitude to the weight of fluid displaced.
Boyle's Law
States that at a constant temperature the volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
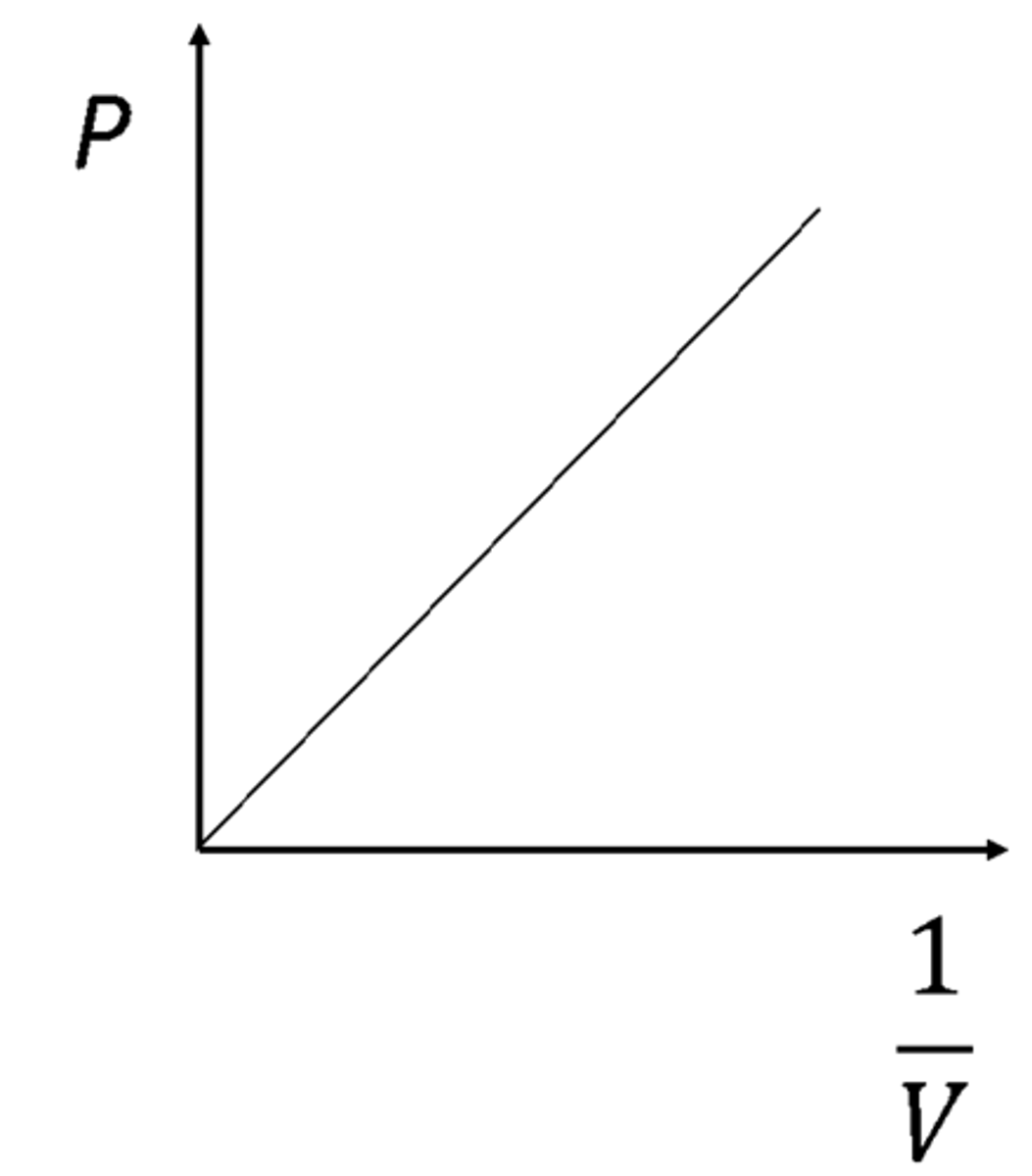
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
States that any two point masses in the universe attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
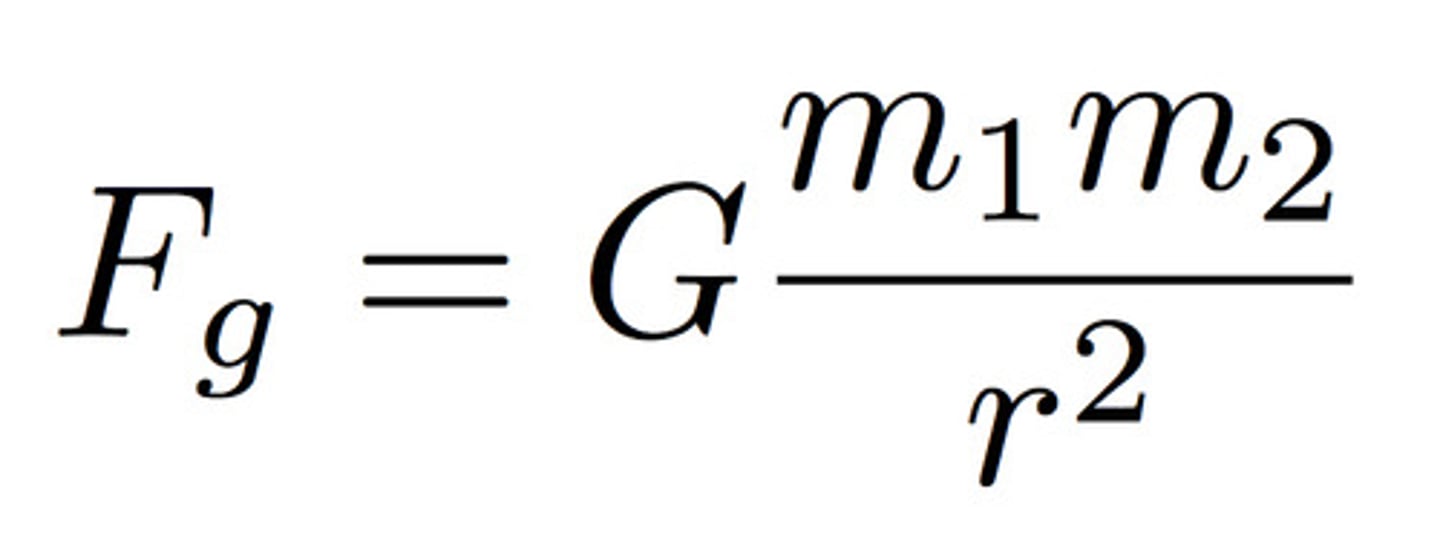
The moment of a Force
the moment of a force, about an axis, is the product of the force times the perpendicular distance between the axis and the line of action of the force.
Conditions for equalibrium
-When a body is in equilibrium, the sum of all forces acting on it is zero.
-The sum of the clockwise moments about any axis is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments.
Couple / Torque
Two parallel forces with the same magnitude acting in opposite direction.
Work
Work is done when a force moves a body. The amount of work done is equal to the product of the force times the distance moved in the direction of a force.
The joule
One joule is the work done when a force of 1 Newton acts for a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force.
Energy
Is the ability to do work. The amount of energy something has is the amount of work it can do.
Principle of Conservation of energy
States that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only be converted from one form to another.
Kinetic Energy
Of a body is the energy that body has due to motion.
Potential Energy
Of a body is the energy it has due to its position or condition in a force field.
Renewable source of energy
A source of energy that does not get used up.
Power
Is the rate at which work is done.
Unit of power
The power is one watt if work is being done or energy is being converted at a rate of one joule per second.
Angular velocity
Is the rate of change of angle with respect to time
Unit of angular velocity
radian per second
Centripetal Force
Any force that causes a body to move in a circular path. The force constantly acts at right angles to the direction of the body's velocity.
Centripetal acceleration
Its the acceleration a body has towards the center of the circle if that body is moving in a circle.
Period of an orbit
The time taken for a satellite to go once around the central body is called the periodic time or simply the period (T) of the orbit.
Hooke's Law
States that when an object is bent, stretched or compressed by a displacement s, the restoring force F is directly proportional to the displacement - provide the elastic limit is not exceeded.
A body is moving in simple harmonic motion if
1. its acceleration is directly proportional to its distance from a fixed point on its path.
2. and its acceleration is always directed towards that point.
Periodic time (T)
of a particle executing simple harmonic motion is the time for one complete oscillation. T is measured in seconds.
Frequency (f)
Is the number of cycles per second. It is measure in cycles per second - Hertz (Hz).
Temperature
is the measure of the hotness or coldness of a body.
Thermometric Property
is any physical property that changes measurably and uniformly with temperature.
Heat capacity
Of an object is the heat energy needed to change the temperature of that object by 1kelvin
Specific Heat capacity
Of an object is the heat energy need to change the temperature of 1kg of that substance by 1kelvin
Latent heat
Of an object is the heat energy needed to change its state without a change in temperature.
Specific latent heat
Of a substance is the amount of heat energy needed to change the state of 1 kg of that substance without a change in temperature
Specific latent heat of fusion
Is the amount of heat energy needed to change 1kg of a substance from a solid to liquid without a change in temperature
Specific latent heat of vaporisation
Of a substance is the amount of heat energy needed to change 1kg of that substance from a liquid to a gas without a change in temperature
Conduction
Is the movement of heat energy through a substance by the passing of vibrating molecules. There is no overall motion of the substance.
Radiation
Is the transfer of heat energy from one place to another in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Convection
Is the transfer of heat through a fluid by means of circulating currents of fluid cause by heat
U-value
Of a structure is the amount of heat energy conducted per second through 1 metre squared of that structure when a temperature difference of 1 degrees Celsius is maintained between its ends.
Solar constant
The average amount of the sun's energy falling per second perpendicularly on 1 metre squared of the the Earth's atmosphere is the solar constant.
Traveling Mechanical wave
Is a disturbance carrying energy through a medium without any overall motion of that medium
Traveling wave
Either mechanical or electromagnetic, is a disturbance that travels out from the source producing it , transferring the energy from the source to other places through which it passes
Transverse wave
Is a wave where the direction of the vibration is perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels
Longitudinal wave
Is a wave where the direction of vibration is parallel to the direction in which the wave travels
Amplitude
The maximum distance of any particle from its undisturbed position
Oscillation or cycle
The distance produced by one complete vibration of the source
Wavelength
The distance from any point on one cycle to the corresponding point on the next cycle
Frequency
The number of cycles per second. The unit of frequency is the hertz
Velocity (c)
Is the distance traveled by one cycle in one second.
Reflection of waves
Is the bouncing of waves off of an obstacle in their path
Refraction of waves
Is the changing of direction of a wave when it enters a region where it's speed changes
Diffraction
The sideways spreading of waves into the region beyond a gap or around an obstacle
Interference
Is when waves from two sources meet, a new wave is produced. The displacement produced at any point by this wave is the algebraic sum of the displacements that each wave would produce on its own.
Constructive interference
Is when waves from two sources meet and the amplitude of the resulting wave is greater than the amplitudes of each individual wave
Destructive interference
Is when waves from two sources meet and the resulting amplitude is less than the amplitude of each of the individual waves
Coherent sources
Two sources of periodic. Waves are said to be coherent if they are in phase or if there is a constant phase difference between waves from each of the sources. If this so, the sources must also have the same frequency and amplitude.
Interference pattern
When waves from two or more coherent sources meet, the resulting wave pattern formed is called an interference pattern.
Stationary wave
The amplitude of the wave at any point is constant. This occurs when two periodic travelling waves of the same frequency and amplitude moving in opposite directions meet, they interfere with each other.
Polarization
is the restriction of a transverse wave, so that it vibrates in one plane
The Doppler effect
Is the apparent change in the frequency of waves due to the relative motion of the source or the observer.
If a source emits waves of frequency f, the observed frequency f' will be greater than f if the source moves towards the observer or the observer moves towards the source. The observers frequency f' will be less than f if the source moves away from the observer or the observer moves away from the source.
Acoustics
The correct balance of reflection and absorption of sound
Overtones
Frequencies which are multiples of a certain frequency are called overtones of that frequency. If f is a given frequency 2f is its first overtone and 3f is its second overtone
Loudness
Of a sound wave depends on its amplitude and frequency of the sound wave. The greater the amplitude the greater the loudness
Pitch
of a note depends on the frequency of the wave. The higher the frequency the higher the pitch, the lower the frequency the lower the pitch.
Quality
Of a musical note depends on the number of overtones present in the note and the relative strengths of the different overtones present.
Frequency Limits of Audibility
are the highest and lowest frequencies that can be heard by the normal human ear. The range is 20 Hz to 20000 Hz
Resonance
The transfer of energy between two bodies of the same natural frequency
Sound intensity at a point
is the rate at which sound energy is passing through unit area at right angles to the direction in which the sound is travelling at that point