Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Taxable Prizes and Awards
Gambling, raffles, lotteries, game/reality shows, MVP award winnings, contests for non-cash prizes, any other prize or award
similar to the treasure trove principle: must include the fair market value of the property in taxable income at the time ownership of the property
Expenses incurred to receive these prizes/awards ___ reduce the amount of income reported
DO NOT
Exclusions for awards for recognition of civic or other achievements
must be for civic, artistic, educational, scientific, or literary achievements,
the recipient must be selected without action on their part,
is not required to perform services,
AND does not accept the award and the organization granting it sends it directly to a tax-exempt or governmental organization
example of exclusion for award for recognition of civic or other achievements
ex: obama winning the Nobel Peace Prize as he did not nominate himself and did not complete any action on his part, he won $1,400,000 and Nobel committee were directed by him to pay the awards to ten qualified charitable organizations
exclusion for olympic medal
as of the 2018 winter olympics the value of the olympic medal and cash received for winning from the the U.S. Olympic Committee are no longer taxable
EXCEPT olympians who have an AGI of more than $1,000,000 must pay tax on the value of their winnings
Scholarships
can exclude amounts received as scholarships from income to the extent the funds do not exceed required expenses to earn credit for courses
ex: tuition, books, fees, supplies, and equipment
work-learning-service program payments are also excludable if the participation in the program is required to earn the degree *must be in the nature of training for learning purposes
value of a tuition waiver a graduate assistant receives in return for rendering services is excluded form income
scholarship money not excluded from income
free room and board is treated as earned income
scholarships in excess of required tuition, fees, books, supplies, and equipment is considered earned income (not subject to withholding for social security and medicare taxes)
cash wages received by graduate assistants
payments from the university in return for services rendered are taxable as wages even if services are condition for receiving the degree/required of all candidates for the degree
scholarships on a tax return
report taxable scholarships on form 1040, line 1 as wages, the amount of scholarships provided by an educational institution is shown on form 1089-t
why are excess scholarships taxable?
to try to create fairness between students who receive excessive scholarships and students who must work to pay for education and living expenses. those working must pay income tax on all wages, so excess scholarships are taxable income as well as that money would be spent on similar things as the student who works for their income.
Alimony
court ordered financial provision for a former spouse after a divorce
separate maintenance payment
financial support that one spouse is legally required to pay to the other spouse during the divorce process while they are separated
*tax laws for alimony also apply to separate maintenance payment as legally separated under state law are considered divorced for federal income tax purposes and exist to replace the income a spouse was accustomed to benefiting from the other spouse earned
child support
made by noncustodial divorced parent to support one’s minor child or children
not taxable to the parent receiving the payments and not deductible by the parent making the payments
same for payments before 2019 and after 2018
clarification on tax consequences for divorce agreements
transfers of property to a former spouse under a divorce decree are not taxable events
recipient does not have income and the payor does not receive a deduction
transferor’s basis in the property transfers to the transferee
gift or inheritance income tax consequences
if someone receives cash or other property as a gift or inheritance, then the value of the property is not taxable
an individual giving a gift must recognize income accrued on the property up to the time of the gift
after the gift has been given, any income accruing is taxed to the receiver of the gift
a donee will have three different bases in gifted property
gain basis, loss basis, and depreciable basis
gain basis
donor’s adjusted basis for the gifted property
loss basis
the lower of: fair market value of the asset at the date of gift OR donor’s adjusted basis for the gifted property
depreciable basis
equal to the gain basis
Inheritance tax consequences
basis of property acquired from a decedent is the fair market value at the date of death OR the fair market value on the alternative valuation date if the executor of the decedent’s estate elects it as the valuation date
the alternative valuation date is the date 6 months after the date of death
the executor can elect the alternative valuation date only if the value of the decedent’s gross estate is less on the AVD than on the date of death and the estate tax liability is also reduced
damage award rules
was the injury or sickness physical in nature?
if yes, you can exclude all damages received except for punitive damages
was the amount received due to punitive damages?
if yes, then that amount is always taxable
was the amount received due to lost wages?
if yes that amount is taxable unless the underlying injury or sickness is physical
was the amount received for medical expenses?
if yes, the amount can be excluded unless it is taxed because of the tax benefit rule
consequences of the receipt of life insurance proceeds due to the death of the insured
taxpayers can exclude from income proceeds of life insurance received due to the death of the insured
the tax law treats life insurance policy purchased from the owner of the policy like a property transaction
the policyholder’s basis in the policy when selling it is the amount paid for the policy plus the premiums paid to thee life insurance company after the purchase date
when the insured dies, the current owner of the policy has income for the proceeds in which they exceed the basis in the policy
aka taxable income if the owner of the policy sells it before insured passes
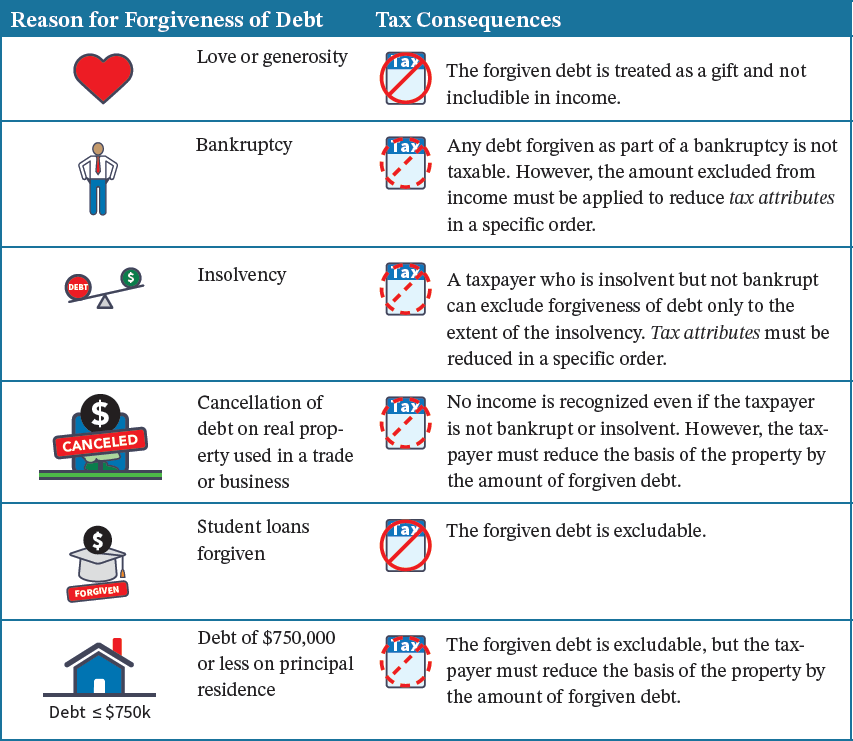
forgiveness of debt rules to determine when an individual must include forgiven debt in income
generally the forgiveness of debt results in income to the borrower unless the forgiveness is a gift, or the forgiveness is related to bankruptcy or insolvency
if the taxpayer files for bankruptcy, any debt is forgiven as part of the bankruptcy is not taxable
however, there are still tax consequences to the forgiveness because the taxpayer must reduce tax attributes such as net operating losses, credit carryovers, and the basis of property in an amount equal to the forgiven debt
a taxpayer that is insolvent, but not bankrupt, can exclude forgiveness of debt only to the extent of the insolvency
assess other increases in wealth as either inclusions for or exclusions from taxable income
individuals who care for foster children can exclude payments received form the state if they are reimbursement for expenses incurred to care for the foster child
those who receive welfare payments from governmental programs, such as the temporary assistance for needy families (TANF) and the supplemental nutrition assistance program (SNAP), do not include them in income
a minister, priest, or rabbi can exclude from income the rental value of the parsonage or the cash rental allowance for a parsonage
income in respect of a decedent (IRD) is income that the decedent had earned before his death but had not recognized as income because they were a cash-basis taxpayer and it had not been received
the person who receives the IRD is taxed on it rather than the decedent, and it has the same character as it would have had if the decedent had recognized it
acquisition indebtedness
indebtedness incurred at the time the taxpayer purchased, contracted, or made a capital improvement to the home
the basis of the property is reduced by the amount of forgiven debt
alimony
court-ordered financial provision for a former spouse after a divorce
alternative valuation date (AVD)
6 months after the date of the death
** executor can elect the AVD only if these two things apply
the value of the decedent’s gross estate is less on the AVD than on the date of death
AND
the estate tax liability is less if the AVD is used than if the date of death is used
bankruptcy
legal process for individuals or corporations where some or all of one’s debt is discharged
cash surrender value
the amount an insurance company pays to a policyholder who voluntarily terminates the policy before the insured person dies
child support
court ordered payments, typically made by a noncustodial divorced parent to support one’s minor child(ren) NOT taxable to the parent receiving the payments and is not deductible by the parent making the payments
chronically ill
an individual cannot perform at least two of the following activites for at least 90 days: eating, toileting, transferring, bathing, dressing, and continence
the individual can exclude the proceeds from income only to the extent they are used to pay for the insured’s long-term care if they are receiving the proceeds from life insurance prior to death
compensatory damages
awarded to recompense the injured party for loss or injury, damages because of physical injury/sickness are excluded from taxable income
depreciable basis
equal to gain basis (the donor’s adjusted basis for the gifted property); must increase the gain and depreciable basis by the amount of any gift tax the donor paid due to appreciation of the property
estate tax
tax that congress levies on the net worth of a taxpayer at the time of their death; the reason why the recipient of the estate does not have to include it in taxable income as it would be double taxed and people would most likely not invest in life insurance
gain basis
donor’s adjusted basis for the gifted property
gift
voluntary transfer of property from one person (the donor) to another (the donee) without full, valuable consideration; the valuable of the property is not taxable to the recipient
income in respect of a decedent (IRD)
income where a decedent earned before death but had not yet recognized as income because they were a cash-basis taxpayer and had not yet received payment
the person who receives the IRD usually the estate of the deceased or the heir is taxed on it rather than the decedent
inheritance
anything received form the estate of a person who has died, the value of the property is not taxable to the recipient
insolvency
the extent to which the taxpayer’s liabilities exceed their assets
loss basis
the lower of the fair market value of the asset at the date of the gift OR donor’s adjusted basis for the gifted property (aka the gain basis)
net operating losses (NOL)
occur when a taxpayer has a taxable loss for the year due to business losses and casualty losses; can be carried forward to reduce income in future tax years
parsonage
permanent life insurance
punitive damages
separate maintenance payment
tax attributes
term life insurance
terminally ill
welfare
worker’s compensation
forgiveness of debt chart