marine quiz: lab safety, time periods, and convection currents
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
wear safety goggles when working with…
chemicals, flames, or heating devices
or if possibility of flying debris
proper attire in the lab
footwear that completely covers the foot, long hair tied back, no loose clothing
if a chemical spills on your skin…
notify the teacher and rinse with water for 15 minutes
what do you never do with a test tube when being heated
never look into a container as you are heating it
never point the end of a test tube being heated at yourself or others
never heat in a closed container
when is it acceptable to mix chemicals?
when you are instructed to do so
which chemicals are considered dangerous?
all chemicals
when diluting an acid….
pour the acid into the water
light microscope
used to study living organisms when a low magnification is needed
electron scanning microscope
used to study the surface of materials that must be non-living, this has a resolution of about 2 nm
dissecting microscope
used to view the three-dimensional objects and larger specimens up to 100x. study the outside features of an object that cannot be mounted on a slide.
13.7 billion years ago there were 4 main forces, known as the singularity. What are these forces?
weak nuclear
strong nuclear
gravity
electromagnetic
led to big bang
earth formed…
4.6 billion years ago and began as a volcanic planet
how earth get its oceans when it first formed?
water vapor condenses into clouds, rained for 10,000 years giving ½ of our oceans and the rest came from comets
which time period had no atmosphere and ended with the formation of the atmosphere?
precambrian
which time period was known as the age of fishes due to the evolution of tetrapods?
devonian
which time period was the pangaea formed in?
devonian (416-358 million years ago)
which time period included a mass extinction of 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial species?
permian
which time period did reptiles get large and volcanoes melted ice caps?
permian (carbon dioxide leads to global warming which sets the stage for dinos)
which time period did dinosaurs and birds rule in with small mammals ruling towards the end??
jurassic/cretaceous (another extinction)
which time period included the evolution of man and the formation of modern oceans?
Miocene
which time period put the earth in a cooling phase due to a decrease in carbon dioxide? (mammals also evolved during this time)
paleocene
Which time periods did the movement of man occur in?
pleistocene
what are the 4 layers of the geosphere?
crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core
which layer of the earth is the thinnest layer and outermost layer
crust
which layer of the earth is the thickest layer of hot, semisolid rock?
mantle
which layer of the earth is made up of molten metals (liquid)?
outer core
which layer of the earth is a hot ball of solid metal?
inner core
what does the lithosphere contain?
crust and upper mantle
which German scientists proposed the idea of the continental drift?
alfred wegener
what does the theory of plate tectonics suggest?
the lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates
10 major tectonic plates that move 2-5 cm every year
what are the 3 major boundaries types
divergent, convergent and transform
how do divergent plates act?
separate from each other, building new land (constructive)
the asthenosphere pushes up magma, cools, and becomes new land
seabed spreads and mid-ocean ridges forms
youngest rock in middle, oldest at the edges
how do transform plates act?
plates slide alongside each other (neutral)
create earthquakes and tsunamis
what are the three types of convergent boundaries?
continental-continental
continental-oceanic
oceanic-oceanic
how do the continental-continental boundaries act?
neutral, rock and earth is pushed upwards creating mountain ranges
how do the continental-oceanic boundaries act?
destructive, oceanic plate (more dense) sinks under the continental and melts into magma within the mantle - known as subduction
what forms as a result of subduction and continental-oceanic boundaries?
trenches and volcanoes
how do the oceanic-oceanic boundaries act?
destructive
older, more dense plate sinks beneath other, as it melts, land and lava are pushed up and creates island arcs -Japan
what is some evidence that backs up continental drift?
similar species of plant and animals, mountain ranges line up, and age of rock is the same
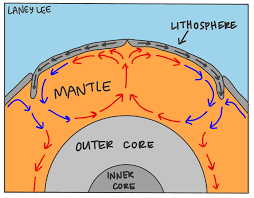
how does the convection current work?
happens when mantle moves bc of density changes caused by temp differences
rock moves closer to the core and warm up, becomes less dense and rises upward towards the crust
as rock cools, it becomes more dense and sinks towards warmer core
cycle continues
what are paleomagnetic stripes
the pattern of magnetic stripes on the ocean floor due to reversals in the earth’s magnetic field and seafloor spreading
explain paleomagnetism
seafloor contains paleomagnetic stripes
within igneous rocks are a naturally magnetic iron mineral called magnetite
the magnetite will face the direction of the North Pole at that time
earth’s magnetic field reverses every 250,000 years, changing North to south