envs274 exam 1 and 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
ranking of gasses in the atm according to their abundance (from highest to lowest)
nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide
function of nitrogen in the atmosphere
dilutes O to prevent rapid burning at Earth’s surface, and taken up by organisms to be incorporated into proteins
oxygen
produced by plants during photosynthesis
characteristics used to distinguish different layers of the atmosphere
temperature, chemical composition, and density
order of atmospheric layers in order of increasing distance from Earth
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
stratopause
separates the stratosphere and mesophere
ozone
gasses responsible for generating heat in the stratosphere
because of the temperature profile of the stratosphere, there is little (___) movement of gasses in the stratosphere
horizontal
the temperature in the stratosphere (___) as the altitude (___)
increases, increases
the transfer of heat through space by electromagnetic radiation
radiation
as hot air masses (___), they are replaced by the surrounding cooler, (___) dense air, which we feel as wind
rise, more
physical principal that underlies Earth’s radiation budget
photoelectric effect
incoming solar radiation from the sun is mostly in the form of (___) radiation
infrared
(___) of the long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth escapes to space through the atmospheric window ??
lesat
colder objects emit photons with (___), while hot objects emit light with (___)
low frequency, high frequency
the Earth releases energy back into the atmosphere as (___)
infrared radiation
greenhouse gasses (___) energy emitted by th Earth
absorb and re-emit
process that does not release carbon into the atmosphere
growth of plants
emitters or methane
natural wetlands, agricultural activities, fossil fuel extraction, transportation
nitrous oxide is produced by (___)
agricultural activities, natural biological processes, fossil fuel burning, industrial processes
F-gasses
chlorofluorocarbons, hydrochlorofluorocarbons, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride
Global Warming Potential
a measure of climate impacts based on atmospheric lifetime and energy absorption properties
as greenhouse gas concentrations increase and global temperatures rise, the total amount of water vapor in the atmosphere (___), (___) the warming effect
increases, amplifying
a measure of the speed of the molecules in the gas
temperature

the approximate maximum wavelength of earth’s emissions spectrum
10 micrometre
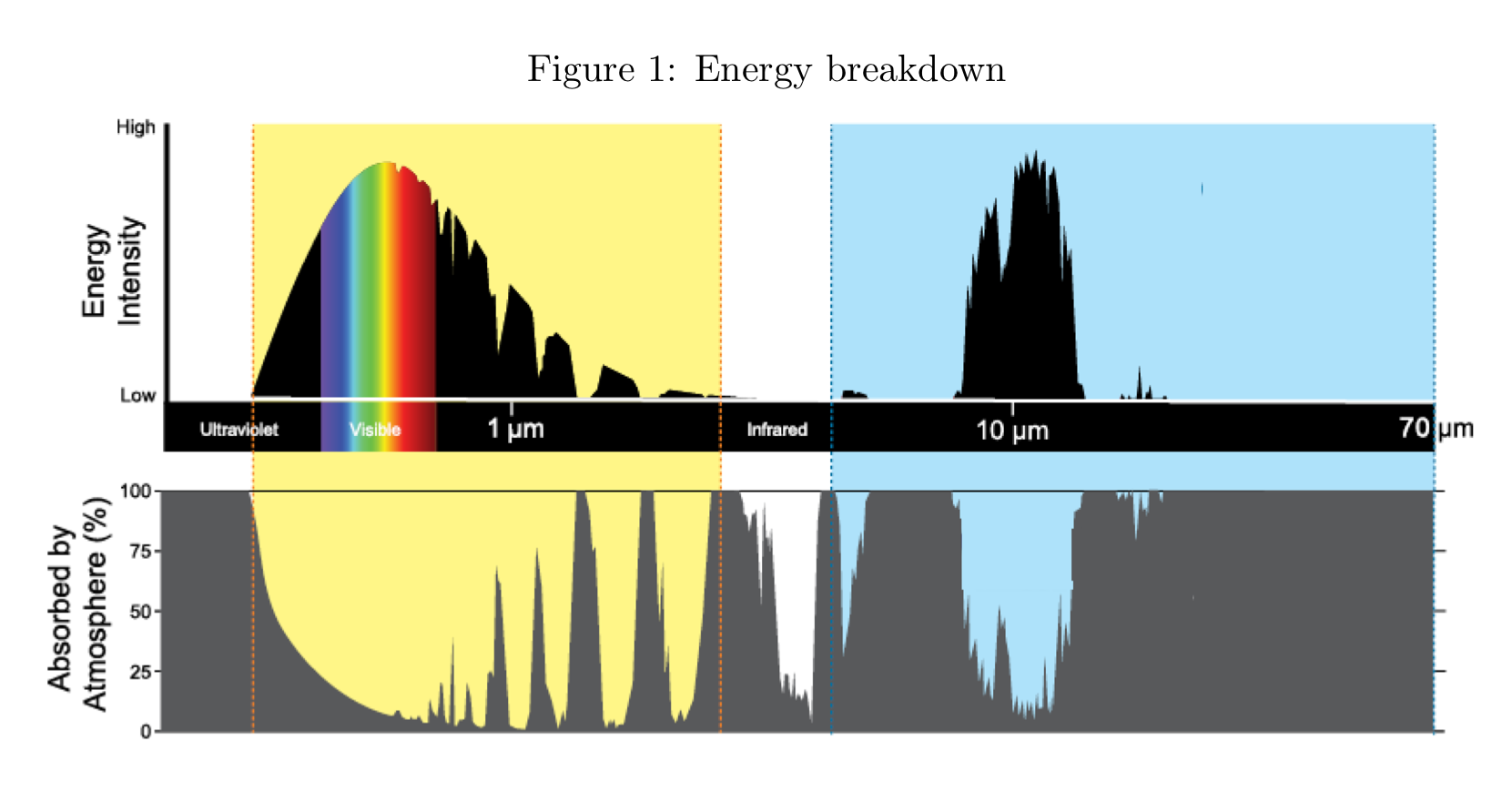
wavelength emitted photons are strongly absorbed by earth’s atmosphere
60 micrometres
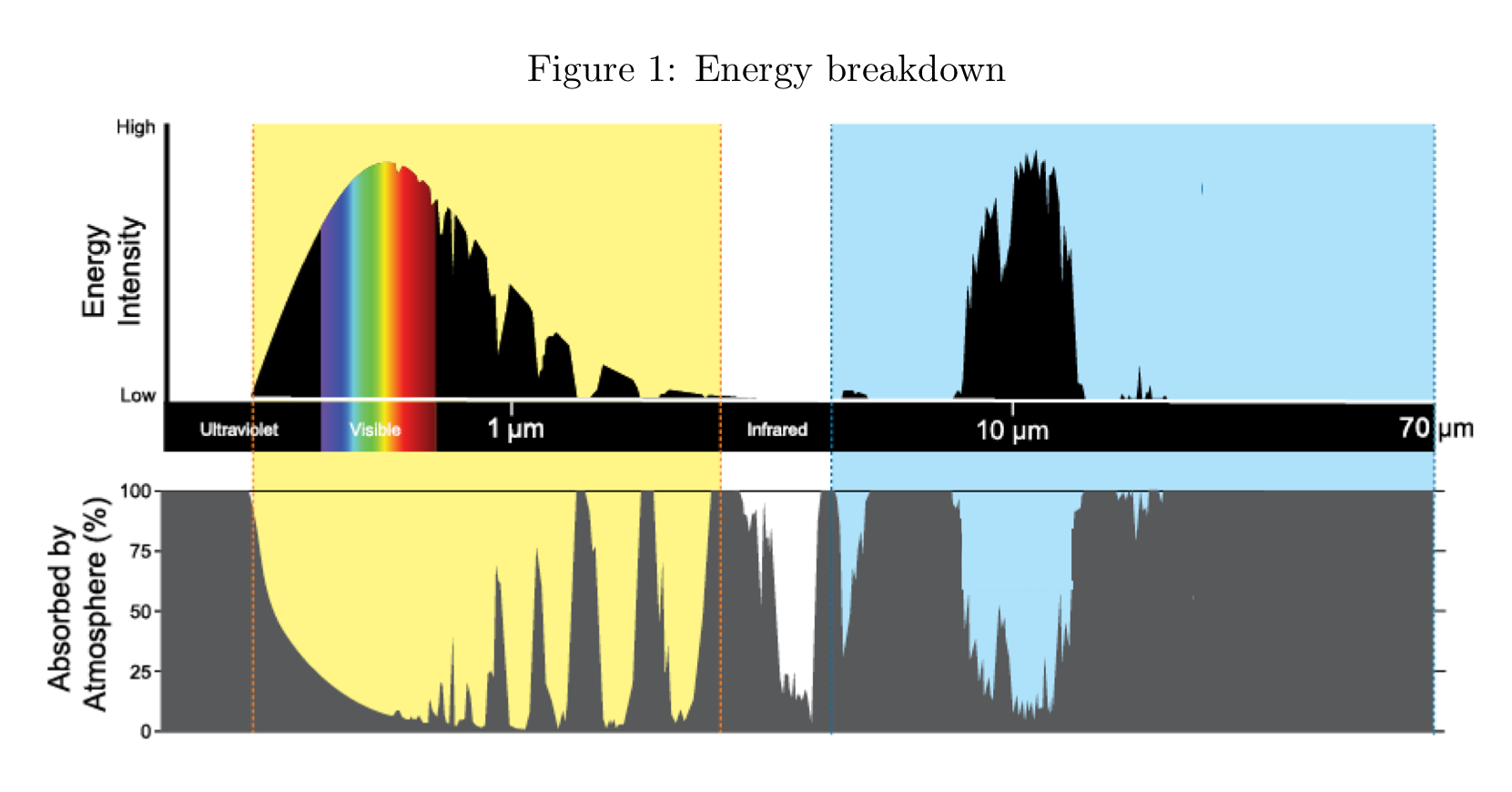
wavelength in the infrared range that would be considered to fall within an atmospheric window
10 micrometre
urban and rural areas
area where ambient air pollution is a problem
nitrogen dioxide
major constituents of photochemical smong and it is formed through the reaction with gasses in the presence of sunlight
ozone
gas that is commonly released from the combustion of fuels in the transportation and industrial sectors
carbon monoxide
a colorless, odorless and tasteless toxic gas produced by incomplete combustion of carbonaceous fuels such as wood, petrol, charcoal, natural gas and kerosene
sulfur dioxide
a colorless gas with a sharp odor produced from burning coal and smelting of mineral ores
breathing air with a high concentration of (___) reduces the amount of (___) that can be transported in the bloodstream to critical organs like the heart and brain
CO, O2
largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere
burning of fossil fuels by power plants
harmful effect of SO2
short term exposures can harm the human respiratory system, high concs can lead to the formation of SOx that contribute to formation of harmful particulate matter pollution, and contribute to acid rain which can harm sensitive ecosystems
bonds of matter
where chemical energy is stored
joule
the standard unit of energy
positive sign
energy given off by a system
to calculate the energy change during a reaction, the difference is taken between the sum of the energies of the bonds in the (___) and the sum of the energies of the bonds in the (___)
products, reactants
exothermic reaction
heat energy is released
heat
the movement of atoms and molecules
ammonia
not considered a member of NOx
NOx in the atmosphere
contributes to nutrient pollution in coastal waters
ozone occurs in the (___) atmosphere
lower
tropospheric ozone is not emitted directly into the air, but is created by chemical rxns of (___) and (___)
NOx, VOC
involved in acid rain formation
NOx and SO2
photochemical reactions
reactions initiated by a photon
free radicals
species with unpaired and an odd number of electrons that are very reactive
during a temperature inversion, (___) air overlays (___) air creating favorable conditions for smog formation
warm, cold
photochemical smog components
ozone, NOx, aldehydes
not a toxic chemical produced in photochemical smog
benzene
best way to prevent smog formation
control release of NOx
boiling points of non-volatile chemicals
high
stratosphere
where most ozone is concentrated
UVB
radiation that ozone absorbs, preventing it from reaching the planet’s surface where it causes health effects
physiological of plants
affected by UVB
linked to destruction of ozone in the ozone layer
Cl and Br
total amount of ozone will decrease in the atmosphere
if ozone is created at a slower rate than it is destroyed
in the stratosphere, (___) is created primarily by the rxn of UV light with (___)
O3, O2
ozone breaks down into free O atoms, which re-join with an O molecule to reform ozone, which converts harmful radiation into (___)
heat