Human Tissue Types and Functions: A Comprehensive Biology Review
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What are tissues?
Groups of cells in the body that work together for a common function.
What is the study of tissues called?
Histology.
Name the four basic categories of tissues.
Epithelial Tissue, Connective Tissue, Muscle Tissue, Nervous Tissue.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissues?
To cover surfaces, line passageways, and make up certain glands.
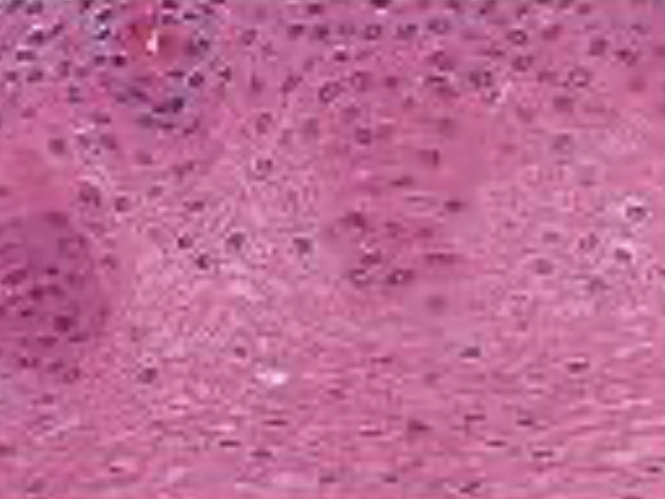
What are the main functions of connective tissues?
To bind things together, provide protection, support, and integration of body parts.
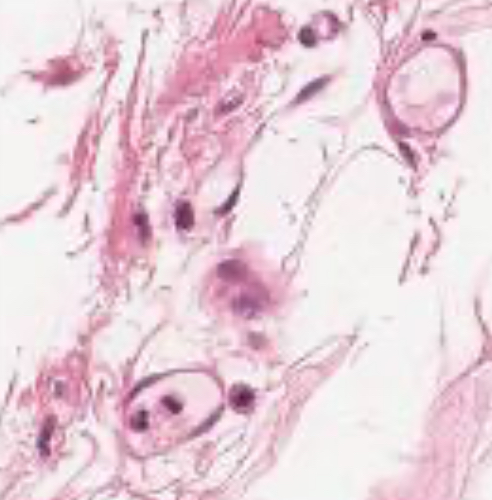
What is the role of muscle tissue?
To respond to stimuli to contract and provide movement.
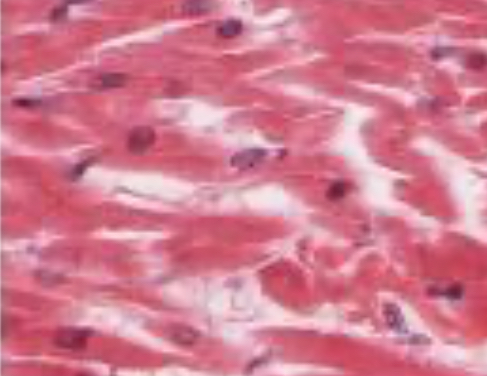
What does nervous tissue do?
Allows the propagation of electrochemical signals for communication throughout the body.

What are the Two Broad Categories of tissue membranes?
Connective Tissue membranes & Epithelial membranes
what is a type of Connective Tissue membrane?
Synovial Membrane
What are the types of epithelial membranes?
Mucous membranes, serous membranes, and cutaneous membranes (SKINN).
Membrane
Thin sheet of cells that create a lining
Epithelial Tissues are
Large sheets of cells that cover surfaces of the body (inner surfaces and outer surfaces)
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Very cellular, cells joined by junctions, has polarity (top= Apical surface, Bottom=Basal Surface)., attached to a basement membrane, avascular, and highly regenerative.
What are the three basic types of cell junctions?
Tight junctions, gap junctions, and anchoring junctions.
What are the Functions of Epithelial Tissue?
• Protect from physical, chemical and biological damage:
• UV radiation
• Bacteria and viruses
• Dirt and debris
• Physical abrasion
• All substances that enter the body must cross an epithelium
Which are Epithelial?
Secretory: mucous; digestive enzymes; messengers; glands
Classification of Epithelial Tissue is based on
Shape
• Squamous
• Cuboidal
• Columnar
Squamous (Epi)
Flat
Cuboidal (Epi)
Cube (Equal Height & Width)
Columnar (Epi)
Tall
Classification of Epithelial Tissue is ALSO based on
Number of Layers
• Simple
• Stratified
• “Pseudostratified”: pseudo
Simple (epi) Layer
One layer
Stratified (epi) Layer
Multiple Layers
“Pseudostratified”: pseudo (epi) Layer
fake; the messy arrangement looks like multiple layers but it isn’t
What is the difference between simple and stratified epithelial tissue?
Simple epithelial tissue is a single layer of cells, while stratified epithelial tissue has multiple layers.
What is the function of goblet cells?
To secrete mucus.
In the lining of the small intestine, columnar epithelium cells are interspersed with goblet cells.
What are glandular epithelia?
Modified epithelial cells whose main purpose is to synthesize and secrete substances.
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Endocrine glands release substances into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands release substances into ducts leading to surfaces.
Endocrine Glands
release their substances (hormones) into the blood stream or interstitial fluid (Ref: 3.1)
• “endo” = inside
Exocrine Glands
release their substances into a duct that leads to the surface
• “exo” = outside
What are the modes of glandular secretion?
Merocrine- Cell remains Intact (skin)
Apocrine- Apical portion of cell is releases as well (body odor glands) (axillary pubic region)
Holocrine secretion- Cell is destroyed as it releases its product and the cell itself becomes part of the secretion. (oil in hair)
Merocrine (Glandular Secretion)
Cells remain Intact (Skin)
Apocrine (Glandular Secretion)
Apical portion of cell is releases as well (body odor glands) (axillary pubic region)
Holocrine Secretion (Glandular)
Cell is destroyed as it releases its product and the cell itself becomes part of the secretion. (oil in hair)
What is the function of sebaceous glands?
To secrete oils that lubricate and protect the skin.
They are holocrine glands and they are destroyed after releasing their contents. New glandular cells form to replace the cells that are lost.
Connective Tissues
Serve to support and connect other tissues and lay down structure.
What are the characteristics of connective tissues?
Cells are spread out within a matrix, which is typically made by the cells living within it.
The make-up of the matrix is unique to each tissue’s function
What is the matrix in connective tissues made of?
Ground substance (fluid, gel, or hardened) and protein fibers (collagens, elastic fibers, reticular fibers).
cyte
cell
blast
cell that builds/makes
clast
cell that destroys/renovates
Connective Tissue
serve to support and connect other tissues and lay down structure.
What functions do connective tissues serve?
Support, connect/bind, protect, transport, and defend.
What does 'form follows function' mean in the context of connective tissues?
Each connective tissue differs in contents and specialized cells based on its function.
Connective tissue types
Connective Areolar Tissue Proper
Adipose Tissue
Reticular Tissue
What is connective tissue proper? (Areolar)
A type of connective tissue that includes fixed cells like fibrocytes, adipocytes, and mesenchymal cells.
Fibroblasts produce this fibrous tissue.
Fibroblasts scattered all around.
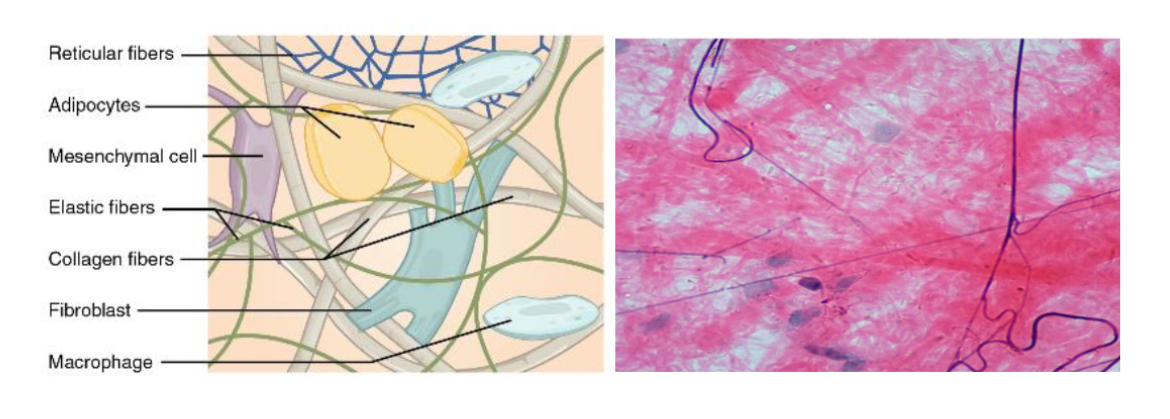
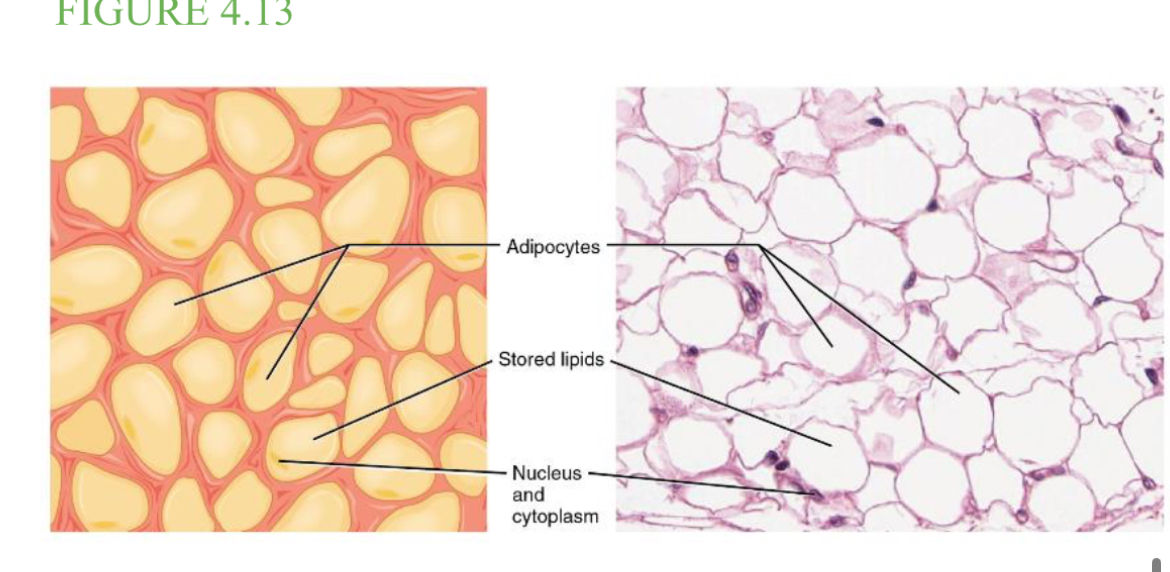
What type of tissue is adipose tissue?
A loose connective tissue that consists of fat cells with little extracellular matrix. And stores fat for energy & provides insulation.
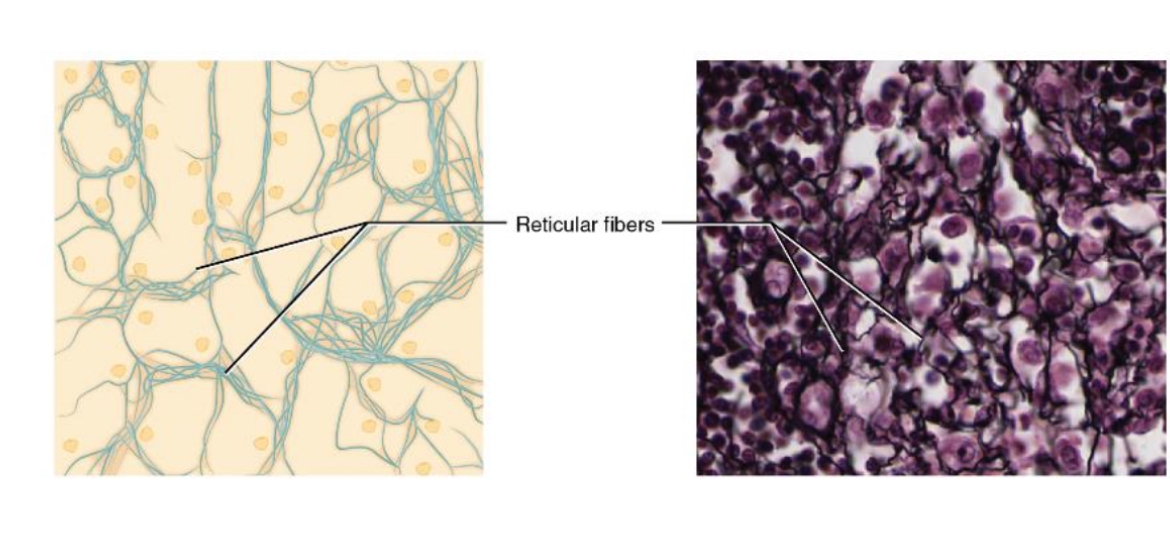
What is the main function of reticular tissue?
Provides a supportive framework for soft organs.
Loose connective tissue made up of reticular fibers.
Found in the immune organs
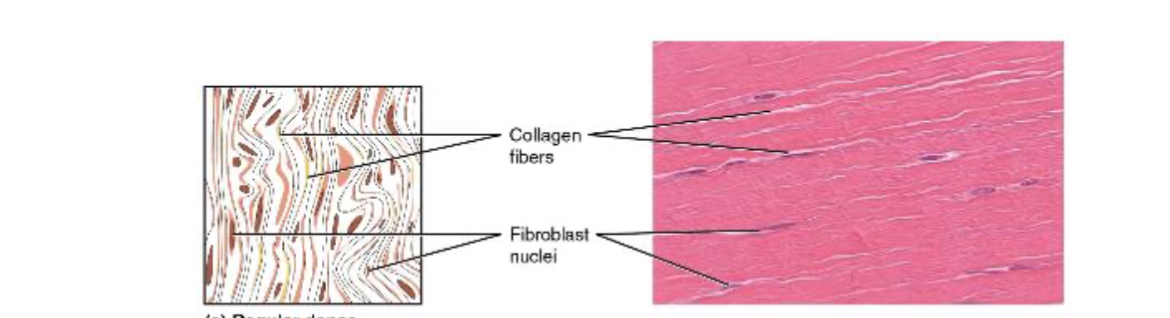
What are the two types of dense connective tissue?
Dense regular connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue.
Dense regular connective tissue
Consists of collagenous fibers packed into parallel bundles.
Fibroblasts found in between parallel collagens
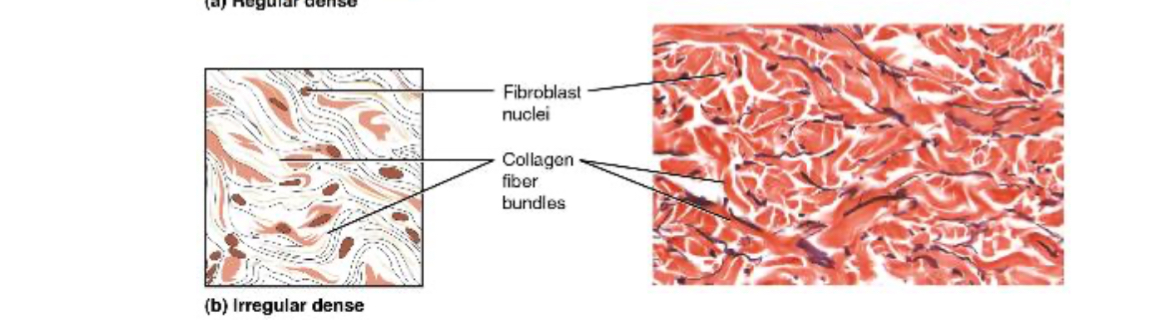
Dense Irregular connective tissue
Consists of collagenous fibers interwoven into a mesh-like network.
Cartilage
A connective tissue consisting of collagenous fibers embedded in a firm matrix of chondroitin sulfates.
What is cartilage primarily composed of?
Collagenous fibers embedded in a firm matrix of chondroitin sulfates.
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
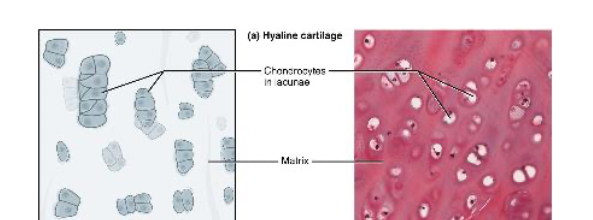
Hyaline Cartilage
Provides support with some flexibility. (ex: dog tissue)
Chondrocytes and a smooth appearing background (matrix)
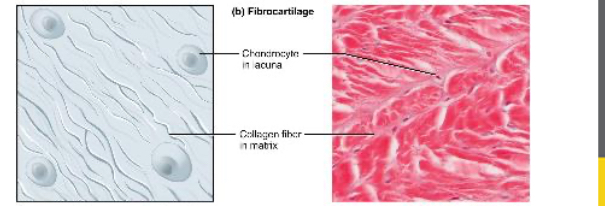
Fibrocartilage
Provides some compressibility & can absorb pressure.
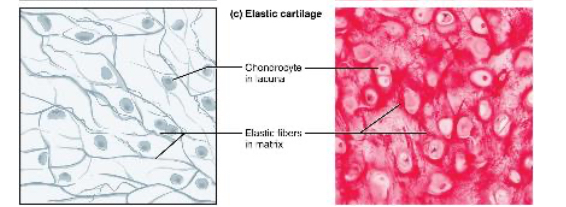
Elastic Cartilage
Provides firm but elastic support.
Chondrocytes and little dark "threads" in the matrix
What is the hardest supporting connective tissue?
Bone.
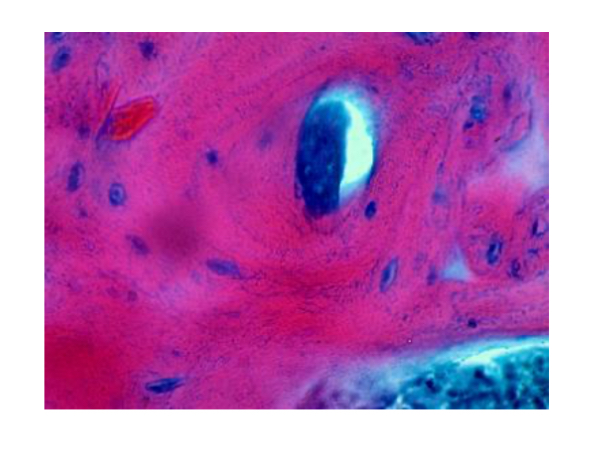
Decalcified Bone.
Seeing all living components
What is the #1 bone salt
Hydroxyapatite
Ground Bone
Can only see samp/ink of salt structure
Dehydrated
What is the extracellular matrix of bone primarily made of?
Collagen fibers in a hardened ground substance, mostly hydroxyapatite.
What are the Cells of Bone
Osteoblasts, Osteocytes, Osteoclasts
What is blood classified as?
A fluid connective tissue.
containing erythrocytes and various types of leukocytes that circulate in a liquid extracellular matrix
Membranes
Are physical barriers that line of cover portions of the body.
To be classified as a membrane—
The covering must consist of an epithelium and at least ONE type of connective tissue
What are the four types of membranes in the body?
Mucous membranes, serous membranes, cutaneous membranes, and synovial membranes.
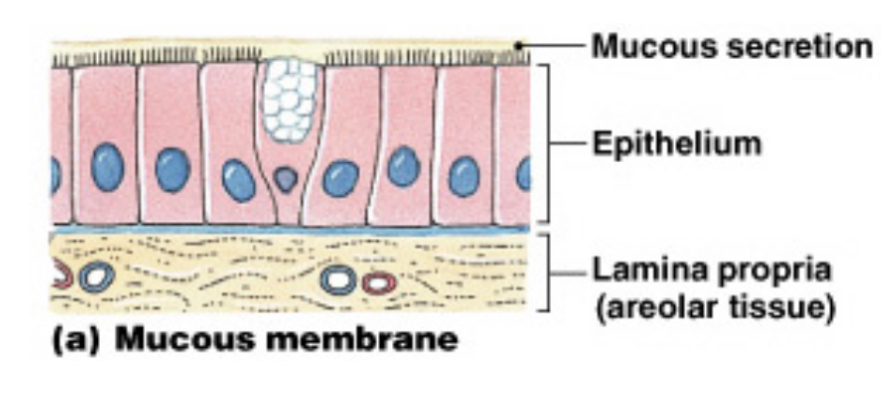
What is the function of Mucous membranes? aka Mucosae
They line passageways with external connections and must remain moist.
• Found in the digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive tracts
• Epithelial surface must be moist to reduce friction and to facilitate
absorption and excretion
• The lamina propria is areolar connective tissue
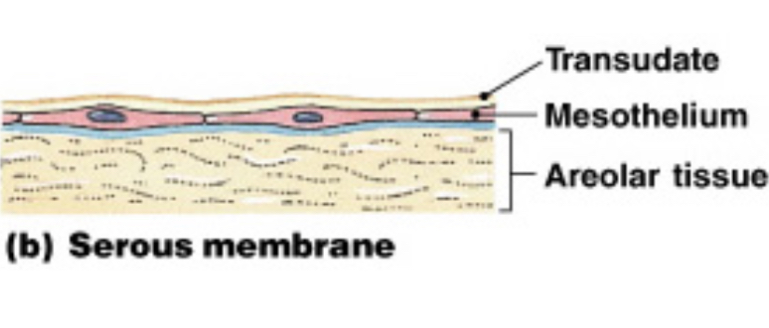
What is the primary characteristic of serous membranes?
They line cavities not open to the outside and have a fluid transudate to reduce friction.
Thin but very strong. Typically double-walled; have a parietal and visceral layer
• Examples: pleura; pericardium; peritoneum
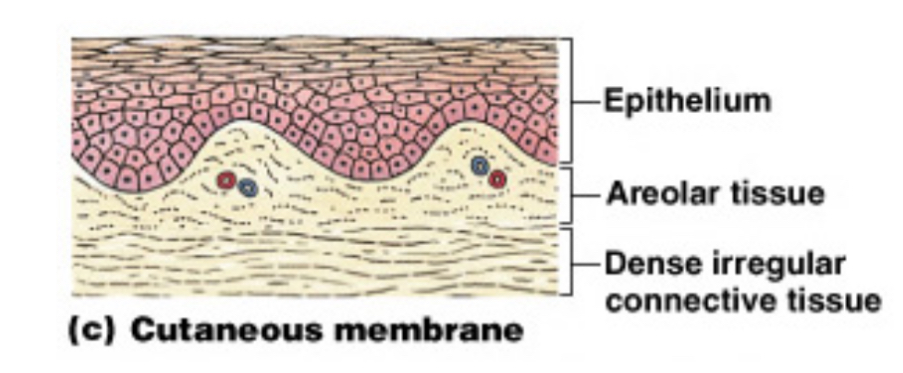
What is the cutaneous membrane?
The skin, which is thick, waterproof, and dry.
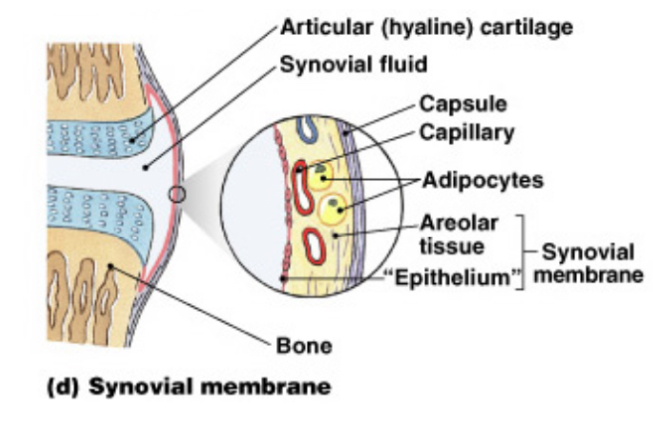
What is the role of synovial membranes?
They line articulating joint cavities and produce synovial fluid for lubrication. Protect ends of bones. Lacks a true epithelium.
Muscle Tissue
Allows for movement of and within the body.
What are the characteristics of muscle tissues?
They are excitable (respond to stimulus), contractile (generate a pulling force), and can be voluntary (Skeletal Muscle) or involuntary (Cardiac & Smooth Muscle)
What distinguishes skeletal muscle cells?
They have prominent striations and nuclei located on their periphery.
What distinguishes Smooth muscle cells
Have a single nucleus and no visible striations.
What distinguishes Cardiac Muscle cells
appear striated and have a single nucleus.
Nervous Tissue
To Allows the exchange of information around the body using electrochemical signals.
What is the primary function of nervous tissue?
To allow the exchange of information around the body using electrochemical signals.
'Excitable; “action potentials”
• Send information
Neuron
The cells which propogate information
Neuroglia
The cells which support the neuron
Astrocytes
Blood-brain barrier for protection
Microglia
Immune function
Schwann Cells and Oligodendrocytes
create Myelin
Ependymal Cells
create Cerebrospinal Fluid
What is the function of astrocytes in nervous tissue?
They form the blood-brain barrier for protection.
What role do Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes play?
They create myelin, which insulates axons.
What is the function of ependymal cells?
They create cerebrospinal fluid.
What occurs during tissue healing?
Collagen fibers are laid down randomly by fibroblasts to repair the area. (Wound Repair)
the Neuron
Cell body/Soma contains the nucleus and mitochondria. The dendrites transfer the nerve impulse to the soma. The axon carries the action potential away to another excitable cell.
Nervous tissue-
Made up of neurons and neuroglia. The cells of nervous tissue are specialized to transmit and receive impulses.
What changes are observed in tissue during cancer development?
Changes in Cell size, Nucleus size, and Organization.
Skeletal muscle tissue : Histology
Long cylindrical fiber, striated, many peripherally located nuclei
Skeletal muscle tissue : Function
Voluntary movement, produces heat, protects organs
Skeletal muscle tissue : Location
Attached to bones and around entrance points to body (e.g., mouth, anus)
Cardiac muscle tissue : Histology
Short, branched, striated, single central nucleus
Cardiac muscle tissue : Function
Contracts to pump blood.
Intercalated Disc
Cardiac muscle tissue : Location
Heart
Smooth muscle tissue : Histology
Short, spindle-shaped, no evident striation, single nucleus in each fiber
Smooth muscle tissue : Function
Involuntary movement, moves food, involuntary control of respiration, moves secretions, regulates flow of blood in arteries by contraction
Smooth muscle tissue : Location
Walls of major organs and passageways