AP Microeconomics Unit 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Quantity supplied
amount that will be sold at a specific price
point on the curve
Supply
quantities producers are willing to sell at various prices at a specified time, Ceteris Paribus
Increase in supply
rightward shift of the supply curve
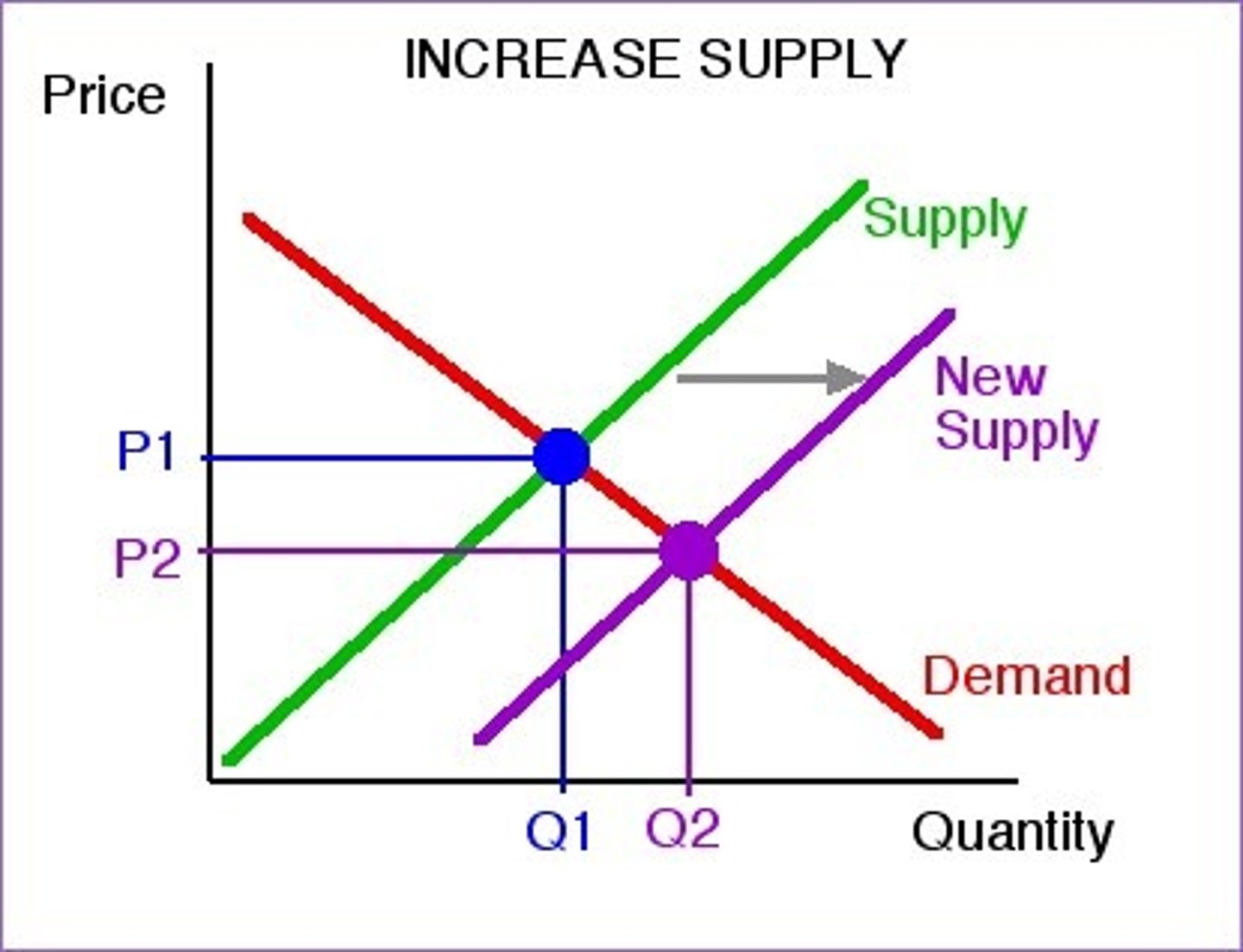
Decrease in supply
leftward shift of the supply curve
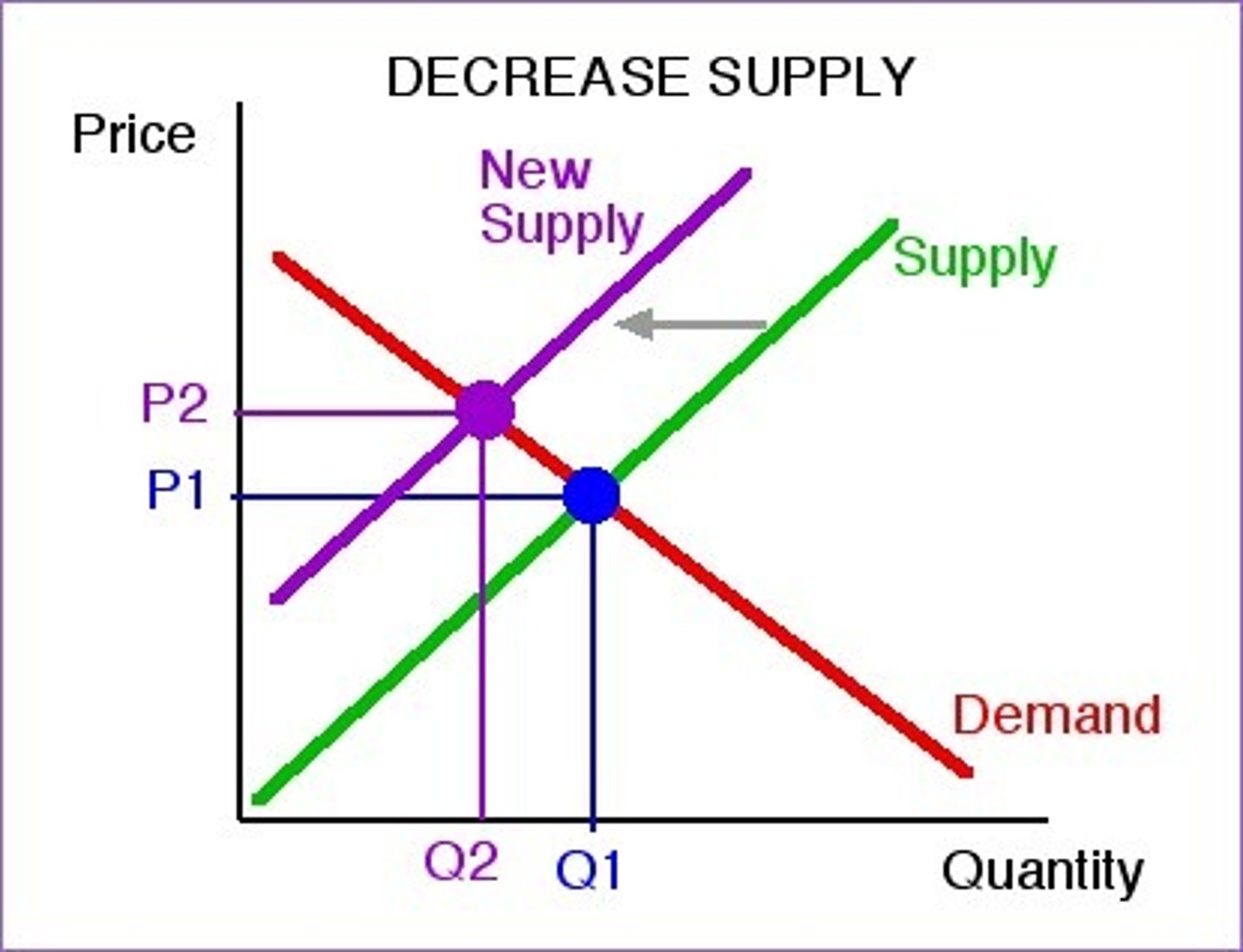
What are the determinants of supply
change in number of suppliers
change in input costs
change in the physical availability of resources
change in technology in the long run
change in expected future prices by supplier
change in gov't regulations, taxes
Quantity demanded
amount that will be bought at a specific price
point on the curve that is changed by price
Demand
prices consumers are willing to pay at a specified time, Ceteris Paribus
What conditions must be met to count as 'demand'
being both willing to and able to purchase a good or service
What are the determinants of demand
change in the number of consumers
change in income (Y) normal goods (YED > 0)
change in income (Y) inferior goods (YED < 0)
change in taste or preferences
change in the price (P) of a substitute (XED > 0)
change in the price (P) of a complement (XED < 0)
change in expected future prices (EFP) by consumers
change in expected future income (EFY) of consumers

equilibrium price
price paid or received at the equilibrium quantity
equilibrium quantity
quantity bought and sold at the equilibrium price
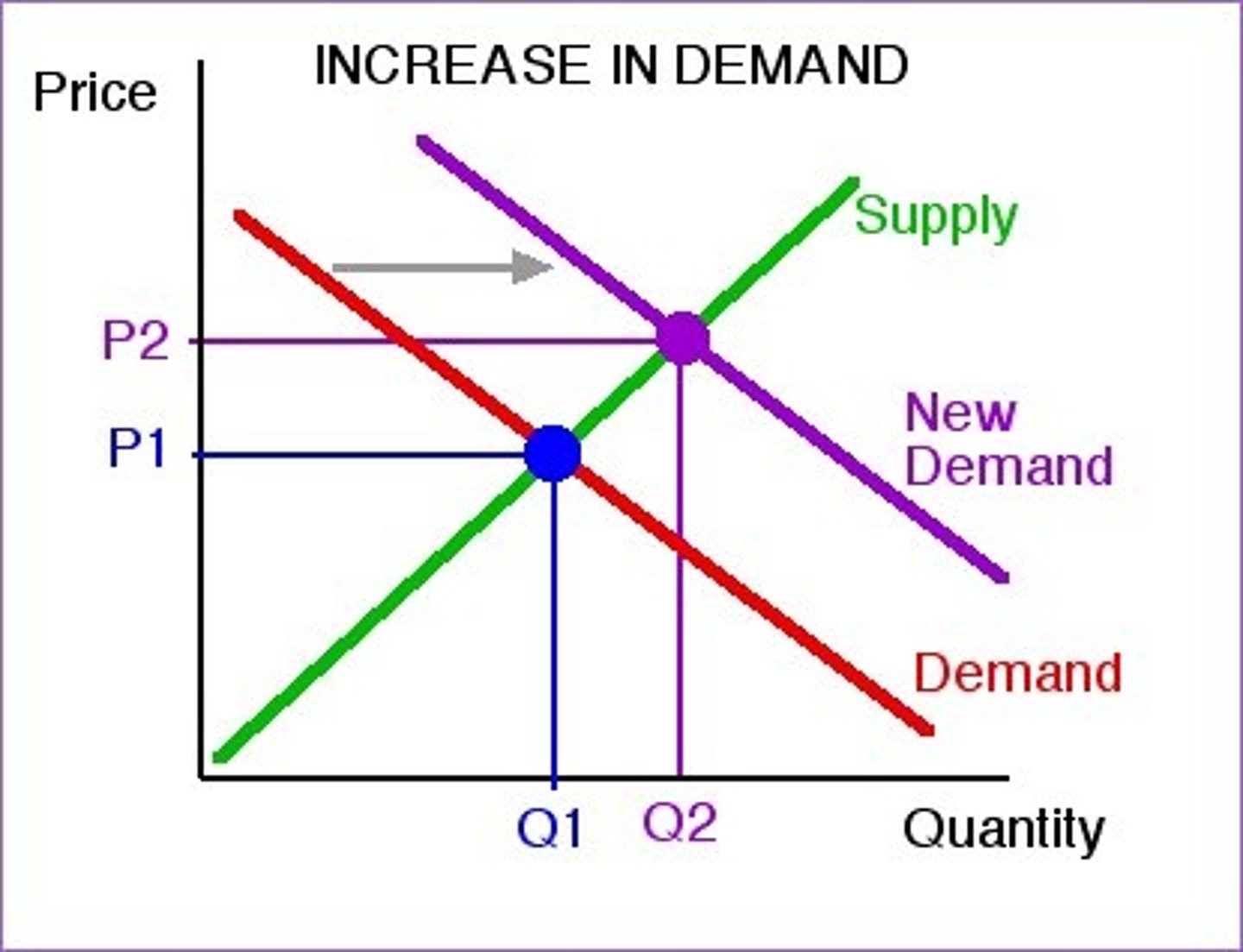
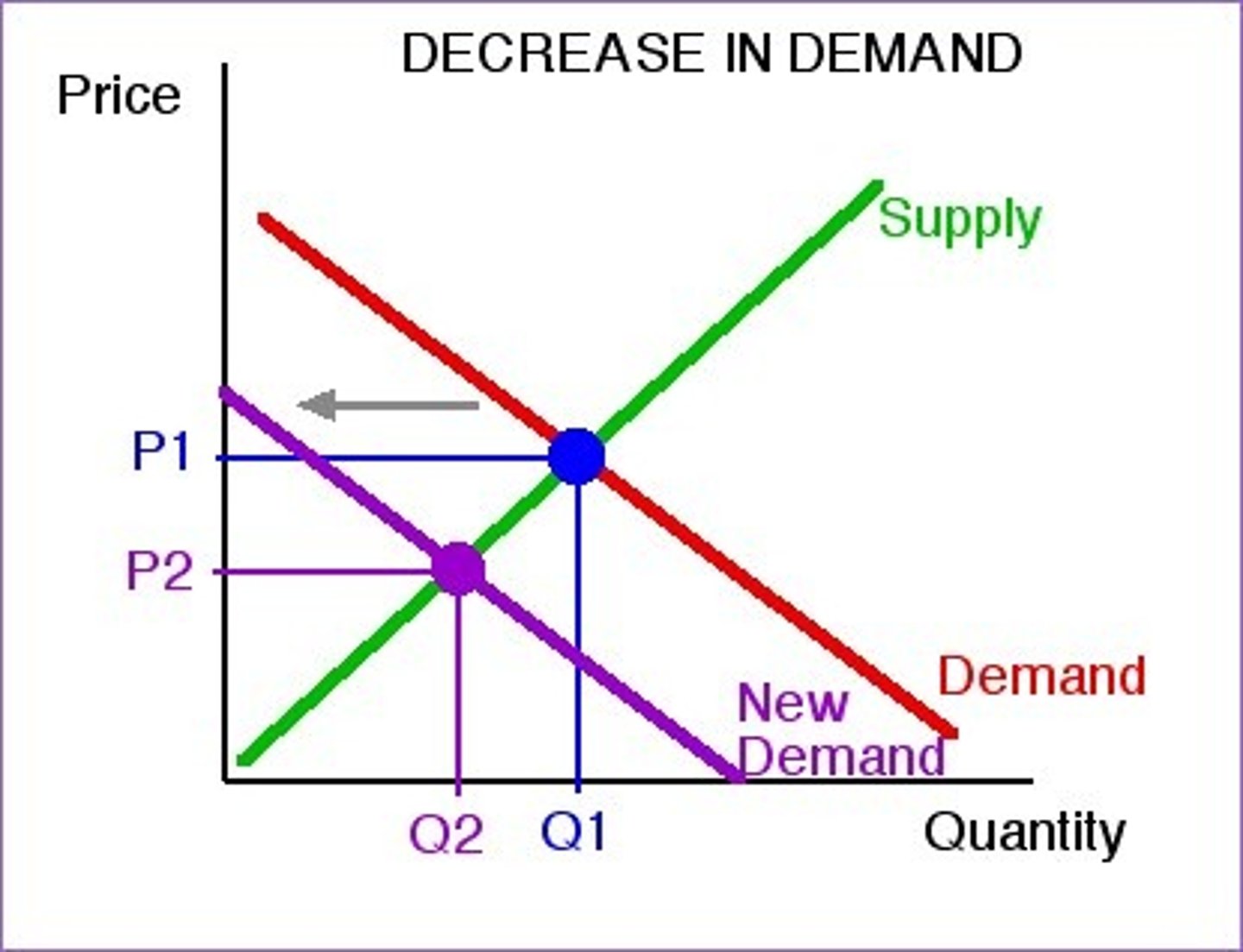
Increase in demand
rightward shift of the demand curve
Decrease in demand
leftward shift of the demand curve
Income effect
when the price decreases for a product consumers can afford to buy more with the same income and vice versa
Substitution effect
when a closely-related product is at a lower price consumers have the incentive to buy what is now a less expensive good for similar products that are now relatively more expensive
Diminishing marginal utility
when a consumer purchases more of a good or service, the satisfaction received goes down; consumer will continue to purchase if the price goes down
Marginal utility
additional satisfaction obtained from acquiring one more unit of a product
Total utility
total amount of satisfaction obtained from consumption of a good or service
Utility
satisfaction or usefulness that is measured in utils
Elastic demand
consumers are sensitive to small changes in price as it causes major effects on the quantity demanded; relatively flat curve with a negative slope; PED or PES > 1
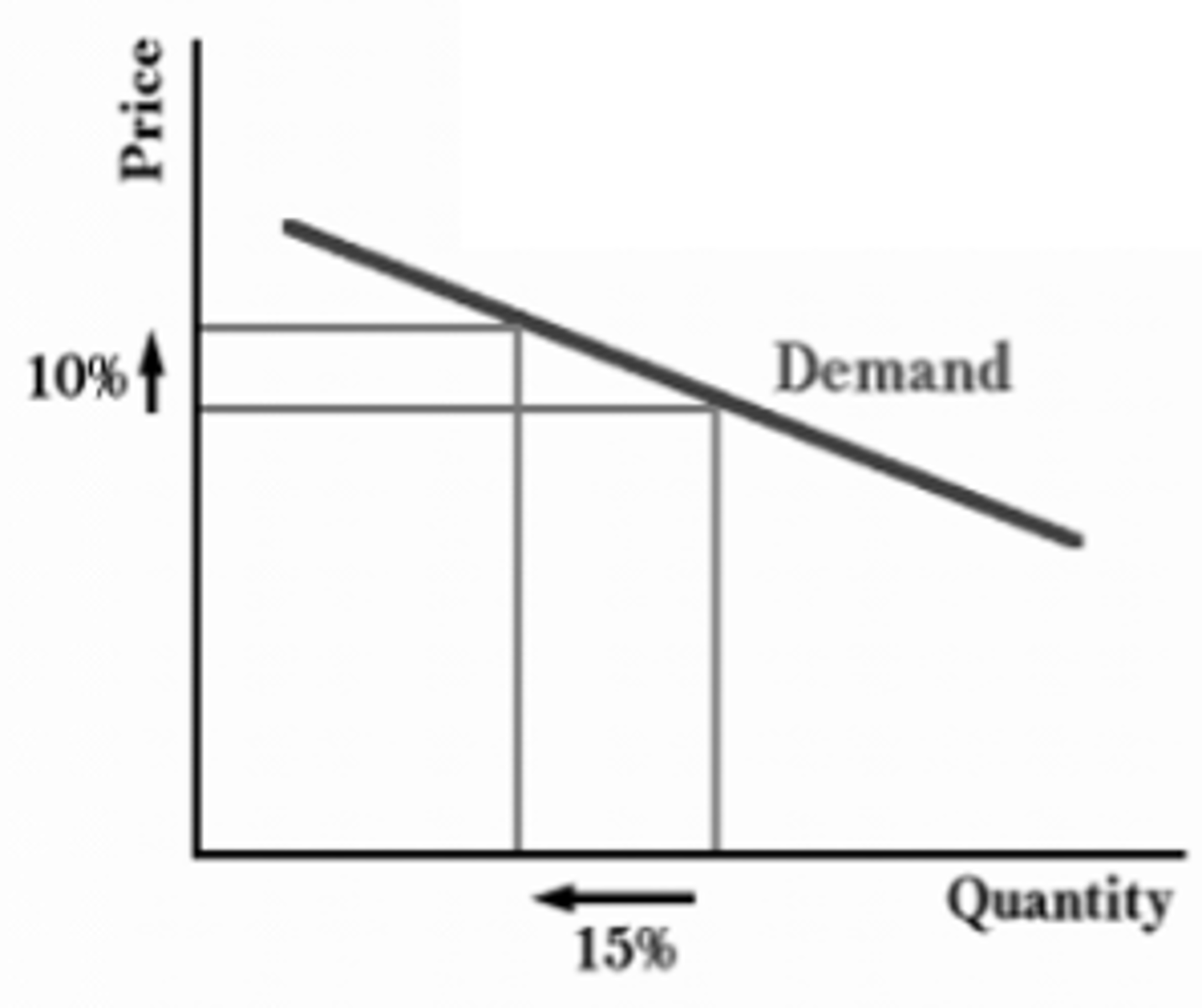
Inelastic demand
consumers are insensitive to small changes in price as it causes little effect on the quantity demanded; usually a necessity; relatively steep curve with a negative slope; PED or PES < 1
Characteristics of elastic goods/services
many substitutes
luxuries
large portion of income
plenty of time to decide (long run)
easy to manufacture
Characteristics of inelastic goods/services
few or no substitutes
necessities
small portion of income
required now, rather than later (short run)
not easy to manufacture
Total revenue test
Check to see how elasticity shows changes in price will affect total revenue

Total revenue
total amount of money a firm receives by selling goods or services
change in total revenue retained by producers is negative
total revenue = price × quantity
total revenue ≠ profit
Total expenditure
total amount of money a consumer spends by buying goods or services; total expenditure = price × quantity
Unit elastic
percentage change in price and quantity demanded are the same
PES or PED = 1
Price elasticity of demand
measure of how consumers react to a change in the price of a good (decimal value)
PED = (%ΔQd / %ΔP)
%ΔQd = (|ΔQ| / ([Q₁ + Q₂]/2))
%ΔP = (|ΔP| / ([P₁ + P₂]/2))
Marginal revenue
additional income from selling one more unit of a good
MR = (ΔTR / ΔQ)
Income elasticity
sensitivity of quantity demand relative to changes in income (decimal value)
YED = (%ΔQd / %ΔY)
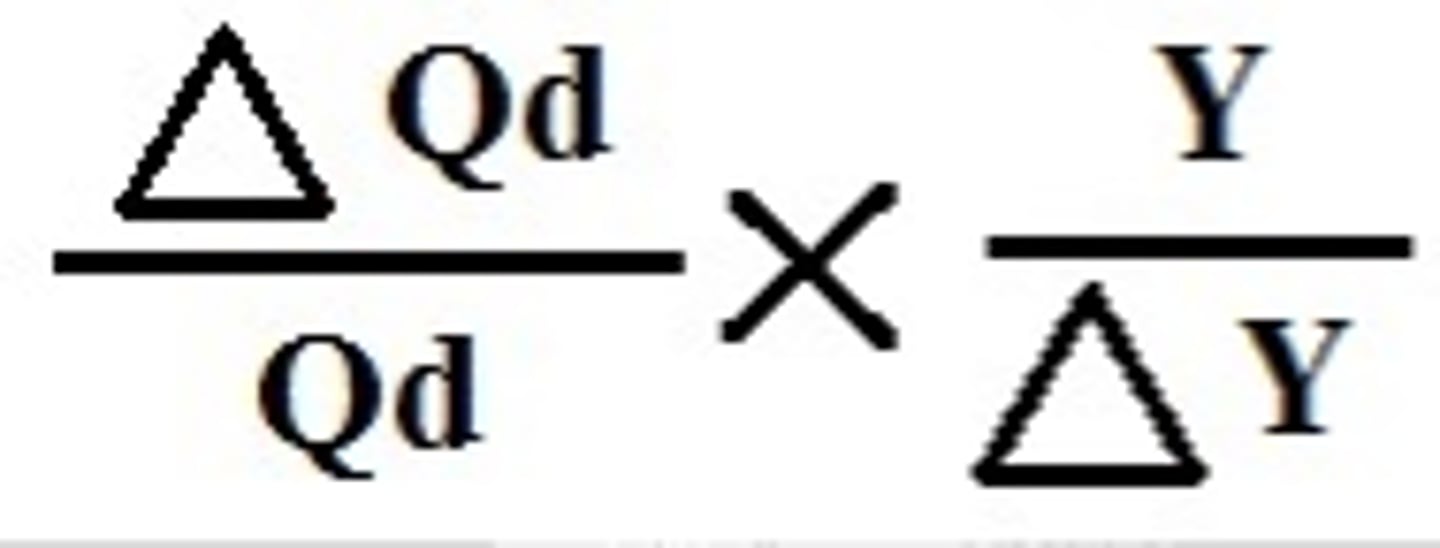
cross-price elasticity of demand
measures the responsiveness of demand for a product following the change in the price of another related product (decimal value); XED = (%ΔQd of B / %ΔP of A)
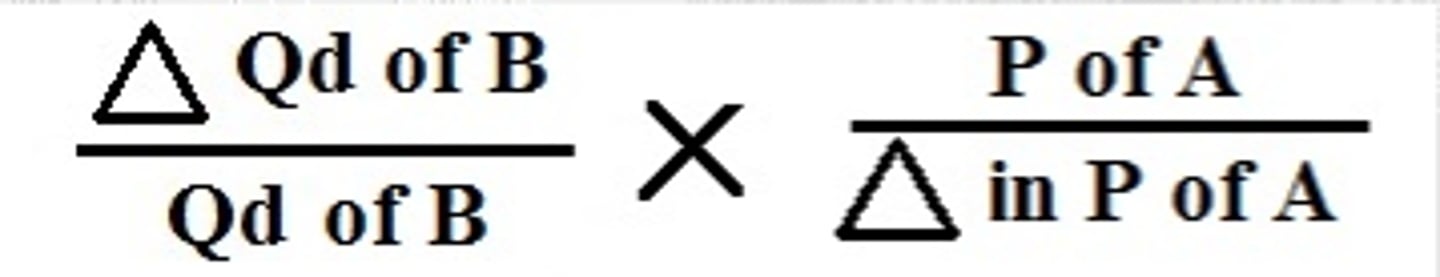
Price elasticity of supply
measure of how much the quantity supplied of a product responds to a change in price and how quickly firms can ramp up production (decimal value); supply inelastic in the short run and more elastic in the long run
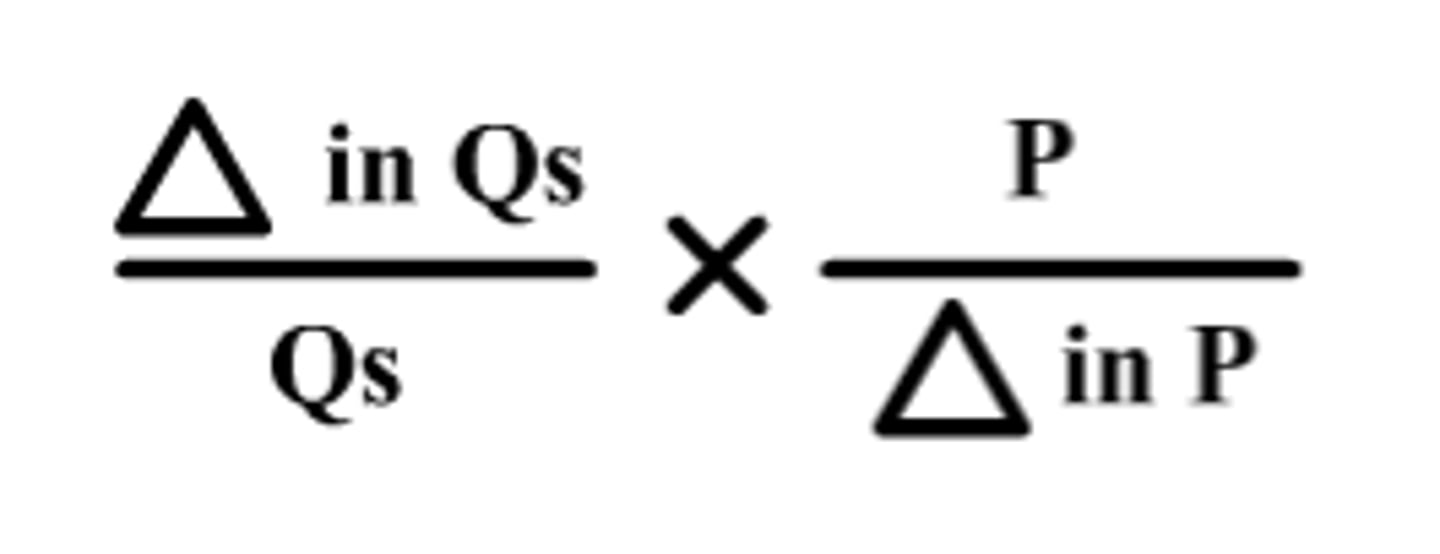
Law of supply
when prices rise, quantity supplied rises and when prices fall, quantity supplied falls, ceteris paribus
Law of demand
when prices fall, quantity demanded rises and when prices rise, quantity demanded falls, ceteris paribus
Perfectly elastic
change in price causes an infinite change in the quantity demanded; PES or PED = ∞
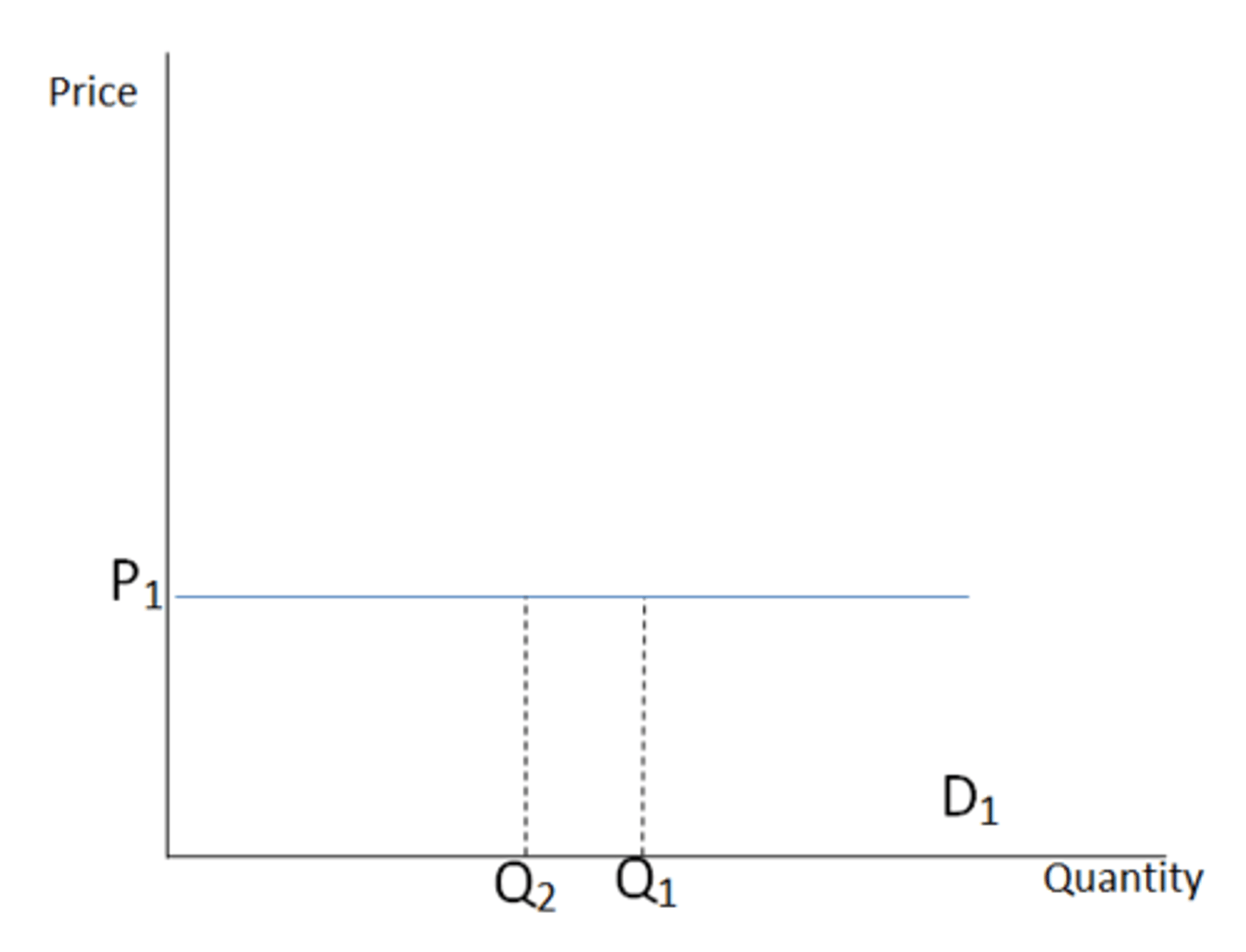
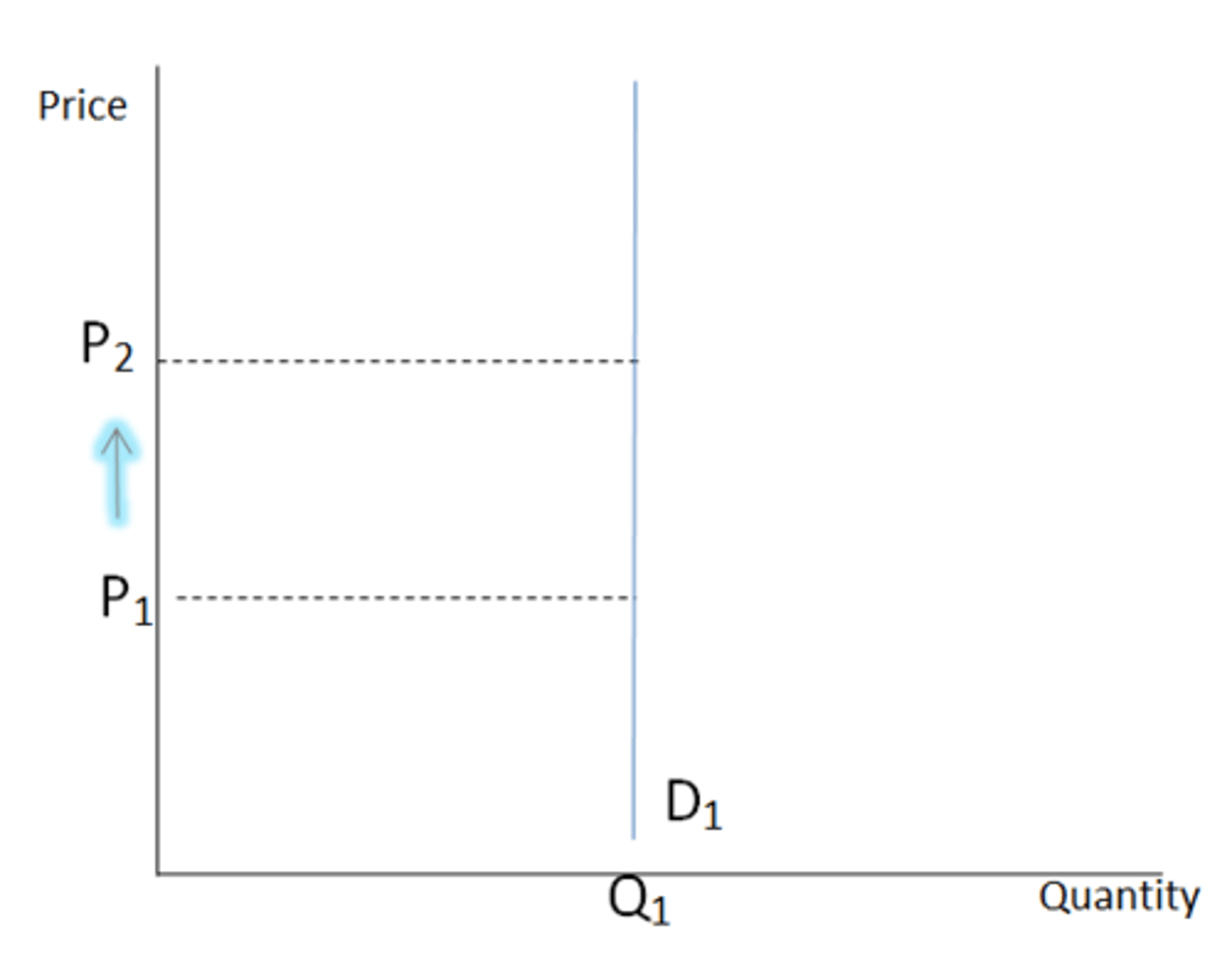
Perfectly inelastic
price is the same at any quantity demanded; PES or PED = 0
Welfare economics
study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being
Individual consumer surplus
buyer's willingness to pay minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it and measures benefit that the buyers receive as they perceive it
Market consumer surplus
sum of individual consumer surplus; indicated by the whole triangle above the price and below the demand curve
Individual producer surplus
amount a seller is paid for a product minus the seller's cost and measures the benefit to sellers participating in the market
Total surplus
sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus
Market producer surplus
sum of individual producer surplus; indicated by the whole triangle below the price and above the supply curve
Efficiency
property of a resource allocation of maximizing the total surplus received by all members of society
Market efficiency
when a market is capable of producing output high enough to meet consumer demand
Market
institution that allows buyers and sellers to exchange goods and services
Utility-maximizing rule
principle that to obtain the greatest utility, the consumer should allocate money income so that the last dollar spent on each good or service yields the same marginal utility
Market equilibrium
point where resources are efficiently allocated; Qs = Qd
Price floor
minimum price that can be legally charged for a product that occurs when the government sets a price above the equilibrium price
effective price floors lead to a surplus (Qs - Qd)
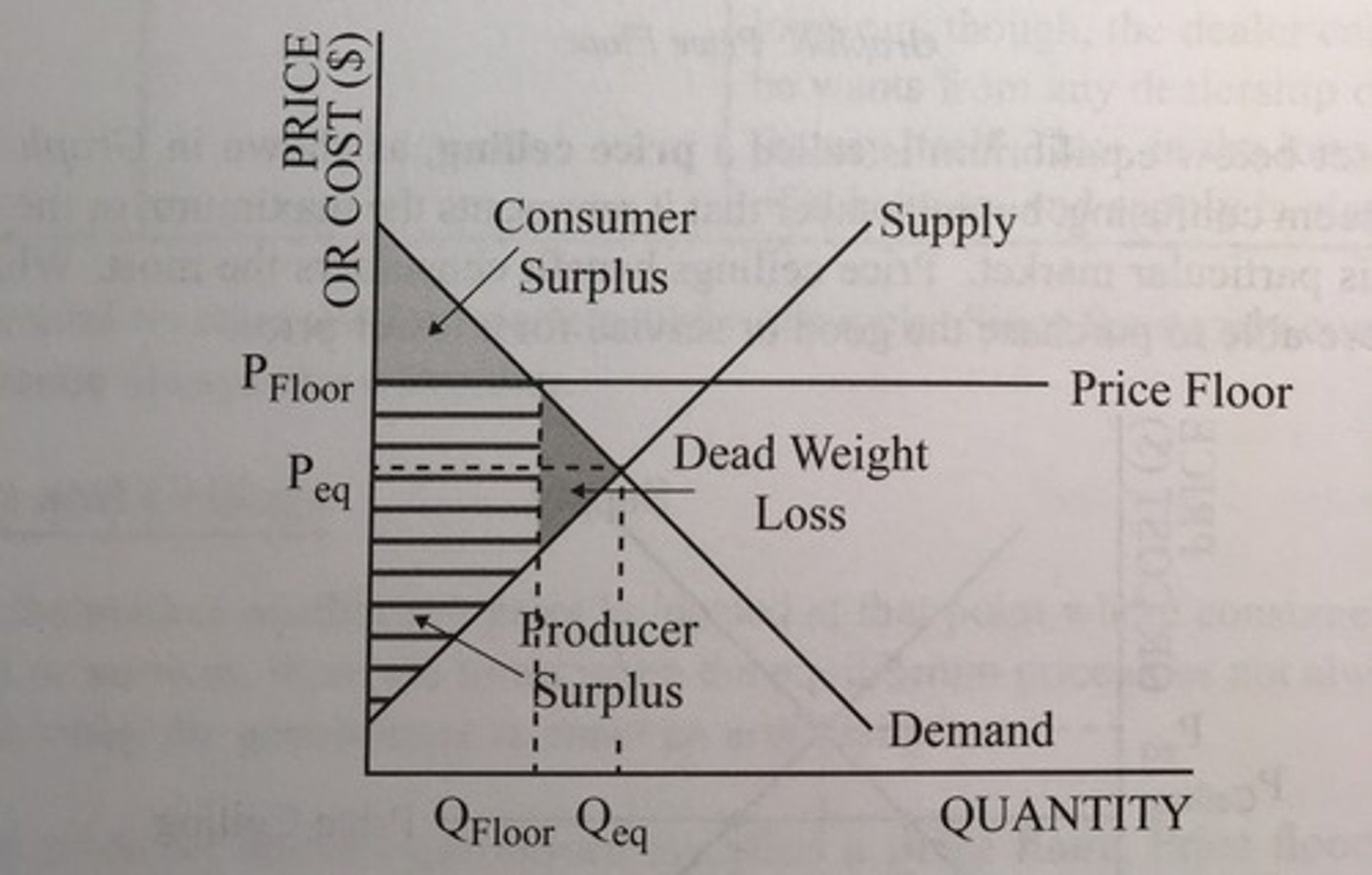
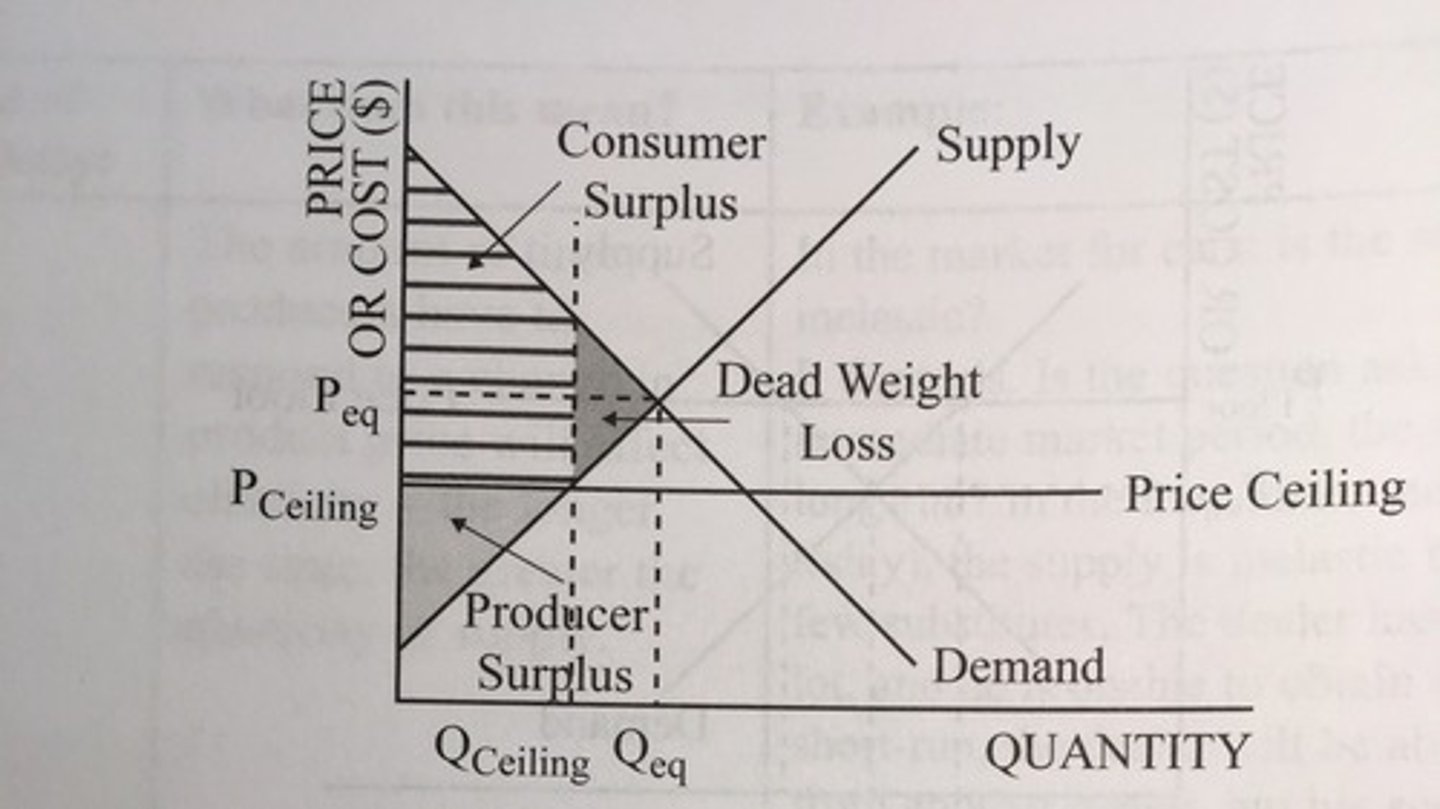
Price ceiling
maximum price that can be legally charged for a product that occurs when the government sets a price below the equilibrium price
effective price ceilings lead to shortages (Qd - Qs) and black market activity
Dead Weight Loss (DWL)
reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium (allocative inefficiency)
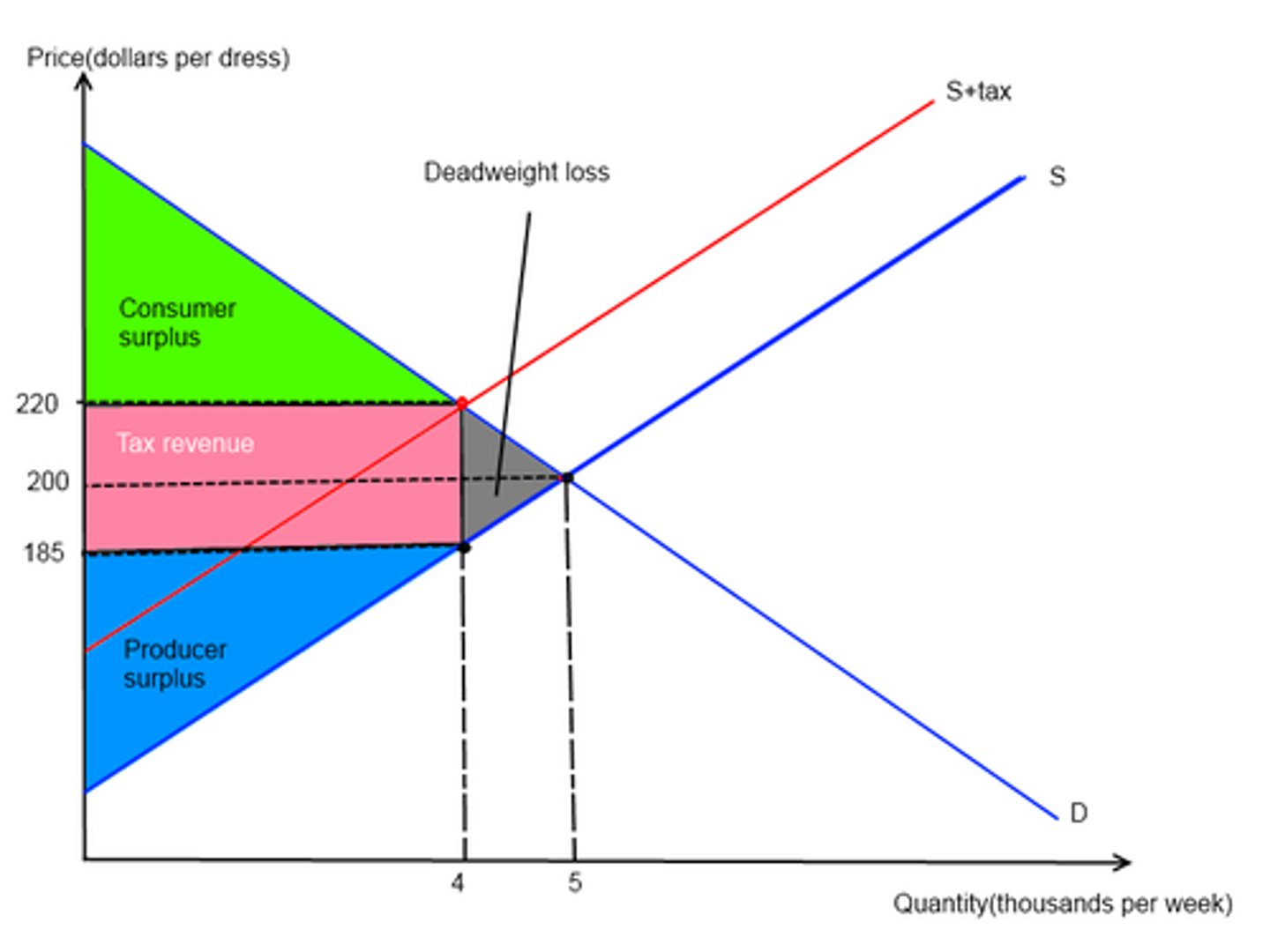
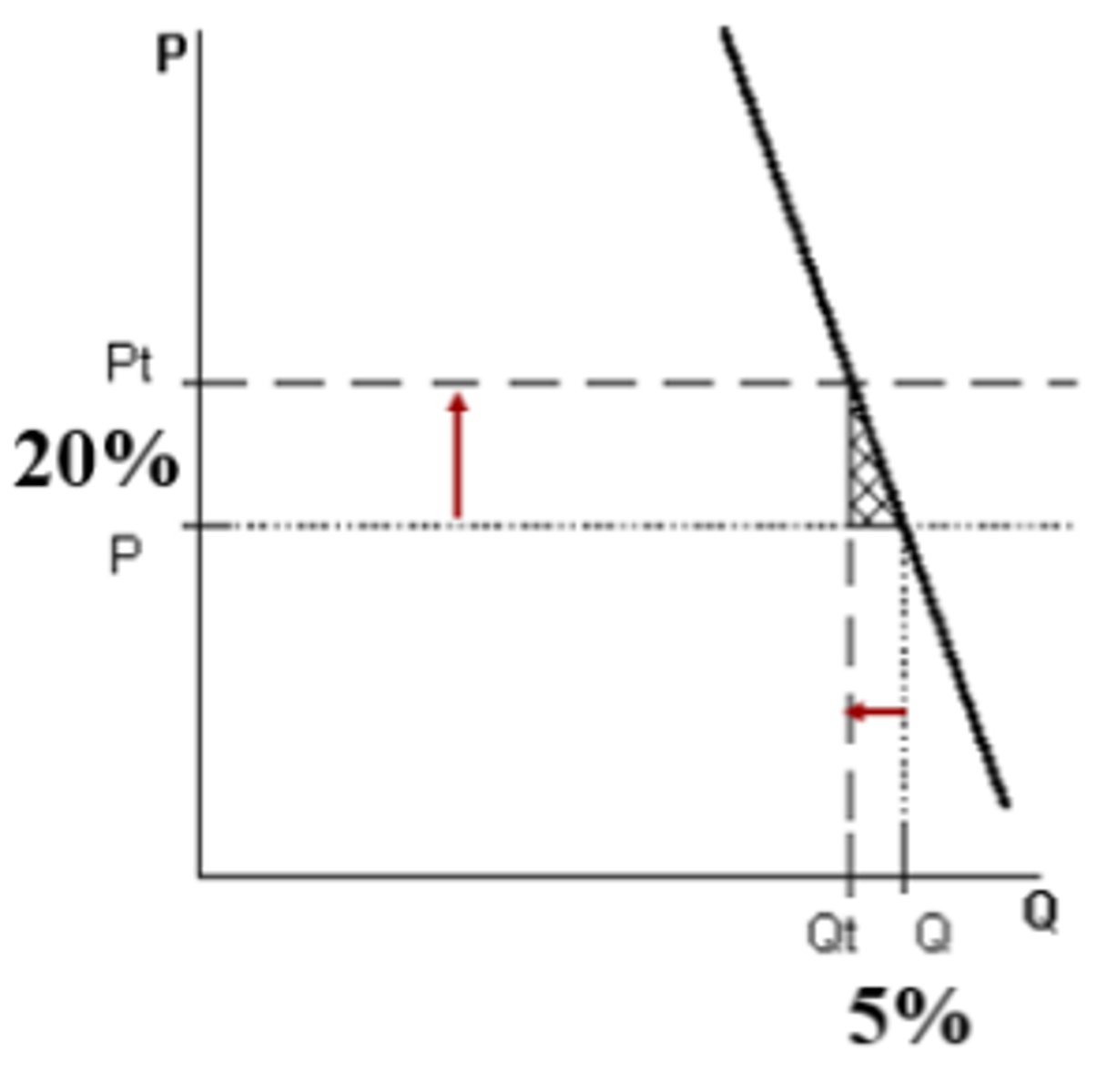
Excise tax
per unit tax applied to specific items, such as luxury or undesirable goods; shifts supply curve to the left with a more inelastic curve having a larger tax burden paid by consumer

Marginal utility per price
utility per price that the consumer gets from an extra unit of a good or service
Short run
period of time during which at least one of a firm's inputs is fixed; equilibrium price is lower; more immediate
Long run
period of time in which a firm can vary all its inputs; equilibrium price is higher; in the future