History Final
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
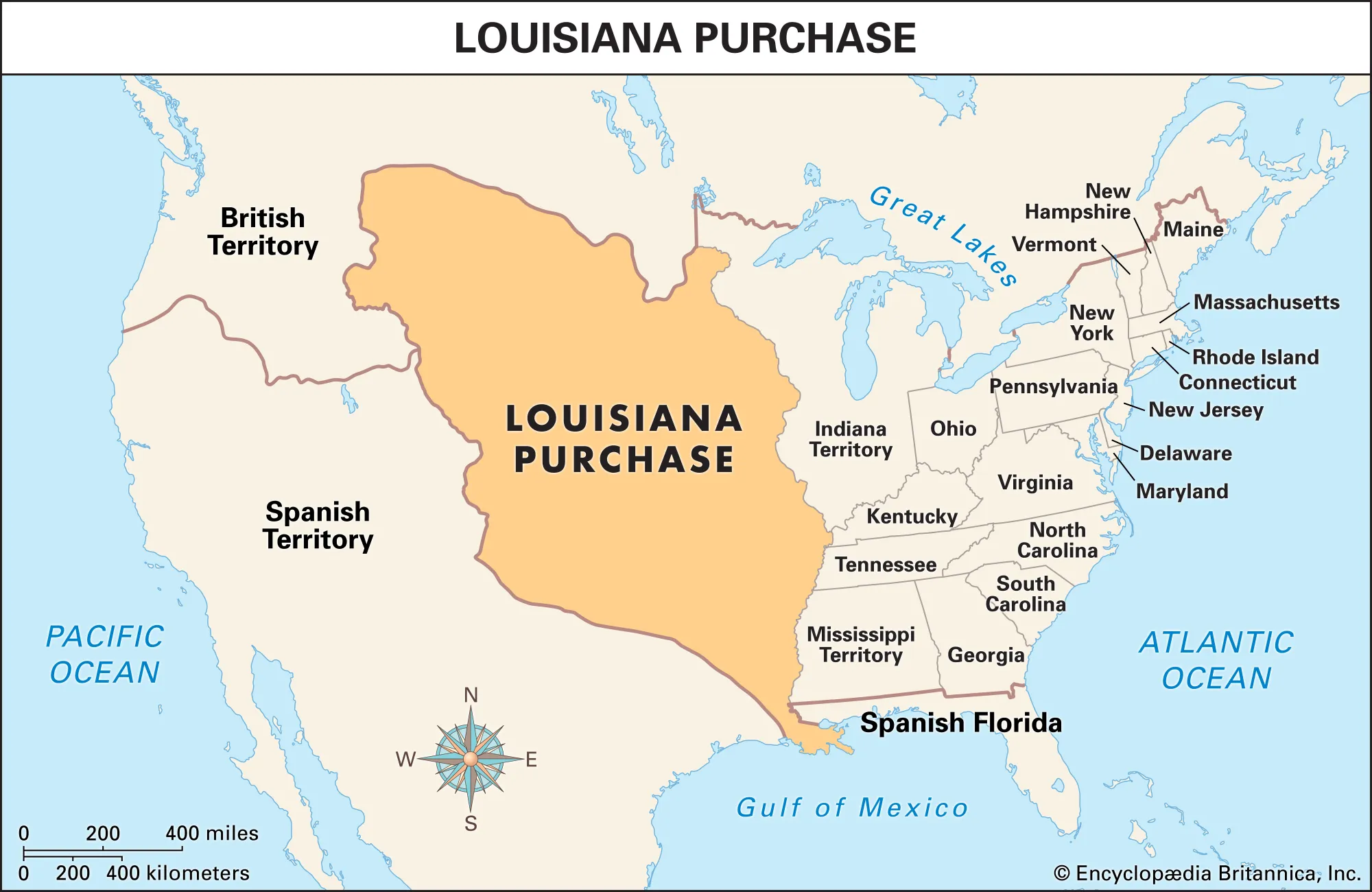
The Louisiana Purchase
In 1803, America bought the entire Louisiana territory from France for $15 million (approximately $18/square mile)
A bargain, because Napoleon was struggling financially
The nation doubled in size
Spain controlled the territory prior to 1800
Jefferson was personally torn in making the decision to purchase the territory because the constitution didn’t specifically say that he could
Takes decades for Americans to populate the territories
Mississippi was entitled to the land from it but was never given it
Opened the West for Settlement
Lewis and Clark Expedition
Leaders of the Corps of Discovers
Goals:
To get an idea of the flora and fauna (plant and animal life)
Hoped to find a wooly mammoth
Figure out what Native American tribes were living there and to establish positive relations with them
To keep the British, Spanish, and French settlers out
Effects:
Made peaceful relations with Native Tribes
Established borders with Spain
Expedition was done in 2 years - efficient
Corrupt Bargain
25% jump in voter turnout. Andrew Jackson was seen as a common man
Henry Clay was a powerful representative in Kentucky. He was Speaker of the House and dropped out of the race
Clay convinced voters in the House to vote for Adams because he was a large influence
Clay ensured Adams would become president so when Adams was elected as president he appointed Clay as Secretary of State
Based on past statistics, Secretaries of State usually lead to the presidency
Andrew Jackson accused Quincy Adams (Future President) and John Clay (Secretary of State under Quincy Adams) of a corrupt bargain
Jackson lost the Election of 1824 even though he had the popular vote
In the next presidential election, Jackson wins
Republicans supported John Quincy Adams and the Democrats were the “Jacksonians”
Indian Removal Act
Andrew Jackson signed the Indian Removal Act of 1830
Forced relocation of certain Native American groups (Most famously the Cherokee group)
Immoral and destructive
Forced removal of many tribes (Cherokee was just the largest and most substantial)
Passed by only 5 votes
The Cherokee took the case to the Supreme Court of the U.S.
Cherokee land overlapped with a lot of state territory
Led to the Trail of Tears and the Panic of 1837
Panic of 1837
One of the most severe depressions in US history
What caused it?
Real estate bubble
Many Americans were desperate for land so much so that they ended up paying very inflated prices which were less than the land was worth
Many Americans were not able to pay off interest fees for the land to the bank
Unpredictable American banking policy
Indian Removal Act
Overvalued property
The Bank of the U.S. lost its charter and 850 banks were able to issue a private form of currency (banknotes) which swelled money supply
Decentralized banking
Wildcat banks - They could do whatever they wanted
Jackson’s Specie Circular of 1836 only allowed the use of coin money in gold or silver to pay for land and people weren’t allowed to trade in their banknotes for coin money
Creates a run on the banks
A lot of people panicked and tried to get rid of all the paper money to buy gold and silver - but many banks didn’t have their money
What was it?
6 year depression after an economic crisis
Who is to blame for it?
Andrew Jackson
The Banks
American Progress
1872
Painting by John Gast
America wants to spread the light that they’ve created (knowledge of technology) into the darkness (the unknown territory; the West)
They thought the only way they could was by chasing the Native Americans away
Mountains may be the Rockies
Telegraph line could symbolize American communication being spread into the West
The woman can represent an American angel
Homestead Act
Expansion Motive
1862: Allowed settlers to pay a small filing fee for a 160-acre plot of public land
Native Americans were negatively impacted by the Act because they were displaced from the lands they settled for generations
The Homestead Act was so difficult to pass because these two groups were against it:
Owners of factories in the East
Scared of losing their workers
Powerful southern slave owners in Congress
Didn’t want the small farmers to have plantations
In the first two decades of the 20th century immigrants (group of people) from Europe participated in the system.
You got 160 acres, but in return you had to live on the land for five years and improve the land (putting up fences, barns, homes, etc.). Then, after five years you could apply to get clear title to it
Only 40% who applied got it
There are many 160 acre (¼ square mile) plots of land that still exist today from the Homestead Act
Forty-niners
Doctors, lawyers, farmers, sailors, and soldiers came from the West to find gold during the Gold Rush
Empresario
Entrepreneur
Ex. Stephen Austin
American citizen
Makes a deal with the Mexican government - Gives control of massive territories (especially Texas) to him
Mexico was having trouble defending its northern border against native American tribes
He was the person who was given the right to settle on land in exchange for recruiting people and taking responsibility for them
Land Grant - He doesn’t have governance over the area but he can bring in American families to settle in the land
Result: in 1825, Stephen Austin brought 300 families from the U.S. to colonize the region
They had to follow a lot of rules that the Mexican government put in place
This led to more Americans living in Texas (aka Northern Mexico) than Mexicans
He became known as the “Father of Texas”
Texas Revolution
Southern slave owners moved into the territory - illegal in Mexico
National religion was Roman Catholic, but most Americans were not
Had to pledge allegiance to Mexico, write official documents in Spanish, and send children to Spanish schools - Which they didn't do
Texans began their own revolution against Mexico
Texans (Mostly Americans) vs. Mexicans
1835 -1836
March 1836: Battle of the Alamo
April 1836: Battle of San Jacinto
Result: big win → Texas gained independence
Republic of Texas - Their own country
Battle of the Alamo
March 1836
186 American settlers hide up inside the building and thousands of Mexican soldiers surround the building
Loss for Texas
“Remember the Alamo”
Americans see the Mexican soldiers as murderers
Part of the Texas Revolution
Spot Resolution
1847 Resolutions by the House of Representatives
Offered by Lincoln, a lawyer and representative from Illinois
He challenged Polk’s claim that the first American blood was spilt on American land
Asks for specific information about the incident
He doesn’t believe that Polk was justified in starting war
Results:
He was called the “Benedict Arnold of our district”
Traitor reference
The Whig party did not renominate him and he is forced to take a break from Congress
He was heavily criticized
Mexican-American War
1846-1848
Territorial dispute between the United States and Mexico over the Southern border of Texas
Where is the southwest border of Texas?
The US would say the Rio Grande River
Mexico would say the Nueces River
Troops start to move to this disputed territory
The US attempted to negotiate (Polk dispatched US envoys) but Mexico refused
Genuine effort?
1845: Polk sent General Zachary Taylor (will become a President) to occupy the disputed area between the rivers
1846: Polk began to plan a war message to Congress
Justified it because Mexico refused to negotiate
Whigs wanted to focus on the states we already had
April 25, 1846: Mexican troops crossed the Rio Grande River and attacked Taylor’s troops, killing/injuring 16 of them
May 11: Polk addressed Congress in his revised war message:
Mexico “Invaded our territory and shed American blood on American soil”
He’s trying to say that if the US lets this slide, who knows what Mexico will do next - Making them the aggressor
May 13: War is declared by Congress
Lopsided victory for the US
Mexico is unprepared for war
Their internal politics were a mess
Their cavalry (Mexico was still relying on men on horses) couldn’t keep up with the technologically advanced Americans
Americans had a Navy and Mexicans didn’t
US was on offensive - Used amphibious warfare
Ended with the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and US gained a lot of land from it
The US did not have a careful respect for the rights of Mexico before the War
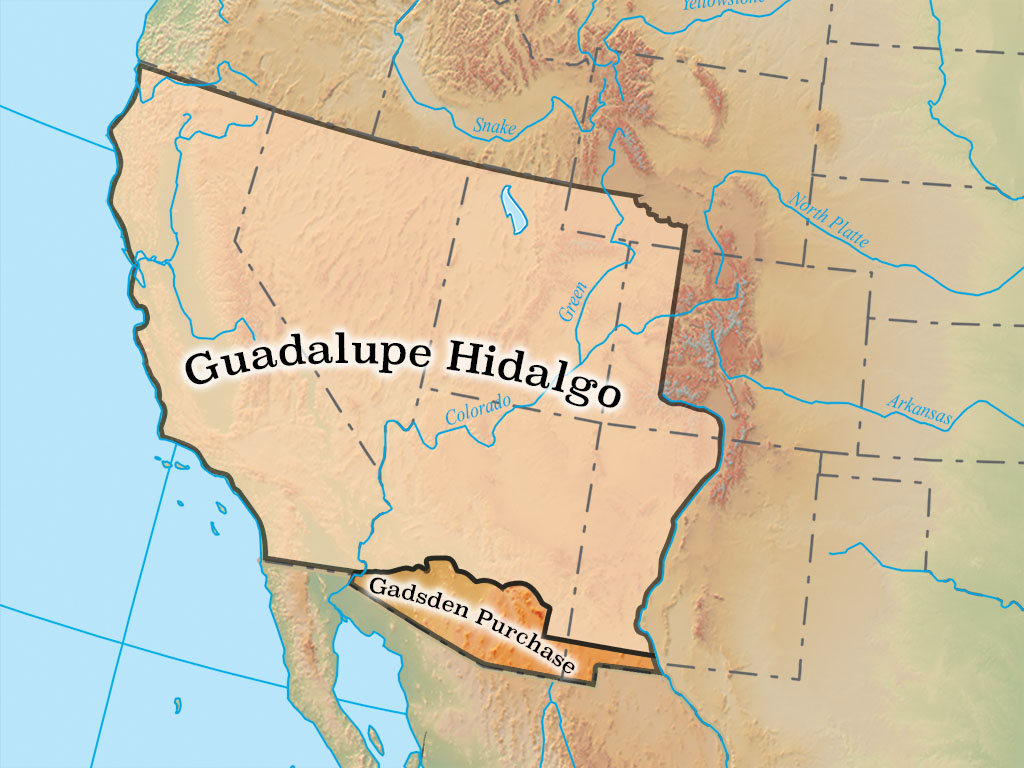
Annexation of Texas
1836
Tried to join the US two times, but Congress rejected it
Because it might look bad to Mexico and Texas would have to come in as a slave state, something Congressmen were opposed to
It was an independent country for 9 years (1836-1845)
1845
The US annexed the Republic of Texas
The President (James K. Polk) was very pro-expansion and wanted to complete the goal of Manifest Destiny
Time has passed - Wouldn’t look like the US was so land hungry and backed the revolution
Indentured Servitude
Someone who works for someone else for a set number of years
Servants could be sold, just like slaves
Servants (Europeans who wanted to come to the American colonies but couldn’t afford it) signed a contract, for usually 7 years, in order to come to the New World to serve someone.
They got free food and shelter
Indentured servants enjoyed more freedom than slaves
Were usually white, which is why they were treated better
Eventually, slavery replaced indentured servitude completely
The end of the England civil war meant a large drop in amount of indentured servants
Slaves were cheaper in the long run
English indentured servants demanded to be treated as English citizens, while Africans could be treated harsher
Voluntary - Sign a contract
Working for a safe passage from Britain to US (ex)
Essential qualities of slavery
If any slave resisted their master, it would not be a felony if their master killed them
Established slaves as property - 1705
If their master passed away, they would be passed down just like property would be
If anyone came from a country that was not Christian, they would be considered enslaved
Molados - Derogatory term for a Mixed person
Enslaved people were not allowed to bear arms
Involuntary
Claiming ownership over someone’s life
Can’t be benevolent, even if people say George Washington treated his slaves well
Abolition of the slave trade
The gag rule made it illegal to talk about the slave trade for 20 years after it was abolished - Abolished occurred when it expired
Ended the importation of humans into the united states for purchase
Outlawed in 1808
Fugitive Slave Act
Fugitive Slave Clause
Any slave that escaped to find freedom must be returned back to their owners
Not enforced, and northern states did not comply
South felt like they were being ignored by the federal government
1850 - Reinforcement
Video
Everything goes back to the Fugitive Slave Clause (Article 4, Section 2) of the Constitution
The 1793 statute demands runaway slaves were returned to owners, however it was not well enforced.
What did the 1850 Fugitive Slave Act do?
Harsher punishments
6 months of imprisonment
Fines
They punished people who harbored runaways
How did the enforcement of this Act contribute to the beginning of the Civil war?
The Act wasn’t enforced
Southern states complained about northern state laws interfering with the federal laws
Created tension between the south and the federal government
Northern cities encouraged the people to not comply with the Fugitive Slave Act
Southern cities encouraged people to follow the Fugitive Slave Act through rewards
Part of a group of laws that form the Compromise of 1850
Citizens of free states also had to cooperate
Effects
Slave Catchers
Strengthened slave catcher’s ability
Made it more enticing to kidnap free blacks, because now they have the law on their side
Rewards were given for the delivery of an alleged slave
Anyone who looked like a description was accepted as the runaway
This happened to any black person, whether they were an escaped slave or not
The North
This law infuriated the North
They were free states and shouldn’t be aiding the southern slavery system
Federal marshals could require citizens to enforce the law
Punishment: Could be fined $1,000 and placed in jail for 6 months
Committees arose to protect escaped slaves
Many states began passing personal liberty laws, which directly contradicted the federal law
(Similar to nullification) - The Constitution directly states that the Federal law takes precedence over the state laws, but the northern states didn’t care
Some banned the use of state prisons to house suspected fugitive slaves
Allowed trials by jury
Slave bounty hunters had to present evidence that this individual was in fact a slave
Was a major reason states started to secede
Fugitive Slave Act pleased no one
Southerners weren’t a fan because it wasn’t enforced
Nat Turner’s Rebellion
Violent approach to abolition
His goal was to lead people because he believed he was selected by God
He gathered 6 men and killed his master’s family
He gained 40 people eventually and killed all the white people they encountered
Whites were terrified
They did this for 4 days before they were stopped
Because of this, slave codes were passed
Restricted rights to move, educate, preach, and assemble
They had to carry passes
Led to over 100 African-Americans being killed by whites out of fear and paranoia
Harriet Beecher Stowe
1811 - 1896
Female
White
Free her whole life
Born into a wealthy, prominent family
Abolitionists
Death of her son
Compassion for slaves losing their children
Slaves were separated from their families on a daily basis
Her main method of persuasion was through writing
Uncle Tom’s Cabin
A fictional story
Plot: Slave named Tom is sold at auction and is separated from his family and the book shows his struggles
Tom was a slave
Legree told Tom to whip Lucy because Tom tried to help Lucy by giving her cotton because she was sick (to meet the quota)
2nd best selling book in the 19th century
Credited for laying the groundwork of the Civil War
Really upsetting to some people and really powerful to others
Exposes the horrors of slavery to Northerners
Abraham Lincoln called her as the “Little lady who started this big war,” referring to the Civil War
Underground Railroad
Harriet Tubman was a “conductor” on the Underground Railroad
Guide
Went to the South to liberate slaves and guided them to the North
19 trips over 10 years
300 slaves → Freedom
“Never lost a single passenger”
Wasn't actually a railroad
Renting out/Hiring out
If a slave owner didn’t have an immediate need of slaves on their own property, they would be rented to someone else
Sometimes, the slaves would get a portion, and sometimes the owner would get all of the money
Pottawatomie Massacre
Abolitionist John Brown led a brutal attack on a pro-slavery settlement at Pottawatomie Creek
Used the kind of violence that scared even his anti-slavery supporters
Brown and six followers killed five men, hacking at them with broadswords and cutting their throats before shooting them
Mahala Doyle, the wife and mother of three of Brown’s victims, expressed her bitterness and pain in this letter to John Brown
She sent it to him in November 1859 as he awaited execution after the Harpers Ferry raid
Even the popular sovereignty compromise of the Kansas-Nebraska Act couldn’t stop the violence
Part of Bleeding Kansas, which was caused by the Kansas-Nebraska Act (granted Kansas popular sovereignty)
Dred Scott Decision
Dred Scott was owned by John Emerson, who was an army doctor
After Dred Scott and his wife had children, they moved from Missouri to Minnesota because of Emerson’s job, and then went back to Missouri
Emerson’s wife got back his property (Dred scott)
After Dr. Emerson passed, his wife decided to sell the Scotts’ children. As a result, Dred and Harriet decided to sue
Scott argued that Emerson legally brought Dred Scott from Missouri to Minnesota, which was free territory - So, he became free even though he was later returned to Missouri. He didn’t escape to free territory, he was legally brought there
Chief Tawney ruled that Dred Scott was still a slave when the case made it to the Supreme Court
“The black man has no rights that the white man can respect”
Asserts that black americans are not citizens
Invalidates the Missouri Compromise
It doesn’t matter if a slave moves into a free state, they will still be considered property
Harper’s Ferry Raid
John Brown + Harriet Tubman were involved
John Brown gathered an army of 18 men and raised money to get weapons
Army gathered in the farmhouse - Only came out at night
The raiders seized citizens and held them as hostages
16 killed - 10 were Brown’s men
2 years before the Civil War
October 16th - October 18th (2 days)
The Maryland side of the Potomac River
Causes
John Brown’s goal: wanted to abolish slavery in the area and would do this by killing slave holders/owners
Sectionalism
Slavery
Effects
John Brown is executed
Sixteen people were killed in the raid, including ten of Brown's men
Rebels are unsuccessful
“Advanced the cause of disunion more than any other event that has happened since the formation of the Government”
Made Civil War seem inevitable - Compromise was not possible
American Colonization Society
Garrison helped form anti-slavery organizations (American Anti-Slavery Society)
Part of this becomes the American Colonization Society
Pushed for immediate emancipation
Freeing slaves
Mission
They wanted to end slavery by deporting all black people to Africa
But, many southerners started this, which is strange
Freed African Americans opposed the society
The society was harmful to their interests
Colonization was a pro-slavery conspiracy
Puts money in the pockets of slave owners
ACS purchases slaves in order to send them to Africa
It legitimized racist assumptions about blacks
Separate but equal philosophy (Justification for why they are sending them back to Africa)
Division of families
They felt like America was just as much their country, if not more, than the white people
Many of them had lived in America for their whole lives
Slows down the emancipation of slaves
William Lloyd Garrison denounced the society eventually because colonization slowed down the process of abolition because it legitimized slavery and it made people want to send their slaves to Africa instead of freeing them, which wouldn’t solve the issue of slavery
The invention of the cotton gin harmed the society because many who had supported ACS were now arguing in favor of pro-slavery because they knew they could profit off of it. The society faced economic troubles from this and even collapsed multiple times
Cotton gin dramatically increases demand for enslaved people
Gag Rule
Gag - prevention of speech/communication
Was done in the original constitution - No one could talk about the slave trade for 20 years
1836
Congress was being overwhelmed with petitions related to abolition
Government had other things to worry about
No legislation should be introduced or discussed pertaining from slavery
Abolition laws were not permitted
Done in order to reunify the country
John Quincy Adams believed the gag rule violated the Constitution because he believed that not hearing a petition was violating the people’s rights to petition
Calhoun introduced the Gag rule and agreed that if states wanted to outlaw slavery, they could, but it was not up to the Federal government
Is passed
Not much going on until 1850 because of the gag rule
Election of 1860: Political Parties
The Democratic party has split into Southern Democratic and Northern Democratic
Because they were divided on slavery
Constitutional Union Party
Election of 1860: Results
2 years after Lincoln-Douglas debates
People didn’t expect Lincoln to win
He didn’t even win the Senate election
Dark horse candidate
Oregon became a state - 1846
Sectionalism - Even more so than last election
Lincoln carried the lower states in the North over to the Republican side
States start to leave (secede) right after Lincoln wins
Lincoln wins 59% of the electoral vote and 40% of the popular vote
Border States
Missouri
Kentucky
Maryland
Delaware
West Virginia
These states are slave states but still fight on the part of the Union
Fort Sumter
(April 1861)
Fort Sumter is a fortification in Charleston, SC
Federal troops controlled it but it is in the Confederacy
Lincoln was nervous that the federal troops weren’t strong enough to control it, so he decided to provide humanitarian relief (food and clothes) but not arms
Weapons would be seen as a sign of aggression
Done to prevent a Confederate attack on the North
Federal government refuses to surrender to the South
Confederate Response: bombarded the Fort
Lincoln didn’t want them to shoot, but also didn’t want them to leave
For 34 hours
Union troops eventually start firing back
No one was killed
Official start of the military conflict in the Civil War
Us Major Anderson realized there were not enough provisions so he surrendered
Confederates take control of the Fort
Government building
The day the Fort is surrendered, Lincoln calls for 75,000 additional troops/volunteers
Lincoln knew so fast of the events because of telegraphs
Lincoln knew marshalls couldn’t fix this by themselves
These volunteers would go to the South and act like police officers
Overwhelming response of volunteers
Expectations for the amount of volunteers from each state/territory
Ex. Iowa contributed 20 times the expected number of volunteers
Why were so many people so eager to enlist?
Lincoln’s proclamation told all the people that if they had any integrity or honor, they would enlist
Lincoln told them that the mission of the army would be to take back the property that the Confederacy took, which was reassuring because the people just thought they would be peacekeepers
Lincoln tells the Southerners that they must vacate the post offices and the Forts they took within 20 days
The Southerners don’t leave
Lincoln calls an emergency meeting to happen on July 4th for everyone to come into session and pass legislation regarding the southern states seceding
Since they U.S. is in a time of rebellion and insurrection, Lincoln can suspend habeas corpus and send people to prison for no reason
4 more states seceded
Scary for Lincoln
7 states seceded before Fort Sumter
War Goals
Anaconda Plan
Blockade Southern ports
So that the South can’t sell it’s natural resources - to hurt them economically
Control Mississippi River
Split Confederacy
Capture Richmond, VA
Confederate Capital
Emancipation Proclamation
Jan. 1, 1863
Lincoln only freed slaves in any state that was against the Union (The Confederate States) through the Emancipation Proclamation
Didn’t free all slaves because there were some slave states that were part of the Union (border states) that would be upset if Lincoln did this
Historians might see The Emancipation Proclamation as a strategy to win the Civil War
Instituted a draft, where blacks were exempt and people could pay to be exempt
Caused by Antietam
Surrender at Appomattox
April 1865
Union troops finally closed in on Richmond, VA
Last part of Anaconda Plan
Two commanders met and agreed on the terms of surrender
Lee didn’t have much bargaining power
The South was allowed to surrender with dignity
General Grant could have demanded all the horses, weapons, and uniforms or humiliate them, but he instead allowed Confederate officers to ride off on their horses and keep their side weapons
Lee’s men were sent home on parole
Lincoln wasn’t looking to really punish the South
Combat During War
Most troops fought on foot, marching in tight formation and firing at relatively close range
The North aimed to economically squeeze the South with the Anaconda Plan
Lincoln’s Assassination
Booth was unhappy with Lincoln because he wanted to do something significant and powerful and also because he thought nothing else would get done with Lincoln as President
The door to Lincoln’s balcony was unguarded and opened, so John Wilkes Booth entered and shot him in the back of the head
Lincoln’s assassination was a part of a bigger plot to overthrow the government
There were other conspirators
There was an attempted assassination of the secretary of state, William H. Seward
Lincoln is assassinated right after the Civil War ends
Reconstruction
1865 – 1877
The period during which the United States began to rebuild after the Civil War
The process the federal government used to readmit the Confederate states
1865 (war’s end) - 1877
Difficulty → 3 different plans
Lincoln
Outlook: Leniency
Not very harsh to the South
Lincoln’s whole mission was to keep the country together
Since it was not legal for the states to secede, they technically never left the union so they shouldn’t be punished
Proposal:
Presidential Pardon → rationale & exceptions
Even if you're found guilty of a crime, the President can declare you innocent
Pardons the whole Confederacy of treason
Oath (10%) & Emancipation Proclamation → Statehood
10% of white, landowning males/voters in each state would have to pledge an oath of allegiance to the Union & state government would have to promise not to have slaves in order to be readmitted into the Union
Supporters: some Confederate states
They knew they likely would not get a more lenient plan
Was not the plan that was chosen
Johnson
Andrew Johnson’s initial plan for Reconstruction failed to require the southern states to draft new constitutions
Outlook: Leniency
Born in North Carolina and was a Southerner
Spent a lot of his life in Tennessee (Senator there)
Came from a history of farming and slavery
Empathizes with Confederacy
If not as lenient as Lincoln, even more so
Proposal:
Readmission w/ 4 conditions
Oath w/ exceptions
People argued that this was not helping slavery be abolished because even though “slaves” were being paid, they were not being paid enough to live and therefore had to keep working on the plantation
Supporters: white southerners
Congress
Outlook: No leniency - Retaliation
Wanted to punish the South
Proposal:
Citizenship & Right to Vote
Granted more rights to Blacks
Message to the South that the people who they enslaved would now live the same way as them
Military Oversight
They didn’t trust that the South would uphold the Amendments
South split into 5 military districts with martial law in each
Did not recognize states already readmitted into the Union by Lincoln or Johnson
States had to ratify the 14th Amendment (¾ of legislature has to agree) and get rid of all former confederate leaders from their government
Supporters: Radical and moderate Republicans
Ex. Sumner & Stevens
Factions of the Republican party
White supremacy organizations hurt Congressional efforts to aid African Americans after the Civil War
Reconstruction Acts
Freedman’s Bureau Act of 1866
1866
One year after the War
The Act was to enlarge the Bureau
Congress would set aside more money for them
Johnson vetoed it → Congress overrode it
Happens several times during the Reconstruction period
Civil Rights Act of 1866
Outlaws black codes
Reconstruction Act of 1867
A success of Congressional Reconstruction
What it did:
Did NOT recognize state governments recognized by Lincoln and Johnson
This meant that some states (ex. Louisiana) that were admitted by Lincoln or Johnson would still have to go through Congress’ process of readmittance to actually join the US
Divided Confederate region into 5 military districts w/ Union general
Readmission Conditions:
African Americans given right to vote
3 years before ratification of the 15th Amendment
14th Amendment ratified
Johnson vetoed → Congress overrode
3 laws in a row where this happens
Congress was in control politically
Enforcement Act of 1870
Johnson doesn’t veto this because he is not able to
Johnson’s presidency is over by 1868
Grant is President and is not at odds with Congress because he is Republican
Issue: Expected that Confederate states would not obey Reconstruction laws
Gave the federal government more power
To ensure laws were being followed
To punish those who tried to prevent African Americans from exercising their new rights
Ku Klux Klan
Terrorist organization
They bring children into their beliefs
Began in 1865 in Tennessee (Christmas Eve)
Same year the Civil War ends (shortly after the Civil War)
Original members:
All 6 ex. Confederate soldiers
Nathan Bedford Forest is the first leader
Hoods and robes were worn, meant to scare blacks or even white american sympathizers, but it eventually escalated into murdering them and lighting crosses on fire
Lynching
Tried to get blacks to leave their community
The robes and tactics of the clan are less popular now, but they now use the internet as a place to target people in order to conceal their identities
The KKK wouldn’t want black people to join their party
Compromise of 1877
Election of 1876 was a controversial election in terms of electoral votes
Republican reports of voter fraud and black Americans in the South being barred from polling stations
A congressional committee/commission (dominated by Republicans) investigated these reports
8 Republicans
7 Democrats
8 votes for Hayes and 7 votes for Tilden in every state that there were accusations in, which is why Hayes got the votes in the electoral college
Some southern states even threaten to secede a second time
Southern Democrats accept that Hayes gets the disputed vote on two conditions
Guarantee of federal aid to the south
Removal of all remaining federal troops from the south
Considered the end of Reconstruction
Congress is done punishing the south and the south gets autonomy back
Lynchings
Hanging based on race (4,000 black Americans are lynched after the Amendments were passed)
Part of Jim Crow system
De facto segregation
Plessy v. Ferguson
Made it legal for blacks and whites to be separated, as long as the facilities are equal
Separate but equal
But the resources provided were never equal
Plessy
From New Orleans, Louisiana
⅛ black and still considered black
Vice President of a group working to improve the education system
Claimed that they violated his 13th and 14th Amendment
He claimed that he was being treated as if he was still a slave and that he was not being treated equally under the law because he was black
Plessy sued a judge on the court
Separate Car Act (1890)
Legalized separating train cars by skin color
Plessy boarded a whites only car and was arrested
Committee of Citizens planned this and bailed Plessy out in order to challenge the Separate Car Act in court
Ferguson
Judge of Louisiana state court
Majority opinion → There’s nothing in the Act that makes the black cars in the train worse than the white ones
Court case took a while (4 years) to make it to the Supreme Court
Legalized segregation, which already existed anyway
There were 8 justices. (7-1) If there was a tie, the inferior state Court decision would stand
Proved the power that the judicial branch has over the way Americans live
The Great Migration
1916-1970
6 million African Americans moved out of the rural South to the Northeast, Midwest, and West
Caused by segregation and lynchings
De facto segregation
Literacy Tests
Used to prevent blacks and sometimes poor whites from voting by assessing them on literacy skills, but the test was designed to fail people
Many were not able to pass the test because it was impossible and they did not get educated because they were slaves
De jure segregation
They had to get a perfect score in order to pass
White people didn’t take it because of the “grandfather clause”
Laissez-faire (hands off) Supreme Court allows the states to pass laws to undermine the 13th, 14th, and 15 Amendments
Official purpose: To make sure the voting population is educated
Hidden purpose: To bar blacks from voting
Segregation
Jim Crow
Came from people who would burn corks and smudge the color on their face and imitate African Americans
One of the “characters” someone created was Jim Crow
What: A regime of racial inequality
Where: The American South
When: 1890-1965
Why: To legalize segregation and restrict black rights
“Three headed monster”
1. Political disenfranchisement
Taking away the right to vote
Undo/counter the 15th Amendment
2. Threat of lynching and mob violence
3. Racial segregation of public space
Separate schools, drinking fountains, and movie theaters
De facto Segregation: Segregation that happens by fact, not by law
Lynchings
The Great Migration
De jure Segregation: Segregation enforced by law
Poll Taxes
Literacy Tests
Dwight D. Eisenhower
President Eisenhower had troops escort the students to and from the school during the Little Rock 9
Brown v. Board of Education
Ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segregated schools are otherwise equal in quality
Chief Justice Earl Warren’s opinion
U.S. Supreme Court Justice Earl Warren delivered the unanimous ruling in the landmark civil rights case Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas. State-sanctioned segregation of public schools was a violation of the 14th amendment and was therefore unconstitutional
Stated that Plessy v. Ferguson was incorrect
Stated that the segregation of public schools negatively impacted the mental development of Blacks
Stated that separate is inherently unequal
Plessy v. Ferguson
Made it legal for blacks and whites to be separated, as long as the facilities are equal
Separate but equal
But the resources provided were never equal
Plessy
From New Orleans, Louisiana
⅛ black and still considered black
Vice President of a group working to improve the education system
Claimed that they violated his 13th and 14th Amendment
He claimed that he was being treated as if he was still a slave and that he was not being treated equally under the law because he was black
Plessy sued a judge on the court
Separate Car Act (1890)
Legalized separating train cars by skin color
Plessy boarded a whites only car and was arrested
Committee of Citizens planned this and bailed Plessy out in order to challenge the Separate Car Act in court
Ferguson
Judge of Louisiana state court
Majority opinion → There’s nothing in the Act that makes the black cars in the train worse than the white ones
Court case took a while (4 years) to make it to the Supreme Court
Legalized segregation, which already existed anyway
There were 8 justices. (7-1) If there was a tie, the inferior state Court decision would stand
Proved the power that the judicial branch has over the way Americans live
Freedom Rides
Public bus trips taken by racially integrated groups to the Deep South
The intentions were to sit wherever they wanted on buses and trains and demand unrestricted access to restaurants and waiting rooms
Angry white mobs would throw rocks and bricks at the windows of these buses, slash the tires, and throw firebombs through the windows. As the freedom riders fled the bus, baseball bats were thrown at them
Led to the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
Sit-in Movement
African Americans were refused service at stores
By bringing in lots of students to sit in at stores, it brought pressure upon store owners and their racist regulations
Originated in Greensboro, NC but eventually spread to a lot of the South
Affected 20 total states
The Greensboro 4 started this
A series of nonviolent protests against racial segregation at lunch counters
The goal was to bring awareness and attention to racial inequality
Protesters were met with violence and assault
Students at Warsaw University completed a 2 day sit-in and did not attend class or lectures
The Sit-In Movement led to the Freedom Rides and Freedom Summer
W.E.B. DuBois and Booker Washington
Washington
Born into slavery
Worked at an early age
Didn’t get a lot of education
From Virginia, segregated community
Approach to slavery was conciliatory, which means that he wanted to gain support in order to reduce hostility
He fundraised for the Tuskegee Normal and Industrial Institute as well as other Black organizations
Believed that economic independence and ability to prove themselves to society were the only way to achieve equality
DuBois
Born into freedom
Excelled in early education
From Massachusetts, integrated community
Approach was publishing influential works about the conditions of Black Americans
Dubois thought that education and civil rights were the only way to achieve equality
Washington and Du Bois were both born in the same era, were highly accomplished scholars, and were committed to the cause of civil rights for Black people in America. They were both black and were victims of racism at points
I feel that Dubois’ approach was more effective because he ended up founding a political group called Niagara, which was dedicated to his cause and later formed the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). Dubois continued to champion the civil rights movement, with and without the NAACP. Washington, on the other hand, quickly lost the political influence when Woodrow became President.
March on Washington
The Washington Monument to the Lincoln Memorial, Washington, D.C.
Organized by Philip Randolph, MLK Jr., Bayard Rustin, and more
Philip Randolph
Civil Rights Leader and Activist
Organizer of the march
MLK Jr.
34 years old at the time of the march
Bayard Rustin
Singer for equality in all white clubs
Helped Randolph organize the march
Devoted his life and career to the civil rights movement
John Lewis
Chairperson of the SNCC
Representative for young people and gave a speech at the march
James Farmer
Co-founder of CORE
250,000 people came
The goal was to gain civil rights and equality
Kennedy’s Civil Rights Bill
The march pressured him to pass the bill
The protest was meant to earn equal rights, jobs and freedom, federal protection, and desegregation
The march consisted of performances and speeches
Influenced the signing of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965
“I have a dream” speech
250,000 people gathered in Washington, D.C.
Protesting for equal rights
It was almost impossible for blacks to become employed
MLK wanted to end economic and employment inequality
17 minutes long
MLK read his speech up to a point, but he started improvising with what he wanted to say about his dreams
His speech was influenced by Mahalia Jackson and also his father
1963
Before his “I have a dream” speech, there were versions of it called “The American Dream”
Known to be one of the most iconic speeches in U.S. history
Power resonated with the audience
References the Emancipation Proclamation and the Gettysburg Address
Helped create Civil Rights Act of 1964, Voting Rights Act of 1965, and helped end racial segregation as a whole
MLKJ and Malcolm X
MLKJ
Most influential and effective leader in the civil rights movement
MLK Sr. was a pastor at a church
MLK skipped grades 9 and 12 and went to college at 15
Went to the first black school in Georgia
Worked at Dexter Ave. Baptist Church in Montgomery
Was very religious
Was influenced by Rosa Parks
Worked with her to end segregation of buses in Montgomery, and then nationwide
His home was bombed in 1956
Founded the SCLC in 1957
Put together organized protests and speeches about social justice
“Give us the Ballot” speech
In NY, King was stabbed and nearly killed
“I’m so happy that I didn’t sneeze”
Studied Gandhi
Traveled to India in 1959
King wrote “Letter from the Birmingham Jail”
“Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice anywhere”
1963 Time Person of the Year
1964 Nobel Peace Prize
Youngest man to ever win it
Donated the money he won from it to further the Civil Rights Movement
Organized a march that influenced the 1965 Voting Rights Act
Advocated for underrepresented groups, not just blacks
“Poor People’s Campaign”
King was assassinated in 1968
Funeral was an international event
Arrested 29 times
Malcom X
Malcom X was born as Malcom Little in 1925 in Omaha, Nebraska
Before he was part of the Nation of Islam, he was sent to jail for 7 years
W.D Fard was the original creator of the Nation of Islam.
After a trip to Mecca, W.D. claimed that God was black
Claimed that white people were devils and blacks were angels
Malcom X started the newspaper “Muhammed Speaks” →“By any means necessary” invoking violence
The Ballot or the Bullet Speech → Cleveland Ohio
Most famous speech. Bullet represents blacks' last resort to self defense
Malcom believed in black rights → BLM. He was NOI, then converted to Sunni Islam
Started the Black Panther Party → invoked violent beliefs and wanted change immediately → Black Nationalism.
Pan Africanism → Black people come together and form a powerful society
Malcom spread his ideas through speeches and his newspaper
MLK and Malcom X did not see eye to eye but MLK admired his work ethic
Then changes his views and wants black people to stand up for themselves
Malcolm → assassinated by NOI members that believed Malcolm was against their beliefs
Malcolm’s work helped the black community prosper but also created a false impression of what Islam was
They were both assassinated
Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965
The March on Washington rally was to convince Congress to pass the Civil Rights Act
1964: Civil Rights Act
Why: First major legislative victory in the civil rights movement
MLKJ referred to it as a “second emancipation”
Who: President Johnson (Lyndon Johnson - Basically the opposite of Andrew Johnson)
What:
Outlawed discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or origin
Required equal access to public places and employment
Enforced the desegregation of schools and the right to vote
Legislative formalization of Brown v. BOE
1965: Voting Rights Act
Why: March from Selma to Montgomery
Advocated for equal voting rights
There were still poll taxes and literacy tests at the time
Who: President Johnson
What: Enforced the right of African Americans to vote
Prohibited states from imposing voting qualifications like literacy tests and poll taxes
How: Supervision by the Dept. of Justice
Examiners - Federal agents who went to southern states to ensure that the act was being followed
Result: Voter turnout of Black Americans in South rose