1.5.1 Structure of DNA and RNA
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Describe the function of DNA
Holds genetic information which codes for proteins
Describe the function of RNA
Transfers genetic information from DNA to ribosomes
Name the two types of molecules from which a ribosome is made
RNA and proteins
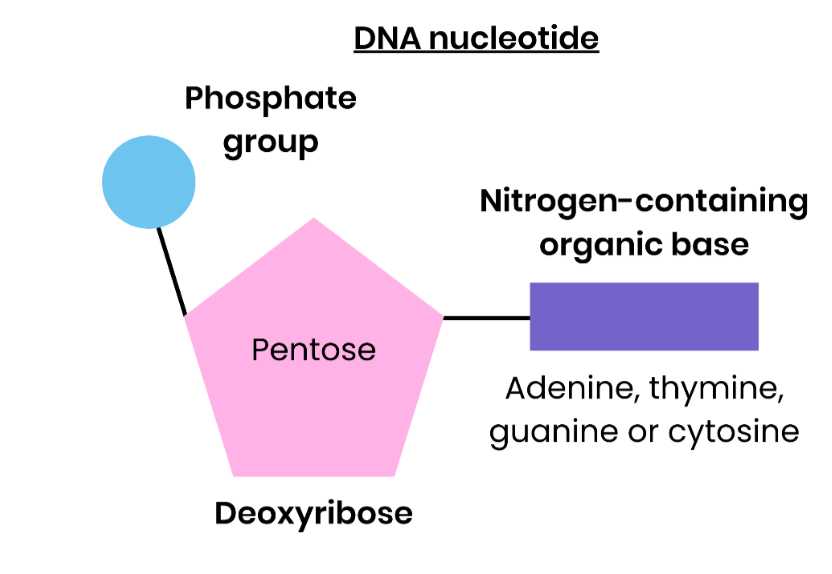
Draw and label a DNA nucleotide
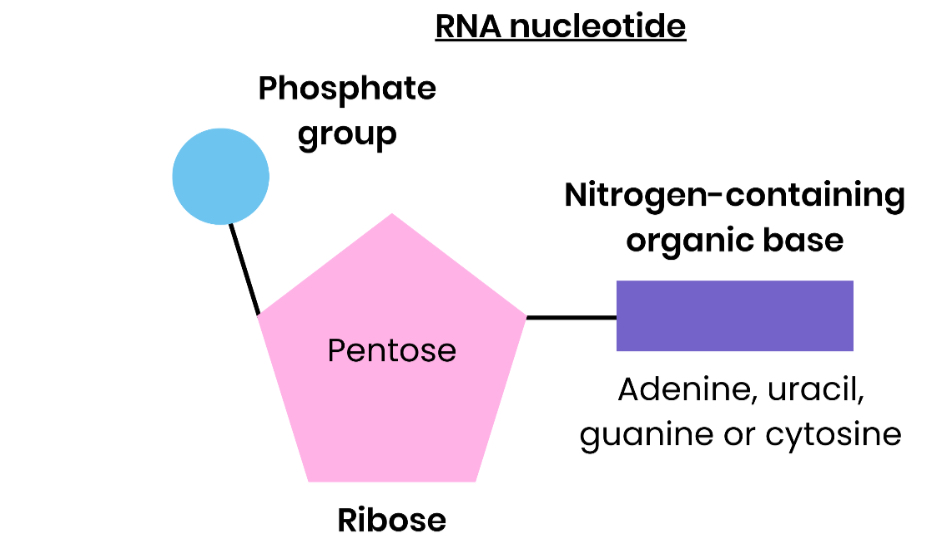
Draw and label an RNA nucleotide
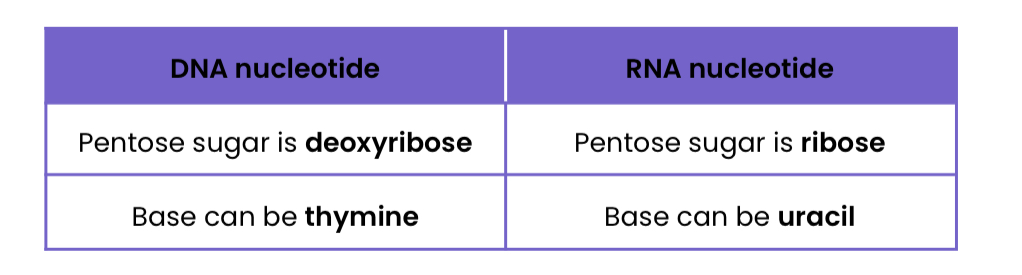
Describe the differences between a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide
Describe how nucleotides join together to form polynucleotides
Condensation reactions, removing water molecules
Between phosphate group of one nucleotide and deoxyribose / ribose of another
Forming phosphodiester bonds
Describe the structure of DNA
Polymer of nucleotides (polynucleotide)
Each nucleotide formed from
deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a
nitrogen-containing organic base
Phosphodiester bonds join adjacent
nucleotides
2 polynucleotide chains held together by
hydrogen bonds
Between specific complementary base
pairs - adenine / thymine and
cytosine / guanine
Double helix
Describe the structure of (messenger) RNA
Polymer of nucleotides (polynucleotide)
Each nucleotide formed from ribose, a phosphate
group and a nitrogen-containing organic base
Bases - uracil, adenine, cytosine, guanine
Phosphodiester bonds join adjacent nucleotides
Single helix
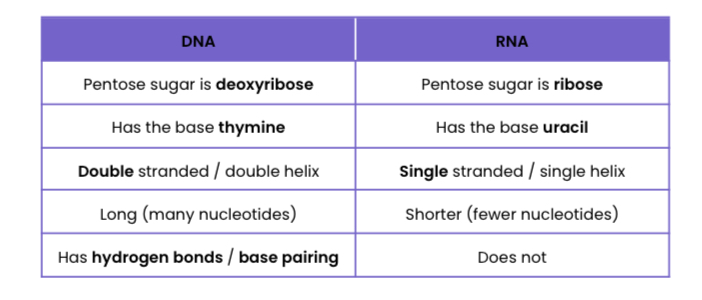
Compare and contrast the structure of DNA and (messenger) RNA
Suggest how the structure of DNA relates to its functions
Two strands → both can act as templates for semi-conservative replication
Hydrogen bonds between bases are weak → strands can be separated for replication
Complementary base pairing → accurate replication
Many hydrogen bonds between bases → stable / strong molecule
Double helix with sugar phosphate backbone → protects bases / hydrogen bonds
Long molecule → store lots of genetic information (that codes for polypeptides)
Double helix (coiled) → compact
Suggest how you can use incomplete information about the frequency of bases on DNA strands to find the frequency of other bases
% of adenine in strand 1 = % of thymine in strand 2 (and vice versa)
% of guanine in strand 1 = % of cytosine in strand 2 (and vice versa)
Because of complementary base pairing between 2 strands