Crystalline Anthropathy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are Crystal Induced Arthropathies
Crystal Induced Arthropathies are metabolic disorders associated with articular crystal deposition or deposition of crystals in the joints
→ presents as attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis
1) There are two kinds
→ Gout - monosodium urate crystals that are needle shaped
→ Pseudogout and Pyrophosphate Arthropathy - calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals that are rhomboid shaped
What is Gout?
Gout is a disorder affecting adult men and is the most common inflammatory arthritis in males over the age of 40. It is a clinical diagnosis rather than a lab diagnosis
1) There are several risk factors for gout such as obesity and dietary influences.
→ genetic influences often include PRPP synthetase hyperactivity and HGPRT deficiency
2) Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid within the blood results in deposition of monosodium urate crystals in the joints and tissues. These needle shaped crystals will trigger acute inflammatory arthritis
→ Often influenced by conditions like hyperuricemia, temperature, dehydration and pH of the tissue
→ Gout is a result from overproduction or underexcretion of uric acid
What is Hyperuricemia and what are its causes?

Hyperuricemia is serum uric acid above 2 standard deviations above the mean for a standard gender/age matched healthy person
→ for USMLE the serum uric acid range is 3.0-8.2
1) Importantly, patients with gout may not have hyperuricemia due to deposition of the monosodium urate crystals into the tissue
→ this leads to the absence of hyperuricemia because all of the urate is going into tissues
→ the majority of patients with hyperuricemia will not develop Gout
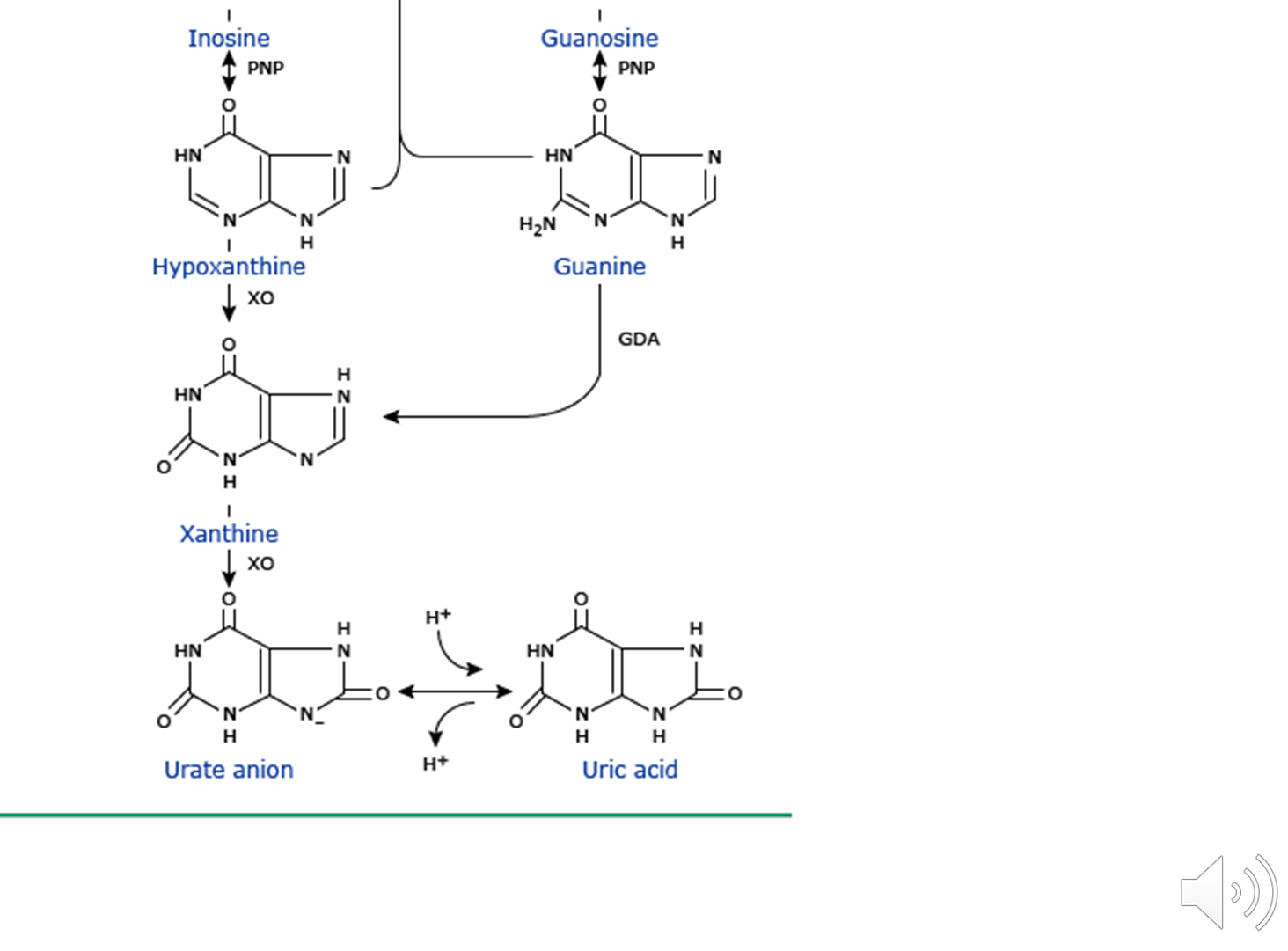
What are the important steps in uric acid metabolism?
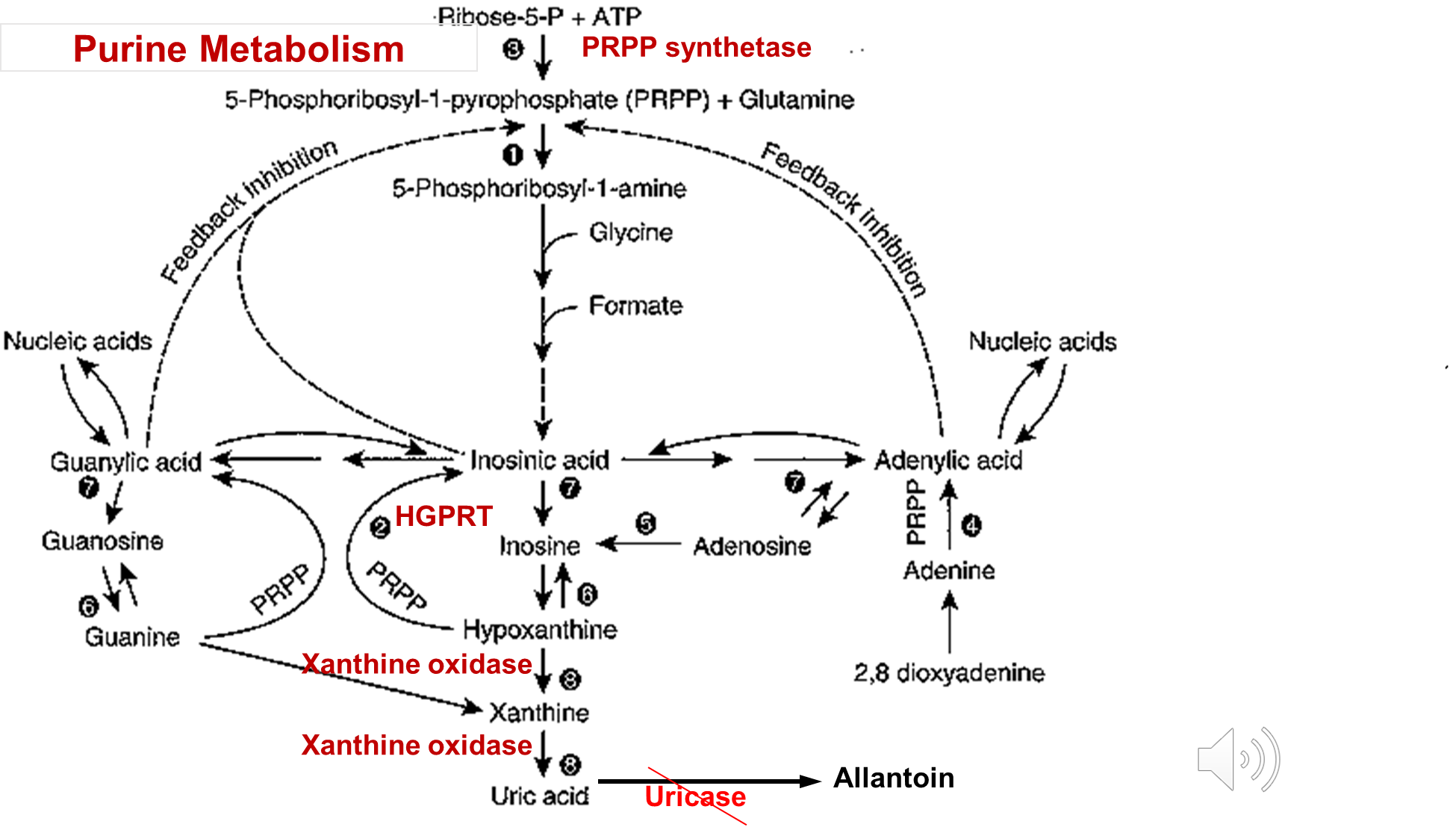
Uric Acid Metabolism is dependent on four major enzymes
1) Xanthine Oxidase
→ xanthine oxidase is responsible for conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine and then to uric acid
2) Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phospho-Ribosyl Transferase (HGPRT)
→ HGPRT is responsible for the conversion of hypoxanthine back to inosinic acid
→ deficiency in HGPRT can lead to gout
3) Phospho-Ribosyl Pyro Phosphate (PRPP) Synthetase
→ PRPP Synthetase is present at the beginning of the purine metabolism cycle and is important for genetic causes of gout (hyperactivity)
4) Uricase (not expressed in humans)
→ while not expressed in humans, uric acid can be converted to allantoin via this enzyme
What is Saturnine Gout

Saturnine Gout is secondary gout caused by lead nephropathy
→ lead nephropathy leads to an inability to excrete uric acid causing gout
→ associated with moonshine
What are the two causes of hyperuricemia?
1) Hyperuricemia can occur due to high purine load (less common)
→ can come from our diet like organ meat
→ alcohol like beer can lead to increased uric acid production due to accelerated turnover of ATP along with its high purine content
→ tumor lysis or high cell turnover
→ or excessive PRPP synthetase or deficiency in HGPRT (Lesch-Nyhan)
2) Hyperuricemia can occur due to impaired excretion of uric acid (more common)
→ things like impaired tubular secretion through medications like thiazide diuretics can cause hyperuricemia
→ lead toxicity can also impair uric acid excretion
How does gout classically present?

Gout classically presents with sudden onset joint pain that occurs at night
1) They will have severe pain, warmth, erythema, and swelling that occurs typically over the distal joints, typically the Metatarsophalangeal joints of the feet
→ because it often affects the MTP joints of the feet, it causes podagra which is acute gout involving the MTP joint of the first digit
→ differentiated from pseudogout which typically affects the knee first
2) Will typically resolve on their own with some patients also having systemic manifestations
→ fever
→ elevated WBC count and serum C-reactive protein
What happens when the monosodium urate crystals are deposited into the joints?
Gout occurs due to the monosodium urate crystals binding to toll-like receptors on resident macrophages/synoviocytes ound in the joint
1) this triggers assembly and activation of NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome (NLRP3)
→ NLPR3 will cause the release of IL-1 beta from monocytes/macrophages as well as other cytokines triggering inflammation of the joint
2) Crystals will also activate complement
→ crystals will bind to IgG leading to increased levels of phagocytosis and neutrophil activity as well
How do monosodium urate crystals appear under polarizing microscopy

Monosodium Urate Crystals are needle shaped with strong negative birefringence
→ they are yellow when the crystals are oriented parallel to the axis of the first-order red compensator
→ they are blue when perpendicular
What is Chronic Tophaceous Gout?
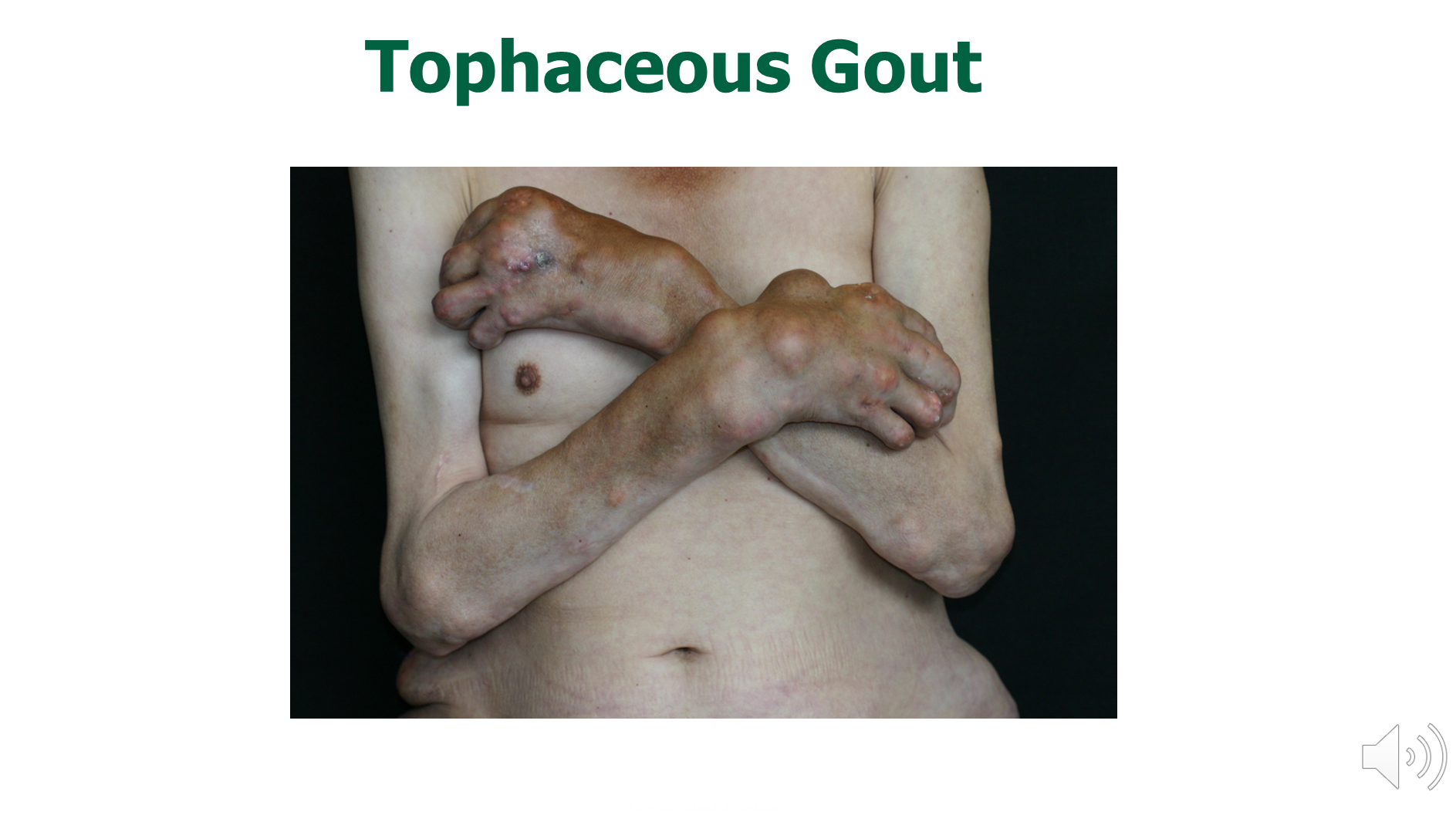
Tophaceous Gout is chronic form of gout that occurs when gouty arthritis is untreated
1) Urate crystals will appear in other places besides the joints like our earlobes, elbows, and spine causing the formation of tophi
What are the radiographic findings of chronic gout?
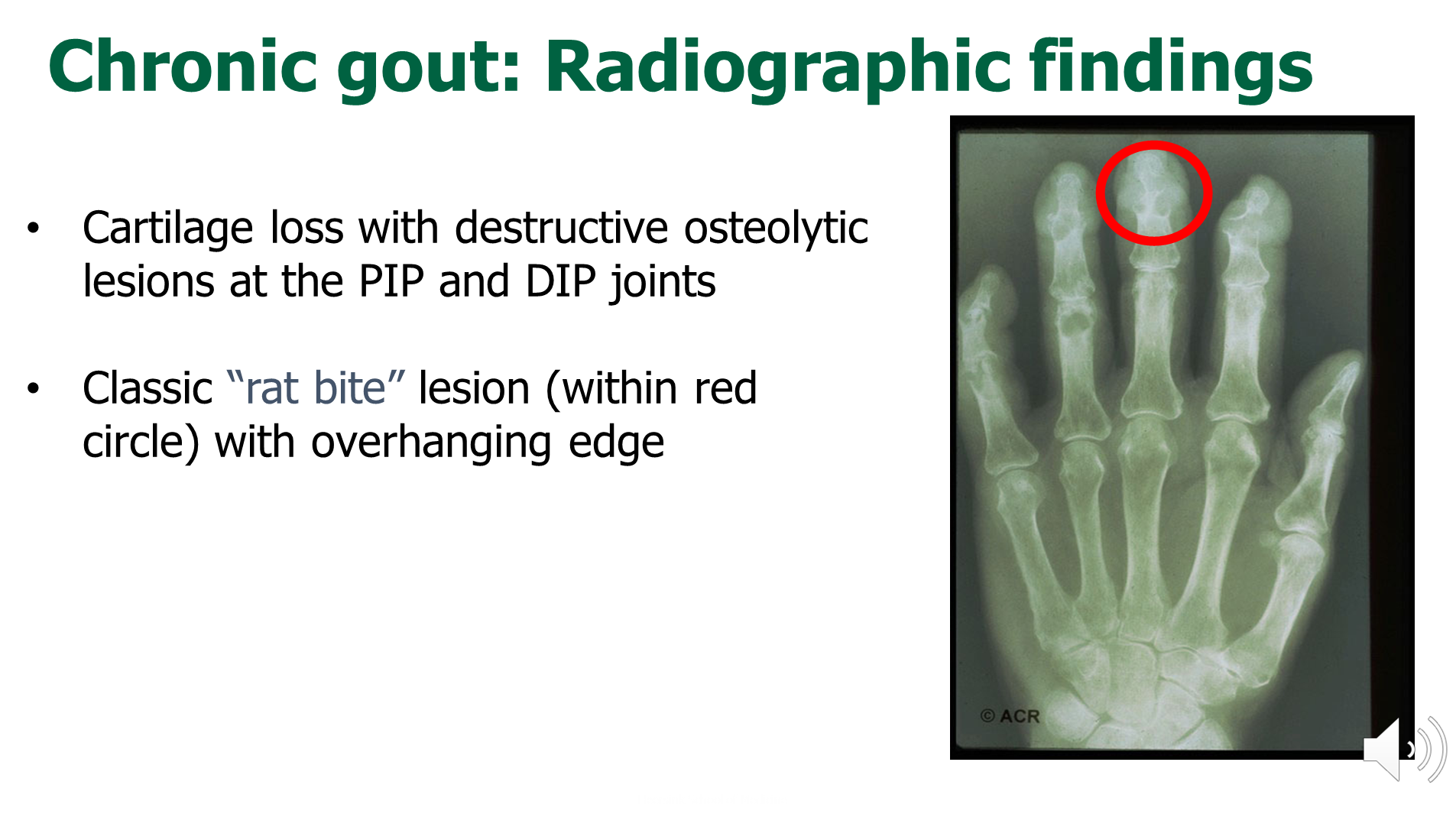
Chronic episodes of gout will show as cartilage loss and the formation of osteolytic lesions at the PIP and DIP joints
→ they are described as looking like rat bites
How is Gout managed?
Gout is managed differently depending on if its acutely or chronically managed:
1) Acute Treatment
→ NSAID
→ Colchicine - blocks microtubule polymerization, disrupting chemotaxis and phagocytosis
→ Corticosteroids
→ Anti IL-1B therapy
2) Chronic Treatment is used to lower serum urate levels below 6.0 mg/dL
→ Allopurinol/Febuxostat are oral xanthine oxidase inhibitors
→ Probenecid is a competitive inhibitor for the reabsorption of uric acid at the proximal convoluted tubule
What is Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease?
CPPD is a spectrum of diseases characterized by deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the mid-zone layers of joint cartilage
1) Caused by an overproduction of pyrophosphate by articular chondrocytes
→ the pyrophosphate will cross cell membranes via the transmembrane protein ANKH
2) The formation of these rhomboid shaped crystals will trigger inflammation leading to pseudogout
→ triggered by phagocytosis of crystals by neutrophils and synovial cells triggering release of cytokines, chemokines, etc
3) Episodes of pseudogout are triggered by trauma or illness, some sort of bodily injury
→ affect the knee first most of the time
What is CPPD associated with?
Mutations in the ANKH gene (CCAL2) which is responsible for transporting pyrophosphate from the cytoplasm to the outside of the cell, is associated with Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease
1) Also associated with three major metabolic diseases
→ hyperparathyroidism
→ hemochromatosis
→ hypomagnesemia
What is chondrocalcinosis?
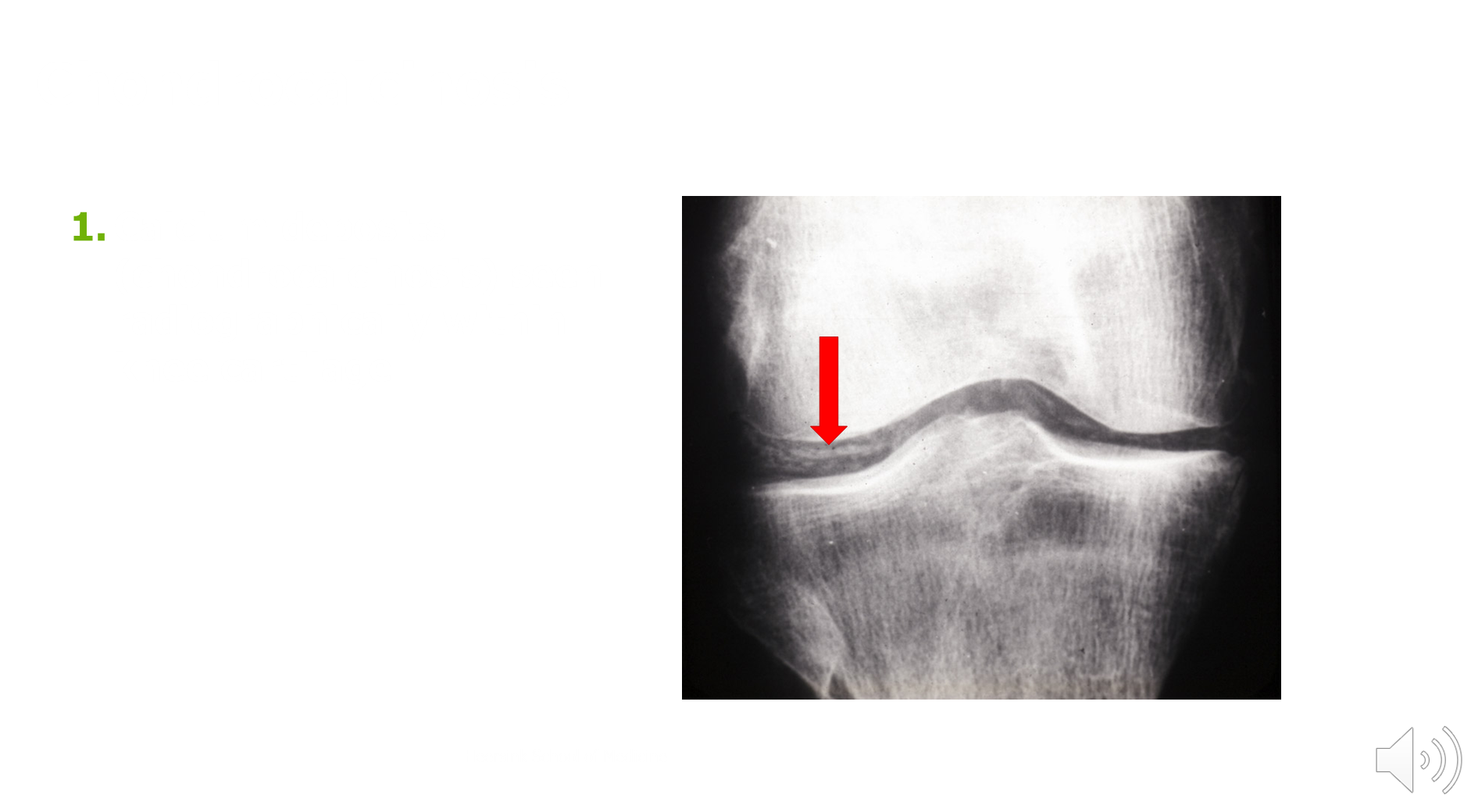
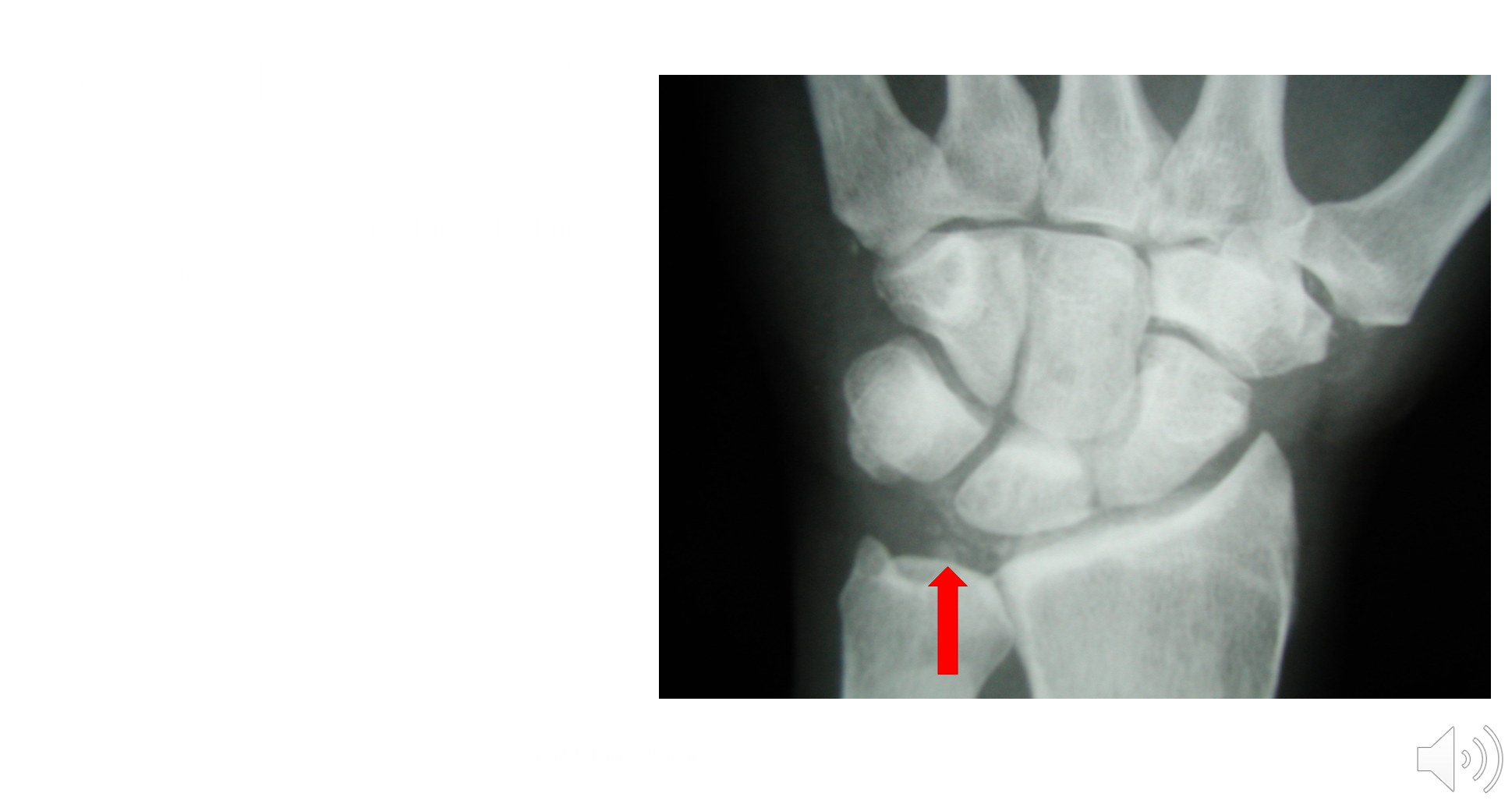
Chondrocalcinosis is a radiographic finding consistent with CPPD
→ shows calcium crystals in the articular cartilage
How do CPPD crystals appear on polarized microscopy?

CPPD crystals are rhomboid shaped and exhibit weak positive birefringence
→ will appear blue when parallel with the compensator