Equine Nutrition Exam 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Definition of roughages
high fiber feedstuffs (>18% crude fiber or >35% NDF)
Importance of fiber
maintains gut health and motility, serves as key source of energy, requires more chewing (increase saliva production)
What are the key differences in nutrient content between grass forages and legume forages? (ie, which is higher in DE, protein, NDF, Ca, vitamins?)
Legume forages are higher in protein, calcium, pectin, lignin, vitamin E, and beta-carotene (vit A precursor) compared to grass forages (grass forages are higher in hemicellulose and NDF)
What types of carbohydrates are in forages vs. the carbohydrates in grain?
Forages contain more structural carbohydrates-> insoluble fibers such as hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin; whereas grains contain more non-structural carbohydrates such as starch and sugars.
How does plant stage of growth (forage maturity) affect the nutrient content of forage?
As the plant grows from early-late maturity, there is an increase in fiber (hemicellulose, cellulose) and lignin. However, there is a decrease in NSC, protein, minerals, DE, and digestibility.
What criteria should be used to select a suitable hay?
Select a hay suited to the horse -> see chart
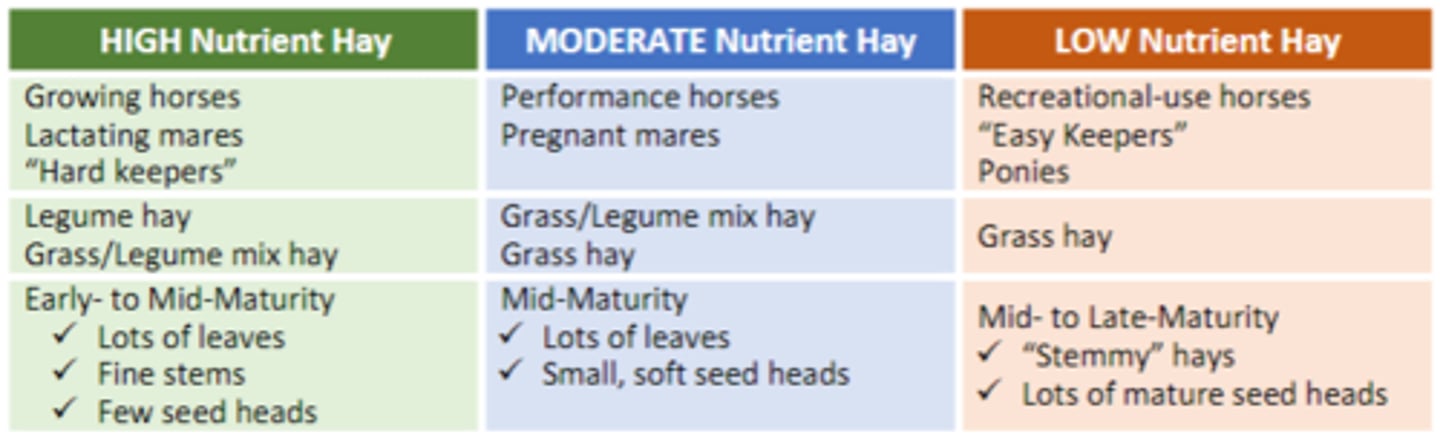
How can plant stage of maturity be visually assessed?
- presence/ appearance of seed heads/flowers (early-mid maturity= small, soft seed heads, late-matuirty= large, dry, crumbly seed heads)
- leaves vs. stems (more stems = more mature, decreased quality)
- stem diameter = larger diameter = more mature, lower quality
- forage length (long = mature)
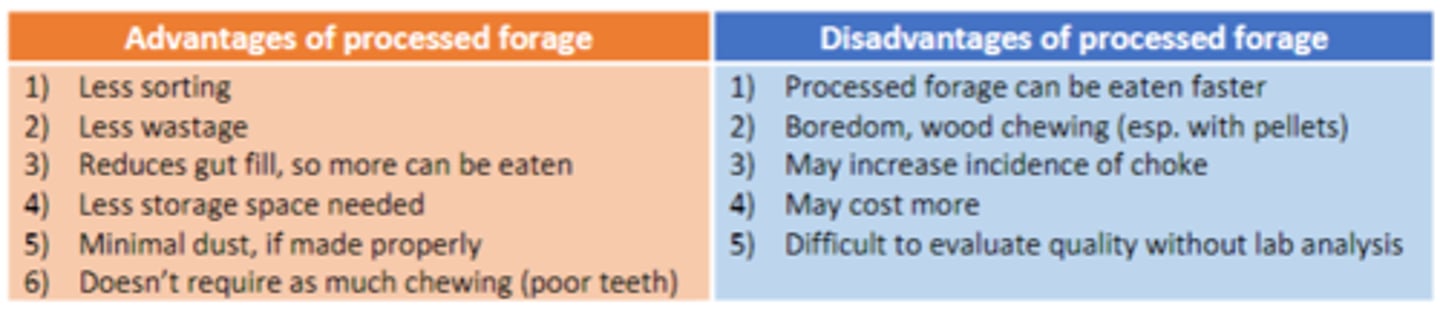
What are the advantages and disadvantages of processed forages?
processed hay = chopped, cubed, pelleted
What is the minimum amount of forage needed? What level of forage is ideal?
minimum amount of forage in diet is 1% BW (DM basis), ideal level is 1.5-2.0% BW (DM basis)
What are some high-fiber alternatives to forage (ie, alt. roughages)? How does their DE content compare with forages?
Beet pulp -> large proportion of fiber is pectin, meaning it is highly digestible, DE content is similar to oats
Hulls -> high fiber, low digestability, similar DE content to grass hay
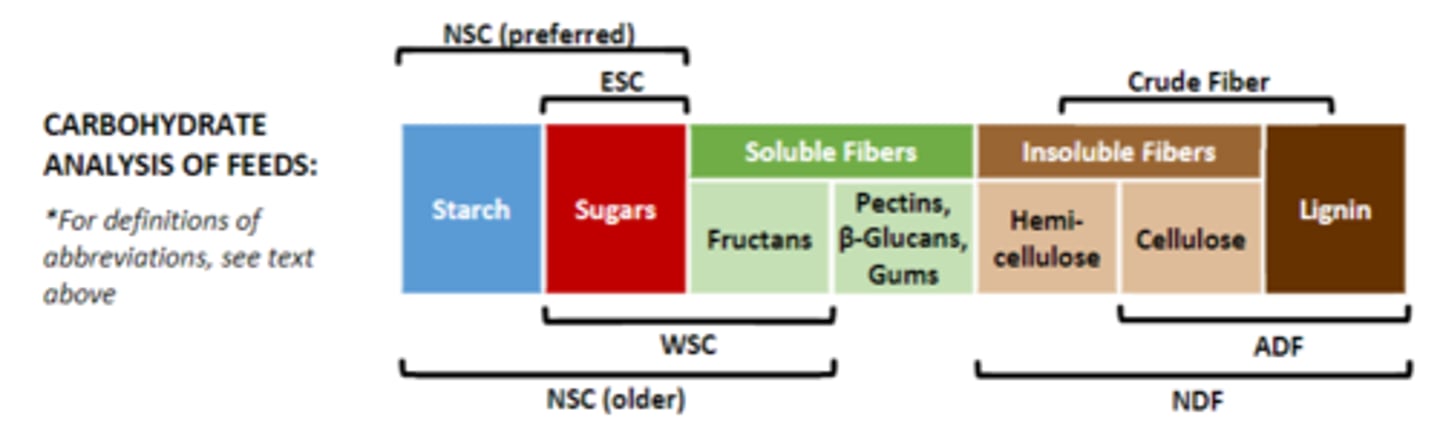
Can you differentiate between the analysis methods for identifying the different carbohydrate fractions in feeds?
Water soluble carbohydrates = sugars + fructans
Ethanol soluable carbohydrates= sugars
To calculate total NSC:
Older method= NSC= starch + WSC
Preferred method = starch and ESC
know chart
How does the nutrient composition of grains compare to forages? (ie, which is higher in DE, fiber, Ca, P?)
Grains have increased DE, starch, and potassium compared to forages
Grains have decreased fiber, calcium, vitamins
Does processing improve the starch digestion of all types of grain?
No, processing (altering the physical form of the whole grain) improves digestion of the whole grain, except for oats. Processing oats is only beneficial if the horse has dental problems.
Is the nutrient content of grain byproducts (eg, brans, wheat midds) more like a grain or a forage?
Hull (outer papery husk)-> roughage
Bran (skin of germ kernal)-> has more fiber than grains but is more like a grain
starch/flour + germ-> energy feedstuff
Wheat midd-> nutrient comp is similar to the whole wheat grain it is derived from.
What mineral is high in all brans?
Phosphorus
What is special about rice bran compared to other brans?
Rice bran is high in fat
What feedstuffs are high in fat?
animal fats/tallow, plant + vegetable oils, flaxseed, whole roasted/heat-processed soybeans, rice bran, blended fat supplements, fat-added commercial feeds
What nutrient does vegetable oil provide? What nutrients does oil NOT provide?
very high in DE, does not provide any other nutrients
What feedstuffs are used to fortify commercial feeds with protein?
oilseed meals, legume seeds, animal proteins, marine proteins, milk products (whey, casein), non-protein nitrogen
Why is the replacement of starch with fat & fiber sources considered a "safer" source of energy in commercial feeds?
Grains and grain byproducts are high in starch, which have an increased risk for digestive upset, therefore fat + fiber sources replace the grain as the energy source
If given a feed tag, be able to identify:
The type of horse it's intended for (based on protein content)
10-12% CP = adult idle or light work
12-14% CP = performance, stallion, 2 yr-old
14-16% CP = broodmare, weanling, yearling
16-18% CP = creep feed; milk replacer
If given a feed tag, be able to identify: Is it a Fat-added feed? Fiber-added feed? Fat-and-Fiber-added feed? Or does it contain no additional fat or fiber ("traditional")?
Fat added: >/= 5% crude fat
fiber added: >/= 12% cruder fiber
If given a feed tag, be able to identify: Can you identify feeds from the ingredient list that are classified as energy feeds, high fat feeds, protein feeds, or roughages?
see mod 7 notes
Concentrates will likely be needed in the diet for what kinds of horses?
horses where a forage-only diet does not meet their requirements... growing horses, performance horses, lactating mares, horses needing to gain weight, if low quality forage is the only forage available.
What is the maximum amount of concentrate that can be fed in a single meal? Why?
0.5% BW/meal, consequences of feeding excess grain = obesity, excitability, digestive upset (explain mechanism)
What is the maximum amount of the total daily ration that can be concentrate?
no more than 50% of total DM intake/ day should be concentrate, important to maximize forage in the diet.
What is a "complete feed"? What level of crude fiber should it have?
complete feeds are designed to be all-in-one feeds including a combination of roughage and fortified concentrate. Crude fiber should be >/= 18%
What mineral must be added to the diet of all horses?
salt (NaCl)
What vitamins can be made by the horse (or hindgut microbes) and which must be provided by the diet?
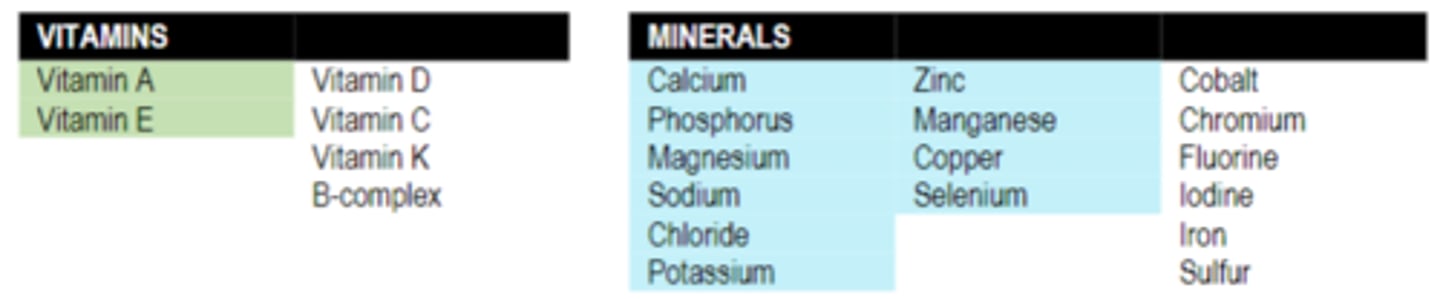
What are the options for supplementing vitamins and minerals?
supply single supplement missing -> risky and potential for toxicity
cafeteria style -> ineffective, horses have no nutritional knowledge
feed a complete mineral/vitamin product (mineral block, premix, ration balancer)
In what situations is a vitamin/mineral supplement likely to be needed?
forage-only diet
forage + unfortified grains
forage + insufficient amount of fortified feed
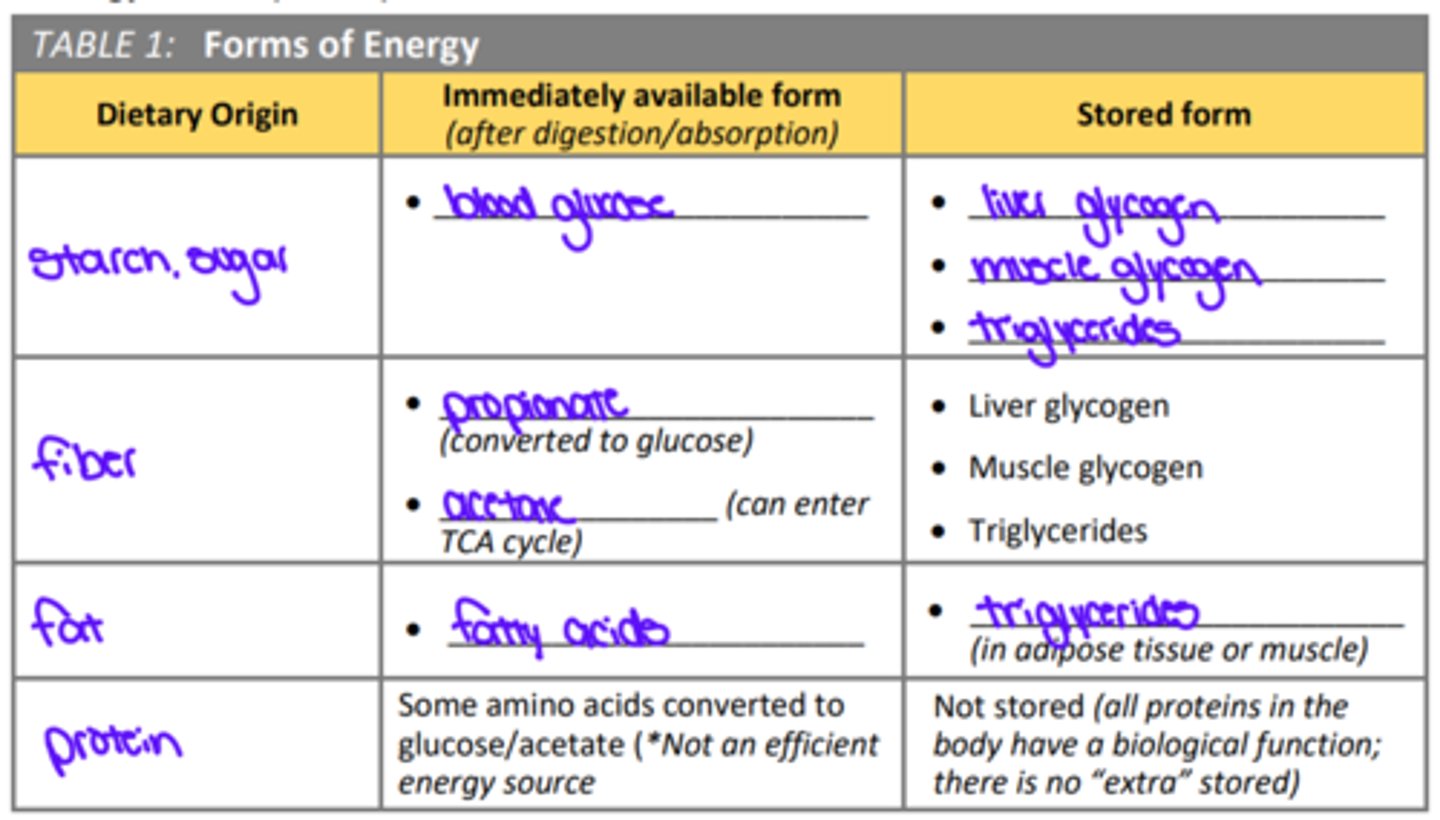
What are dietary sources of energy? What is their form immediately after absorption? What are the stored forms of energy in the body?
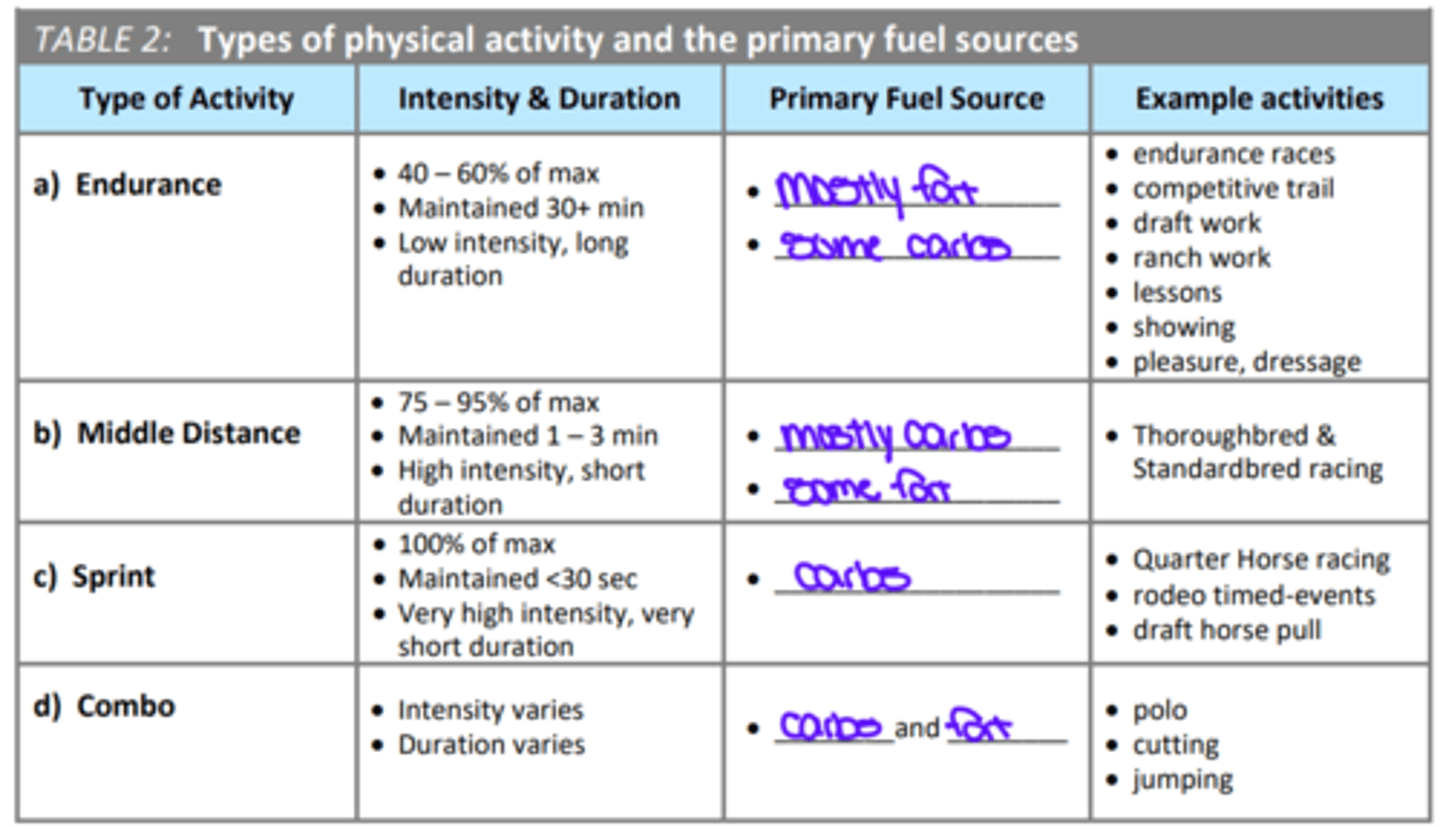
How does the type of exercise affect which energy sources ("fuels") are used?
What nutrient requirements are affected most by exercise?
1) energy
2) water
3) electrolytes
4) vitamin E
5) other nutrients increase but in proportion to energy
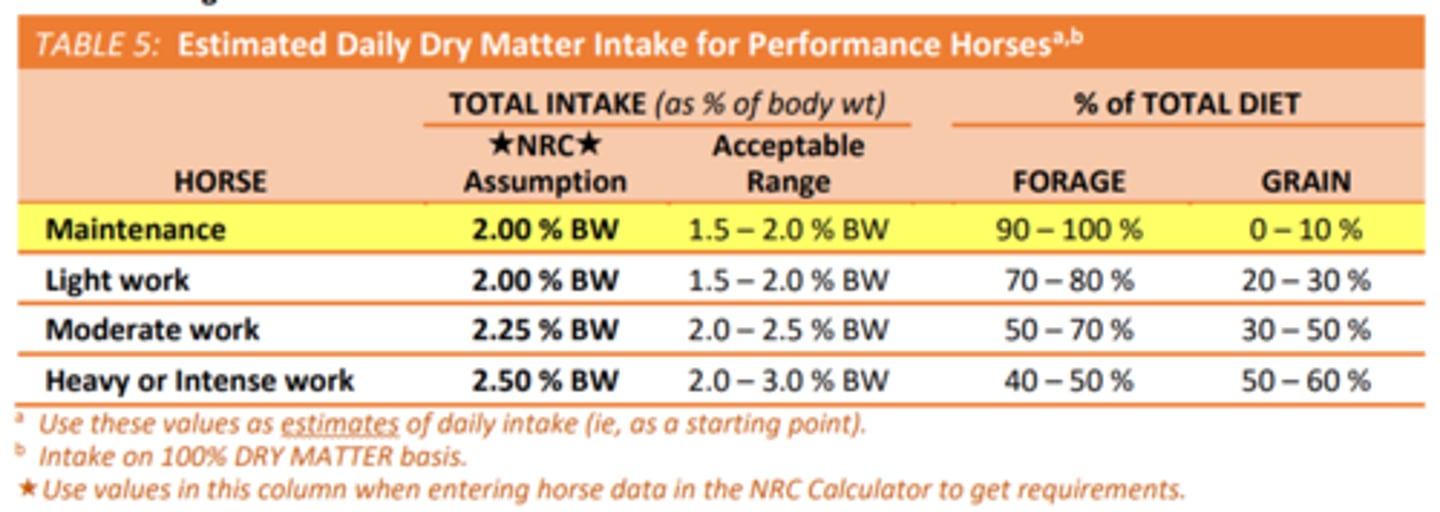
What is the expected DM intake and the proportion of hay and concentrate likely to be needed in the diet for horses at work? (*you’ll need to know these numbers!)
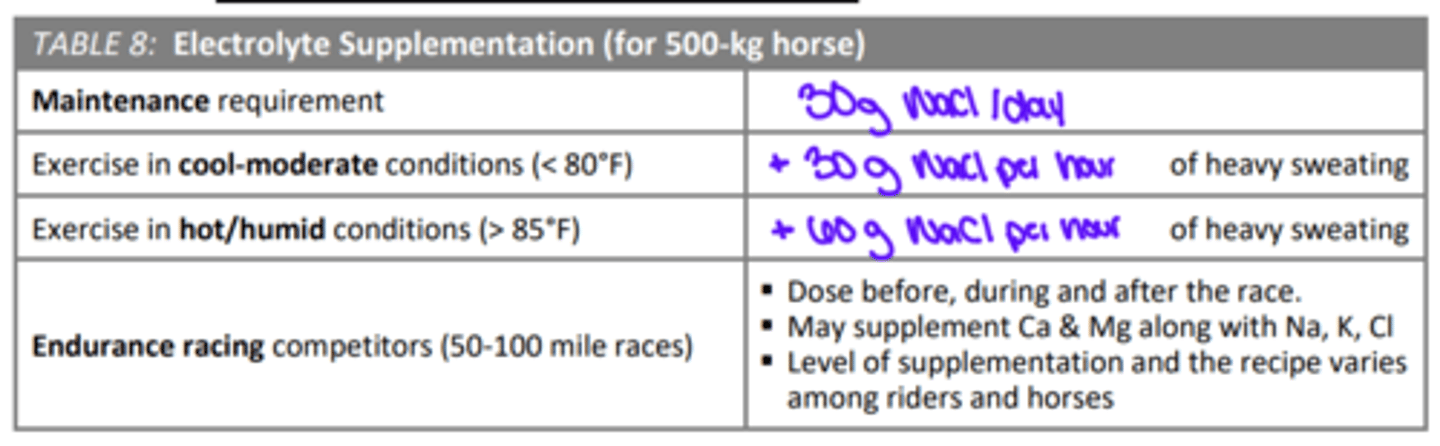
What is lost in sweat? What affects it?
water, electrolytes (Na, K, Cl), horses lose 6-15 liters sweat/ hr, highest losses with high heat, hihg humidity, and increased exercise duration
What are some electrolyte replacement strategies?
salt block, top dress on feed, put in water, oral drench
What are the benefits of adding fat to the diet?
1) High calorie content (very energy dense)
2) reduces thermal load (metabolic heat is reduced), meaning it is best to add during the summer so there is less heat produced
3) safe source of calories compared to starch and sugar components
4) provides essential fatty acids that the horse cannot make (e.g., Omega-3 and Omega-6)
5) improves skin and coat health
6) reduces excitable behavior, compared to starch/sugar that can trigger hyperactivity
7) increase absorption of fat soluble vitamins (Vitamins A, D, E, and K)
Is a high protein diet harmful to most horses? What happens to the excess protein?
A high protein diet is usually not harmful, as any excess protein consumed will just be excreted. It is important to ensure exercising horses have adequate DE in diet.
What happens when a horse eats a meal of grain? How long do these effects last? How might this impact fuel availability during exercise?
Eating a large grain meal results in elevated insulin levels -> this puts the body in storage mode, resulting in glucose being converted to glycogen and stored, this halts liver from undergoing gluconeogenesis and lipolysis in adipose. As a result, there is reduced fuel (glucose) available to muscle for exercise. Effects of insulin last 4 hours after a large grain meal.
What happens in the body when a horse eats a large meal of hay? How long do these effects last?
Eating a large hay meal results in increased gut fill and body weight (20-50 lbs) and decreased blood volume to increase fluid to hindgut. These effects last 4 hours.
How might a big hay meal impact the horse during exercise? Would this change with small meals of hay?
Eating a large hay meal may negatively impact the horse's ability to preform at high speeds and will require the horse to work harder during exercise. This can be minimized by feeding smaller, continous meals.
How does any large meal affect blood flow to the gut?
Increases blood flow to gut, which decreases blood supply to the rest of the body. If exercised within 2 hours, then blood is drawn away from the gut, increasing risk for colic because of the slow digestion that occured due to lack of blood flow.
What is a good PRE-exercise feeding strategy? WHY should they be fed this way? (link physiological responses to a meal with fuels needed during exercise to explain feeding plan)
avoid large meal within 4 hours of exercise, feed a small meal or allow pasture access before exercise, during prolonged exercise allow access to hay during breaks, do not feed a large concentrate meal within 4-6 hours of exercise, can feed small grain meal 1-2 hrs prior, ensure horse has access to unlimited water. It is important to not feed large grain meal prior to exercise due to the increase in insulin that results. Additionally, horses that eat a large hay meal results in increase gut fill and increased blood flow to gut instead of muscles for exercising.
What is a good POST-exercise feeding strategy? Why?
wait until rectal temp is <102 F to feed, allow access to hay, can give small grain meal 60-90 mins after exercise, and a larger normal, grain meal 2-3 hrs later. To replenish glycogen, feed glucose, ie a concentrate high in starch or a molasses added feed. It is important to offer water immediately post-exercise and supplement with salt or electrolytes to replenish.
What is the difference between RER and PSSM?
RER and PSSM are both types of chronic tying up. RER results from defective calcium regulation affecting contraction and relaxation of muscles, PSSM results from a autosomal dominant mutation in GYS1, gene coding for glycogen synthase that causes an excess amount of abnormal muscle glycogen to be stored.
How does a diet high in NSC trigger RER? How does it trigger PSSM?
RER: Feeding NSC to horses with RER results in excess contraction and destruction of muscle fibers (since the horse already has defective calcium regulation)
PSSM: Nonstructural carbohydrates are digested and absorbed as glucose, therefore they promote glycogen storage, which is abnormal in horses with PSSM
How should RER/PSSM horses be fed? Why?
Minimize NSC in the diet, this can be done by feeding a fat and fiber added concentrate or adding fat (ex. vegetable oil to the diet) to meet DE requirements.
How is nutrition connected to sporadic vs. chronic tying up?
Sporadic tying up can occur when the horse has deficiencies in electrolytes, vitamin E or selenium
Chronic tying up has genetic factors causing it (still widely unknown), however, diets high in NSC can trigger chronic tying up
Know expected DM intake for performance horses (all 4 levels of work) and broodmares (gestation & lactation). Other nutrient requirements will be provided to you.
Performance:
Maintenance: 2% (1.5-2%)
Light Work: 2% (1.5-2%)
Moderate Work: 2.25% (2-2.5%)
Heavy/Intense Work: 2.5% (2-3%)
Broodmares:
Early Gestation: 2% (1.5-2%)
Late Gestation: 2% (2-2.5%)
Early Lactation: 2.5% (2.5-3%)
Late Lactation: 2.5% (2-2.5%)
How does nutrition affect reproductive performance?
Inadequate energy results in weight loss, decreased fertility, increased risk of early embryonic loss, increase long-term disease risk in offspring
Inadequate protein results in failure to ovulate, increased risk of early embryonic loss
What is flushing? (nutrition)
The practice of feeding increasing energy prior to breeding
How does body condition affect reproductive performance in mares?
Moderate to fleshy mares (BCS 5-7) cycle earlier, have fewer cycles per conception, higher preg rate, maintain pregnancy more easily
Obese mares (BCS 8-9) can have decreased milk production and increased risk of metabolic disturbances
Thin mares (BCS <4) may fail to conceive, difficulty carrying pregnancy to term, have decreased milk production
What is the ideal body condition score for mares?
BCS 6-7
What type of mare would the practice of "flushing" going into the breeding season be most effective?
Thin mares, as there is no evidence that flushing benefits mares already in good body condition
When is the most opportune time to improve the body condition of a broodmare? Why?
During early gestation because the requirement of the mare are similar to maintenance as the foal is only growing .1-.2 lbs/day, therefore easier to increase ration to promote weight gain.
Be able to calculate how many kg of gain are needed to improve BCS, as well as how many Mcal DE are needed per kg gain
20 kg BW gain is needed to increase BCS by 1 level
An extra 20 Mcal of DE is needed for 1 kg of weight gain
If given a feed, be able to calculate how much extra should be fed and how long will it take to safely improve body condition.
maximum safe weight gain is 0.5kg/day (takes 40 days to increase BCS by 1 level)
How does gestation and lactation affect the mare's requirements?
increase the mares requirements, highest at early lactation
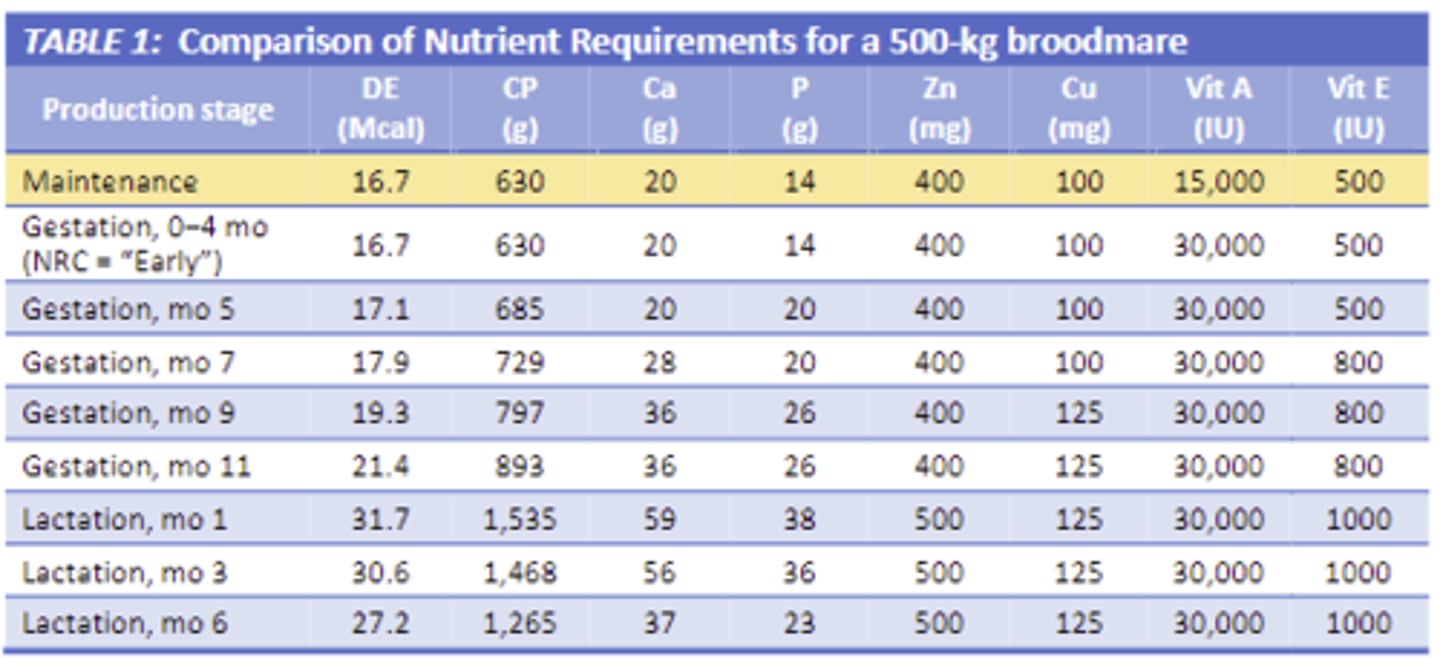
How does stage of pregnancy or lactation affect how we feed mares? (eg, feed selection, proportion of hay vs concentrate, etc.)
Early gestation: req similar to maintenance -> can be fed high quality forage
Late gestation: good quality hay is 70-80% of diet, fortified concentrate (ideally formulated for broodmares is usually 20-30% of total DM intake)
Lactating mares: 50-60% DM intake is good quality forage, 40-50% total DM intake is a fortified concentrate
How should we manage mares consuming tall fescue? Why?
Remove mares from infected pastures 30 days before expected foaling or mow pastures to prevent seed head development. Consuming endophyte-infected tall fescue could result in increased gestation length, stillborn foal, agalactia (reduced or absent milk production), retained placenta, difficulty rebreeding
How should you handle the mare's diet around the time of weaning? Why?
Feed mare normally right up to weaning, although mare's requirements decrease in later phases of lactation, the foal will begin sharing mare's feed. Post-weaning, reduce amount of concentrate gradually.
What is the ideal body condition score for stallions? Why?
BCS 5-6 is ideal. It is important that the stallion has enough body reserves to make it through breeding season, however, too high of a BCS can result in lameness, heart attacks, lower libido, etc.
What affects stallion's requirements?
Number of mares bred, temperament and psychological response to breeding, if stallion is still training or competing during breeding season
How should stallions be fed during non-breeding and breeding seasons?
Stallion should be fed similar to a performance horse in light work during breeding season
Stallion's requirements during off-season are similar to high maintenance if idle, if exercised they are similar to performance horses.