Sed Strat Week 5
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Bedform
Form of the sediment bed (how it looks)
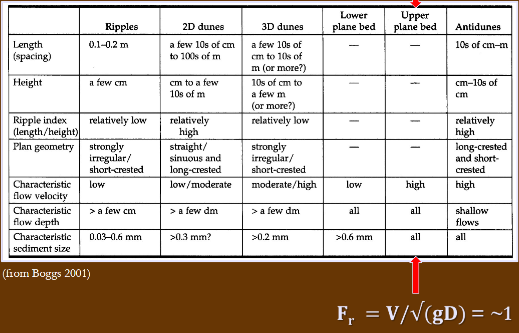
Bedforms of unidirectional flow (river)
ripples → dunes
Froude number
Flow velocity / (square root of gravitational constant * water depth).
Represents velocity of a ripple (gravity wave) on the surface of the water flow
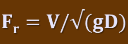
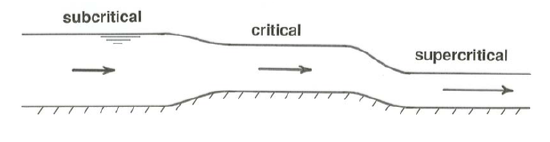
Subcritical flow
Froude number < 1. Slow, deep, laminar flow, ripples propagate downstream and upstream. Flow velocity is less than celerity (gD)
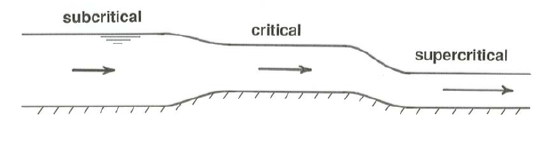
Supercritical flow
Froude number > 1. Fast, shallow, often turbulent flow, ripples propagate entirely downstream. Flow velocity is more than celerity (gD)
Factors influencing grain flow
Grain size, flow depth, flow velocity
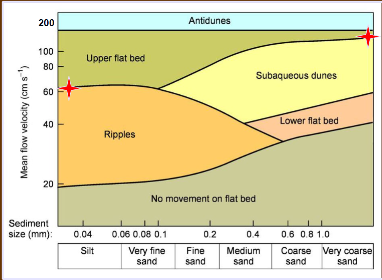
Hjulstrom diagram
Grains in suspension will join the bed as a static grain based on their size in response to the flow velocity.
High velocity flow is required to move heavier particles and fine, sticky sediment off the bed
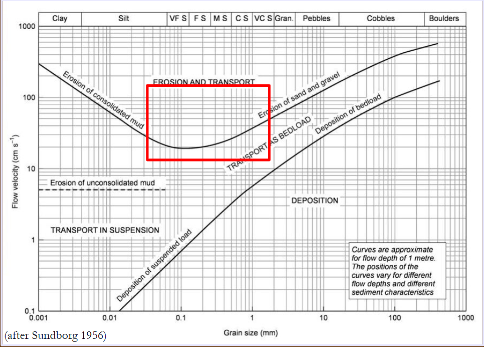
Cohesive and non-cohesive sediment
Slight negative and positive surface charges on clay-sized grains cause them to stick together. There is also large surface/volume ratio due to clay being a flat sheet silicate, causing further cohesion. As grain size increases, cohesion decreases due to lower surface area and weaker charge (sand, gravel)
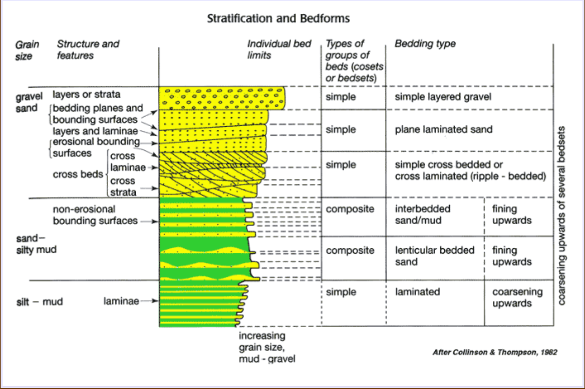
Bedding planes
Surface of a layer of sediment called the bed. Used to determine order/timing of accumulation of sediments that form beds. Characteristics of these (erosion, cementation, boring, etc) are used to aid in sedimentary rock interpretation
Individual beds are produced under constant physical, biological, or chemical conditions
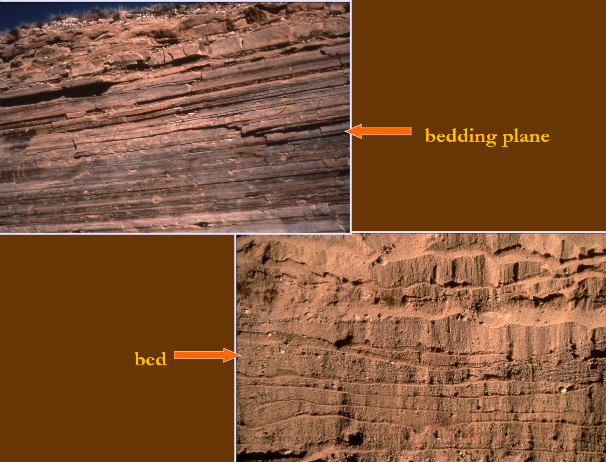
Bed
Building block of stratigraphy. Tabular or lenticular layers (> 1cm) of sedimentary rock that have lithologic or structural differences that distinguish them from the layers above and below. Lithologic composition, geometry, and stacking pattern is used to interpret depositional setting
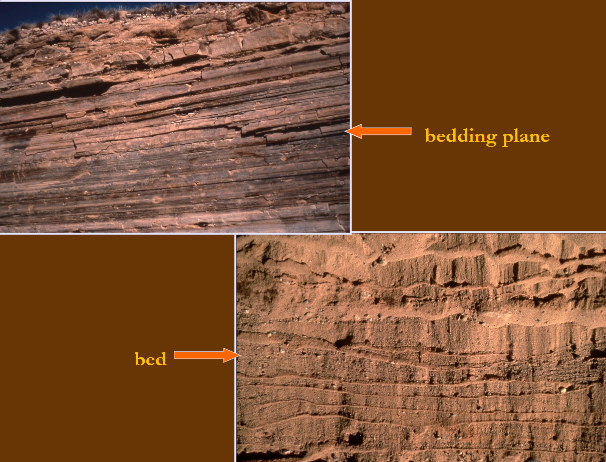
Laminae
Layers < 1cm in width. Alterations of thin layers of different lithologies are interbedded and are considered as one unit

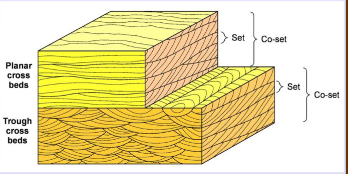
Cross stratification
Any layering in sedimentary rock that is oriented at an angle to the horizontal deposition. Often caused by dune migration; ripples produce cross-lamination

Groups of cross beds
Sets are one unit of planar, cross bedded, or cross stratified sediment. A bed with more than one set of the same structure is a co-set
Composite bed
group of beds differing in composition, texture, or internal structures but associated genetically, representing a common type of deposited sequence (turbidite)
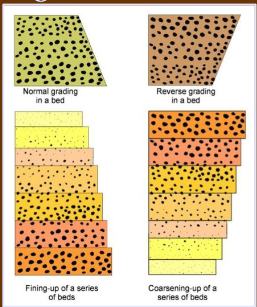
Graded beds
units characterized by distinct vertical gradation in grain-size (upward fining or coarsening)
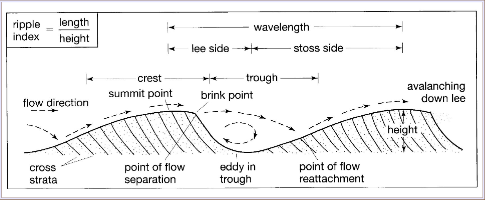
Current ripples
Migrate as sand is added to the crest, accreting on lee slope. Sediment moves up the stoss side and collects in the trough, forming laminae and moving crest/attachment point downstream
referred to as cross laminae; may be straight, sinuous or linguoid
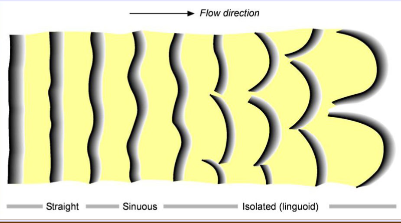
Flow effect on ripple shape
Higher velocity flow causes straight ripples to turn into linguoid ripples
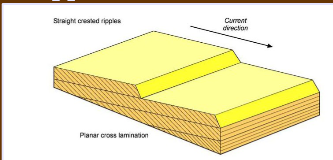
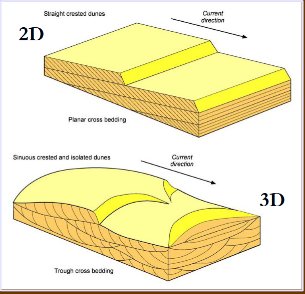
Planar cross laminae (2D ripples)
Cross laminae that all dip in the same direction and lay in the same plane, caused by straight ripples
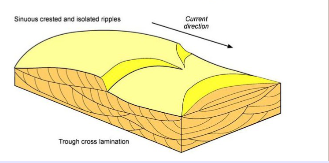
Trough cross laminae (3D ripples)
Curved cross laminae that all dip in different directions are formed mainly in the trough-shaped low areas between adjacent ripple forms; caused by linguoid ripples
Climbing ripple
High sand addition causes no net removal of sand from stoss side, causing ripples to migrate on top of each other.
When rate of sediment addition exceeds the forward movement of the ripple, deposition occurs on the stoss and lee side
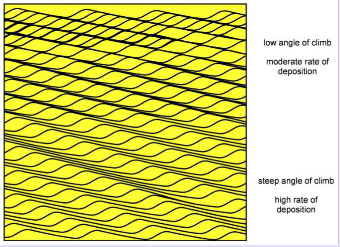
Current ripples do not give a way to estimate ____.
Water depth. They only form in sands with grain size <0.6 mm and are independent of depth
Dune
Beds of sand in rivers, estuaries, and beaches that are much larger than ripples, leaving cross beds. They are different in the sense that dune crests (wavelengths) are larger in spacing and higher than ripples. However, sand migration works in the same way
May have 2D and 3D dune cross beds
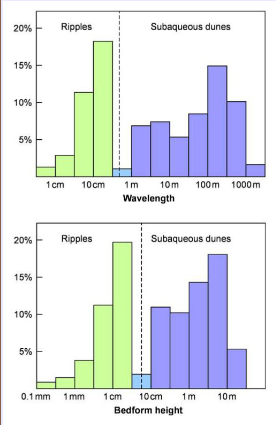
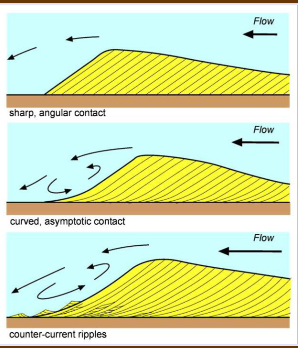
Dune cross bedding types
Planar (low velocity flow), tangential (high velocity flow), tangential with ripples climbing up lee side (highest velocity flow)
Upper plane bed
Only forms at high velocities in fine sand. Ripple and dune bedforms become washed out with increased flow speed. Often have primary current (parting) lineation that shows flow direction where grains have dragged along the surface
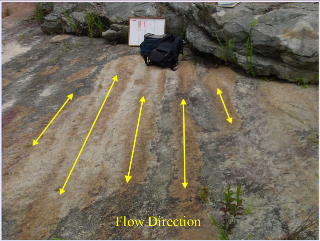
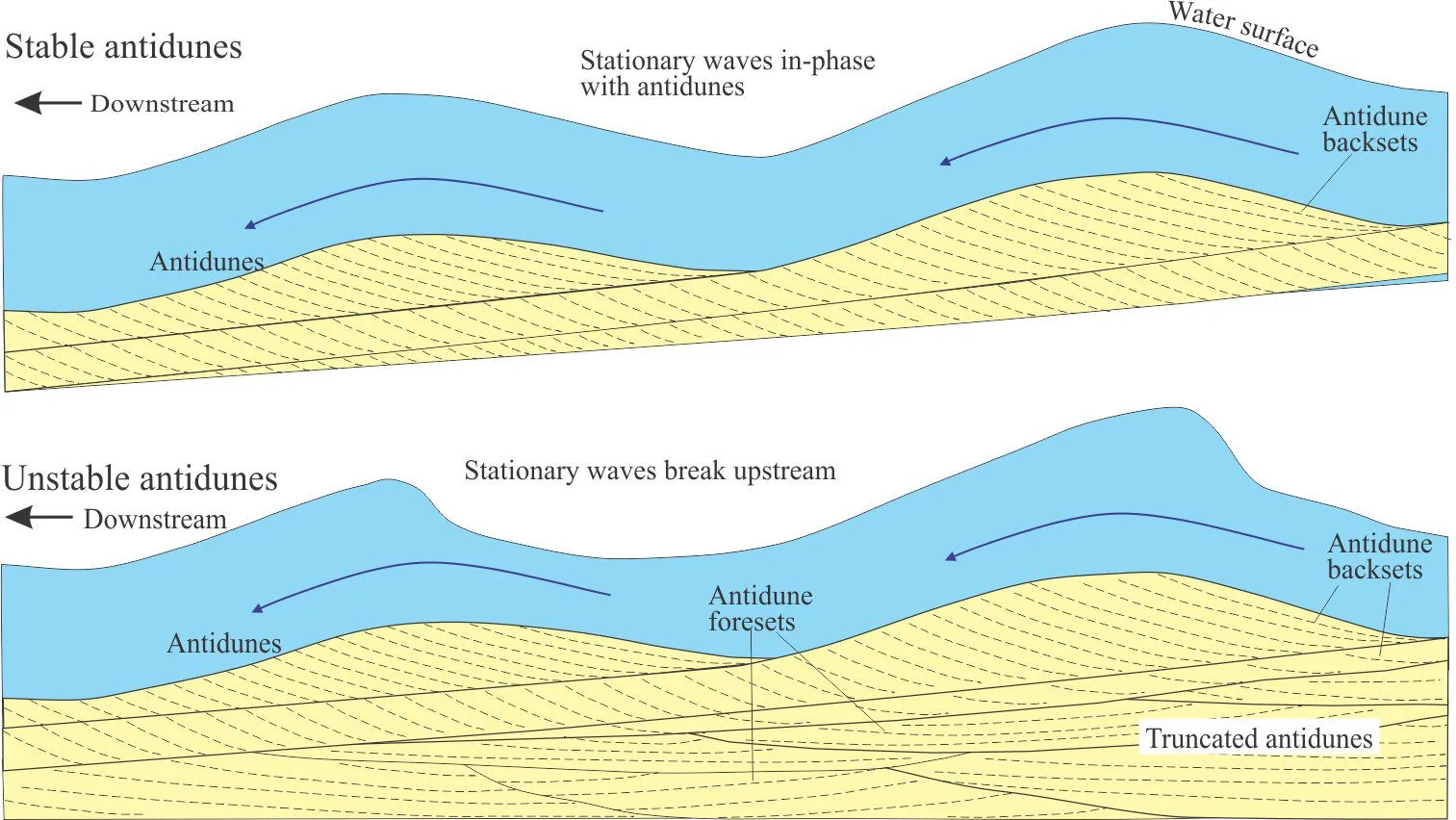
Antidunes
Form when flow is in phase with surface waves. Migrate upstream