Unit 1: Atomic and Periodic Properties
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Chemistry is
The study of matter and the changes it undergoes.
Atom is the ________ of an element.
Smallest representative
A _____ is made it two or more different kinds of elements chemically.
Compound
Compounds can be broken down into elemental _________.
Particles
A hydrate is a compound that __________.
Absorbs water molecules from its environment and includes them as part of its structure. (Example: CoCl2 • 6H2O)
A hydrate is not ________ and can be removed with ______.
Chemically bonded, heat
An ________ is the hydrate minus the water.
Anhydrous salt
Intensive properties are __________.
Are independent of the amount of substance present (Example: Density, boiling point, color)
Extensive properties __________.
Depend upon the amount of substance present (Example: Mass, volume, energy)
Physical properties can be observed _________.
Without changing a substance (Example: Boiling point, density, mass, volume)
Chemical properties can be observed _________.
Only when a substance is changed into another substance (Example: Flammability, corrosiveness, reactivity with acid)
Physical changes are changes in matter. __________.
That do not change the composition of a substance (Example: changes in state, temperature, volume)
Chemical changes result in _______.
New substances (Example: Combustion, oxidation, decomposition)
SI Units of mass, length, time, temperature, and amount of substance
Mass: kg
Length: meter
Time: second (s^a)
Temperature: kelvin
Amount of substance: mole
Common used metric system units for volume are _______ and ______.
Liter ( 1 dm³), milliliter (1 cm³)
Density is a ________ of a substance
Physical property (Formula: d= m/v)
Density of water is ______.
1 g/mL
Temperature is the measure of __________.
Average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample.
Exact numbers have _______ sig figs.
Infinite
Accuracy is the ________ .
Proximity of a measurement to the true value of a quantity.
Precision refers to the _________.
Proximity of several measurements to each other
Dimensional analysis is how we ________.
Convert one quantity to another (Formula: given unit • desired unit/given unit= desired unit)
Percent composition formula is _______.
%Composition= mass of substance A/ total mass • 100
Percent by mass (volume/ mole) formula is _________.
Percent by mass= mass of substance A/ total mass • 100
Mole fraction (X) formula is _____.
X= Mole of A/ total moles
Atom is the _______.
Basic unit of a chemical element.
Elements are _______.
Composed of atoms with a specific number of protons
Isotope are atoms _______.
Of the same element (protons) and different mass (neutrons)
Protons and electrons are the only particles that have a _______.
Charge (1 amu)
The closer the ratio of protons to neutrons is 1:1, _______.
The more stable the nucleus
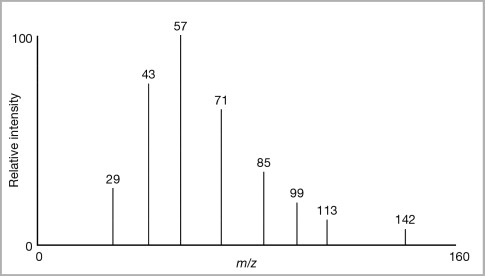
Atomic and molecular masses can be measured by a ______.
Mass spectrometer
_________ is a technique used to determine the molecular mass of atoms/molecules in a sample.
Mass spectrometry
Each peak represents a different isotope of one element
Height of each peak is the relative abundance
X- axis is the mass of the isotope
Elements in the same _____ have similar chemical properties because of their valence electrons.
Group
Elements in the same ______ have the same number of energy levels.
Period
Diatomic elements are seven elements that _______.
Occur naturally as molecules containing two atoms (Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, F2)
Molecular formula represents the _______ composition of a molecule.
Actual
Empirical formula represents the _______ composition of a molecule.
Simplified
Cations _____ electrons and form _____ ions.
Loses, positive (Form by left side of periodic table)
Anions _____ electrons and form _____ ions.
Gains, negative (Form by right side of periodic table)
If the anion in an acid ends with -ide ________.
Change the ending to -ic and add prefix hydro-
If the anion in an acid ends with -ite ________.
Change the ending to -ous acid
If the anion in an acid ends with -ate ________.
Change the ending to -ic acid
Organic chemistry is the study of ______, simple hydrocarbons that contain single bonds are ________.
Carbon, alkanes
Alkane formula and prefixes:
CnH2n+2, meth=1, eth=2, prop=3
The distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves is _______.
Wavelength
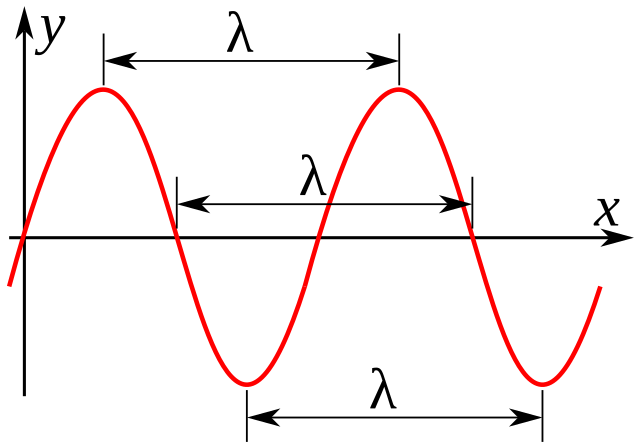
The number of waves passing a given point per unit is the ______.
Frequency
Frequency units are:
1/s, s^-1, Hz
Wavelength and frequency formula:
C (m/s) = λ(m) v(1/s)
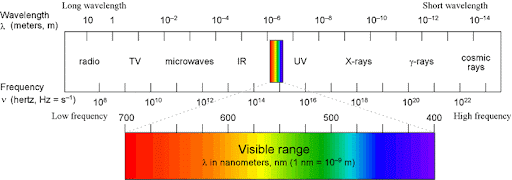
Red light has _______, violet has ______.
Low energy, frequency, high wavelength; high energy, frequency, low wavelength
Energy and frequency formula:
E (J) = h (Plancks constant) v (1/s)
The _______ occurs when matter emits electrons upon exposure to electromagnetic radiation, such as photons of light.
Photoelectric effect
________ is the study of interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation.
Spectroscopy
___________ indicates that radiative energy released by the material.
Emission spectroscopy
The flame test is a basic form of ________.
Emission spectroscopy
The color of light released when falling down to its ground state corresponds with _______.
The amount of energy gained
Atomic emission spectra is evidence that there are _________.
Specific allowed potential energy values by showing the energy difference between some of them (Due to unique electronic structure, nuclear charge, and allowed movements of electrons in an atom)
Energy, speed of light, wavelength, and Plancks constant formula
E= hc/λ
𝜆
).
As energy levels increase, the distance between levels get _______.
Smaller
_________ is the concept in quantum mechanics, saying how every particle can be described in terms as waves.
Wave-particle duality
__________ demonstrates that there is a fundamental limit to what we can know about the behavior of quantum particles.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
For a one electron hydrogen atom, orbitals in the same energy level have the same energy or are ________.
Degenerate
As the number of electron increases, so does the repulsion between them so orbitals on the same energy level are no longer ________.
Degenerate
Pauli exclusion principle is that:
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same energy (Must have opposite spins)
Electron configuration shows the distribution of _________.
All electrons in an atom
Hunds rule is:
Each sub level must fill all up arrows, then fill down arrows
Diamagnetism refers to materials that _________.
Are not affected by a magnetic field
Paramagnetism refers to materials which ___________.
Become magnetized in a magnetic field
Coulomb’s law is used to ________.
Explain periodic trends
____________ is the effect of core electrons repelling outer electrons in an atom, reducing the nucleus's effective charge on the outer electrons.
Shielding
Effective nuclear charge (Zeff) is:
The amount of charge from the nucleus balance electrons experience
Elements in the same family have similar Zeff
With elements in the same period, higher protons will have a stronger Zeff
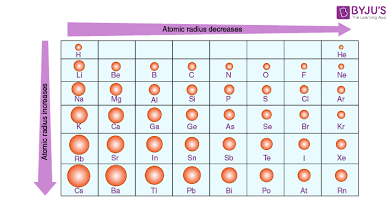
Atomic radius trend:
Decreases left to right due to increasing Zeff
Increases top to bottom due to increased number of energy levels
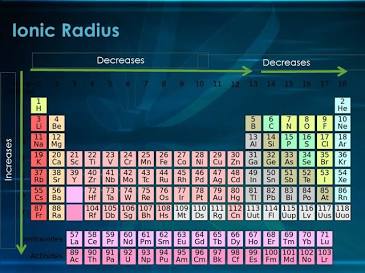
Ionic radius depends upon:
Nuclear charge, number of electrons, and orbitals where the electrons reside
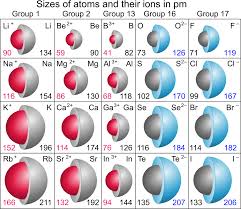
Ionic radius trend:
Increases down a group due to extra energy shells
Decreases across a period due to higher Zeff
Isoelectric series are _______.
Ions with the same amount of electrons (More protons = smaller)
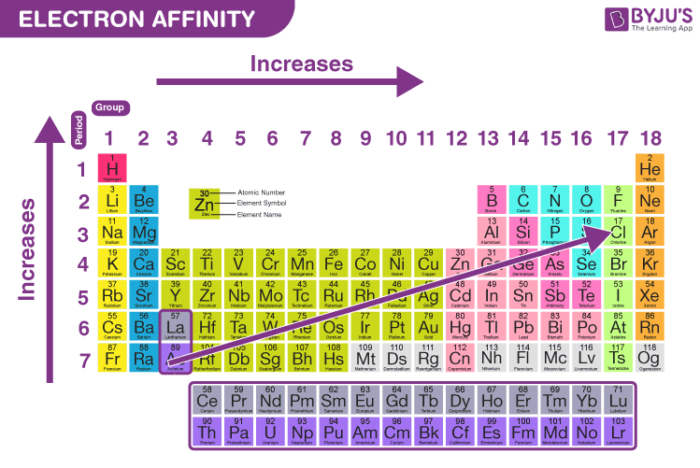
Electron affinity is the ________.
Change accompanying the addition of an electron
Becomes exothermic across a period
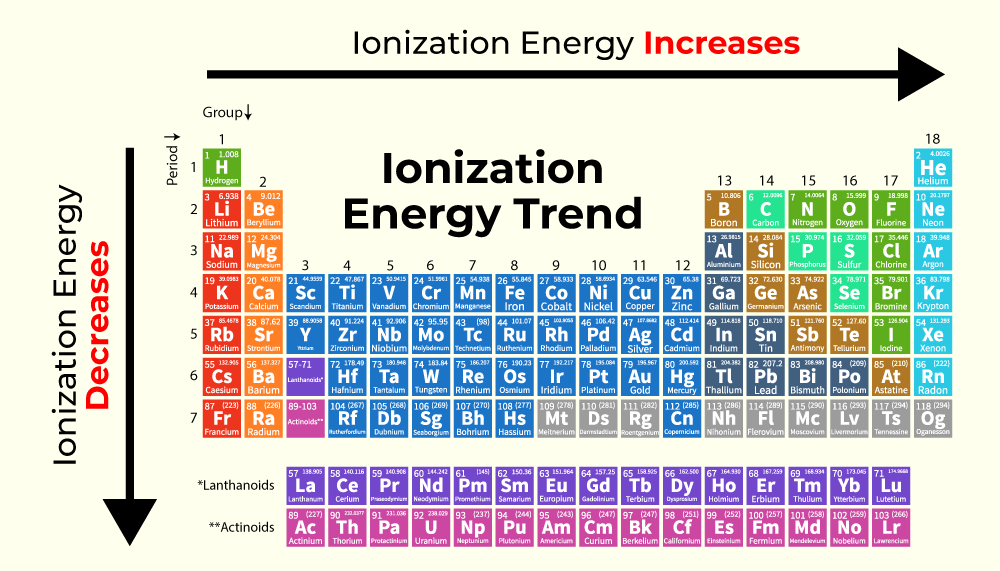
The ionization energy is the __________.
Amount of energy required to remove an electron from the ground state of a gaseous atom or ion (Takes more energy to remove each successive electron)
Ionization energy trend:
Down a family, less energy is required
Across a period it gets harder to remove an electron, due to Zeff increases
Photoelectron spectroscopy is used to determine ______.
Ionization energy (Electrons in lower energy levels have higher ionization energies)
Photoelectron spectra are moved to the left __________.
when a higher binding energy is observed
Alkali metals:
texture
Density and melting points
Ionization energies
React with what
Exothermic with what element
What happens in a flame
Where are they found
soft metallic solids
Low densities and melting points
React with oxygen to form peroxides (expect Li)
Bright colors in flame
Found in nature only
Alkaline Earth Metals:
densities and melting points
Ionization energies React
react with water?
Reactivity increase or decreases down
Higher densities and melting points than alkali metals
Low ionization energies not as much as alkali metals
Most ( expect Be and Mg) react water
Reactivity increases down a group