Biology EOC Review
1/215
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
Karyotype
A picture of organized chromosomes (All lions have the same _________)
10%
How much energy is transferred to the next trophic level?
Food Chain
Pros
Shows only one path of energy
It can show where things may go wrong if one species is removed
Cons
Misconception that certain consumers only eat one species
Food web
Pros
Shows all relations in an ecosystem
You can see how the removal of one species could affect the entire ecosystem
Cons
Misconception created that organisms at the top eat everything in the ____ ___
Owl
What animal is the energy flowing to?
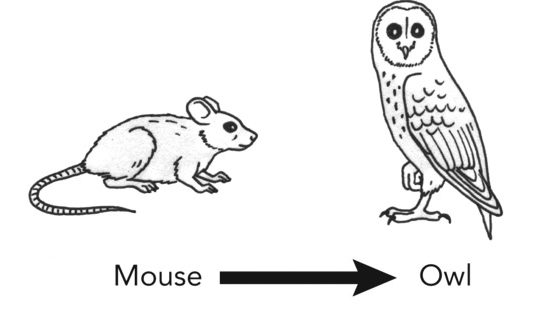
Energy Pyramid
Pros
Shows how much energy is being passed on
Shows a low number of animals
Cons
You can’t display more than 4 trophic levels
Primary Succession
What Process is being shown?
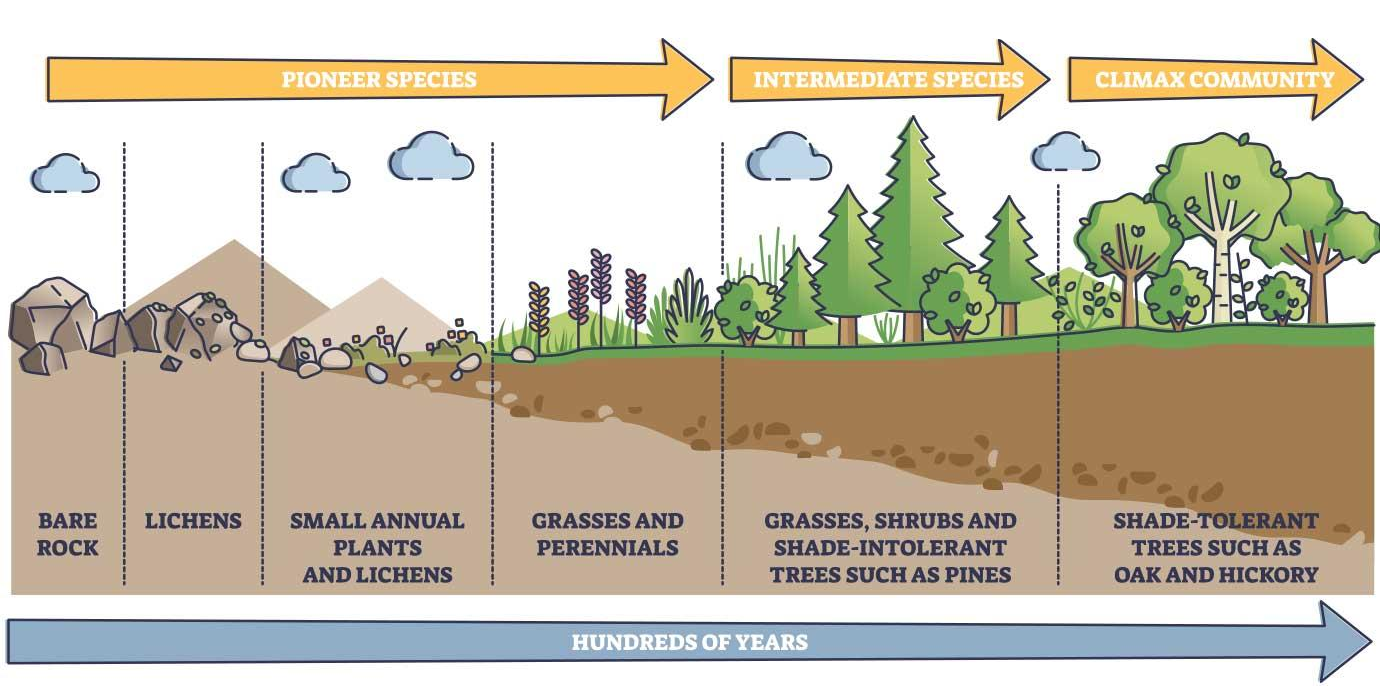
Barren Land
On what land does primary succession occur?
Low growing plants (moss, small ferms, lichens)
What organisms are colonizers?
Primary Succession
barren land is first colonized by plants (No nutrients in the beginning)
Secondary Succession
What process is being shown?
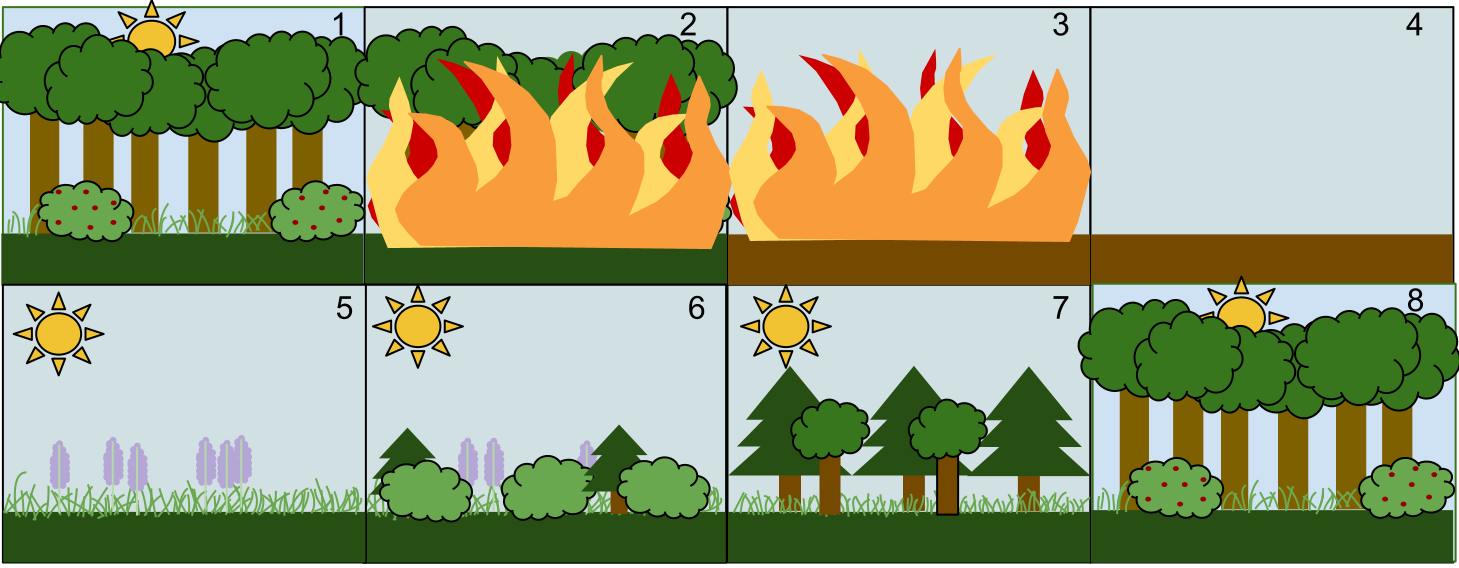
Secondary Succession
when a climax community or intermediate community is impacted by a disturbance.
Climax Community
the “endpoint” of succession
Seral Community
each community that changes is called a _____ _________
Plagioclimax Community
The climax community developed from a deflected succession
Macromolecule
Big arrangements of molecules that create energy to survive (come from food)
Monomer
Made of small molecules
Saccharide
Glucose
Polymer
Small molecules made into large chains
Polysaccharides
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
Carbohydrate Elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (CHO)
Primary Functions of Carbohydrates
Structural - Plants make cellulose for cell wall
Energy - Quick E Glucose/Glycogen
Storage of Energy:
Animals - Glycogen
Plants - Starch
Carbohydrate Monomer
Saccharide (Glucose)
Carbohydrate Polymer
Polysachharide (Glycogen)
Glycogen
Helps regulate blood glucose
Lipid Elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Nitrogen (CHOPN)
Types of Lipids
Phospholipid (makes cellular membrane)
Glycolipid (Lipids with carbs)
Cholesterol (Fluidity of cell membrane)
Primary Functions of Lipids
Energy Storage
Cell protection
Cell Signals
Building Blocks of Lipids
Glycerol & Fatty Acids
Examples of Lipids
Fats
Oils
Waxes
Steroids
Protein Elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur (CHONPS)
Primary Functions of Protein
Do the cells work to maintain life
Enzyme
Energy storage
Motion
Cell to cell signaling
Immune system
Protein Monomer
Amino Acid (20)
Protein Polymer
Polypeptide
Nucleic Acid Elements
Nucleotides (A,T,C,G)
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
Sugar + Phosphate
Nucleic Acid Monomer
Nucleotides
Primary Functions of Nucleic Acids
All the info for inheritance
Instructions to make proteins
DNA
Double Stranded
Deoxyribose sugars
Uses Thymine
RNA
Single stranded
Ribose sugars
Uses Uracil intead of Thymine
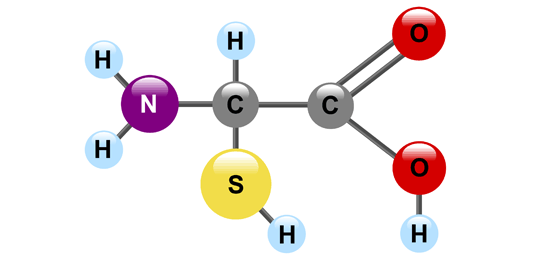
Protein
What Macromolecule is this?
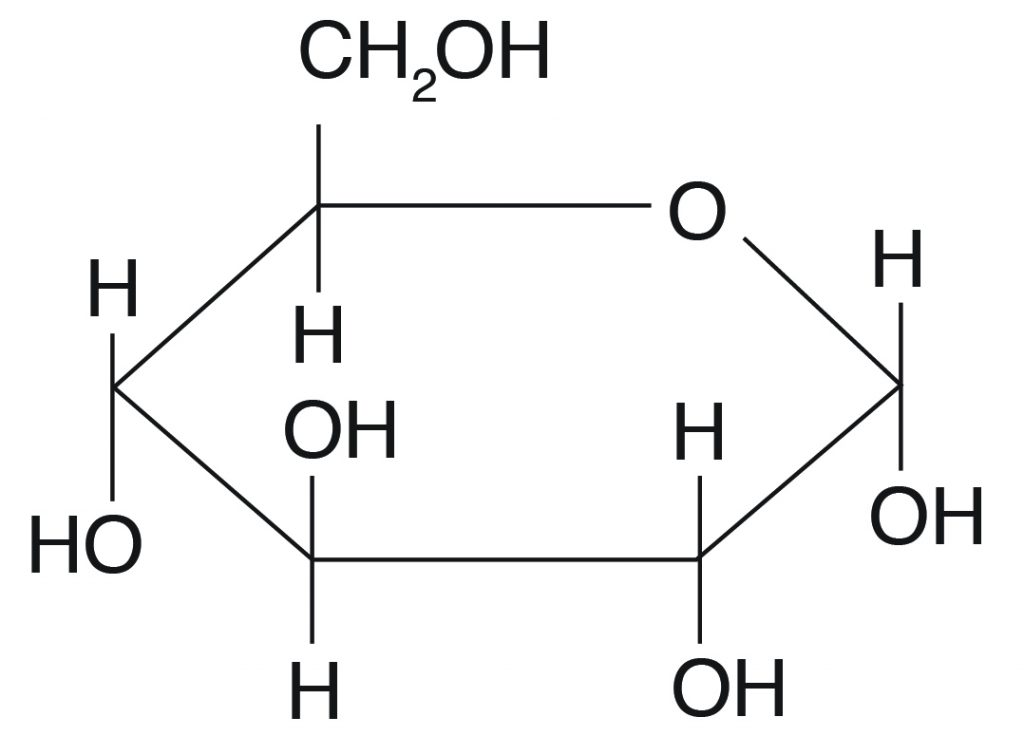
Carbohydrate
What Macromolecule is Shown?
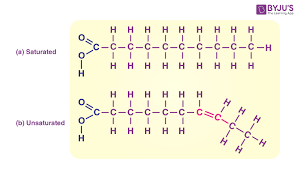
Lipid
What macromolecule is this?
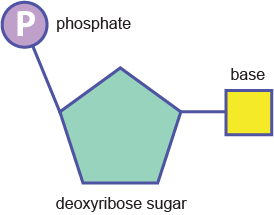
Nucleic Acid
What Macromolecule is shown?
Lipids
What macromolecule is tested with a paper bag?
Simple Carbohydrates
What macromolecule is tested with benedicts solution?
Protein
What macromolecule is tested with biurets solution?
Complex Carbohydrates
What macromolecule is tested with iodine solution?
brown/stained
What color will the paper bag turn if lipids are present?
Orange
What color will the benedicts solution turn if simple carbs are present?
Purple
What color will the biuret solution turn if proteins are present?
Black
What color will the iodine solution turn if complex carbs are present?
Biotic Fixation
Caused by a lightning strike, fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil in a form plants can use
Biological Fixation
Bacteria in root nodules of legume plants fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil in a form plants can use
Bacteria aren’t a part of the plant, they live on the eplant
Animal Elimination (waste)
Animal waste contains nitrogen compounds that combine with soil
Ammonificiation
Happens when organisms die and decay. Bacteria release nitrogen in organisms into soil
Denitrification
Nitrogen in the soil is converted by bacteria and released into the atmosphere
Uptake by plants/autotrophs/producers
Plants uptake nitrogen from the soil, connect nitrogen in soil to plants
Uptake by animals
Must get nitrogen from plants; connect plants to herbivores
Enzymes
Increases speed of the rate of chemical reactions
Lowers activation energy
Catalyst
Activation Energy
The energy needed to start a chemical reaction
Substrates (Reactants)
Molecule(s) that the enzyme bind to
Active Site
Specific place on enzyme where substrates bind
Denature
The enzyme changes shape and can no longer function
Homeostasis
The constant internal balance the body tries to maintain
Producer
Organisms that obtain energy from the sun
Consumer
Any organism on a trophic level that isn’t a producer or a decomposer
Decomposer
Organisms that break down and eat decaying material for energy
Limiting Factor
Resource or condition that affects the growth of a population in an ecosystem
Abiotic
Non-living components that affect organisms (sunlight, temperature, water)
Biotic
Living things or materials that affect organisms (plants, animals, bacteria, fungi)
Ecosystem
The biotic and abiotic factors that make up an area
Carrying Capacity
Amount of organisms an environment can support
Limit determined by availability of resources and interactions between other organisms
Steps of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Heat to seperate strands of DNA
Two DNA strands are cooled and joined by primers
Make more copies of DNA using DNA Polymerase
Niche
A species’ place and role in an ecosystem, including where it lives and how it gets the resources it needs to survive
Ruminants
Mammals with four-chambered stomachs
Characteristics of Life
Respond ot their environment
Grow and Develop
Reproduce
Maintain Homeostasis
Have complex chemistry (metabolism)
Consist of Cells
Niche partitioning
Similar species being able to coexist because of slight differences in each one’s niche
Mitosis
The process of forming new somatic cells
Somatic Cells
Cells that aren’t sex cells
Prophase
Stage of mitosis where the chromosomes condense and become visible, but are still tangled together
Metaphase
Stage of mitosis in which chromosomes move to the center and line up
Anaphase
Stage of mitosis where the chromosomes are being pulled to opposite sides of the cell
Telophase
Stage of mitosis where each group of chromosomes are at either end of the cell and unravel into their previous state
Cytokinesis
Stage of mitosis where the cytoplasm divides between the newly forming nuclei
Interphase
State of non-dividing cells
Autotroph
Organisms that make their own food
Heterotroph
Organisms that can’t make their own food and consume other organisms
Reactants for photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide, water, light energy
Products of photosynthesis
Oxygen + Sugar
Glucose
What is C6H12O6?
Metabolism
The general term describing the processes carried out to acquire and use energy
Glycolysis
A process in which glucose (sugar) is partially broken down by cells in enzyme reactions that do not need oxygen
Krebs Cycle
a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells produce energy in aerobic respiration
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Energy carrying molecule found in all organisms
Products of anaerobic respiration
Lactic Acid + Alcohol/Ethanol
Photosynthesis
The process of turning light energy into glucose
Keystone Species
a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its natural environment relative to its abundance
Population Size
Changes in size when new members join or leave
Birth rate
Number of births per 1000 in a given time period
Most common way of joining a population
Death Rate
Number of deaths per 1000 for a given time period
Immigration
Joining a population