APHG Unit 5: Agriculture and Rural Land Use Patterns and Processes
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Arable Land
AKA "farmable" land

Agribusiness
Businesses that provide a vast array of goods and services to support the agricultural industry.

Aquaculture
Fish farming
-Fed cornmeal

Biotechnology
use of living organisms in the manufacturing of drugs or food.

Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture with the primary goal of making a profit.

commodity chain
A series of activities from the manufacturing to the distribution of a product
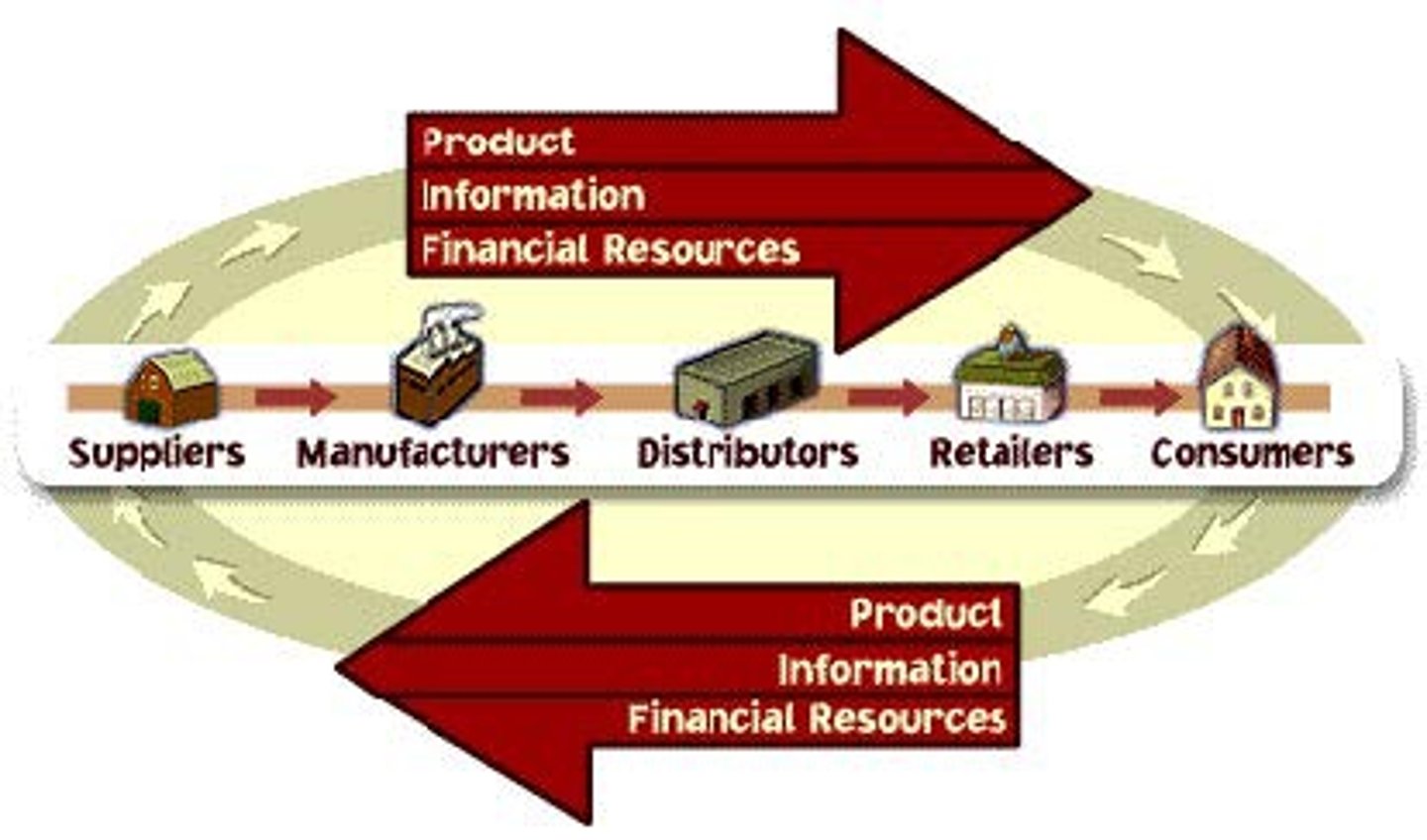
deforestation
the clearing or destruction of forests

Desertification
The degradation of arid or semiarid land so that it becomes a desert.

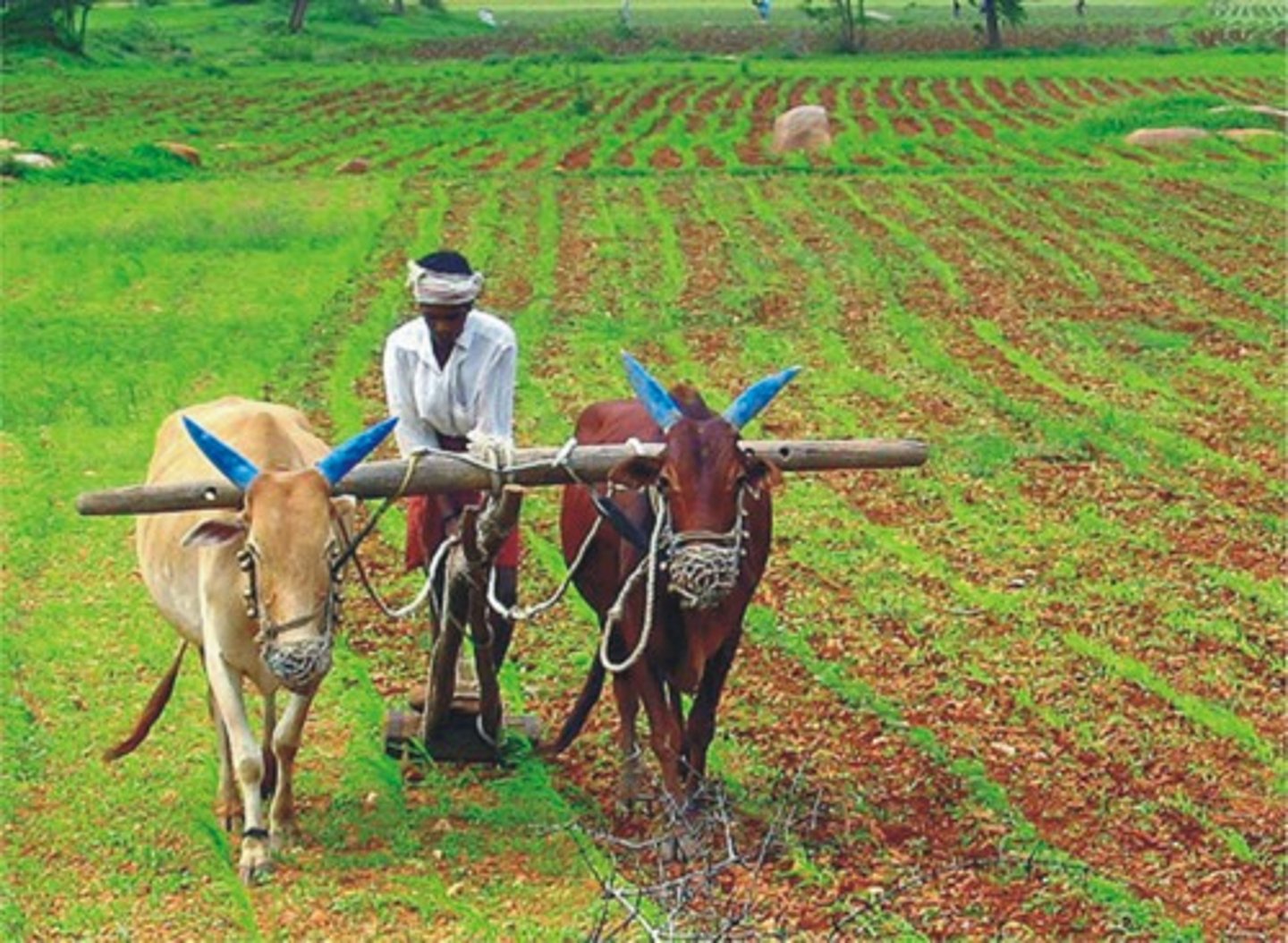
primary economic activity
an economic activity that takes or uses natural resources directly, such as farming, fishing or mining

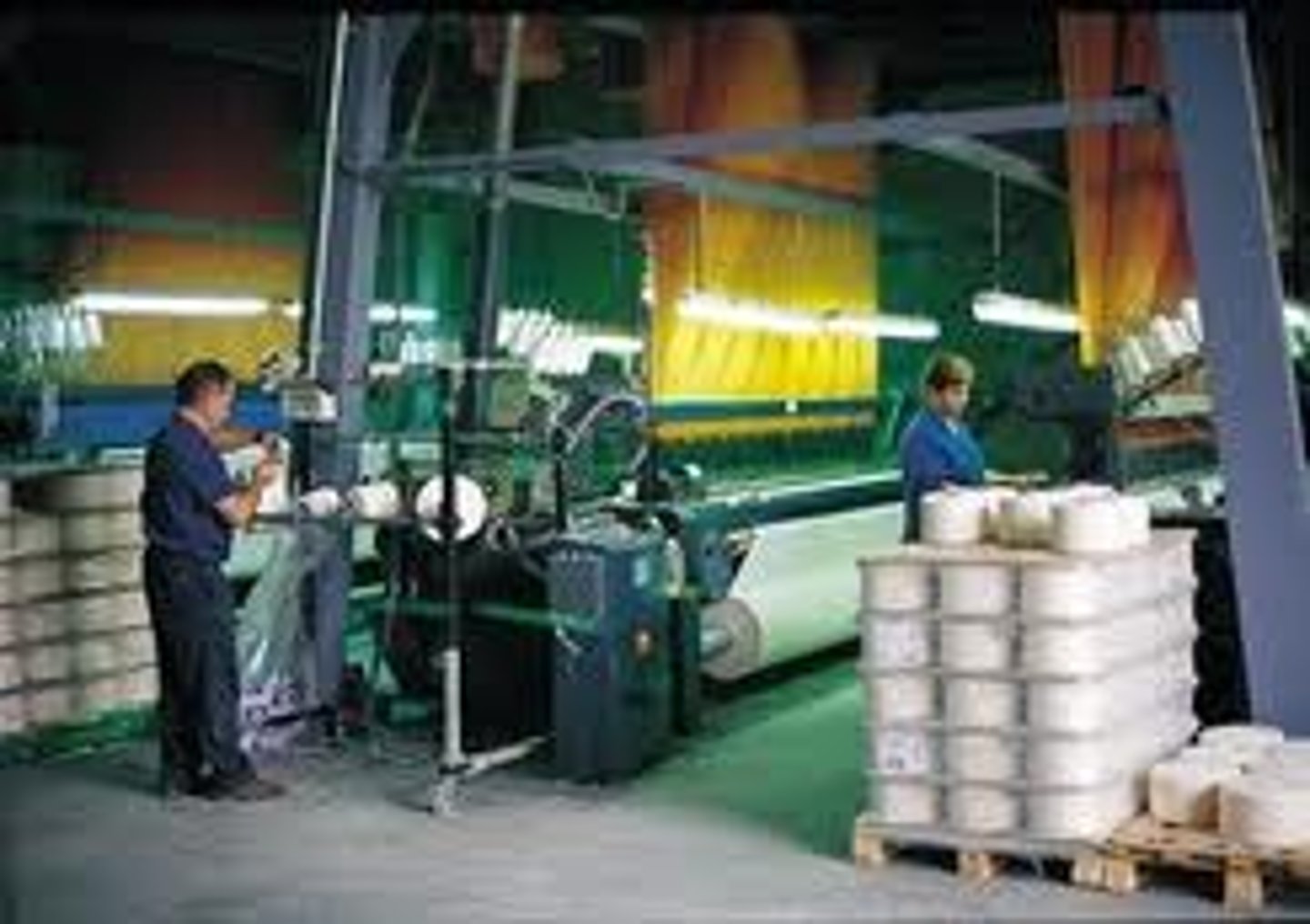
secondary economic activity
when people use raw materials to produce or manufacture new products of greater value

tertiary economic activity
Service jobs - high level: bankers, lawyers, doctors, teachers, low level: retail, fast food,

quarternary economic activity
Providing management and high level money processing (FIRE: Finance, Insurance, Real Estate)

quinary economic activity
Decision making economic activities that depend on research and higher education as prerequisites

economies of scale
a proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production.

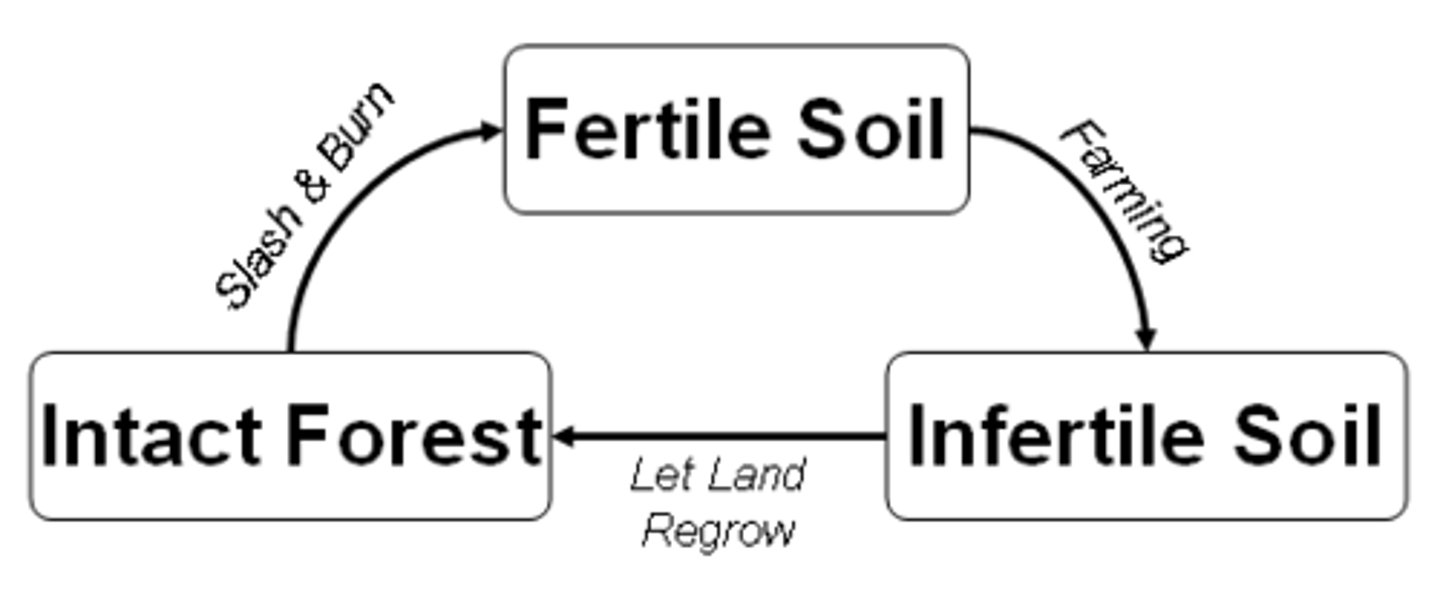
Shifting cultivation
A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another
Pastoralism
the raising of animals for food and other products

genetically modified organisms
organisms that have had their genetic makeup modified by genetic engineering

Horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.

Local food movement
Purchasing food from nearby farms because you want to minimize the pollution created from the transportation of food around the world

Luxury Crops
Non-subsistence crops such as tea, cacao, coffee, and tobacco
-Typically grown in LDC

Mediterranean agriculture
specialized farming that occurs only in areas where there is dry-summer
-Includes a small piece of California

Monoculture
cultivation of a single crop, usually in a large area

organic agriculture
crops that are grown without fertilizers and pesticides

substinence agriculture
growing only enough to provide for you and your family's needs.

extensive agriculture
characterized by low inputs of labor per unit land area includes shifting cultivation and cattle ranching

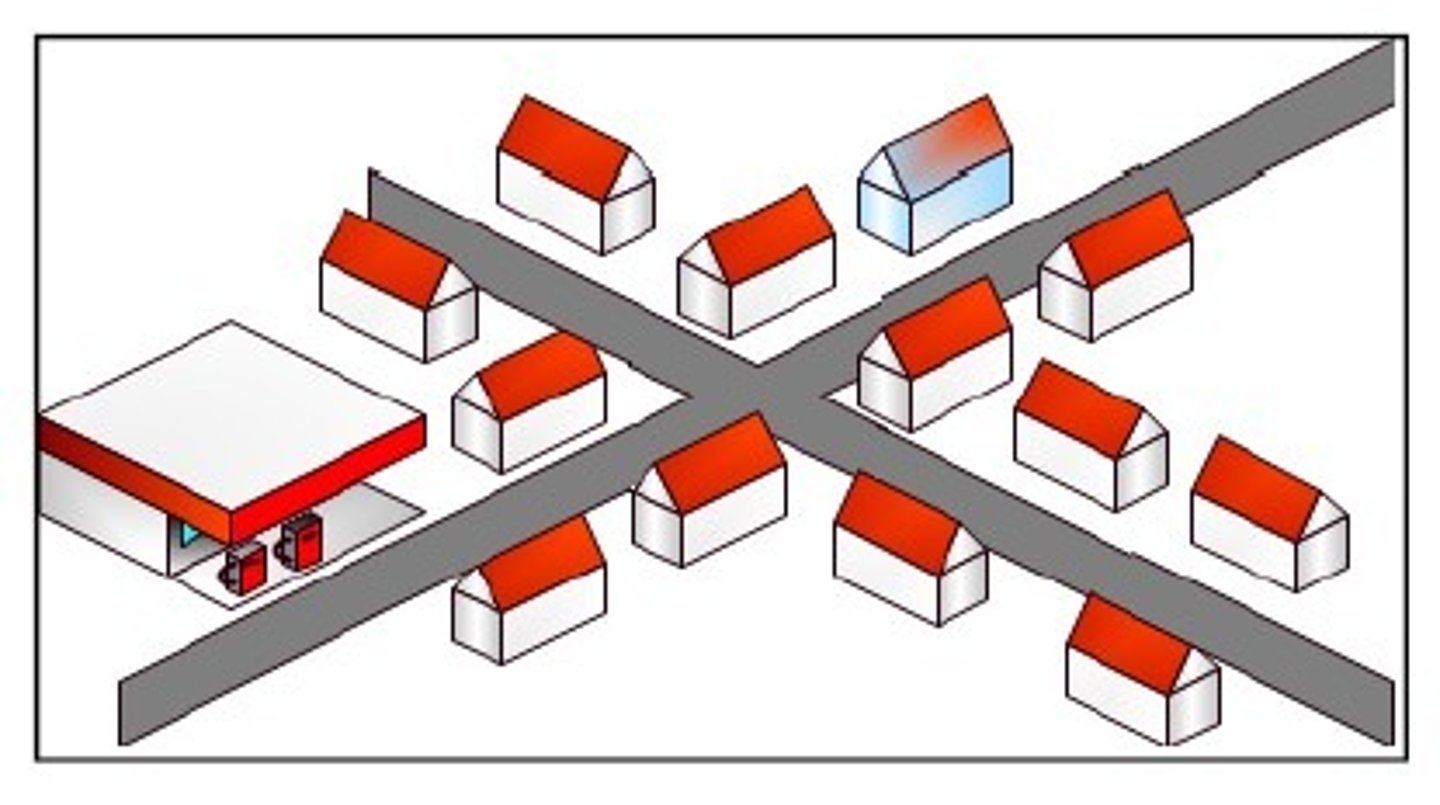
Rural Settlement Patterns
farms, villages, or towns that have any of the following patterns- dispersed, clustered, or linear
intensive agriculture
farming with lots of inputs per acre like labor, fertilizer, chemicals and pesticides
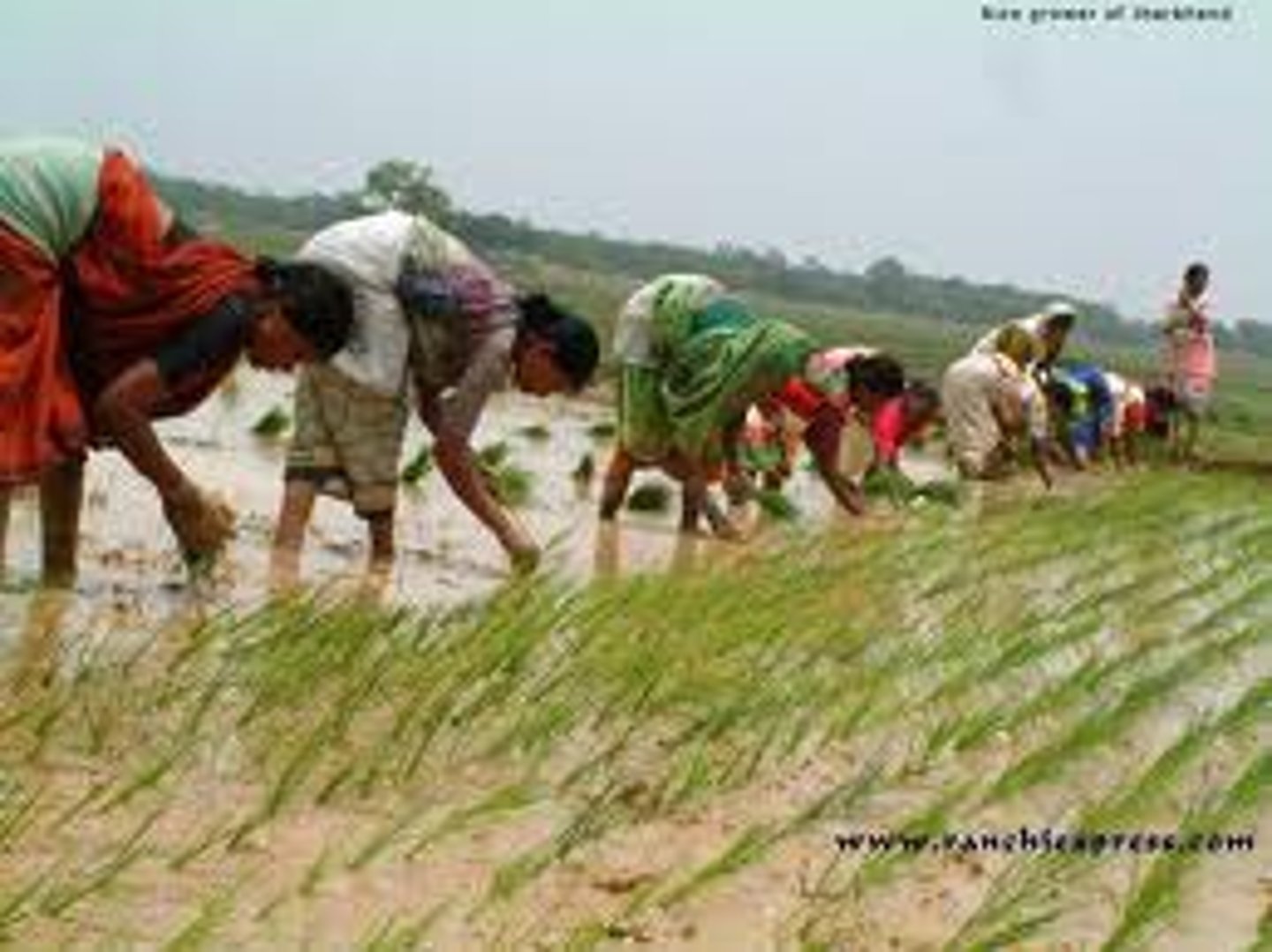

long lot survey
system that divided land into narrow parcels stretching back from rivers,roads, or canals French influence
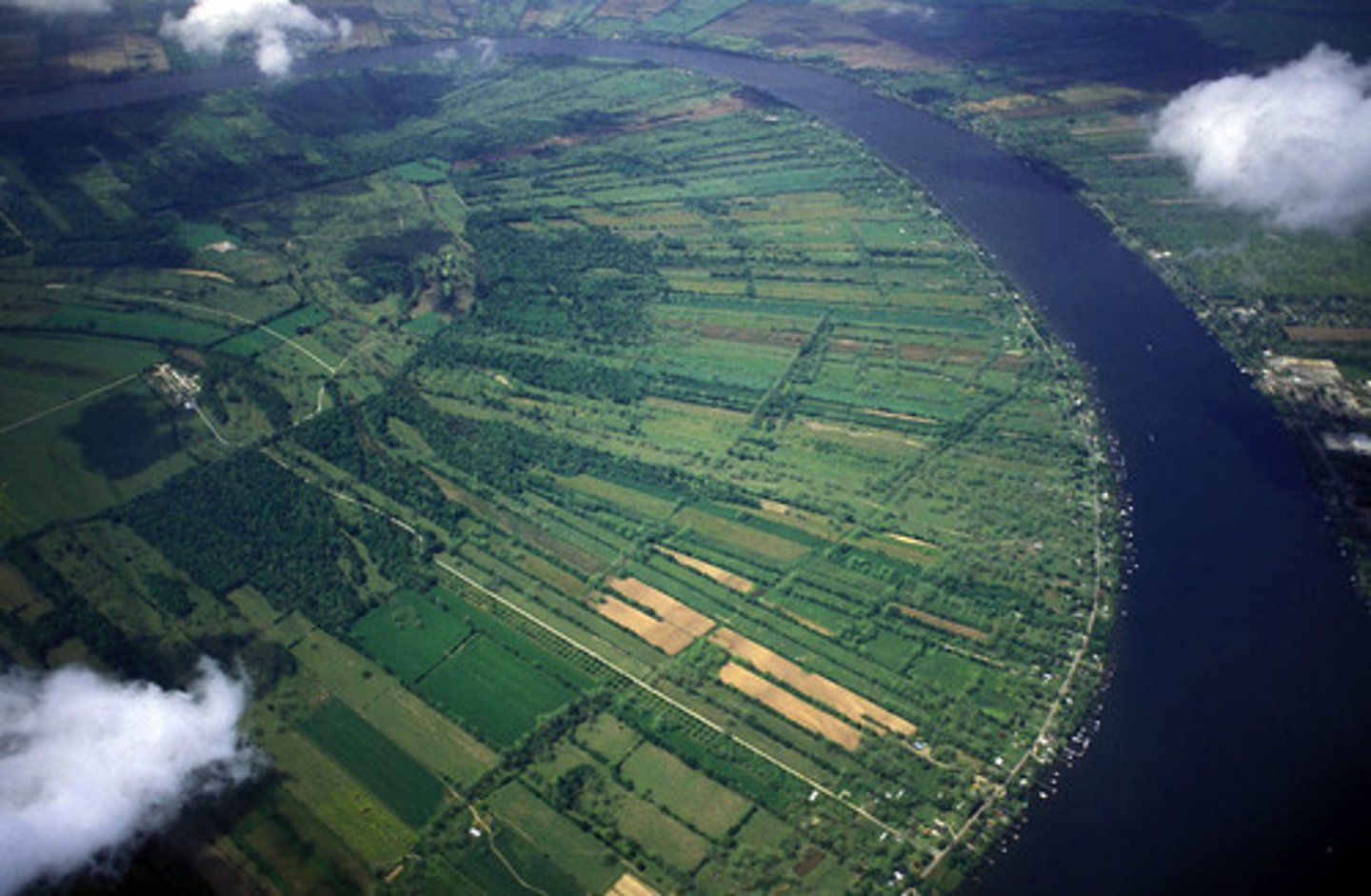

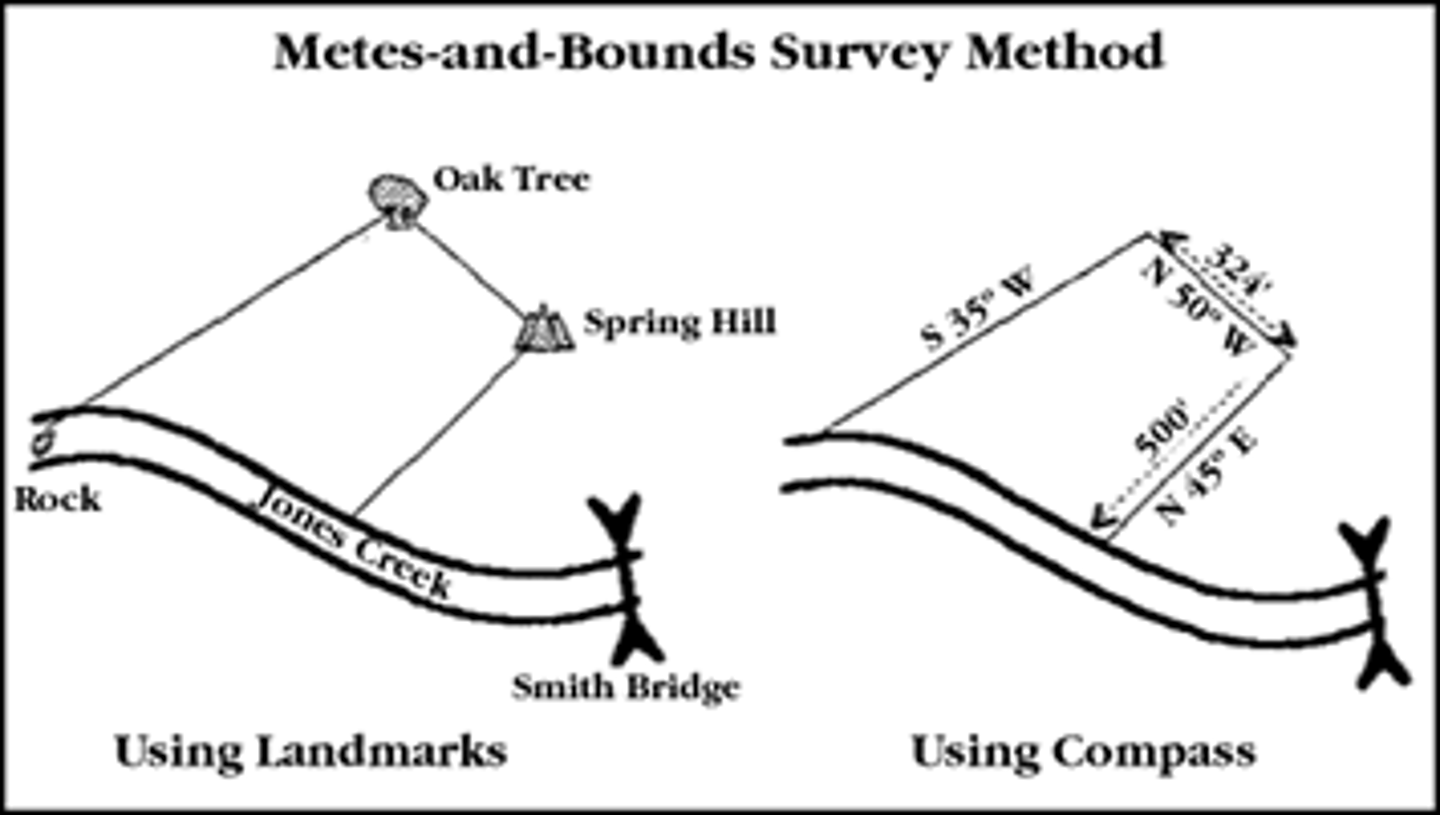
metes and bounds system
type of survey system in which natural features are used to demarcate irregular parcels of land
township and range survey
property lines in grid pattern, one square mile sections that display uniformity
-Most of USA
-Part of Homestead act designating 160 acre plots
Sustainability
Agricultural practices that conserves the fertility of the land

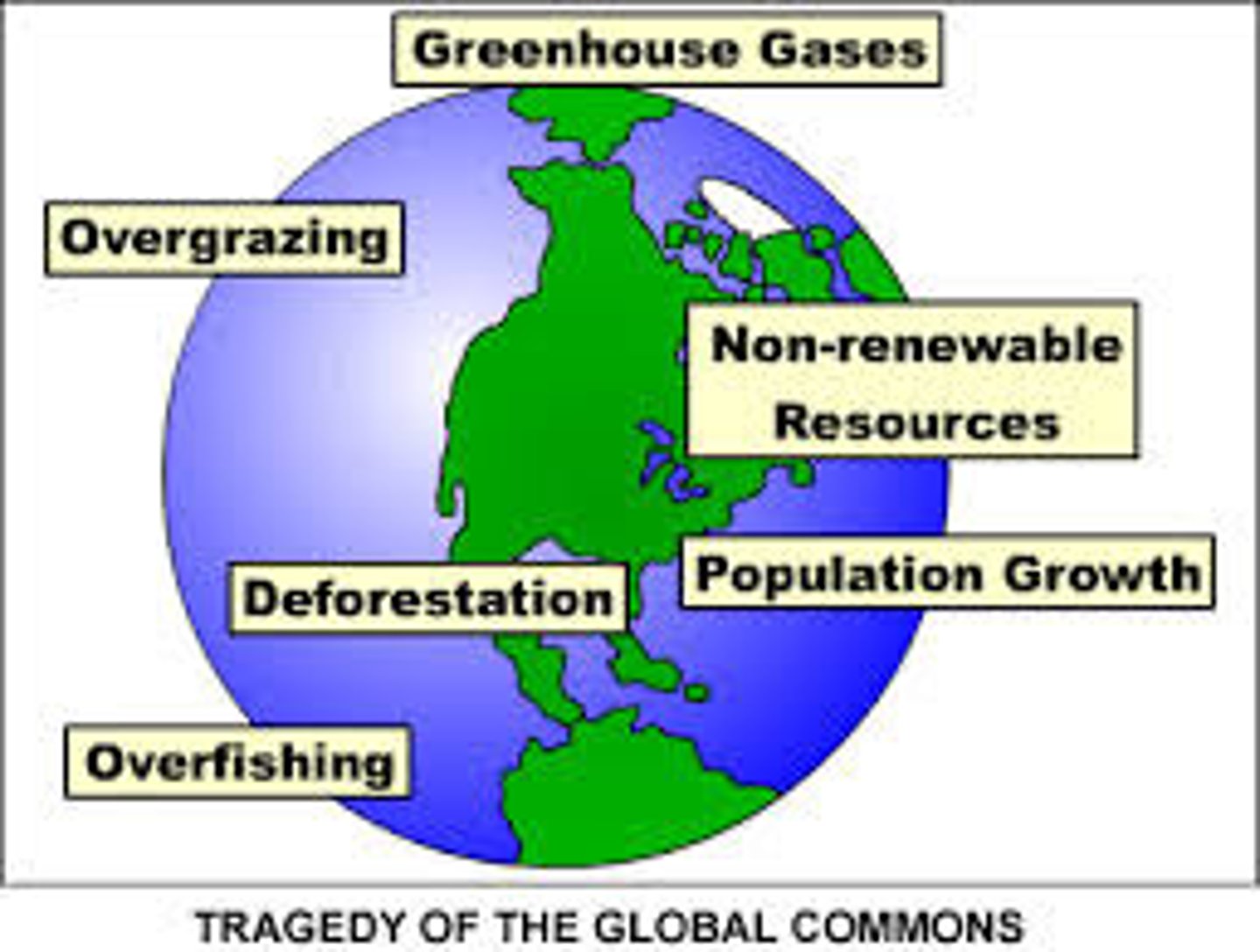
Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
Transhumance
seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pasture areas

luxury crops
coffee, chocolate, tea
food desert
An area in a developed country where healthy food is difficult to obtain

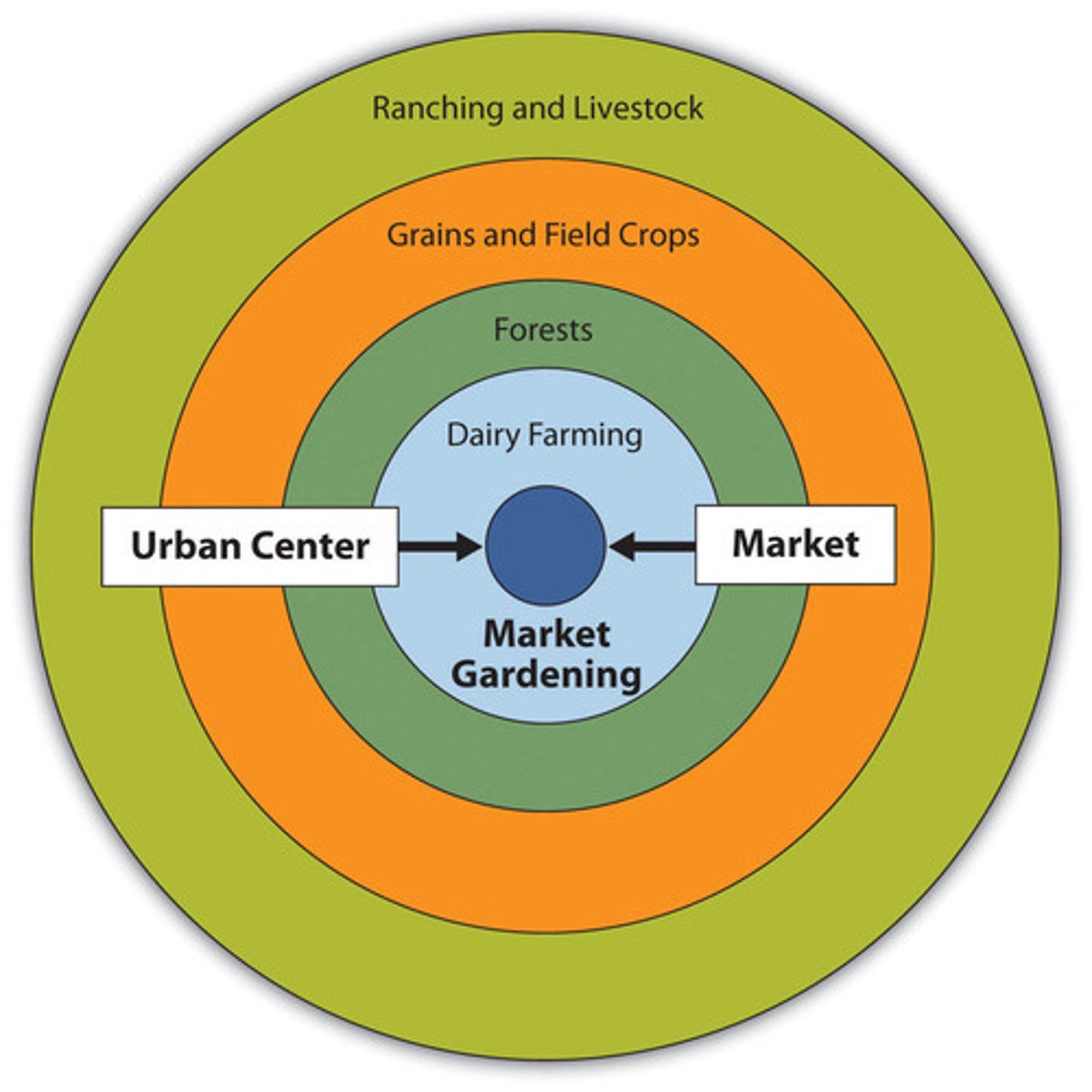
VonThunen
created a model describing rural land use 1830
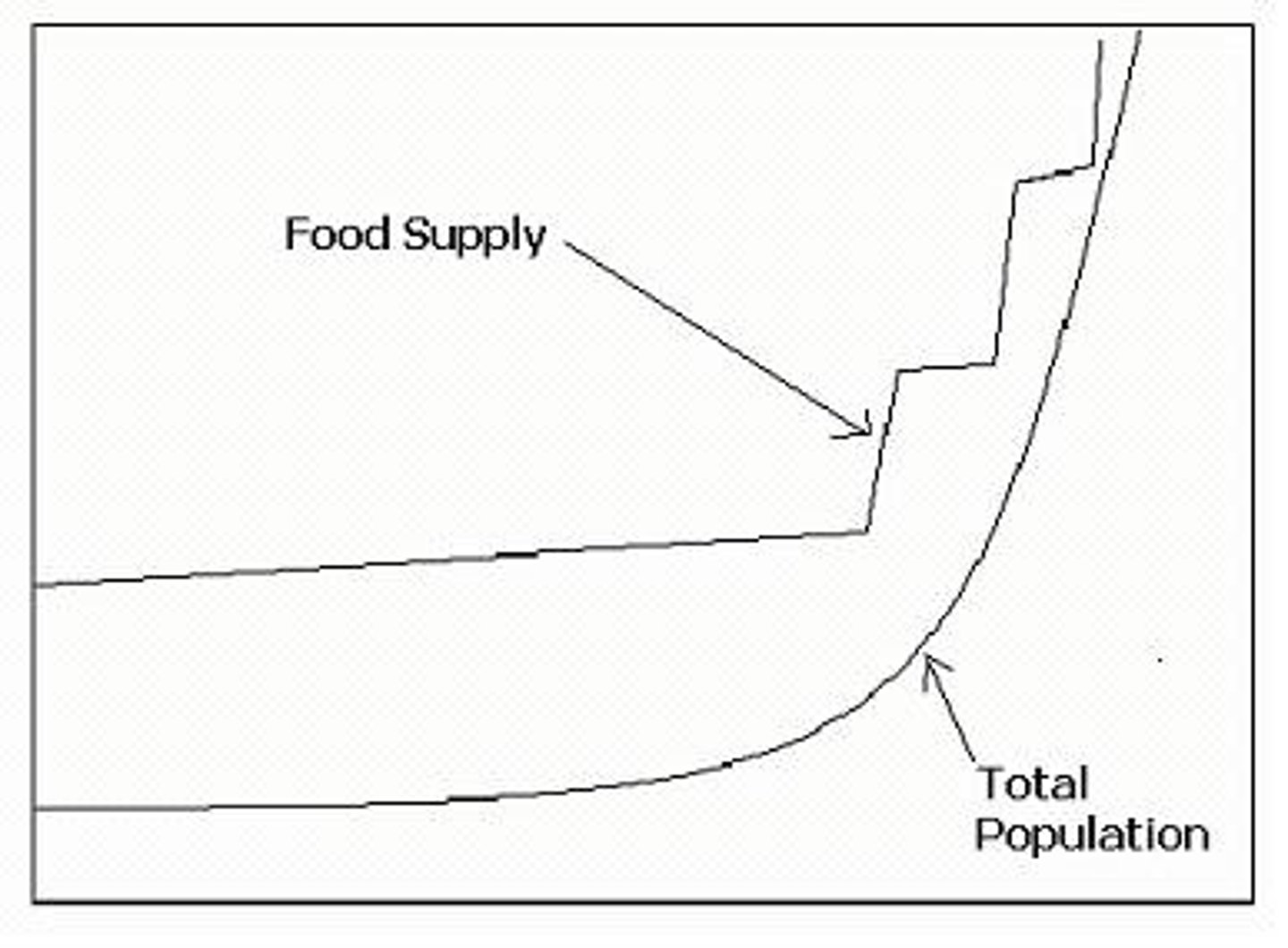
Esther Boserup
agricultural geographer opposed to Malthusian Theory: "subsistence forms of agriculture will become more intensive to support greater populations".
1st Agricultural Revolution
dating back 10,000 years, achieved plant domestication and animal domestication

2nd Agricultural Revolution
period of technological change from the 1600s to mid-1900s beginning in Western Europe with industrial innovations to replace human labor on farms with machines increasing crop yields.
3rd Agricultural Revolution (Green Revolution)
Shift from subsistence to commercial farming worldwide in late half of the 20th century. Increased use of chemical pesticides, fertilizers, irrigation, machinery as well as biotechnology leading to increased crop yields

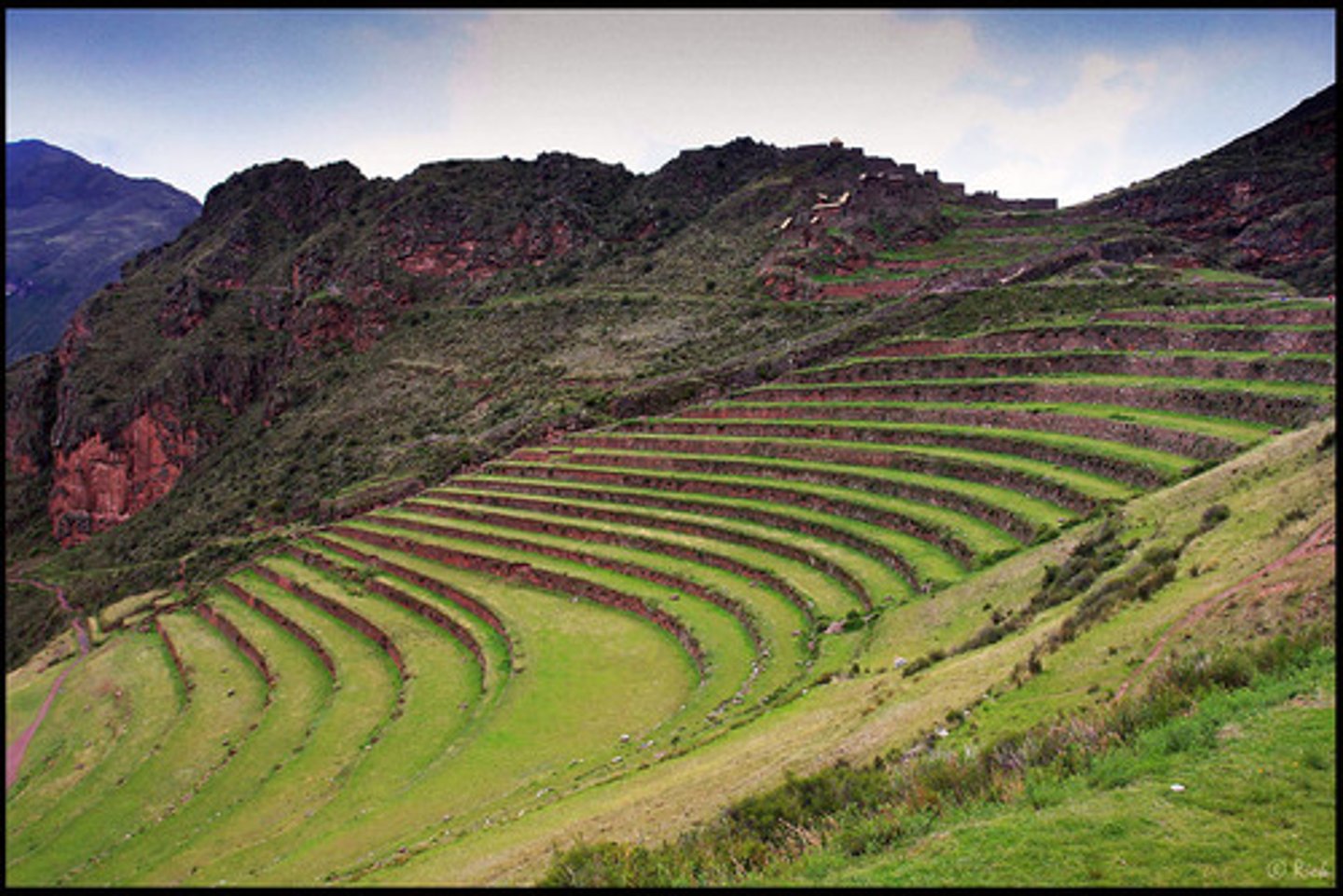
Terracing
make or form (sloping land) into a number of level flat areas resembling a series of steps.

swidden agriculture
The form of subsistence agriculture in which crops are grown in different fields on a rotating basis. Also called shifting agriculture or slash-and-burn agriculture
Enclosure Acts
a series of United Kingdom Acts of Parliament which enclosed open fields and common land in the country, creating legal property rights to land that was previously considered common.
irrigation
The process of supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops.

Market Gardening (Truck Farming)
The small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers.

plantation agriculture
Growing specialized crops such as bananas, coffee, and cacao in tropical developing countries, primarily for sale to developed countries.

milkshed
ring surrounding a city from which milk can be supplied without spoiling

CAFO (feedlot)
concentrated animal feeding operation which is a large feedlot to fatten animals before slaughter
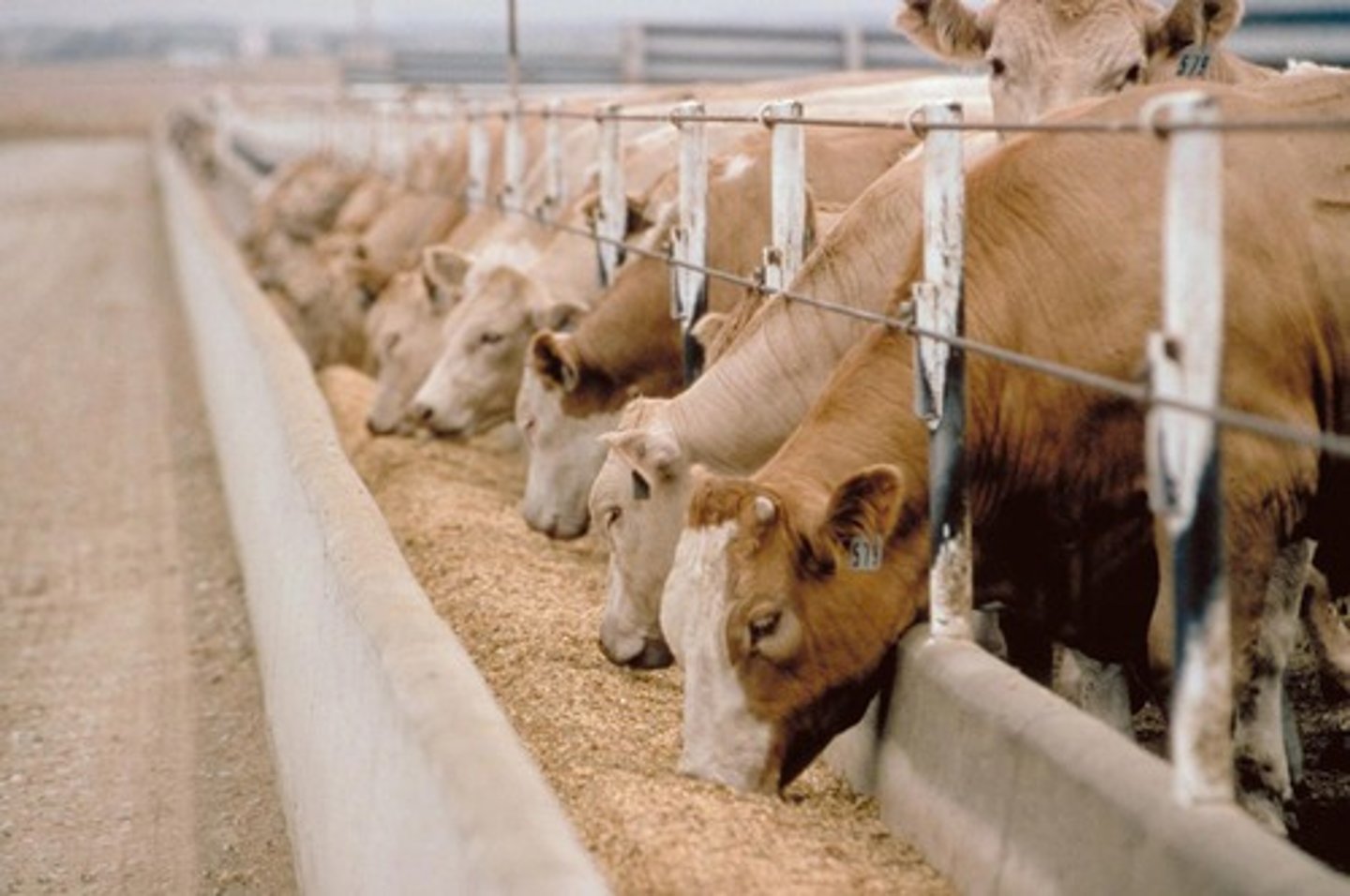

hearth areas
geographic settings where new practices have developed and from which they have subsequently spread
Columbian Exchange
An exchange of goods, ideas and skills from the Old World (Europe, Asia and Africa) to the New World (North and South America) and vice versa.

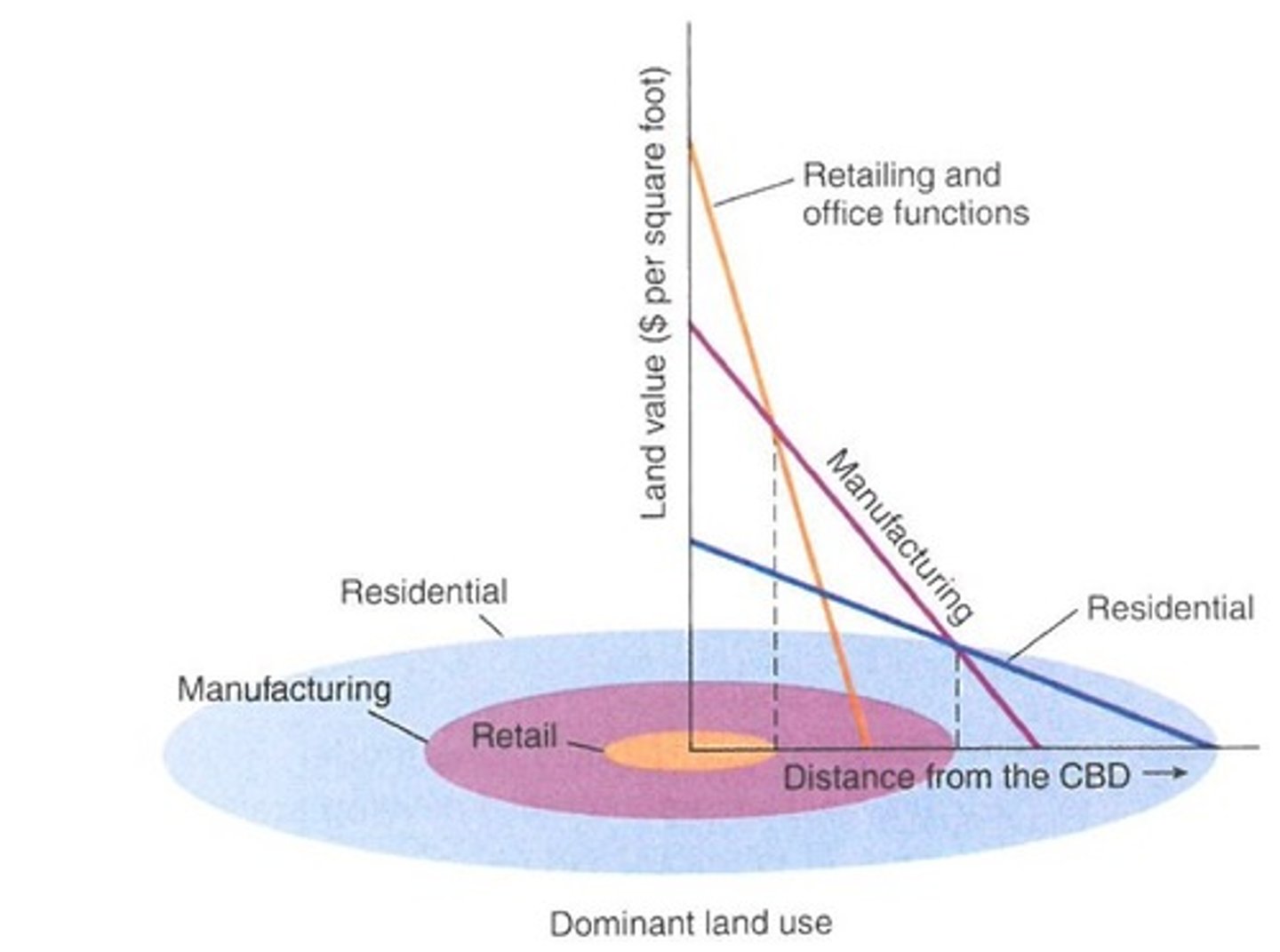
Bid-Rent Theory (Land Rent)
geographical economic theory that refers to how the price of and demand for land changes as the distance from the market area (Central Business District) increases.
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
A system in which consumers pay farmers in advance for a share of their yield, usually in the form of weekly deliveries of produce.

fair trade movement
an alternative method of international trade which promotes environmentalism, fair wages, alleviation of global poverty and a fair price for growers

Biodoversity
the variety of living things in an ecosystem

Specialty farming (truck farming)
A form of "truck" farming ..., where fruits and vegetables that are in high demand by consumers are intensively grown.

mixed crop/livestock systems
The combined farming of crops and livestock (used to improve nutrient cycling) for profit.
