ABD FINAL - all key terms combined
1/434
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
435 Terms
normal A-P measurement for proximal aorta
2 cm proximally
normal A-P measurement for aorta @ bifurcation
tapers to about 1.5 cm at the bifurcation
Any aorta measurement over ___ cm is always considered abnormal.
3 cm
aortic ectasia
mild dilation of the aorta (absence of the aorta tapering distally)
Normal aorta walls are _________ defined.
clearly
On ultrasound, aorta lumen should be __________.
anechoic
What is the 1st branch of the aorta?
celiac axis
What does the celiac axis branch into?
branches to form common hepatic & splenic arteries
appearance of celiac axis
seagull
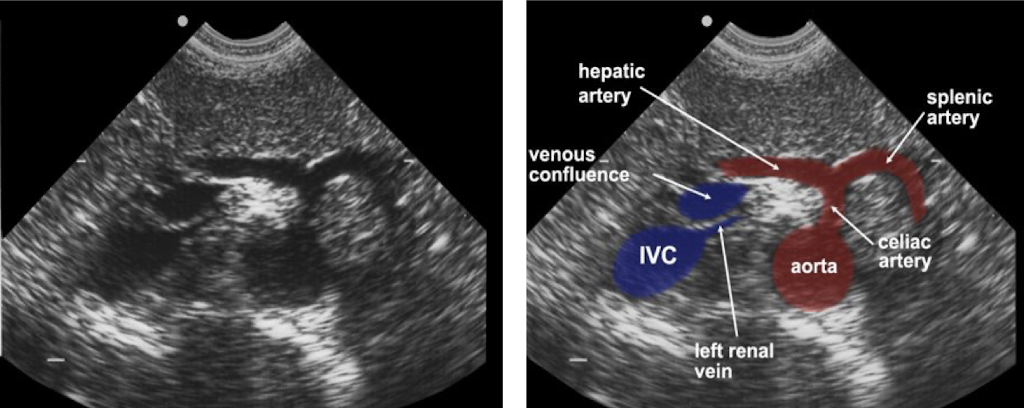
Superior mesenteric artery (SMA) arises just ________ to the celiac axis.
inferior
SMA runs ________ to aorta.
parallel
renal arteries
lateral branches that arise just inferior to the origin of the SMA
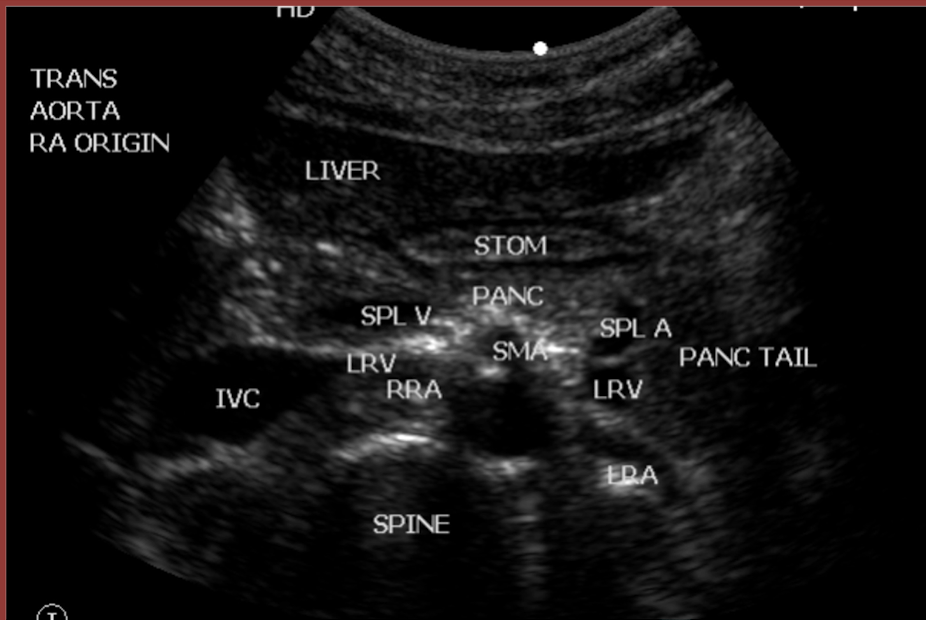
inferior mesenteric artery
rarely seen on ultrasound
arises from aorta at about the L1 level
Distal aorta bifurcates to form the …
common iliac arteries
Common iliac arteries branch to form the …
internal & external iliac arteries
What is an AAA?
abdominal aortic aneurysm
aneurysm definition
permanent localized dilation of an artery
If A-P diameter is greater than ___ cm → AAA
3 cm
What is method of choice to follow AAA’s?
ultrasound
Who should be screened one time for AAA with ultrasound?
men ages 65-75 who have ever smoked
Who should be screened for AAA with ultrasound and a physical exam?
men age 60 & older who have a sibling or parent with an AAA
Is there a recommendation for general screening for AAA in women?
no
What is most common reason for aorta exam?
look for AAA
can also look for aortic dissection or retroperitoneal mass
risk factors for aortic aneurysm/dissection (5)
male
over age 60
former or current smoker (100 cigarettes or more in lifetime)
hypertension
peripheral vascular disease/atherosclerosis
AAA symptoms (4)
asymptomatic
back pain
pulsatile abdominal mass
dropping hematocrit accompanied by back, abdominal, or chest pain
patient interview questions for AAA
ask patient questions related to the reason for exam provided on the physician’s order & based upon known risk factors
examples of patient interview questions for AAA
Do you have high blood pressure?
Are you diabetic?
Do you have a family history of aortic aneurysm?
Do you smoke or have you ever smoked?
Have you been experiencing back, abdomen, or chest pain?
most common reason to evaluate IVC on ultrasound exam
evaluate for thrombus or tumor invasion
image labeling of IVC
artifact definition
structure or feature on an ultrasound image that does not correspond to the actual anatomy being imaged
What are propagation artifacts a result of?
result of the way sound passes through the tissue
What are equipment artifacts a result of?
result of the way the beam is constructed
What are sound tissue artifacts a result of?
result of how the sound interacts with the tissue
slice thickness artifact effect on image
loss of lateral or axial resolution
results in blurring of image (2 structures blended to be displayed as one)
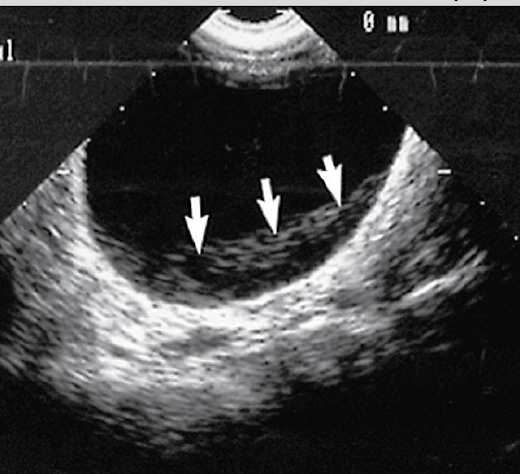
Why does slice thickness artifact occur?
occurs when elevation (height) dimension of sound beam is thicker than interface between adjacent structures (like wall of vessel)
other names for slice thickness artifact
section thickness
partial volume artifact
How can you fix slice thickness artifact?
fix by changing transducer position or focusing the beam so that it is thinner at the area of interest
What kind of artifact is slice thickness artifact?
equipment artifact
speckle artifact effect on image
light & dark spots we see in tissue like the liver
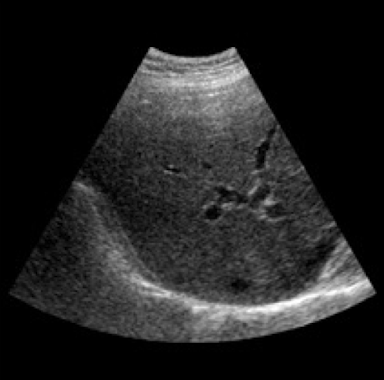
Why does speckle artifact occur?
the combination of constructive & destructive interference between scattered sound waves
As the sound beam is passed through the tissue, scattered sound waves cross each other in either constructive or destructive patterns.
If the cycles (compressions/rarefactions) are IN sync, the result is …
constructive interference
As the sound beam is passed through the tissue, scattered sound waves cross each other in either constructive or destructive patterns.
If the cycles (compressions/rarefactions) are OUT OF sync, the result is …
destructive interference
How is speckle artifact fixed?
newer equipment has processing techniques to reduce the appearance of speckle & give a more accurate visualization of the actual tissue
When does reverberation occur?
occurs when echoes “bounce” between the transducers & a strong reflector
can also be produced by sound bouncing between 2 strong reflectors within the tissues
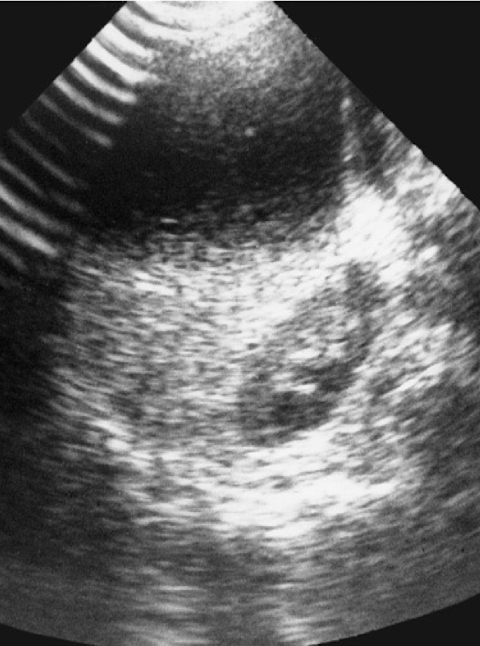
other name for reverberation
multiple reflection
What kind of artifact is reverberation?
sound tissue artifact
special types of reverberation
comet tail, ring-down, resonance, mirror image
How can you fix reverberation?
fix by changing transducer position, rolling patient to a new position, or using a different frequency
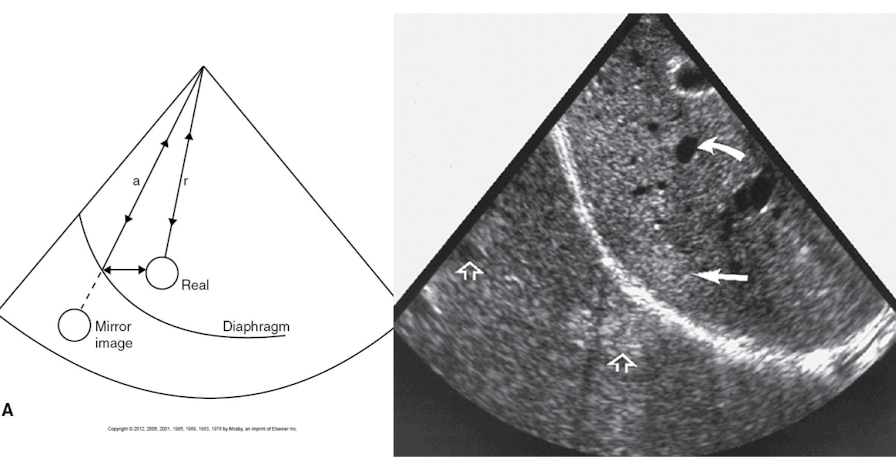
What kind of structure causes mirror image artifact?
caused by sound interaction with large, curved reflector like the diaphragm & pleura
other name for mirror image artifact
multi-path reflection
How does mirror image artifact occur?
Object anterior to the large reflector is interrogated by multiple scan lines of sound
Part of the sound energy that strikes the object is reflected back to the transducer, causing an accurate depiction of the object to be seen on the image
Part of the energy reverberated through the object down to the large reflector, then is belatedly reflected back to the transducer, resulting in an additional depiction of the object deep to the strong reflector
Comet tail artifact is the result of …
multiple internal reflectors within a small, highly reflective structure
Why does comet tail artifact occur?
occurs because of large difference in acoustic impedance between reflector & surrounding tissue, which causes a series of short-path reverberations
What kinds of areas are comet tail artifacts usually seen in?
anechoic or hypoechoic areas
How can you fix comet tail artifact?
fix by changing transducer position
When does resonance occur?
occurs when sound strikes a gas bubble & causes it to expand & contract (vibrate)
the gas bubble then acts as a transmitter of ultrasound, leading to strong echoes being displayed posterior to the bubble
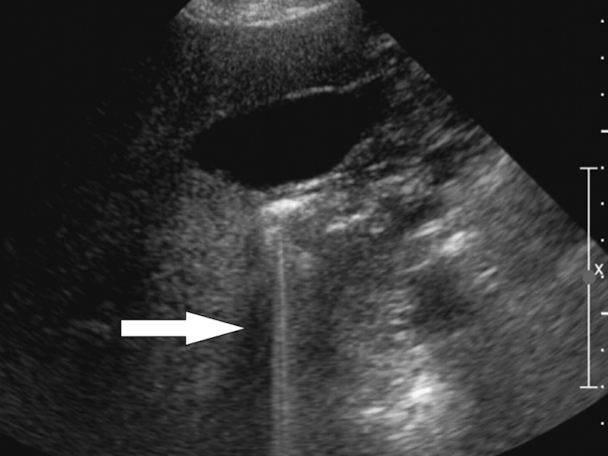
bright echoes distal to the gas bubble that occur in resonance
ring-down artifact
How can you tell the difference between ring-down artifact and comet tail artifact?
ring-down: NO banding seen
What kind of artifact is resonance?
sound tissue artifact
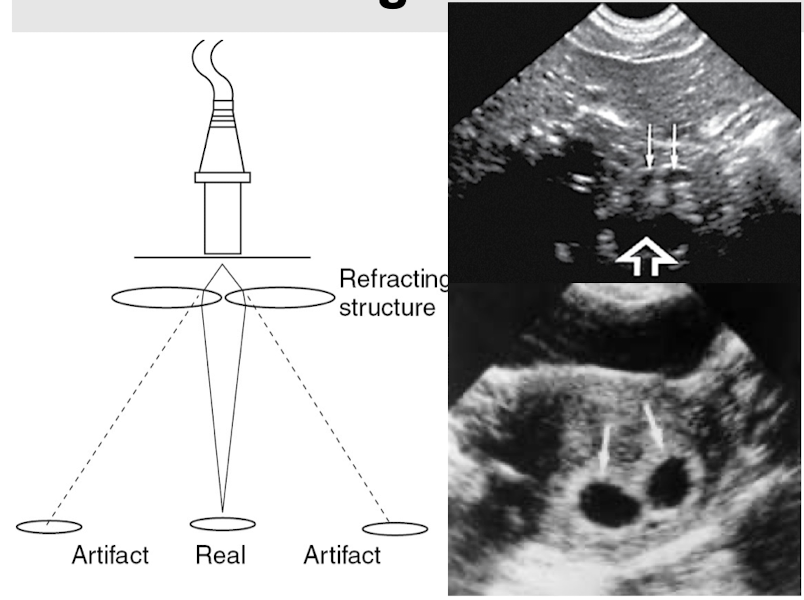
What is refraction?
bending of the sound beam causes a reflector to be displaced laterally on the image & leads to distortion of size & shape
Where does refraction occur?
occurs at boundaries where the tissues involved have different propagation speeds & the sound beam strikes the boundary at an angle
(think about Snell’s Law)
What are the 2 effects on images from refraction?
misregistration & defocusing
misregistration
object not displayed on the image at its true location in the anatomy
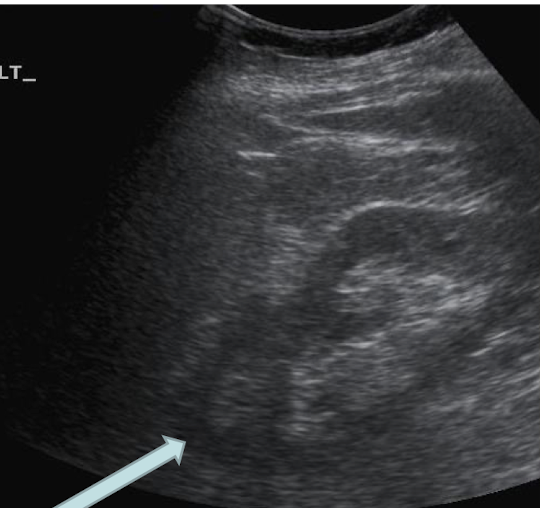
defocusing
loss of resolution due to disturbance of the sound beam structure
What kind of artifact is refraction?
sound tissue artifact
How to fix misregistration (type of refraction)?
fix by changing transducer position
How to fix defocusing (type of refraction)?
fix by using compound imaging or changing transducer position
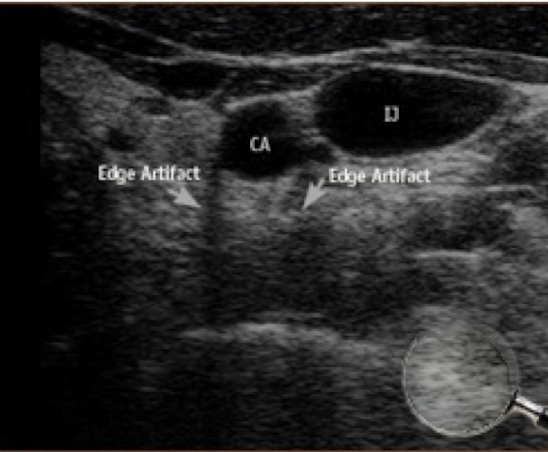
ghost image effect on image
shows duplication of structures posterior to the rectus muscles
Ghost image is a type of __________.
refraction
When does ghost image most often occur?
when scanning through the rectus abdominus muscles (due to the way they are surrounded by fat & the rectus sheath)
What does ghost image most commonly affect?
usually vessels like the aorta and IVC; can also see duplication of gestational sacs
What kind of artifact is ghost image?
sound tissue artifact
How can you fix ghost image artifact?
fix by moving transducer to different angle
(sometimes can eliminate by using more or less probe pressure)
What kind of artifact is side lobes?
equipment artifact
Side lobes artifact is present in _____ transducers.
all
What are side lobes?
have to do with creation of wave-fronts from multiple elements to create the sound beam
off-axis lobes of energy are created outside the main ultrasound beam, resulting in artificial display of echoes along the main beam path
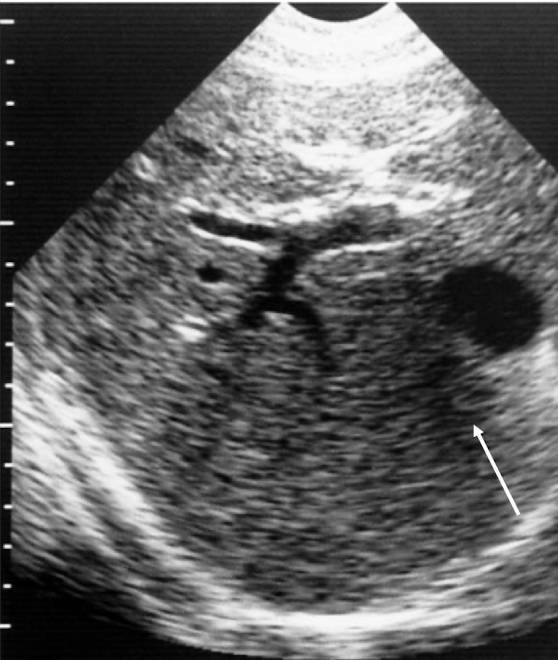
How can you fix side lobes artifact?
fix by changing transducer position or adjusting focal zone
Grating lobes are a type of ___________ ____________.
side lobes
Grating lobes are usually of ___________ intensity than typical side lobes.
greater
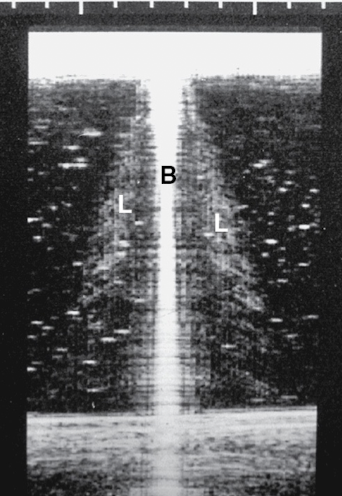
How can you fix grating lobes artifact?
fix by changing transducer position or adjusting focal zone
(same as side lobes)
What is a propagation speed error?
occurs when sound travels through tissue at a speed different from the 1540 m/s assumed by the machine
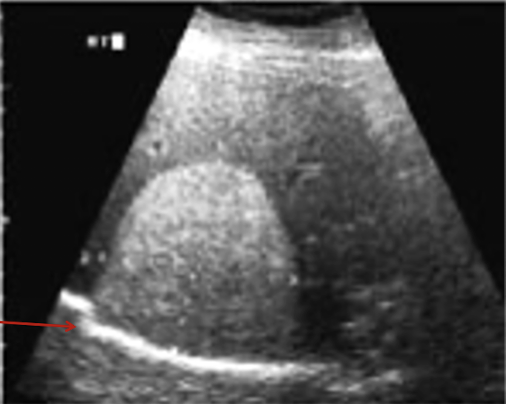
If sound travels faster than assumed by machine, the object will be displayed more __________ than true location.
superficially
If sound travels slower than assumed by machine, the object will be displayed more __________ than true location.
deeper
What is range ambiguity artifact?
the ultrasound machine assumes that all echoes received are generated by the most recent transmitted pulse; but sometimes the echoes aren’t received by transducer until after the next pulse is transmitted
What kind of artifact is range ambiguity?
equipment artifact
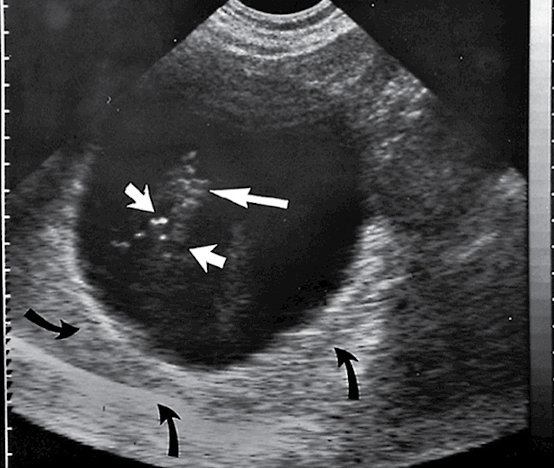
How can you fix range ambiguity artifact?
fix by decreasing PRF
When does dirty shadow artifact occur?
occurs when sound strikes strong interface & reverberates, creating blurry echoes that obscure actual anatomy
Dirty shadow artifact typically occurs when sound beam hits ___________ or ___________.
air or bowel
How can you fix dirty shadow artifact?
fix by compressing tissue to displace gas or rolling patient to different position
What kind of artifacts are dirty shadow and sharp shadow?
sound tissue artifacts
When does sharp shadow artifact occur?
occurs when sound strikes a very strong interface like bone, mineral salts, or metal that prevents transmission of sound beam through the object
How can you fix sharp shadow artifact?
fix by changing transducer position to see tissue posterior to object w/o having to transmit through it
When does posterior enhancement (“moonbeam effect”) occur?
occurs when sound passes through tissue/substance that doesn’t attenuate the beam so that stronger sound waves hit the tissue posterior to the structure w/ lower attenuation that in areas of tissue where the sound beam does not pass through the low attenuator
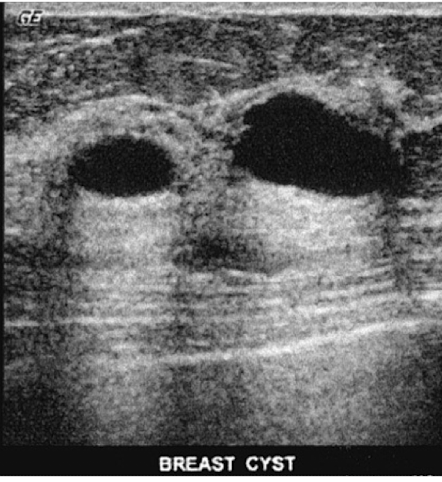
What is the result of posterior enhancement (“moonbeam effect”)?
tissue posterior to the low attenuator appears more echogenic that tissue next to it
How can you fix posterior enhancement (“moonbeam effect”)?
fix by adjusting TGC to reduce amplification of echoes posterior to the low attenuator - like when using the full bladder to see the pelvic organs
Posterior enhancement (“moonbeam effect”) can also be used as a ___________ tool; such as proving that a structure is ___________.
diagnostic
cystic
What kind of artifact is posterior enhancement (“moonbeam effect”)?
sound tissue artifact
What is the effect of noise artifact on images?
see echoes in structures that should be anechoic (like blood vessels)
What causes noise artifact?
caused by setting gain too high
What kind of artifact is noise?
technique artifact