Genetic Engineering: Key Steps
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What are the steps of genetic engineering?
Genetic isolation from genomic DNA
Restriction digestion and DNA ligation
Bacterial transformation and choice of bacterial host
Selection & confirmation of transformed bacteria with recombinant plasmid
What happens during genetic isolation from gDNA?
Obtain a copy of the gene by isolating gDNA
gDNA can be isolated from any cells in the organism
What is gDNA?
Genomic DNA = Total chromosomal DNA of the cell
What happens during restriction digestion?
Both the plasmid vector and DNA containing the gene of interest are cut using the same restriction enzyme
The restriction enzyme cuts the DNA at a specific sequence of bases, known as restriction sites
Restriction enzyme cleavage may generate blunt or sticky ends
Why is the same restriction enzyme added to the plasmid vector and DNA containing the gene of interest?
To produce complementary sticky ends
What are sticky ends?
Exposed specific DNA sequences
What is the relationship between sticky ends generated by the same enzyme?
Sticky ends are complementary to other sticky ends generated by the same enzyme
What happens during DNA ligation?
Sticky ends with the same sequence as those on the plasmid are also created on the gene of interest
Sticky ends now exist at the free ends of cut plasmid and gene
Sticky ends of the plasmid and gene bind together through complementary base pairing between the 2 DNA strands
DNA ligase ligates the sticky ends to form recombinant DNA
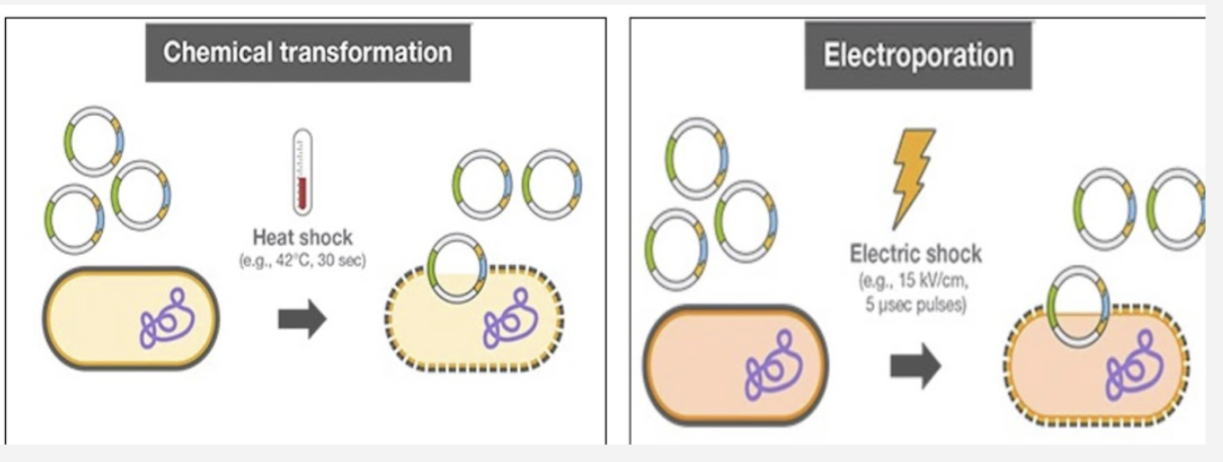
How is the recombinant DNA returned to the bacterial host?
Chemical transformation using heat shock treatment and calcium chloride
Electroporation
*Required because the cell wall is a barrier to entry
What is an important consideration when choosing a bacterial host?
Sensitivity towards the selective marker(s) on the recombinant plasmid
The bacterial host must be immune to the antibiotics as long as it has the plasmid
Facilitates step 4 of genetic engineering
What is the most commonly used bacterial host for gene cloning?
E. coli. A wide variety of E coli strains that harbor different features are available to meet the demands of different cloning experiments
Why are alternative markers now preferred over selective markers?
Potential danger of antibiotic resistance genes being accidentally transferred to other bacteria, including pathogenetic strains
What happens during selection and confirmation of transformed bacteria with recombinant plasmid?
The transformed bacteria are plated on a selection medium containing selective agents, usually antibiotics
Only a limited number of cells of a culture bacteria would have successfully taken up the recombinant plasmid
What are commonly used alternative markers?
LacZ genes and genes for fluorescent substances
Describe the process of genetic engineering for a question
Genomic DNA is isolated form [organism with the gene of interest]
Restriction digestion is performed on [plasmid vector] and [gene of interest] using [restriction enzyme]
DNA ligation is performed to ligate the digested [plasmid vector] and [gene of interest] to form the recombinant plasmid
Recombinant plasmid mix is transformed into [antibiotic]-sensitive bacterial cells made competent with heat shock by calcium chloride / electroporation
Selection is performed by plating the transformed bacteria in a selection medium containing [antibiotic etc.]
Colonies that glow in the selection medium (and give off bioluminescence) are likely transformed bacteria containing recombinant plasmid