GCSE DT: Core Content: 1.5 Mechanical Devices used to produce movement
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Types of movement
Oscillation (swing back and forth)
Linear (straight line in one direction)
Rotary (rotate)
Reciprocation (Move back and forth along a straight line)
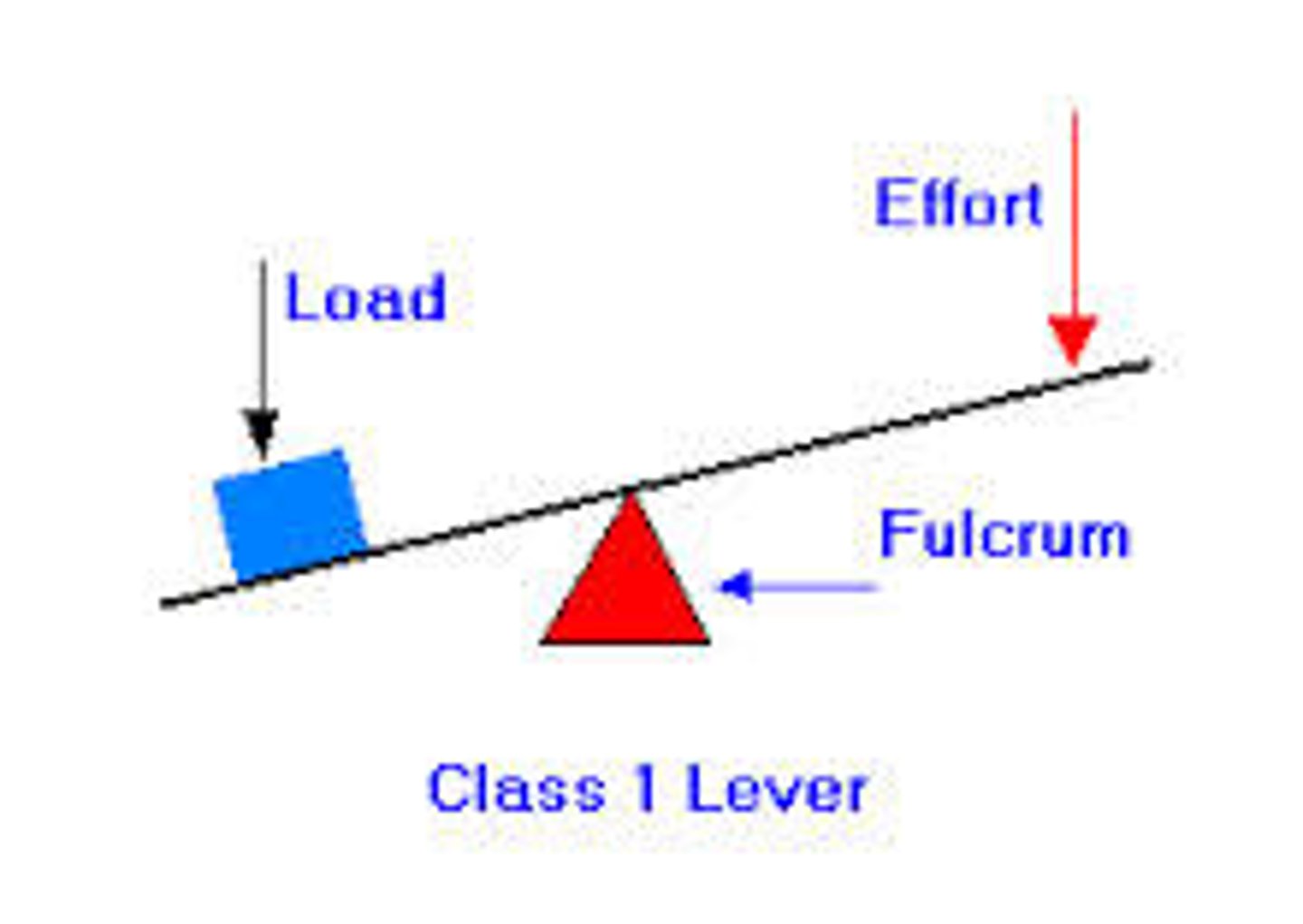
Class 1 Lever
LFE - Seesaw
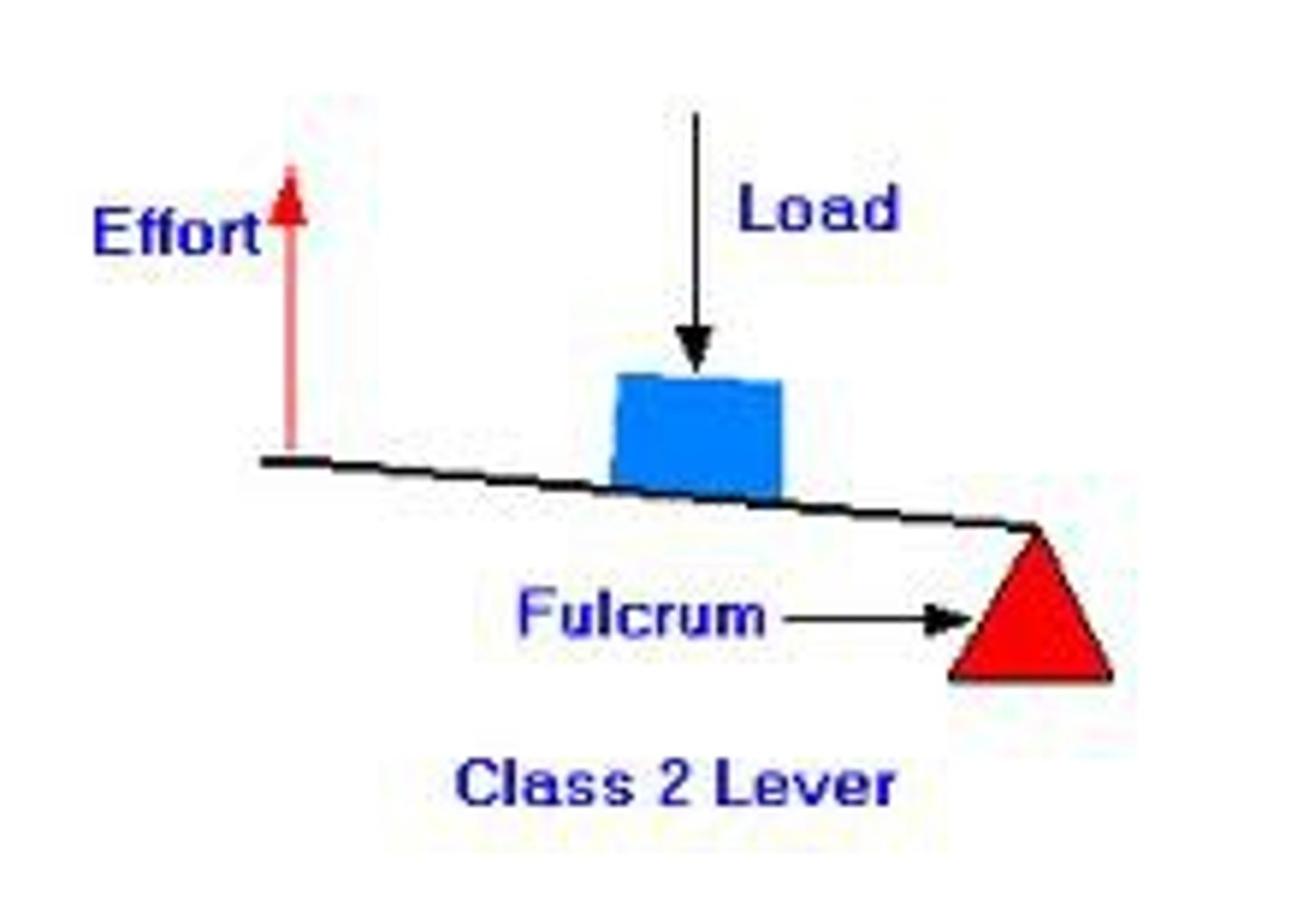
Class 2 Lever
FLE - Wheelbarrow
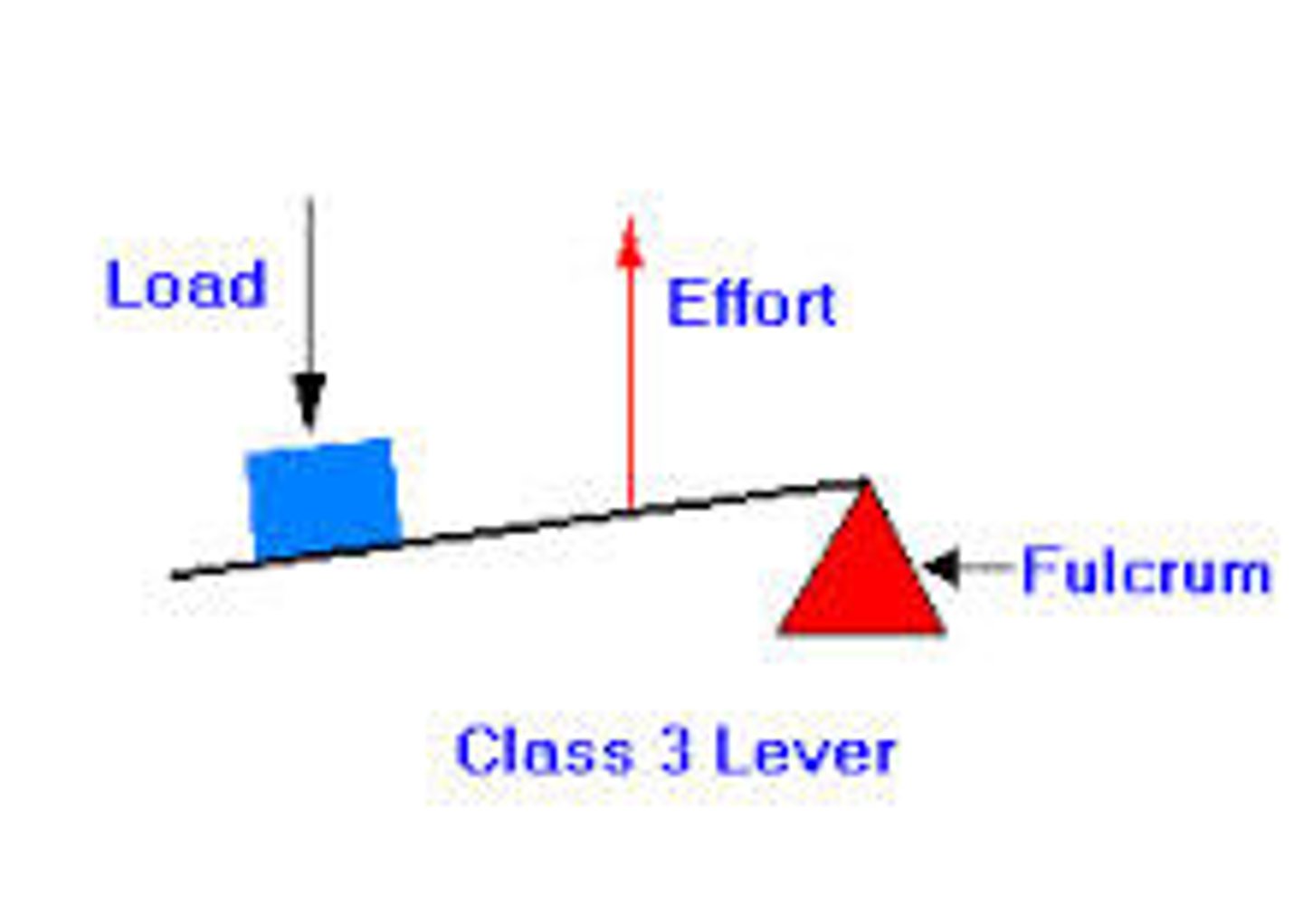
Class 3 Lever
FEL - Tweezers
Mechanical Advantage
Load/Effort
Moment
Force × distance (perpendicular to force)
Velocity Ratio for lever
distance moved by effort/distance moved by load
Efficiency
Mechanical Advantage/Velocity ratio
Linkages
Levers that allow forces and motion to be transmitted in a certain way (e.g., reversing movement or changing its direction)
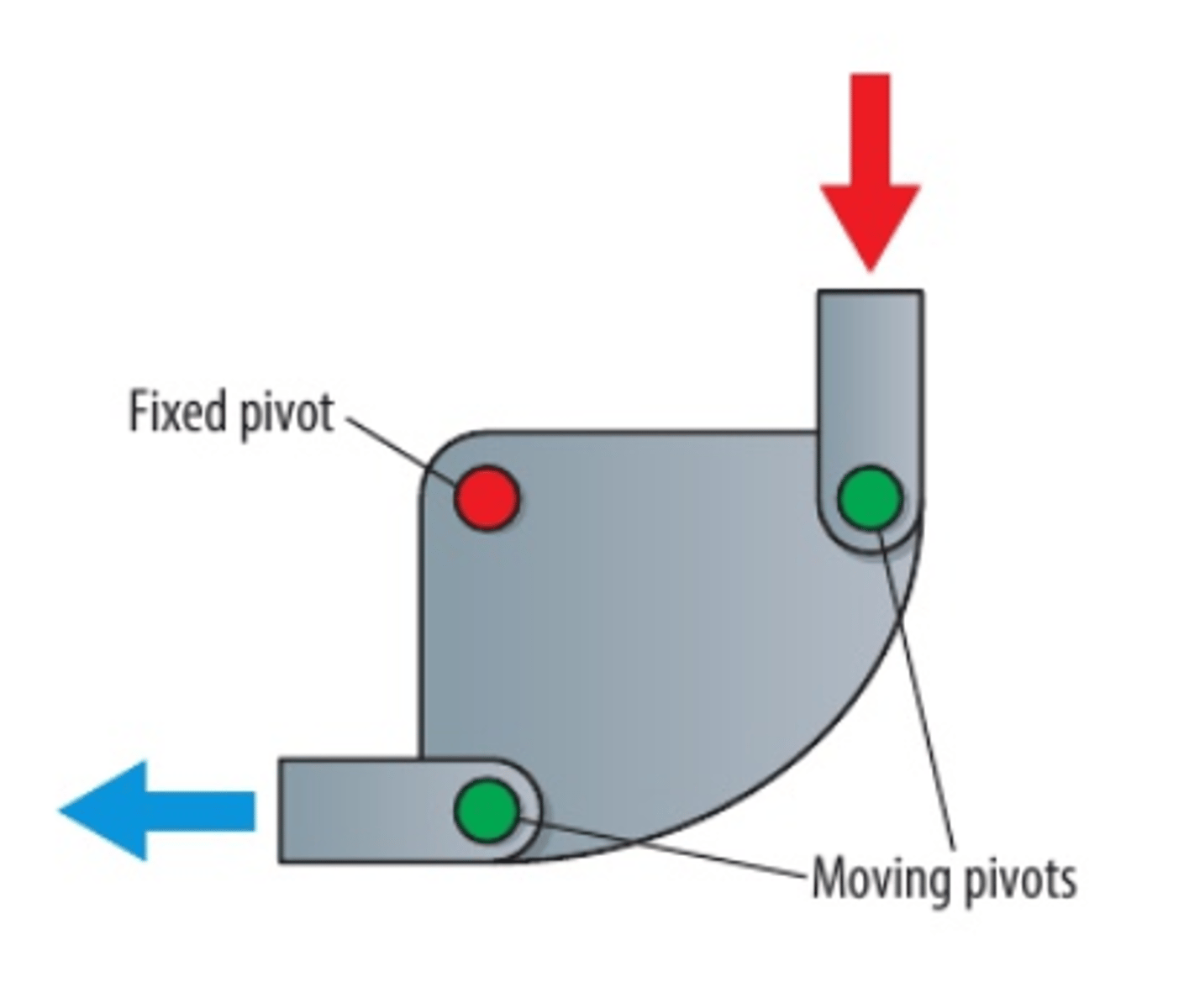
Bell crank linkage
Class 1 lever that can transmit the motion through 90 degrees to allow an input force to be transmitted around a corner
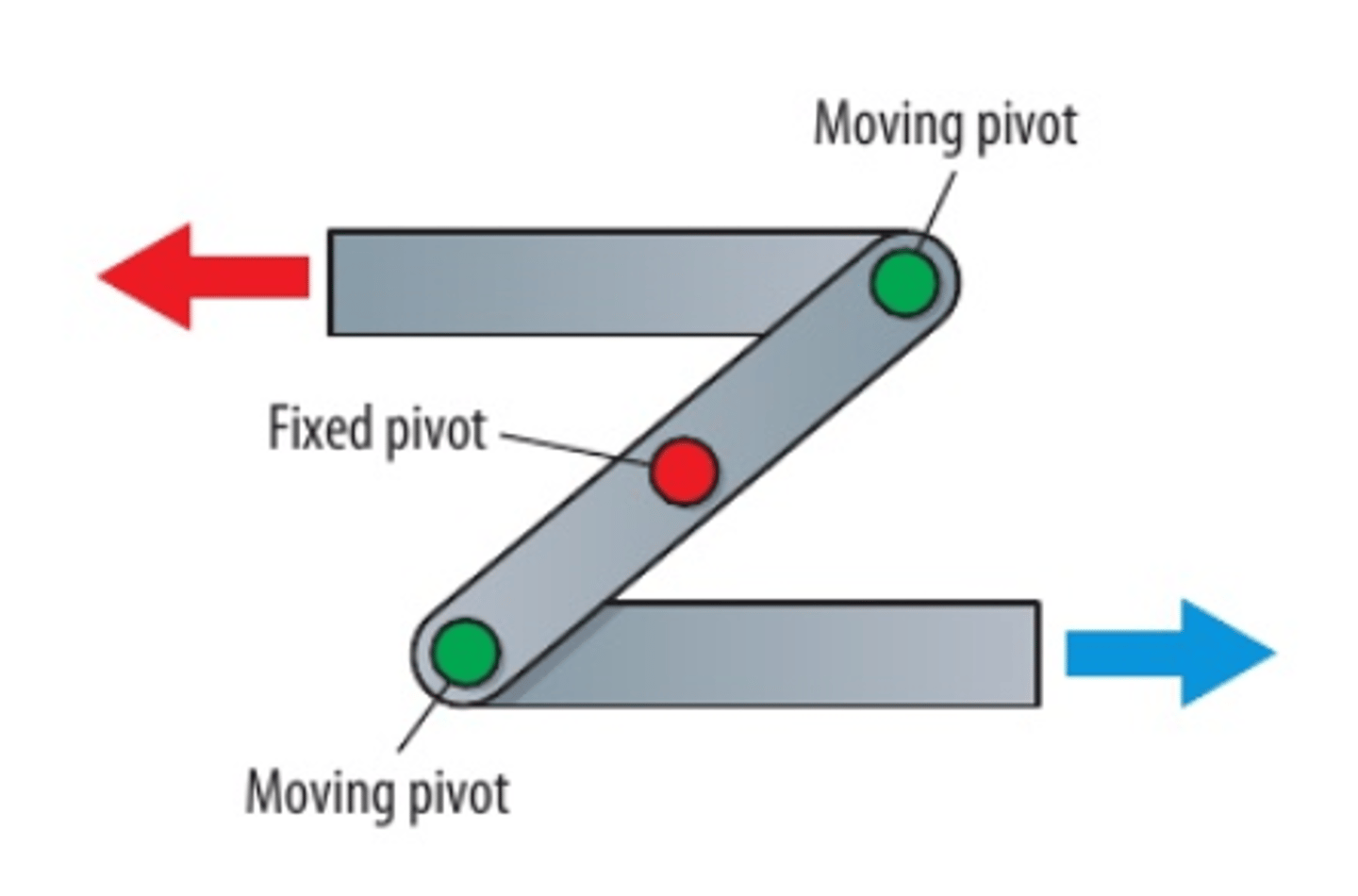
Reverse motion linkage
A class 1 based lever that reverses the motion of the input
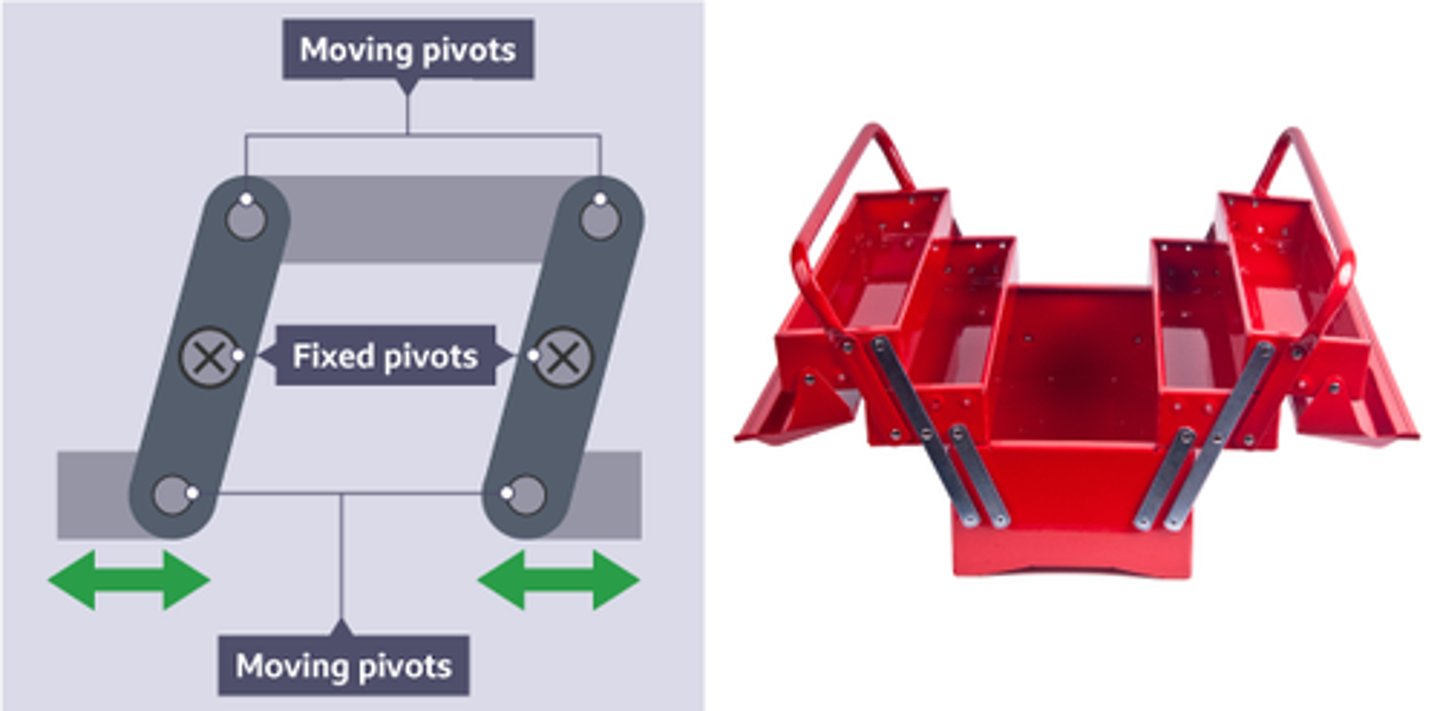
Parallel motion linkage
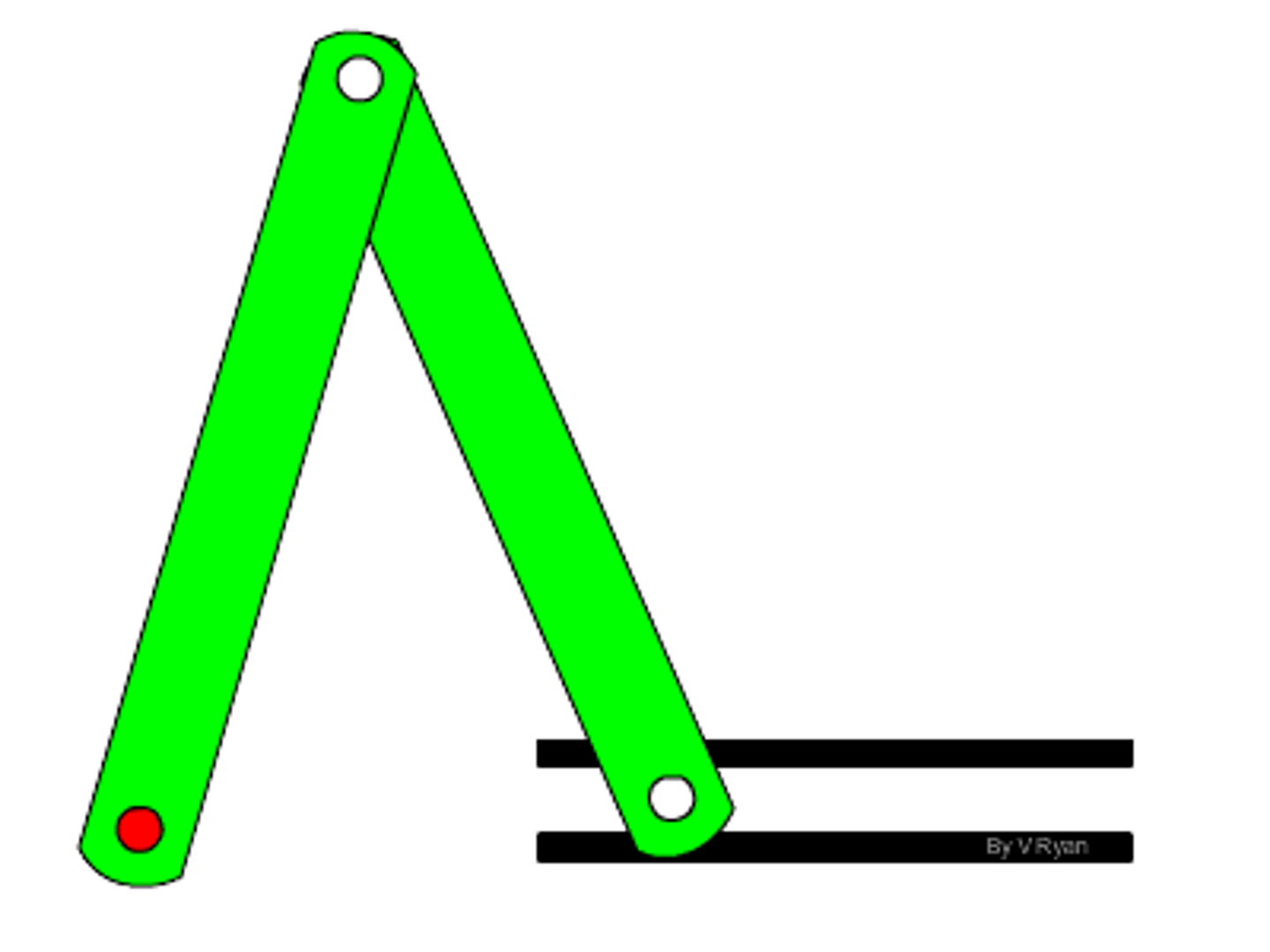
Crank and slider linkage
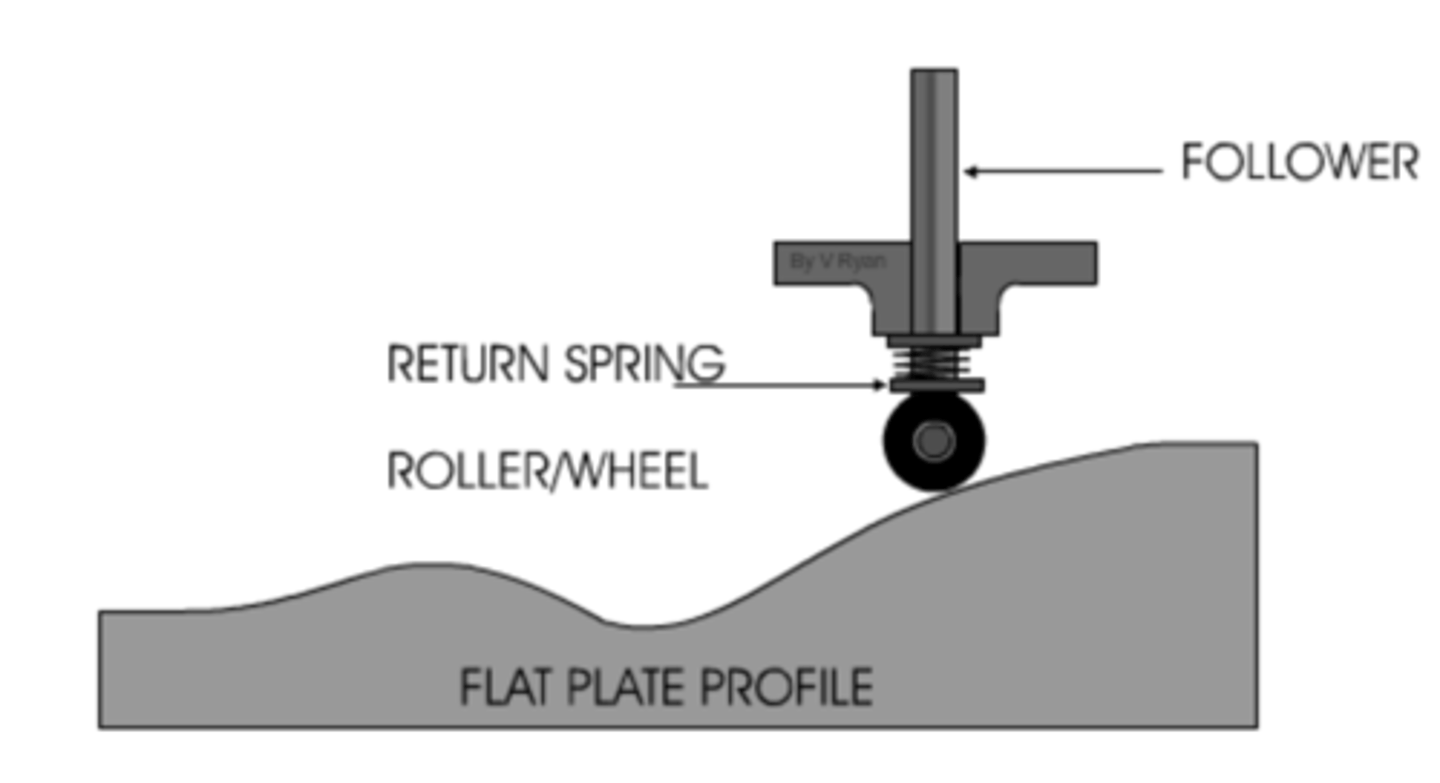
Cam
Converts rotary motion into reciprocating and oscillating motion.
Follower
Follows the movement of a cam profile
3 stages of movement in a cam
Rise (follower moves up)
Fall (follower moves down)
Dwell (follower is stationary)
Main types of cam & use
Pear-shaped (opens & closes valves in car engine)
Eccentric/circular (in a fuel pump or in steam engines)
Snail/Drop (hammers/punches or machines needing a sudden drop)
Swash plate cam
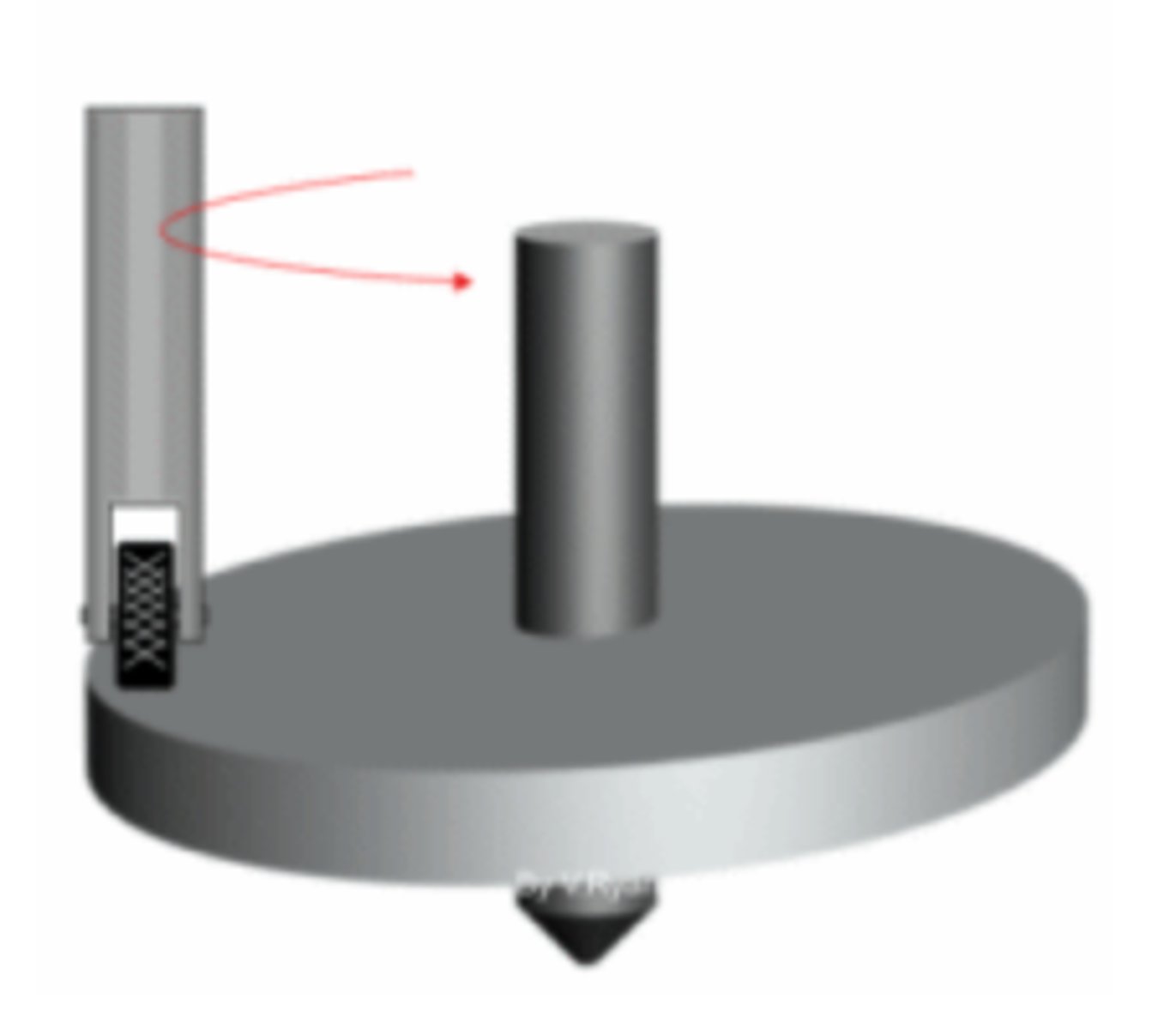
Flat plate/linear cam
Box cam
[image]
Barrel cam
[image]
Types of follower and use
Roller (used with high speed due to its low friction but has more parts with forces pushing them to the side)
Knife edge (used for accuracy in following cam profile but suffers rapid wear and forces pushes them to the side)
Flat (used in high load applications such as steam engines and has reduced forces pushing it but has higher friction)
Quick return mechanism
Rotary → reciprocating motion
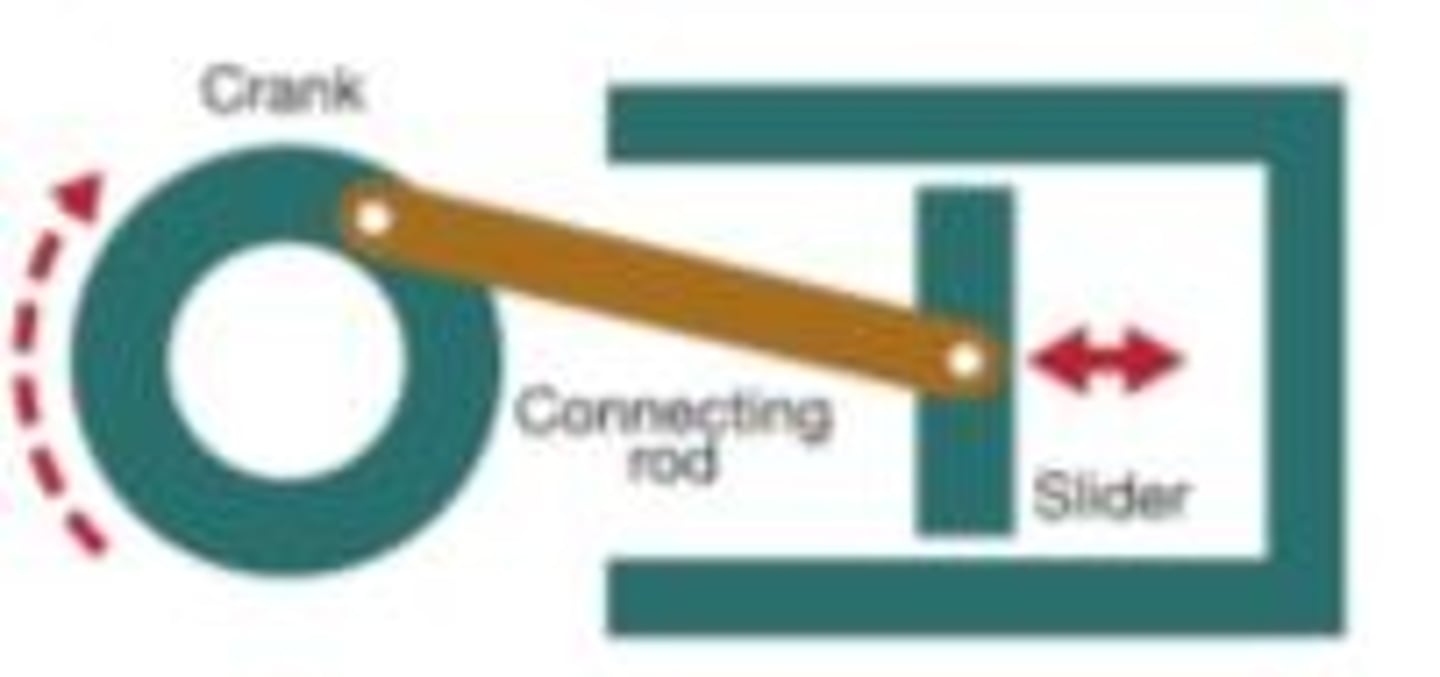
Cranks & sliders (& equation)
Convert rotary motion of crank to reciprocating motion of slider (e.g., crankshaft or compressor) or vice versa (steam engine)
Distance moved by slider = 2 × radius of crank
Instead of crank being wheel, could use a crank arm (its length is radius of crank)
Crank vs crankshaft
Crank: a perpendicular section to the shaft
Crankshaft: A shaft with multiple cranks
Rachet and pawl mechanism
Only turns one way; if you let it go it will not spin back
Pulleys and belts
- Transmit rotary motion from a driver shaft to a driven shaft via. friction (rotate same direction)
- A pulley is a wheel with a groove in its rim and the belt fits the groove to connect the two pulleys
- Having a V-belt increases gripping area by having sloping slides increasing efficiency by reducing any slipping and tightens drive surfaces
Reverse direction for pulley system
Mechanical advantage for pulley system (when using to lift loads)
Number of pieces of rope pulling on load
Velocity Ratio for pulley system (2 formulae)
Driven pulley diameter / Driver pulley diameter
Output speed and velocity ratio
Output speed (rpm) = Input speed (rpm) / Velocity Ratio
Gear
A toothed wheel fixed to a shaft that meshes with other gears to change the speed or direction of rotation of a driving mechanism. They have the advantage over pulley systems as the meshing prevents slippage so greater forces can be applied
Velocity Ratio for gear (ie. gear ratio) (2 formulae)
Driven teeth/Driver teeth
Use of an idler gear
Keeps the gears spinning in the same direction with no impact on output speed so VR is still based on driven and driver gears
Simple vs Compound gear trains
Simple has 2 spur gears
Compound has more than 2 and VR is calculated by first pair's VR × second pair's VR
Bevel gear
Transmits rotary motion through 90 degrees. Two same-sized gears are called mitre gears (equal inp/out speeds)
Rack and pinion (and formula for output movement)
Gear wheel and rack changes rotary motion to linear motion or vice versa
Number of teeth on pinion/Number of teeth on rack per metre
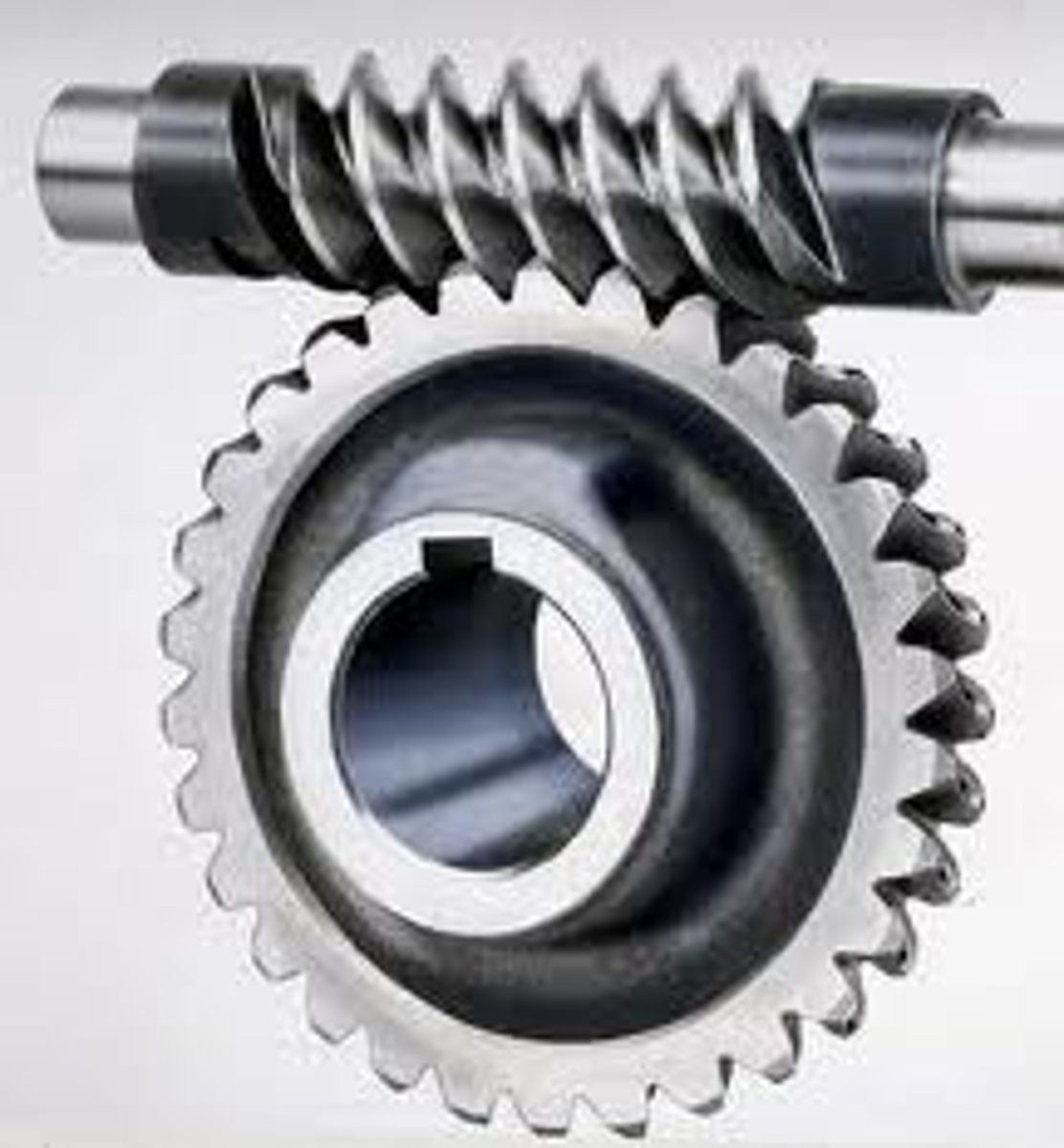
Worm gear (and formula for output movement)
Screw thread: worm (has 1 tooth)
Cylindrical gear: worm wheel
Worm always drives worm gear
VR = Driven/Driver = Worm wheel/1

Chain and sprocket
[ignore chain in VR calculations]
Chain cannot slip on the sprocket, and only need 2 sprockets to transmit motion over a distance
![<p>[ignore chain in VR calculations]</p><p>Chain cannot slip on the sprocket, and only need 2 sprockets to transmit motion over a distance</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/82a04d75-5fa0-45bd-8e99-0cff71e32653.jpg)