Electrostatics and Conductors in Equilibrium
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Conductor
Material allowing free movement of electric charges.
Electrostatic Equilibrium
State where charges are at rest and balanced.
Electric Dipole
Two equal and opposite charges separated by distance.
Capacitor
Device that stores and releases electrical energy.

Operating Voltage
Voltage range within which a capacitor functions.
Electric Field (E)
Force per unit charge experienced by a charge.
Sharp Points
Regions where electric field strength is highest.
Gauss' Law
Relates electric flux through a closed surface to charge.
Coulomb's Law
Describes force between two point charges.
Dielectric Material
Insulating substance that increases capacitance in capacitors.
Electric Field Strength
Measured in volts per meter (V/m).
Charge Density (σ)
Charge per unit area on a surface.
Potential Difference (V)
Work done per unit charge in moving between points.
Electric Field Inside Conductor
Zero in electrostatic equilibrium.
Electric Field Outside Conductor
Perpendicular to the surface of the conductor.
Maximum Electric Field in Air
Approximately 3 x 10^6 V/m.
Voltage (V) Definition
1 Joule per Coulomb (J/C).
Ampere-Hour (Ah)
Unit of electric charge, 1 Ah = 3600 C.
Electric Field Due to Plate
E = σ/ε₀ for infinite plane.
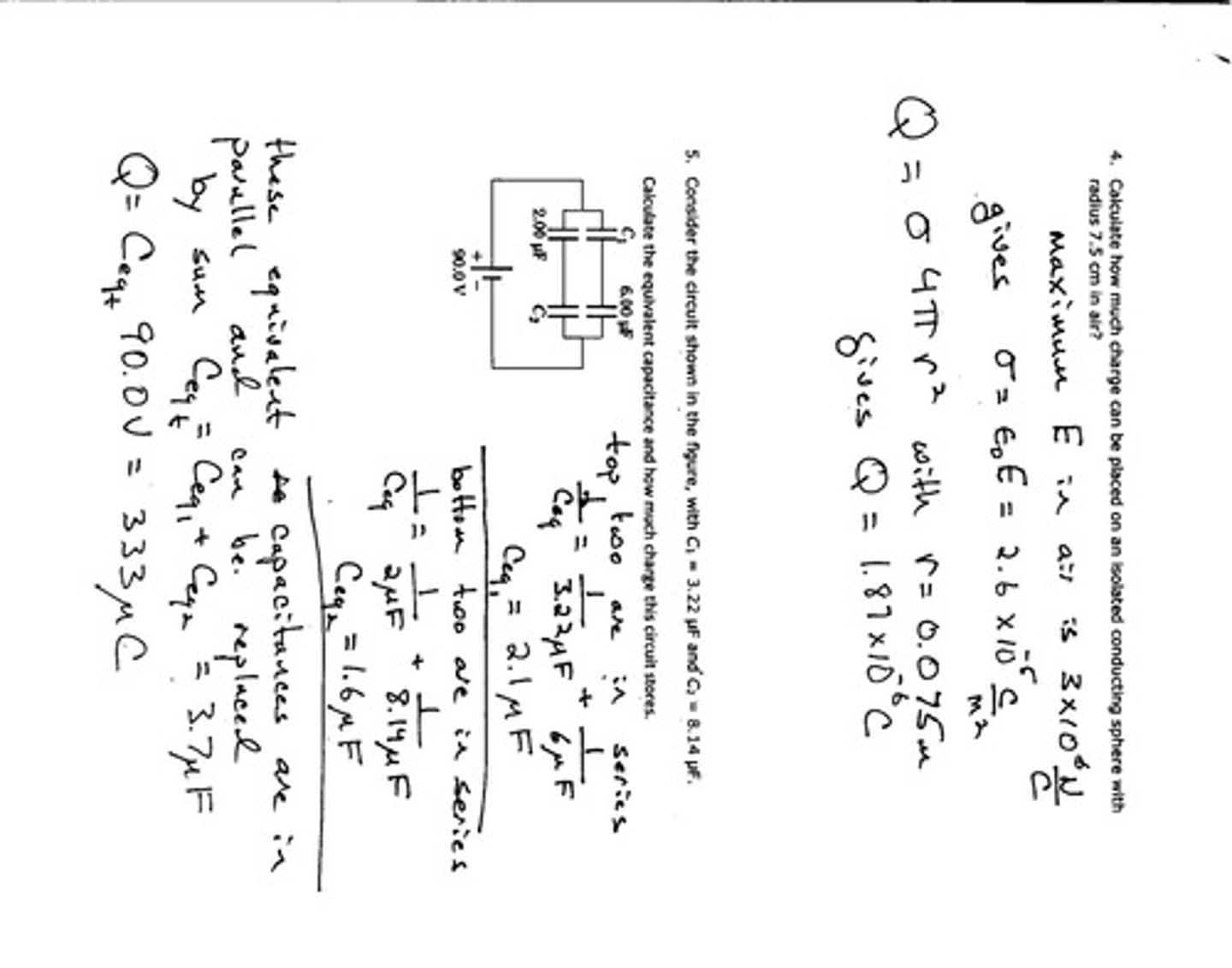
Charge on Sphere
Q = 4πr²σ for spherical conductors.
Equivalent Capacitance
Total capacitance in a circuit configuration.
Electric Potential (V) Formula
V = kQ/r for point charges.
Electric Field (E) Formula
E = F/q, where F is force.
Energy Stored in Capacitor
U = 1/2 CV², where C is capacitance.
Piezoelectric Effect
Electric charge generated by mechanical stress.