liver pathology part 2
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
what is hepatitis
inflammation of liver
most common causes of hepatitis
viruses and alcoholism
what is the #1 cause nationally & globally of hepatitis
virus
what can hepatitis result in
cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma
what levels may increase with hepatitis
AST, ALT, and bilirubin
what type of hepatitis is associated with food contamination
Hepatitis A
hepatitis A is spread primarily by the
fecal - oral route
hepatitis B is transmitted through
body fluids
body fluids that cause Hep B
blood, semen, vaginal secretions, sometimes saliva
Hep B is mostly transmitted ______
parenterally
ways Hep B is trasmitted
sexual contact
needle punctures
blood transfusions
mother to infant
Hep C is transmitted ______
parenterally
Hep C can lead to
cirrhosis
Hep C can do what
stay active in your asymptomatic body and slowly damage liver over time (chronic Hep C)
what is the most common infection in the US that is spread through blood
Hep C
fulminant hepatitis
onset is sudden and severed
fulminant hepatitis may lead to
shock, coma, rapid death
acute hepatitis
mild to massive liver necrosis/failure
acute hepatitis may cause
may look normal
hepatosplenomegaly
non tender mild GB wall thickening
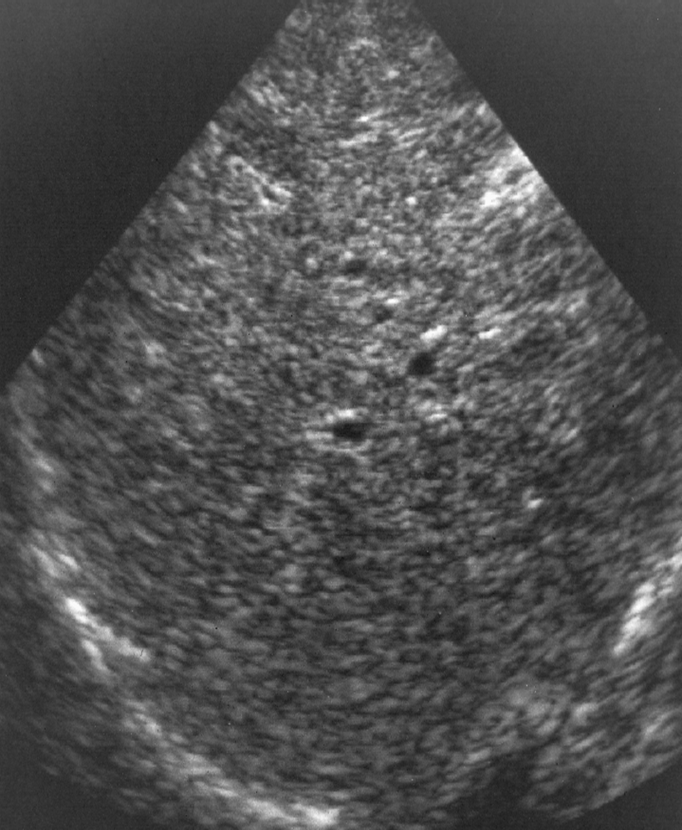
acute hepatitis sonographic appearance
hypoechoic
periportal cuffing (starry sky)
starry sky occurs due to
acute hepatitis
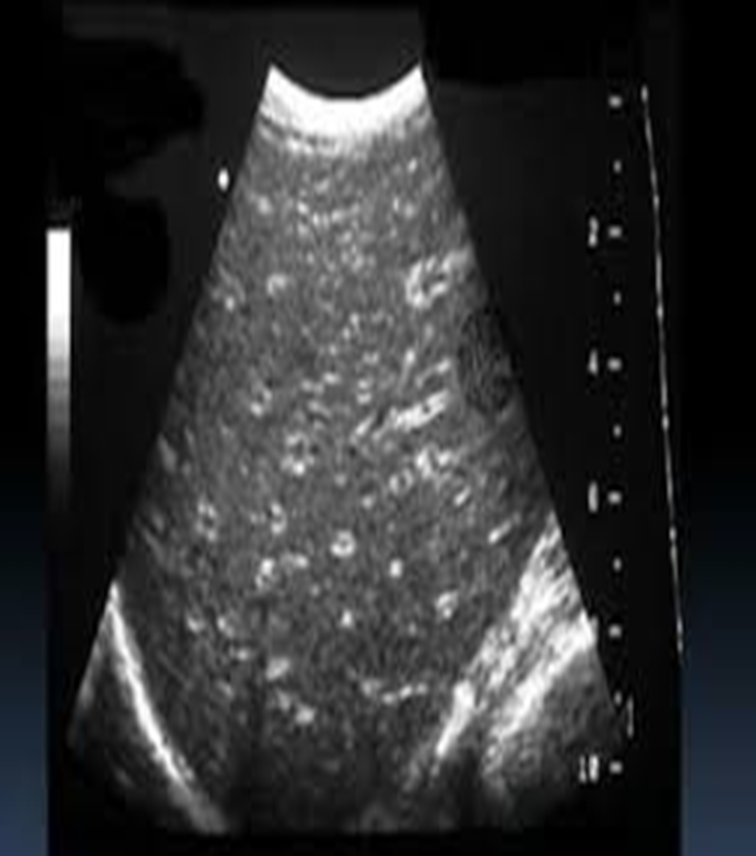
starry sky
likely due to acute hepatitis
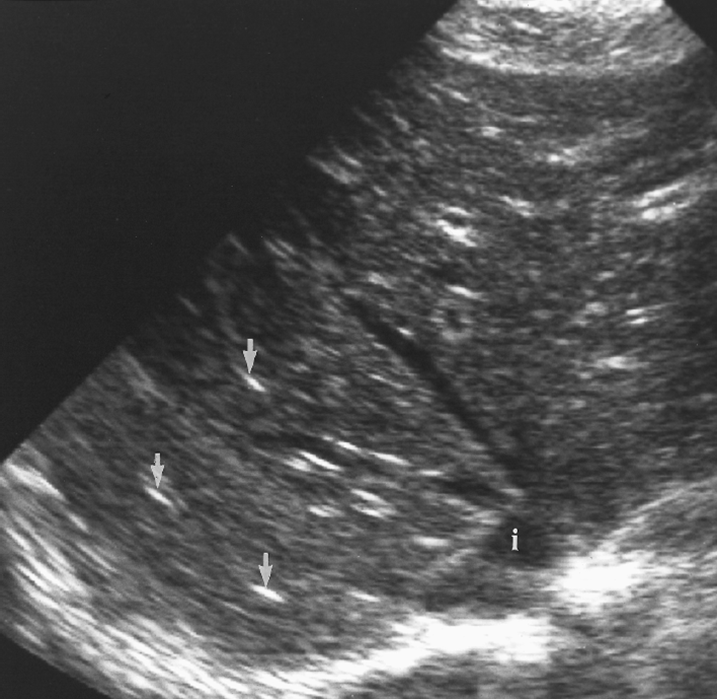
acute hepatitis with starry sky
starry sky aka
periportal cuffing
chronic hepatitis
liver inflammation for at least 6 months
chronic hepatitis may progress to
cirrhosis causing liver failure and increasing risk for liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma)
most specific lab value for hepatocellular damage
increased ALT
steatohepatitis
fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation of the liver
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
Liver inflammation and damage caused by a buildup of fat in the liver.
-It is part of a group of conditions called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease -NASH can progress and lead to cirrhosis
alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH)
Fatty liver caused by alcoholism.
- Characterized by inflammation and fibrosis
gold standard for determining hepatic fat content and staging fibrosis
liver biopsy
non alcoholic fatty liver disorder now called
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
MASLD
MASLD/NAFLD and NASH are typically
asymptomatic
NAFLD and NASH suspected if tests show
increased ALT and AST
liver cirrhosis
chronic degenerative disease where scar tissue replaced healthy liver tissuei
is liver cirrhosis reversible
no
causes of liver cirrhosis
alcoholism, chronic hepatitis, drug abuse, fatty liver
cirrhosis symptoms
nausea, ascites, light colors stool, weakness, abdominal pain
advanced stage cirrhosis symptom
jaundice (excess bilirubin, increased ascites, portal hypertension, liver failure
cirrhosis sonographic characteristics
isoechoic regenerative nodules
decreased visualization of vascular structures
cirrhosis lab values
increased ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, direct bilirubin
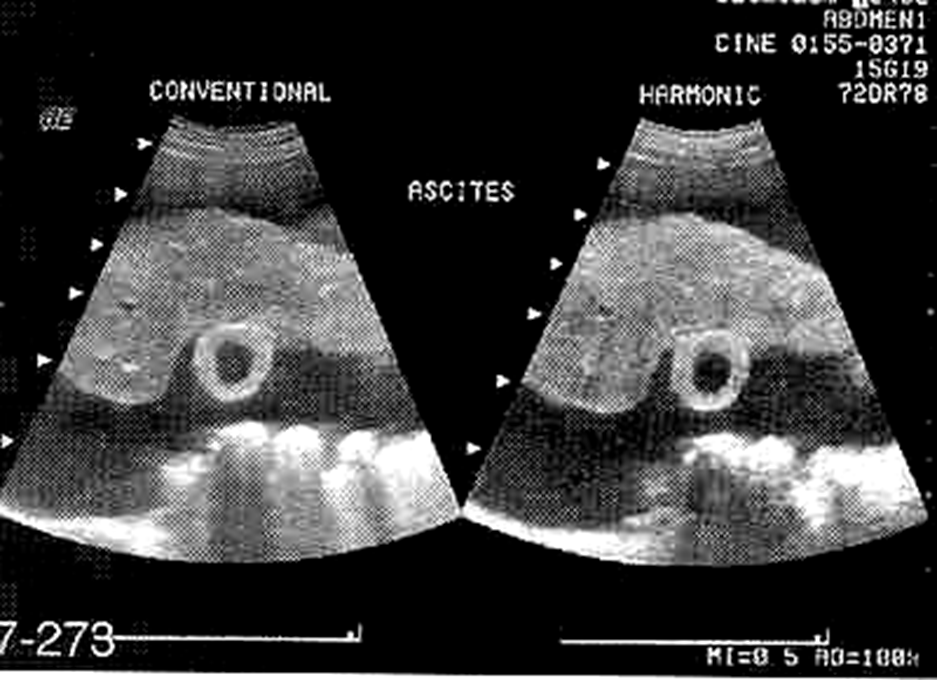
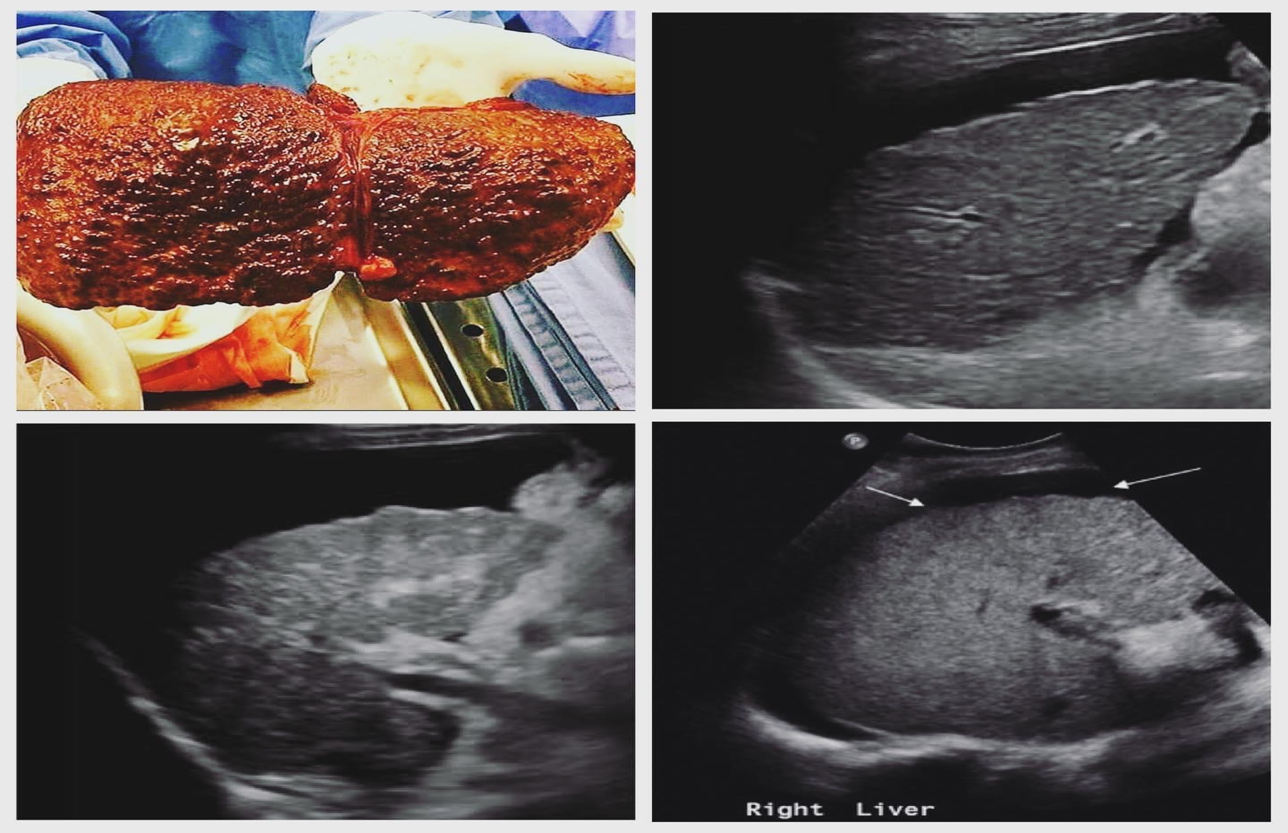
cirrhotic liver with ascites
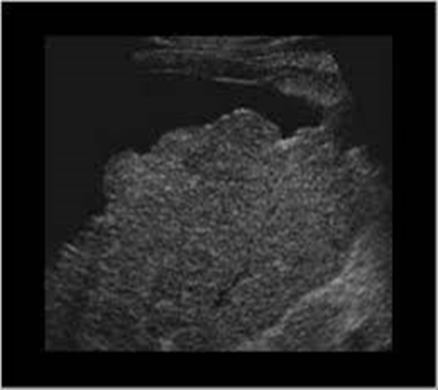
cirrhotic liver
cirrhotic liver
fibrosis and altered architecture of cirrhosis cause a
coarse appearance
inspection of liver surface with what kind of probe demonstrates nodularity
high frequency, linear array
ascites
serous, free fluid that can go anywhere within the peritoneum
caudate lobe hypertrophy
in setting of cirrhosis the caudate lobe may be enlarged
cirrhosis
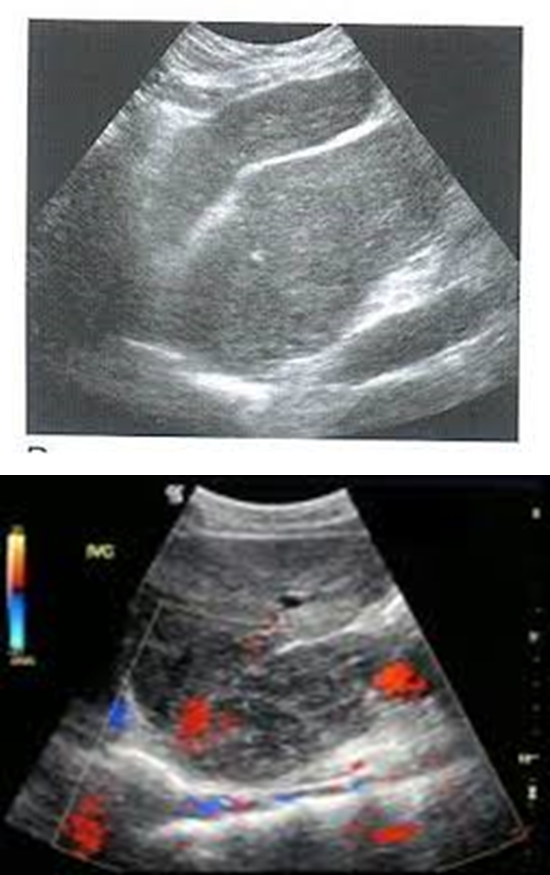
enlarged caudate lobe
hemochromatosis
disease of iron metabolism
hemochromatosis may lead to
cirrhosis
wilson’s disease
inherited excess deposition of copper in the liver and kidneys
wilsons disease may lead to
cirrhosis
von Gierke’s disease
genetic
most common form of glycogen storage disease
von Gierke’s disease aka
type I glycogen storage disease
von Gierke’s may lead to
cirrhosis
von Gierke’s related to
adenomas
budd chiari
occlusion of hepatic veins
presents with triad of hepatomegaly, abdominal pain, and ascites
may lead to cirrhosis
hepatocellular carcinoma HCC
most common primary liver cancer
may lead to cirrhosis
hemochromatosis
causes body to absorb too much iron
stored in liver and pancreas
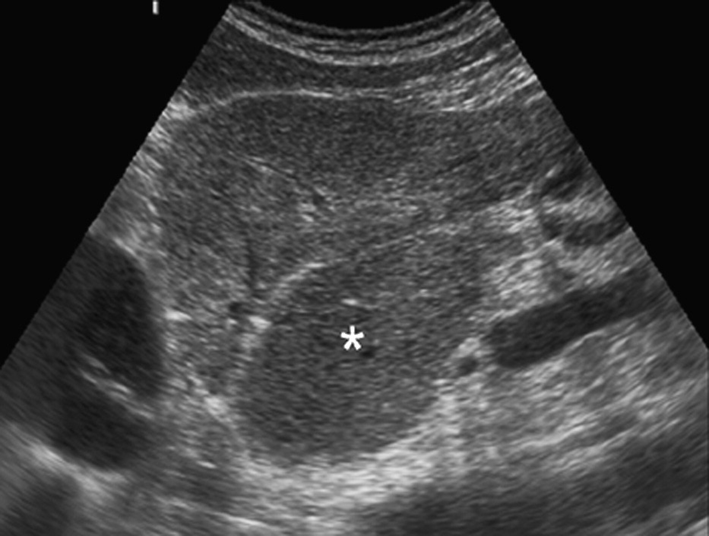
caudate lobe hypertrophy
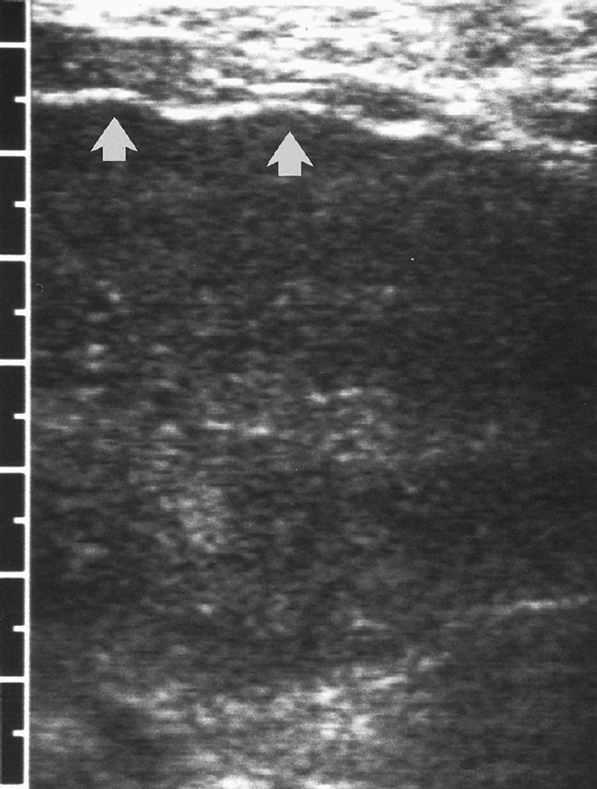
nodular liver surface from cirrhosis
hepatoblastoma
malignant liver tumor found almost exclusively in infants and young children
most common hepatic malignancy in children
hepatoblastoma
what is often associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
hepatoblastoma
clinical indication of hepatoblastoma
elevated alpha fetoprotein
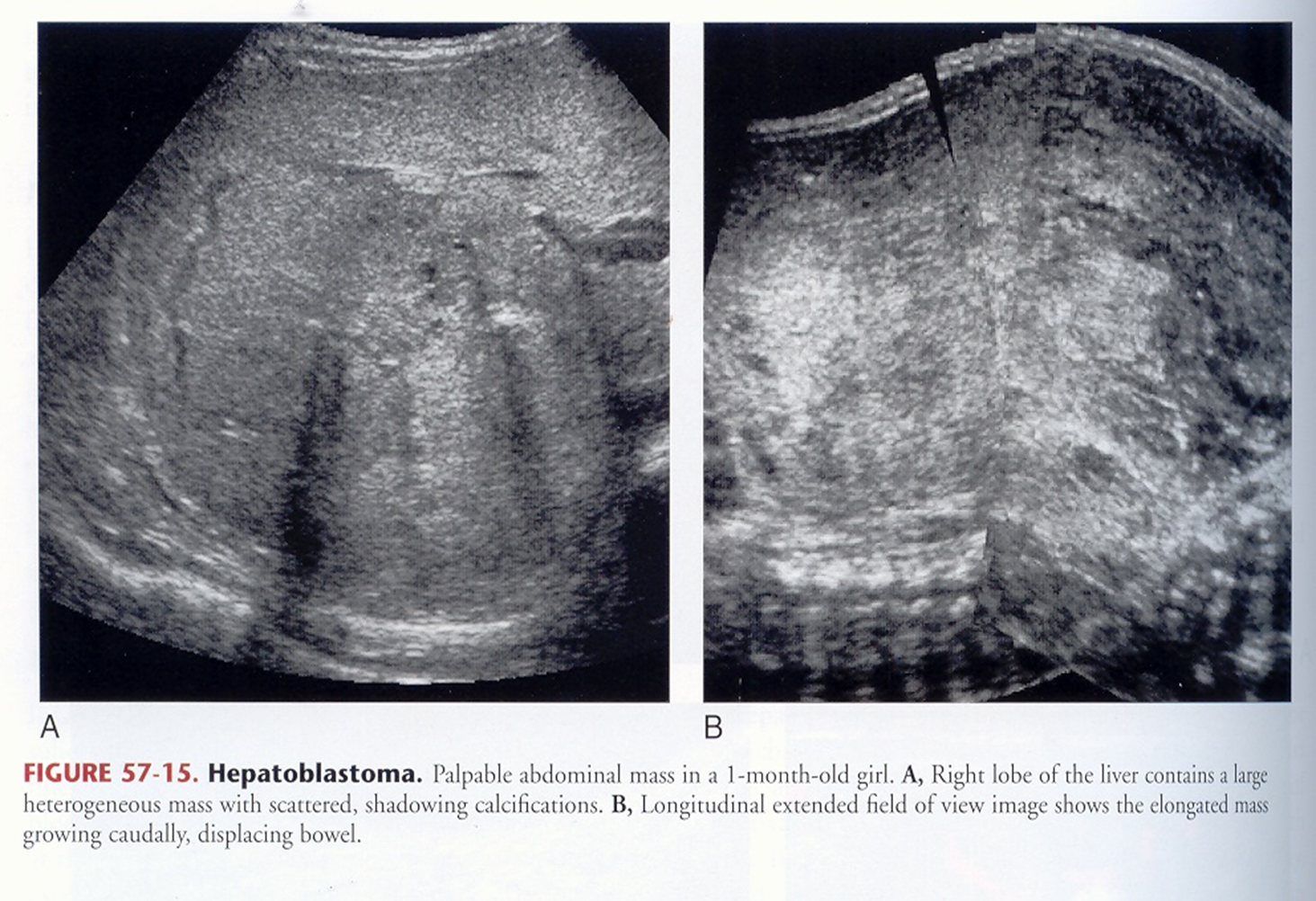
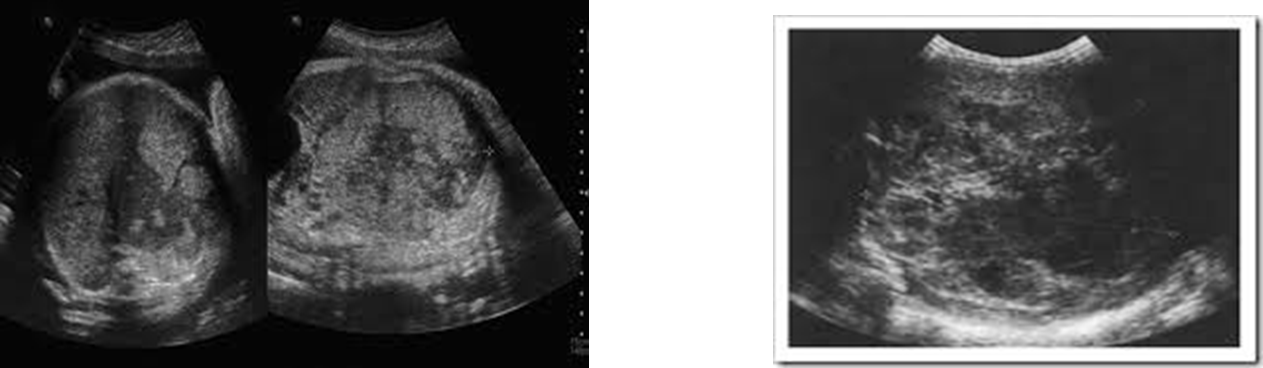
hepatoblastoma