Prof Knowles Study guide
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Identify the 5 foundations of psychological science
evolution
materialism
idealism
modularity
empiricism
evolution
(genes make brain) - the brain is shaped by genes which influences behavior, survival instincts, and mental capabilities
materialism
(brains make mind) - our thoughts and emotions are a product of physical processes in the brain
idealism
(minds make reality) - the brain constructs our reality and we don’t interact with the world directly
modulism
(the mind is a collection of parts) - the brain is made up of modules that have different functions
empiricism
(believe only what you can count) - in psychology, we trust only what can be tested and quantified, not what we assume
3 special problems of psychological science
complexity - human behavior is extremely complex
variability - ethnicity, personality, and how you’re raise creates more diversity
reactivity - humans react differently, compared to a rolling ball, the ball will always roll the same. It is difficult to observe “natural” behavior when the subject knows they are being observed
abstract property
an idea or principle that's based on general ideas, rather than real things or events (happiness)
operational definition
specifies observable conditions that define the concept
abstract property, operational definition, measure relationship
operational definition makes an observable definition for abstract property, measure the operational definition
reliability vs validity
reliability - tendency for a measure to produce the same result
validity - how accurate the measure is to the actual
construct validity
tendency for a clear conceptual relation to exist between abstract property and operational definition
convergent validity
tendency for the operational definitions to be related to other operational definitions
discriminant validity
tendency for measure to produce different results when used to measure different thing
relation between theory and hypothesis
theory is used to derive a testable hypothesis
relation between sample and population
sample is a small part of population, and sample results are used to generalize to population
importance of mean and variability in looking at differences between groups
???
define and give example of observer bias
esearcher’s expectation influence what they record in a study (researcher knows that the numbers should say index is the most common, but some subjects were using index first then moving to the pinky instead, research is tired of this study and puts index as data even though the subject used pinky eventually)
ways to avoid observer bias
double-blind study, study where observer and subject are not aware of the nature of the study
define and give example of subject bias
the subject will change behavior to help the observer or make it more difficult for the observer (researcher says they are seeing if index finger is the preference finger for nose picking, subject knows they use pinky usually, but uses index to “help” the observer)
ways to avoid subject bias
single-blind study
define and give an example of demand characteristics
cues in an experiment might indicate the research objective, causing participants to change behavior
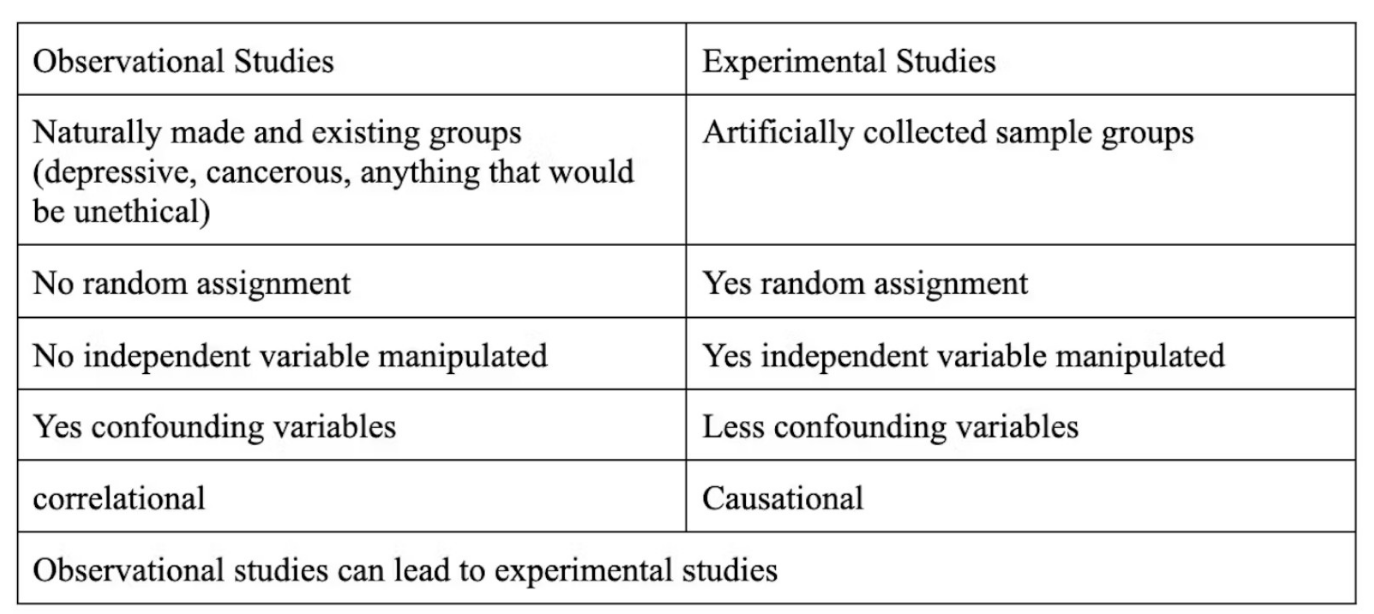
identify what can and cannot be concluded from correlational studies
can conclude correrlation relationship
cannot conclude a causational relationship
key ingredients for an experimental study
manipulate independent variable
control (conditions are consistent in every other way except manipulation)
random assignment
measure
experimental vs observational studies
evolution
a process that results in changes in the genetic material of a population over time
Mechanisms by which Darwinian evolution takes placw
???
4 basics of natural selection
Variation, competition, survival/reproduction, heritability/adaptation
Fallacies of evolution
naturalistic fallacy
deterministic fallacy
nature vs nurture
teology
naturalistic fallacy
things are right because they are natural
ex: it is not right to kill someone for food even when we have instinct drive for food, we have evolved to have morals
deterministic fallacy
things are inevitable because they are natural, or predetermined because of our genes
ex: can’t get over smoking addiction because it’s in my genes to be addicted to nicotine. this denotes the idea of free will
nature vs. nature
it is not one or the other, it’s both that contributes
teleology
evolution is on the way to perfection, but this is a fallacy because there is no end state to evolution, it is random and related to environment and natural selection
evolutionary adaptation
evolved solutions to problems, contributed to reproductive success
3 basic theories of how the brain relates to the mind
dualism - mind and brain are separate, sees mind as one element and the body as one element (mind and body exists, mix of materialism and idealism)
materialism - mind and brain have a causal relationship, the mind is what the brain does (mind is from brain chemicals like happiness)
idealism - reality is a mental construct (everything is created from mind)
what is the placebo effect an example of
dualism. because the placebo effect shows that the mind and the physical exists. the mind is tricked by sugar pill there in turn the physical body feels it
Globalization vs. localization
the brain is just one whole thing or it is made up of parts
What was shown by the case of Phineas Gage?
that different parts of the brain are responsible for different things. his frontal cortex was severely damaged but he was able to breathe still and function, just had bad impulse control
3 methods of localization and examples
accidents (Phineas Gage)
surgery (seeing the effects of brain surgery done on people with severe seizures)
manipulation (electrical stimulation)
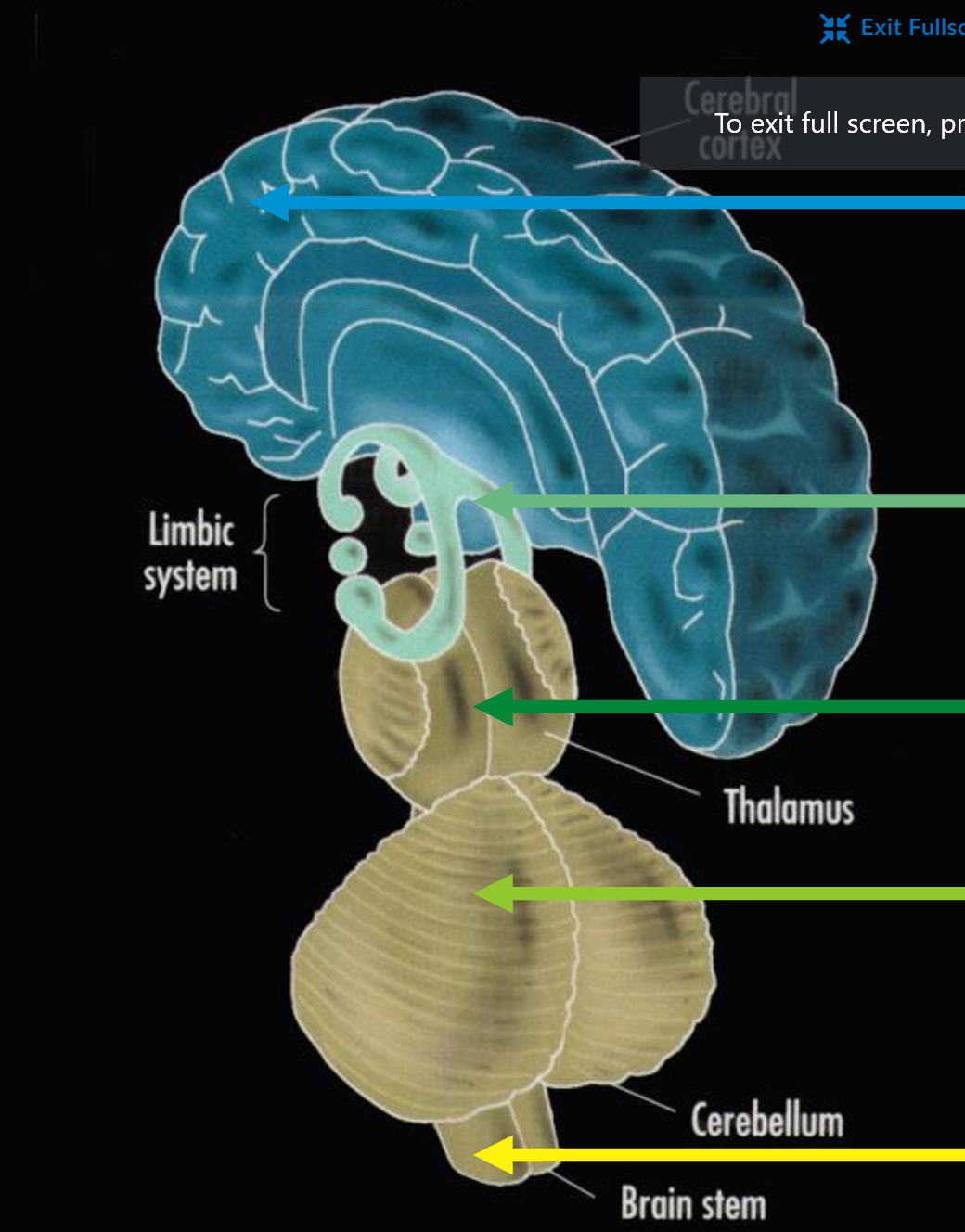
brain stem basic function
basic life function
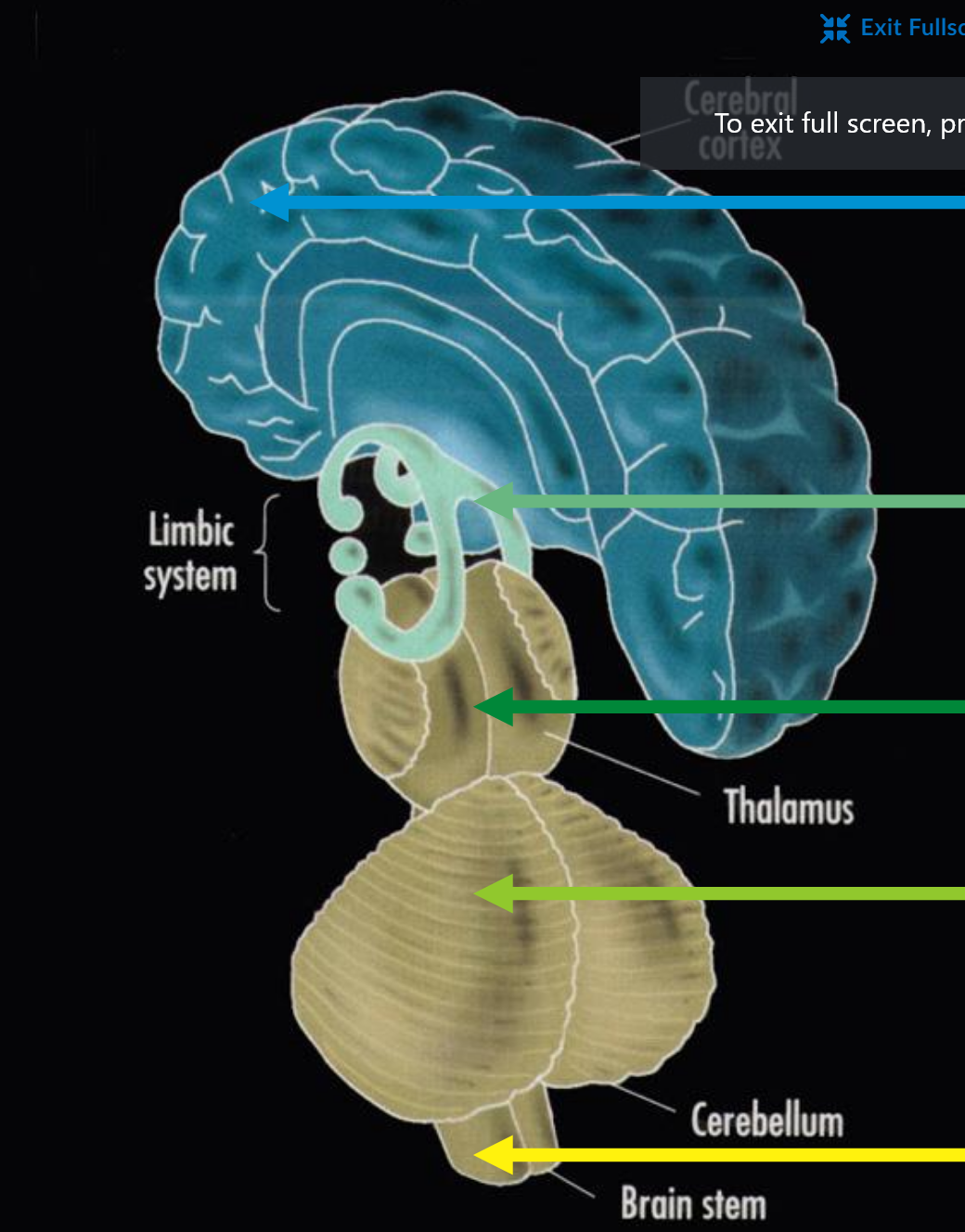
cerebellum basic function
basic motor programs
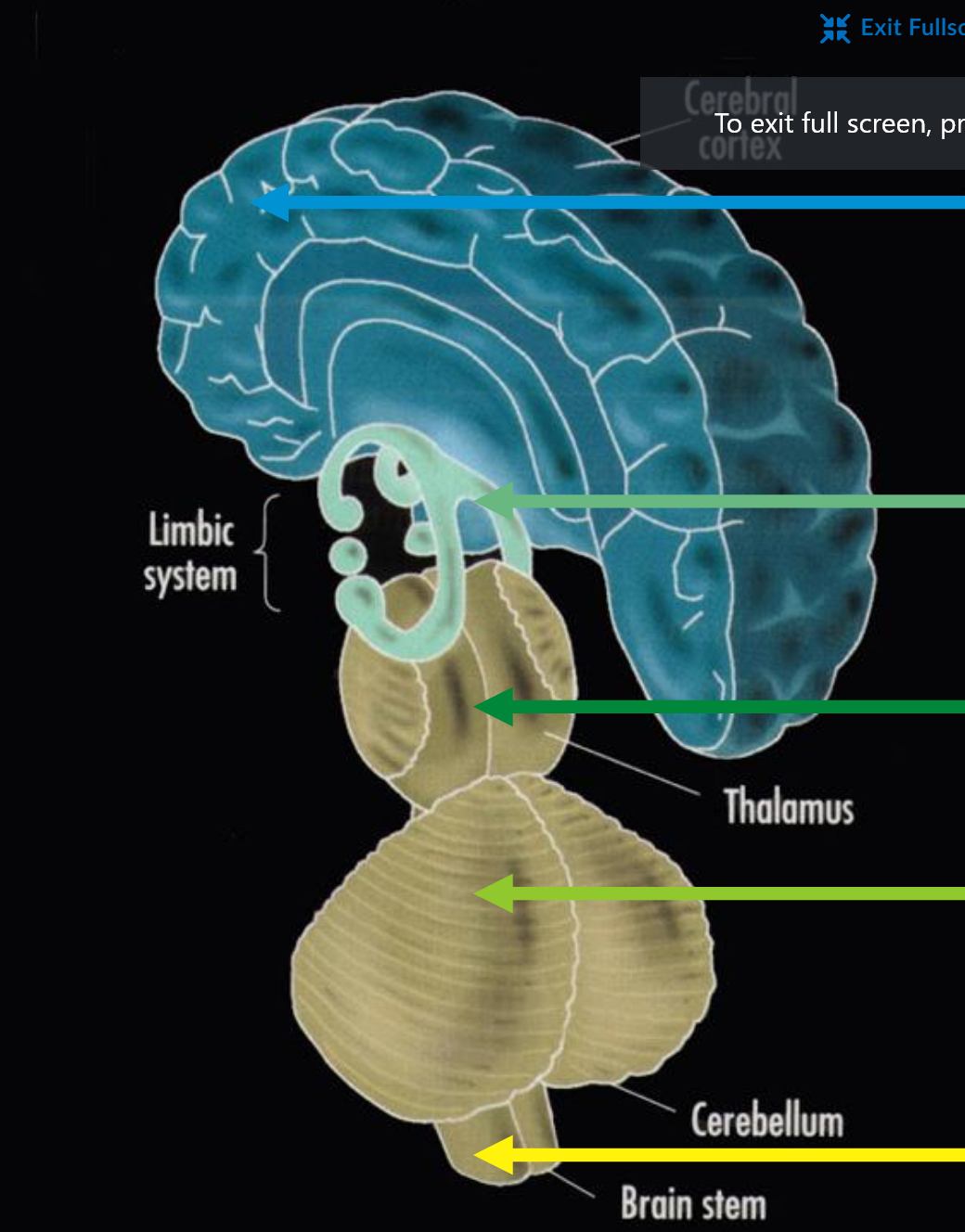
limbic system basic function
emotion, motivation, simple judgement

cerebral cortex basic function
voluntary action, complex judgement, symbolic thought
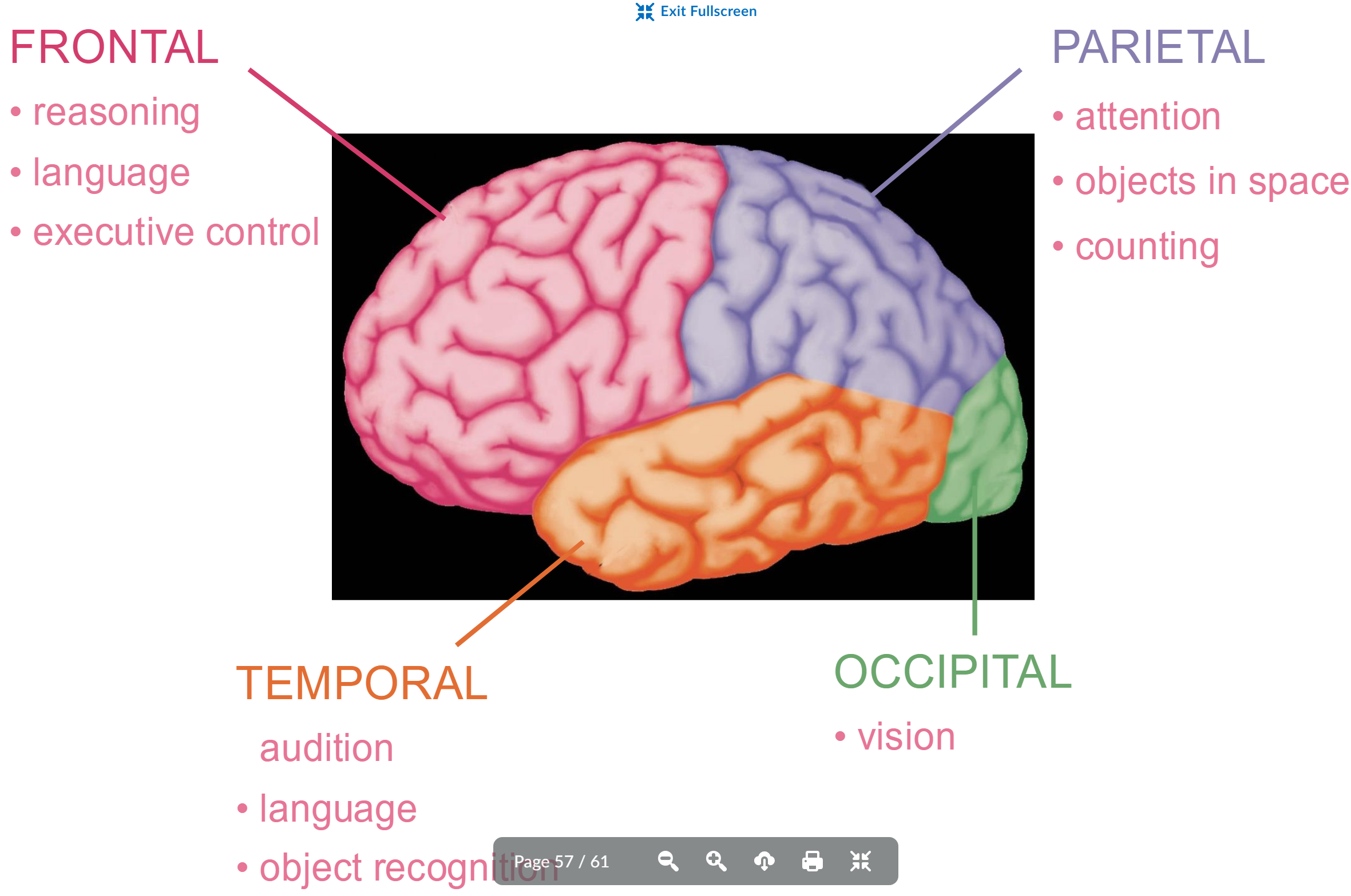
Basic brain organization 4 parts
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
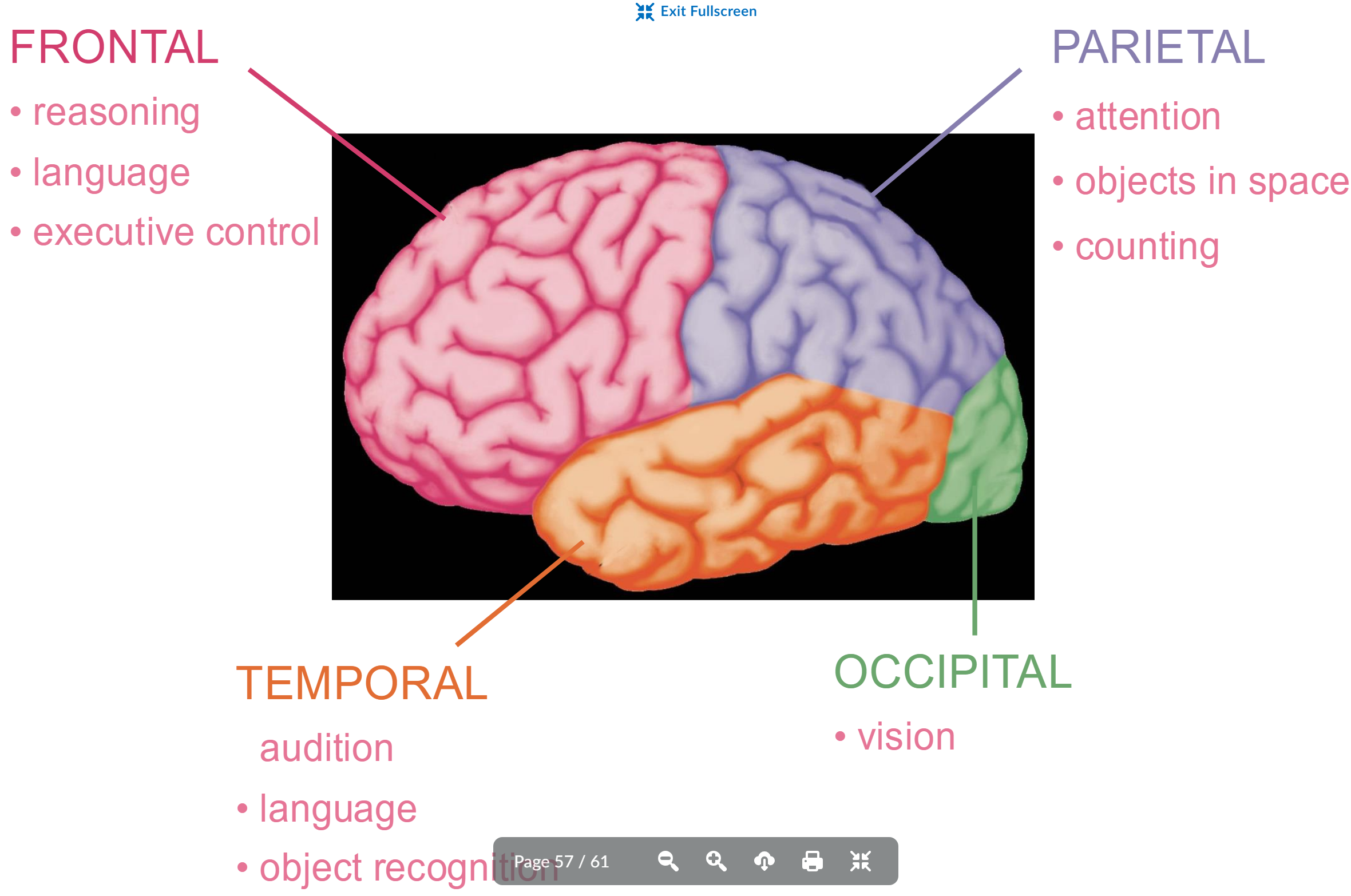
frontal function
reasoning
language
executive control
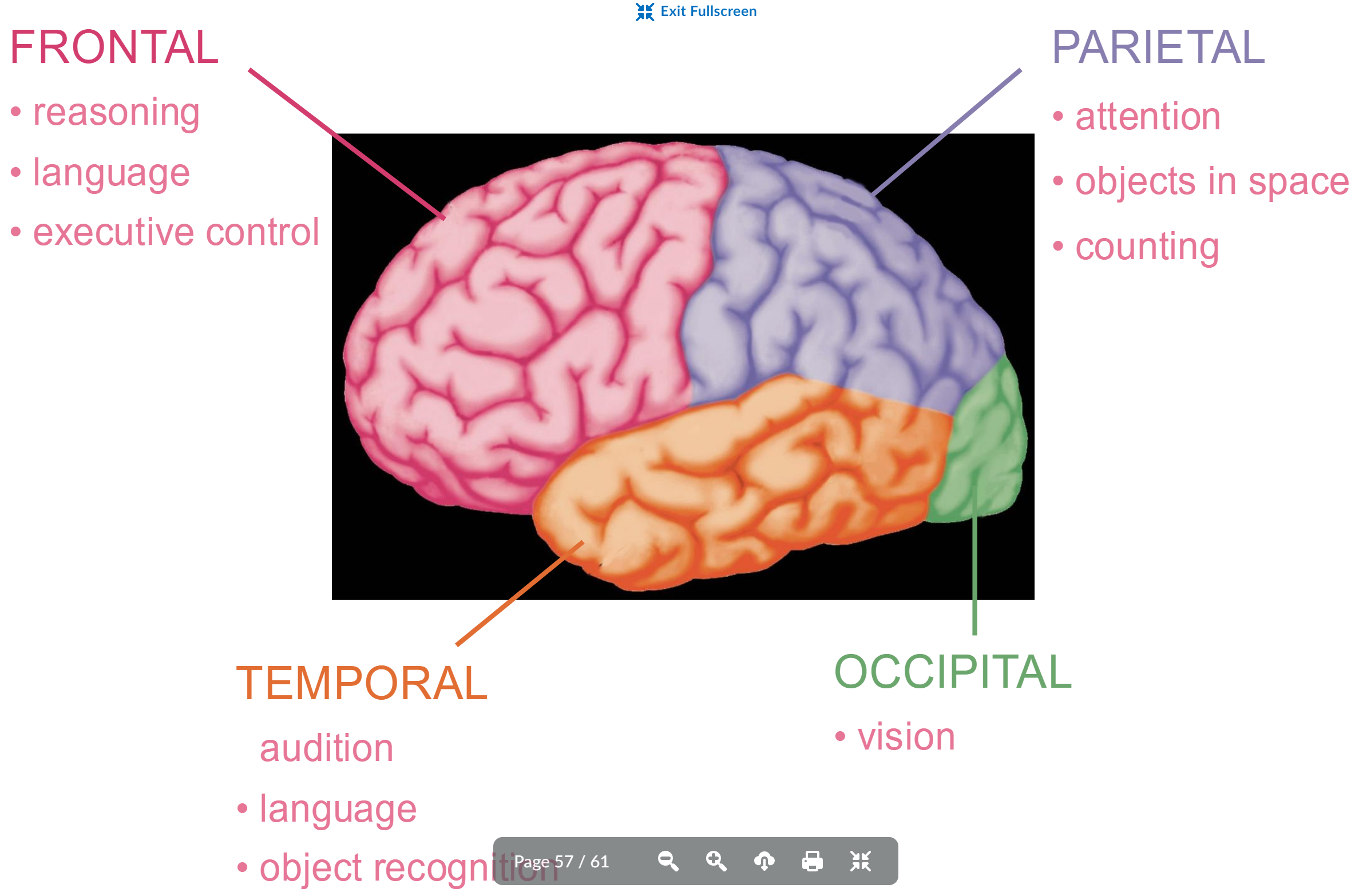
parietal function
attention
objects in space
counting
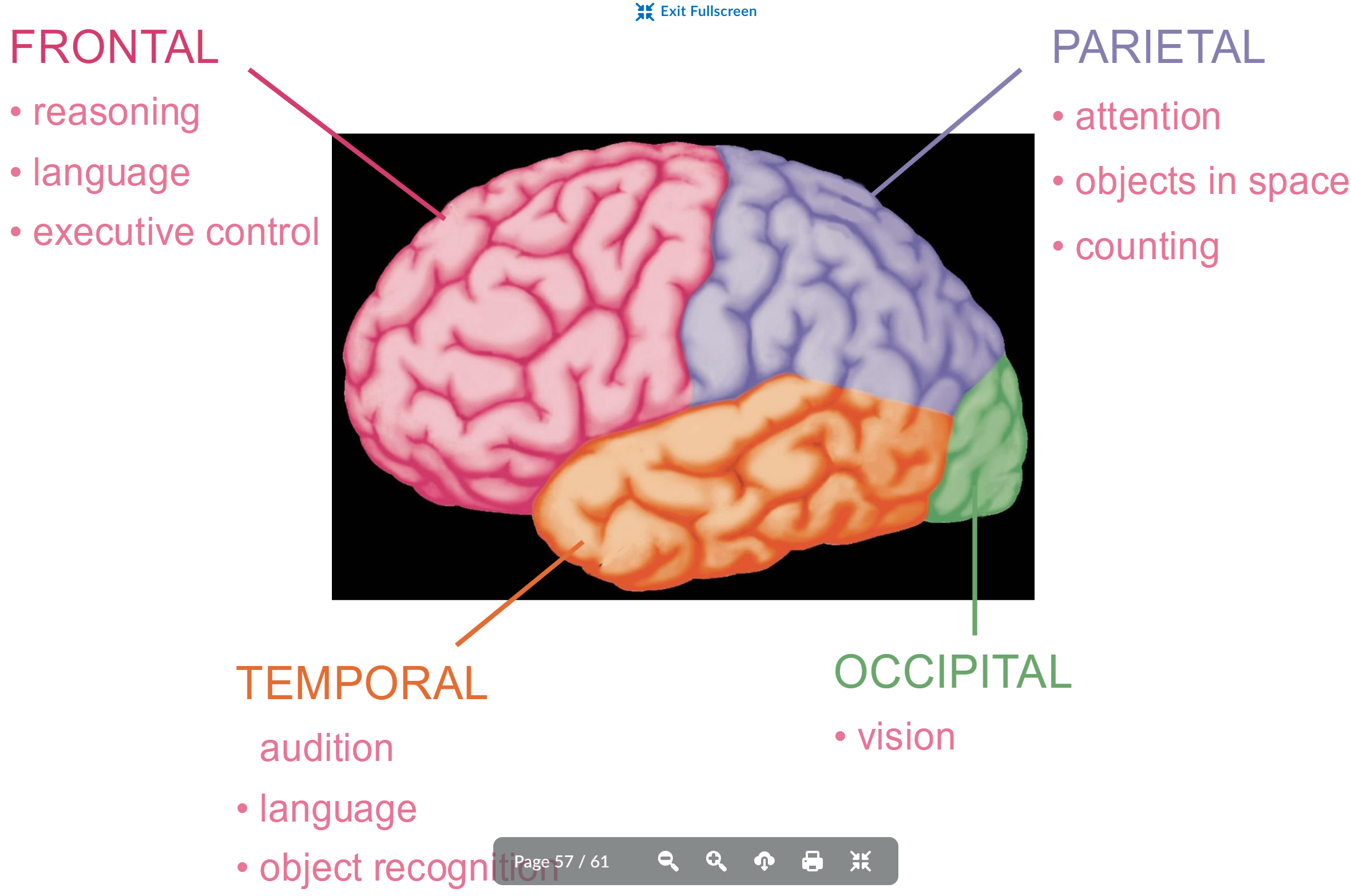
temportal function
audition
language
object recognition
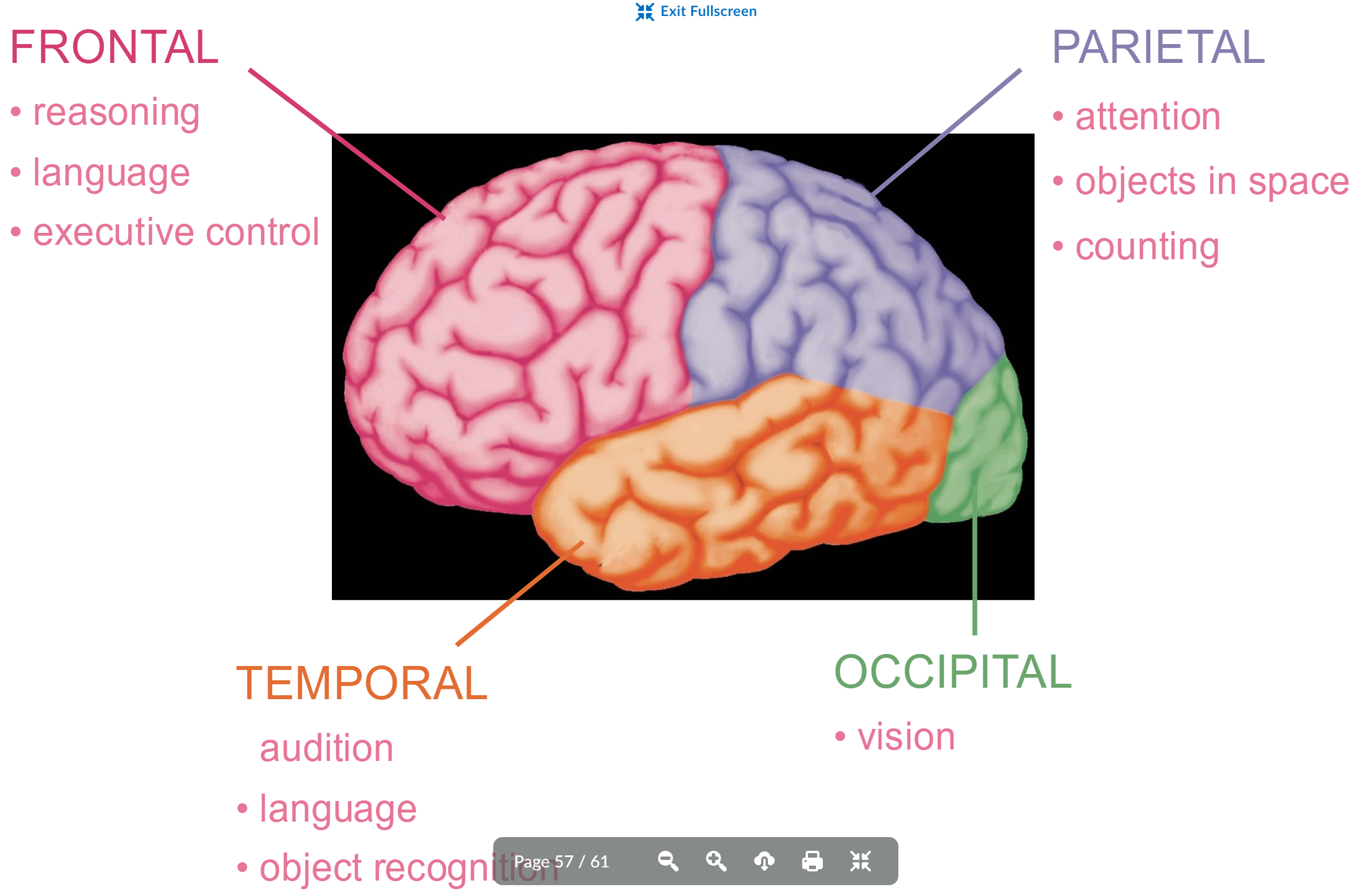
occipitical function
vision