SUPER DUPER FIRE SERVICE QUIZ - FF GIBBONS
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Name the 4 requirements of a knot.
Easy to tie
Easy to untie
Fit for purpose
Doesn’t damage the line
What are the 5 key elements of being a Safe Person
S - Self Awareness
S - Situational Awareness (observational)
C - Competency
C - Communication
D - Decisive
On our radios, there are 6 channels. What are their allocations?
Fire Ground
Command Support
BA
Spare
Command
Aerial
What are signs and symptoms of a collapsing building?
Cracks in walls
Sagging floors
Displaced columns
Cracking/dropping arches
Bulging walls
Buckling columns/beams
Water or smoke being pushed through what seems to be solid masonry walls
Unusual noises coming from the structure
At an incident, what is an E.E.P?
Emergency Evacuation Point
At an RTC, what must be in place for extrication?
Hard & Soft protection
What 3 types of glass can one find at an RTC?
Laminated
Tempered
Polycarbonate
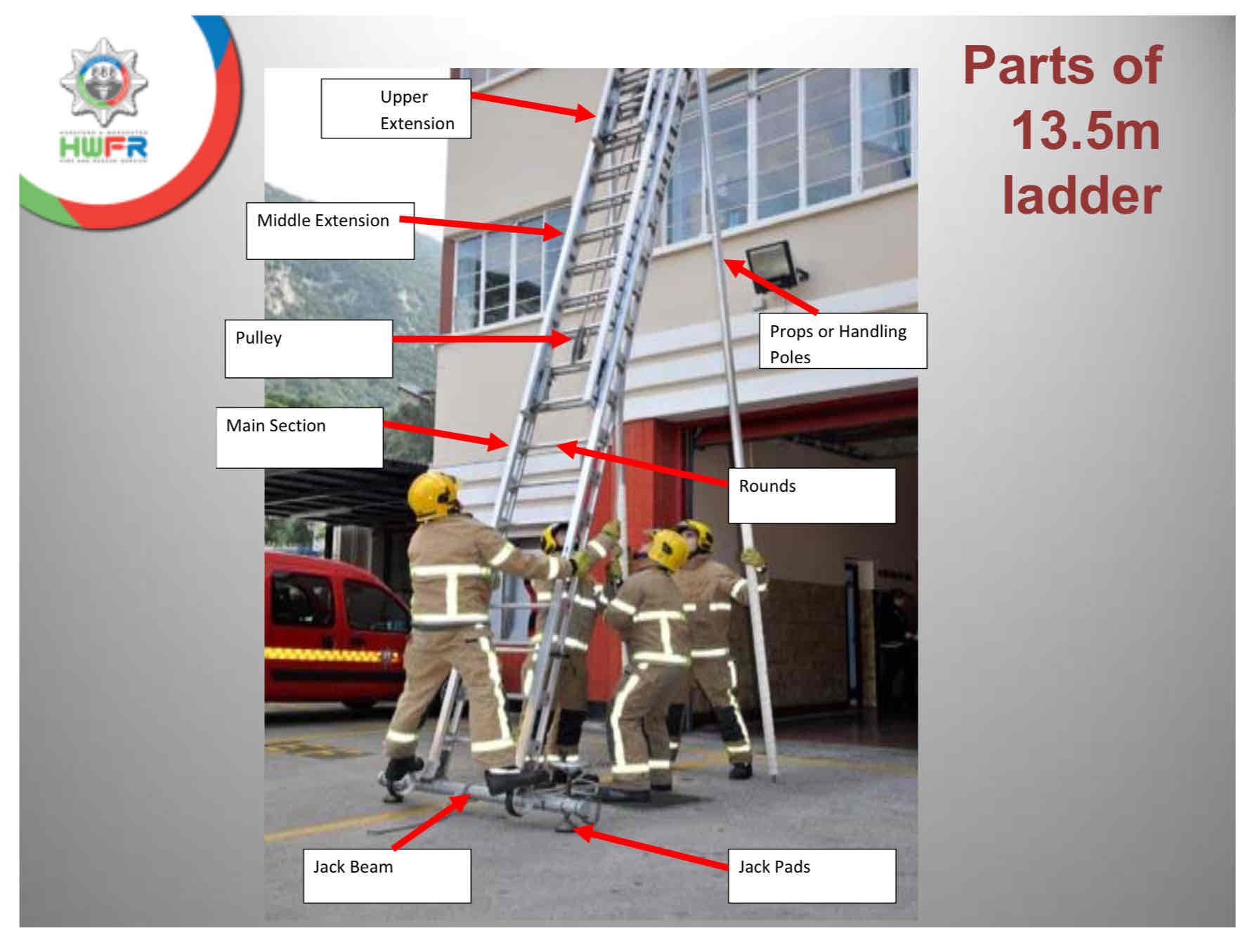
13.5 components - name as many as you can.
Round
Strings
Jack beam
Jack pads
Pulley
Cable
AAD
Poles/Props
Main section
Middle section
Upper section
Rollers
Pawls
Line
What’s the minimum safe distance between a ladder and building?
1/3rd of the working height
What are the purpose of rollers on our ladder?
To roll up the walls of buildings.
How is the Incident Command point indicated on the truck?
A flashing red/orange Beacon
What are the 6 phases of an RTC Rescue?
Scene safety and assessment
Initial access & Stablisation
Glass management/peel & reveal & Tool prep
Space Creation
Full Access
Extrication & Transport
When can you haul someone out of a vehicle?
If they’re not breathing (but think you can still save their life)
Vehicle is in precarious location and/or situation (on fire etc)
What routine vehicle checks would you do on an appliance?
Petrol/Diesel
Oil
Water - coolant, screen wash + FF water
Damage/Drivetrain/Destination
Electrics - lights
Rubbers - tyres
You - license, fit and well
What does METHANE stand for?
My call sign
Exact location
Type of incident
Hazards present/expected
Access routes
No. Of casualties
Emergency services present and required
Name 5 features of the MDT
Mapping information
Vehicle information - crash data
Hydrant locations
Handbook files - library of operational information
Chem information
What is the order of Radio messages at an incident?
Mobile (sent via MDT)
In attendance (sent by MDT)
Assistance
Informative
Stop message
What’s are the two types of pumps found on an appliance?
Centrifugal
Peripheral
What are the checks needed to maintain an LPP pump?
Petrol
Oil
Water
Electrics
Rubbers
Seals
You notice an increase in pressure whilst at work (low pressure gauge). What could be the causes?
Closing down of a branch
Debris/vehicle on the hose
Severe kink in the hose
Blockage at the branch nozzle
What are the causes for a decrease in pressure whilst at work (low pressure guage)
Opening up of a branch
Burst length of hose
Pumping from an open water source, you notice a Decrease Vacuum Reading from 0.5 to 0.3 bar. What could be the causes?
Rise in the level of supply
Suction strainer is unblocked
Branch has closed down
Restriction on outlet side is released
What’s the maximum output from an Akron 1720 Turbojet mainline branch?
475l/min (115 l/min is the lowest)
What helps account for the 2m difference between practical and theoretical lift?
Create the flow
Raising the water
Entry loss
Suction and strainer
Temperature
What amount of pressure is lost for each length of hose, and for each 1m of lift, respectively?
0.2 bar for each length of hose
0.1 bar for each 1m of lift
You’re pumping from Appliance, currently at 3 bar. The pressure raises to 3.5 bar. What could be the reasons?
Branch has been closed down
Blockage in the jet
Something parked on the hose
What are the two types of assessments carried out at an incident?
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Analytical Risk Assessment
There is no vacuum reading at a pump. Why?
Air in the pump
No water
Air leaks in the hose
Lift is too great (crest)
Primer is broken
Faulty gauge
Seals and glands may be dry
What are the structural elements of a compartment called?
Arches
Beams
Columns
Floors
Lintels
Load bearing walls
Connectors
Trusses
Air supported structures

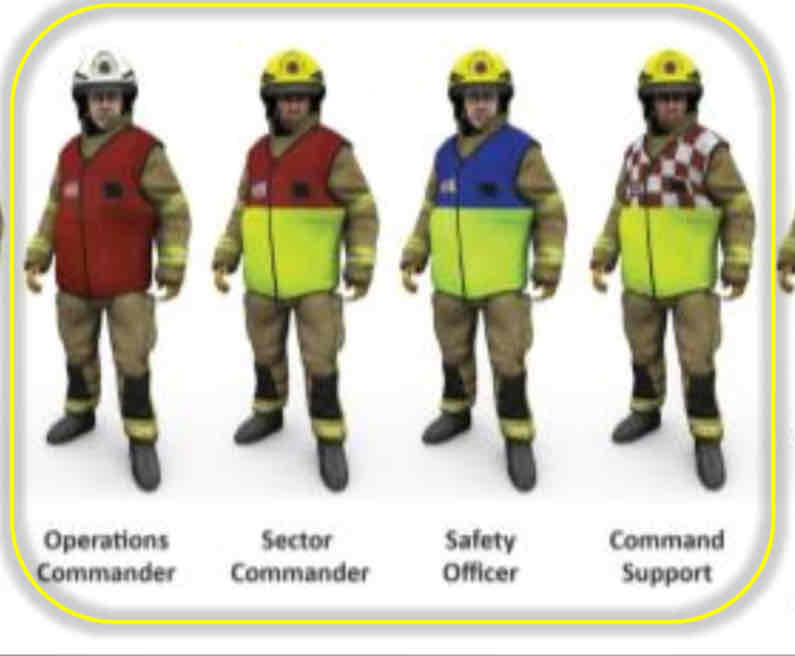
Identify the roles of the firefighter by their tabards.

What are the 4 common airbags found in a vehicle? What are their safe working distances?
Side (5inches)
Drivers (10inches)
Curtain (15inches)
Passenger (20inches)
You’re doing an initial Scene Survey at an RTC. What are you looking for? (Not sure exam question)
Hazardous substances
Fires
Vehicle loads
Access and stability of vehicles
Fuel leaks
Integrity of fuel systems
Type of fuel (Petrol, LPG, Hybrid, Electric)
Specific site conditions
Number of vehicles
Number of casualties in vehicles
Number of casualties NOT in vehicles
People
Road Debris
What does PDA stand for?
Pre Determined Attendance
What are the two types of Tactical Modes?
Offensive
Defensive
Why do we set up an E.E.P at an incident?
Following an emergency evacuation, a roll call will be taken to account for anyone who is on the fire ground
What does ‘Rest’ mean and who can say it?
Only used by Trainers
Given prior to detailing a learning point
Crew must remain still where they are
Countercommanded by the order “Carry On”
What does the Firefighter Safety Maxim say?
The greater the potential benefit of fire and rescue actions, the greater the risk FFs and commanders will accept
Analytical and DynamIc Risk Assements. What are they?
DRA - a process that involves continually monitoring and analysing risk in a changing environment.
ARA - a more detailed risk assessment (written) based on the DRA.
The command “STILL”. Who can say it and when is used?
Order can be given by ANY member of the crew
Only to be used in an emergency (prevention of an accident )
Crew to remain perfectly still
Countercommanded by order “Carry On”
What type of hazards might you find at an RTC (name 6)
Vehicle construction materials
Vehicle deformation
Air bag locations
Seat belt pre-tensioners
ROPS
Sharps
Bodily fluids
Electrics
Extrication tools
Glass dust
What minimum distance should you park a truck away from an incident on a motorway.
50m
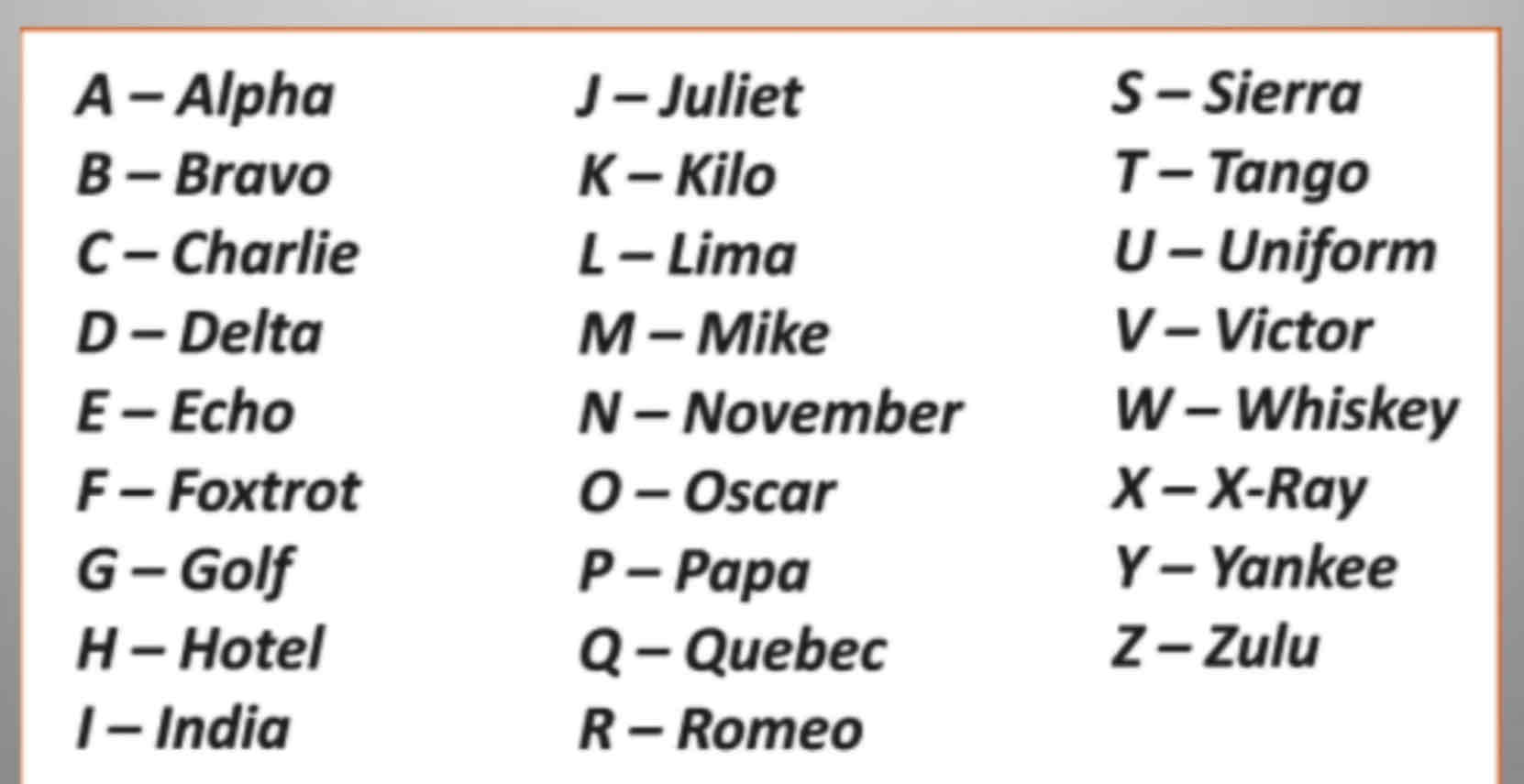
Learn the phonetic alphabet
What does the acronym HAULE stand for?
Height
Area
Use
Location
Equipment
What section of the law gives us our powers at an RTC
Section 44 and 45 of 2004 Fire And Rescue Service Act
How many Lpm is delivered by High pressure hose
200 Lpm
While LPP pumping, you cannot get a prime? Name some reasons why
Air in the system
Basket not under water 300
Lift is too great
Primer broken
Faulty gauge
Seals not sealing
At pump, when you are running out of water. What’s hierarchy of things you can do?
Hydrant
Ask reduce flow
Ask reduce pressure
What can be turned off?
What’s the order of commands for pump op?
Water on
Delivery number 1
4 bar pressure
Working in the open
What distance does suction strainer need to be below water surface to prevent a vortex?
300mm
How many ladders on a truck? Name them
13.5m ladder
9m ladder
Triple extension
Roof ladder
At any speed, when there is no flow, the pressure is at a maximum; it increases/decreases as delivery valves gradually open & the flow increases/decreases?
Decreases & Increases
Name all the commands to pitch a 13.5m ladder.
* Prepare to slip the 13.5m ladder (2&1 on levers facing, 3&4 back to back)
* Slip
* Well (ladder slows down)
* Sight the heal
* Ladder, heal or head left or right
* Under run
* Extend the ladder (strap off, 3 grabs both props, 4&2 extend, 3 aware of cable tension),
* Well, paws and any other height adjustments.
* Head in (props pulled out, then bought back in placed back lightly, outside foot behind props)
* Foot the ladder, ladder footed. (Check x3 points for; 1to3 working height, strings in contact, 3-5rounds above sill, round not on sill,
* Stand clear.
* Drill complete watch
* Ok, knock off make up. Repeated by all,
* Ladder crew,
* Head out (props kicked in couple of inches)
* Extended to lower, well, lower. Lift to lock paws, put strap back on. (Others watch cable as 3 lowers)
* Clear behind
* Under run.
* Ready, brace, lift.
* Re position on truck
* Check then report to watch, drill complete, all gear stowed (done once crew is back in original position)
Climbing the ladder
* Clear the props
* Foot the ladder , ladder footed
* Ladder footed
Before descending
* Clear the props, Foot the ladder, ladder footed
* Paws, step in
* 3,2,1 L or R step off
—-——
9m ladder pitch start to finish
From the mounted position;
* Prepare to slip the 9m ladder
* Slip (2 on gantry, 1 on near side, 3&4 ready to lift and pull ladder down, 3 joins 1 at head once down)
* Well (ladder slows down)
* Release the head
* Sight the heal
* Ladder, heal or head left or right
* Under run
* Extend the ladder (strap off, 4 extends, 3 aware of cable tension),
* Well, paws and any other height adjustments.
* Head in (props pulled out, then bought back in placed back lightly, outside foot behind props)
* Foot the ladder, ladder footed. (Check x3 points for; 1to3 working height, strings in contact, 3-5rounds above sill, round not on sill,
* Stand clear.
* Drill complete watch
* Ok, knock off make up. Repeated by all,
* Ladder crew,
* Head out (props kicked in couple of inches)
* Extended to lower, well, lower. Lift to lock paws, put strap back on. (Others watch cable as 3 lowers)
* Clear behind
* Under run.
* Ready, brace, lift.
* Re position on truck
* Check then report to watch, drill complete, all gear stowed (done once crew is back in original position)
Climbing the ladder
* Foot the ladder, ladder footed
* Ladder footed
Before descending
* Foot the ladder, ladder footed
* Paws, step in
* 3,2,1 L or R step off
Name the parts of a H signs
SOD. Size (mm) Over Distance (m)
Name the types of hose on an appliance
22mm Hose Reel
Lay flat 45mm
Lay flat 70mm
Hard Suction 100mm
Types of knots commonly used
Rolling hitch
Figure of 8
Double sheet bend
Clove hitch
Overhand knot
Bowline
Running bowline
Round turn and two half hitches
What are pump pressures and volumes for low and high pressure pumping?
Low. 4-8bar, 115-475 Lpm
High 20-25bar, 200 Lpm
What’s the size in radius of the action circle at an RY
2-5m
What are the 3 different types of extrication plans at an RTC?
Extrication plans
* Immediate release (no life signs but life can still be potentially saved)
* Rapid release (vital signs are deteriorating rapidly) quick as possible
* Controlled release (casualty is stable in situ )
How is an Incident Command Point (ICP) identified at small incidents?
Identified by red or red/white flashing beacon
Name one function an ICP carries out?
Acts as first contact point for all attending appliances and established radio communications with Fire control
Name one piece of equipment that helps crews to carry out the ICP function?
Incident Command Board and Support pack should be used to support these duties
Circle the correct statement - increase or decrease:
At any given speed, when there is no flow the pressure is at a maximum; it increase/decreases as the delivery valves are gradually opened and the flow increases/decreases
When pump speed increases both pressure and flow increase/decrease
When suction lift increases both pressure and flow increase/decrease
9m ladder commands
Prepare to slip 9M Ladder
Slip
Well
Release the head
Ladder L/R (Heel L&R)
Underrun
Extend
Well, lower
Head in
Adjust Heel L&R
Foot the ladder (ladder footed)
Stand clear
Drill complete, watch
Make up
Ladder crew
Head out
Extend to lower
Well, lower
(Clear behind)
Underrun
Ready, brace lift
Ladder secure
Drill complete, watch all gear stowed
What’s the recognised evacuation signal of any incident?
Repeated Short Sharp blasts in the ACME Thunderer Whistle.
On hearing this signal everyone should blow their whistles to also give the warning, to amplify its importance and ensure all personnel are aware across the whole incident. This means evacuate the incident ground and go to the EEP.