Echocardiography
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Echocardiography
an ultrasonic diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the structures and motion of the heart
Echocardiography uses _______-______ frequency sound waves ( > _______ Hz)
ultra-high; 20,000 Hz
Frame rate
number of updated images per second
The higher the frame rate, the _________ the image
better
Frequency
number of emitted waves per second; measured in MHz
Higher frequency results in _________ resolution images
high
Draw back to higher frequency
low penetration of tissue
Low frequency results in _________ resolution images, but has _________ penetration of tissues
low; higher
What species would a higher frequency be used? Low frequency?
high frequency: smaller animals, like dogs and cats
low frequency: larger animals, like horses
What type of transducer is used for electrocardiography?
sector transducer
sector transducer
creates 512 ultrasound lines in the shape of a triangle
Frequency range of sector transducer
2-16 MHz
Two methods of diagnotic imaging for echocardiography:
1.) transthoracic
2.) transesophageal
transthoracic
probe is placed underneath the animal against the thoracic wall
Why is the ultrasound probe positioned underneath an animal when looking at the heart?
the lungs encase the heart from almost all directions, and only by going underneath the animal can the heart be visualized
Where specfically can the heart be visualized betwen the lungs?
cardiac notch
Three "echo windows" for transthoracic echocardiography
1.) right parasternal
2.) subcostal
3.) left parasternal
transesophageal
endoscope with probe attached on the end is drawn down the esophags to view the heart from above
Purpose of the simultaneos ECG during echocardiography
to allow for exact timing of mechanial events during the cardaic cycle and to relate images to certain phases of the cardiac cycle
During what phase of the cardiac cycle on the ECG will the ventricles be largest?
diastole; just before QRS
During what phase of the cardiac cycle on the ECG will the ventricles be smallest?
systole; by end of T wave
Four modes of echocardiography:
1.) 2-dimensional
2.) 3-dimensional
3.) M-mode
4.) Doppler
2-dimensional echocardiography
heart is displayed in black (blood) and white (soft tissue) in 2 dimensions in real time, and motion of structures (e.g., valves, chambers, walls) can be watched "live"
Four image planes using 2-D echocardiography
1.) right parasternal long axis view
2.) right parasternal short axis view
3.) right parasternal subcostal view
4.) left parasternal apical view
right parasternal long axis view
used for four chamber or five chamber view when the dog in on their right side
For right parasternal long axis view, the four chamber view focuses on the _______ valve while the five chamber view focuses on the _______ valve
mitral; aortic
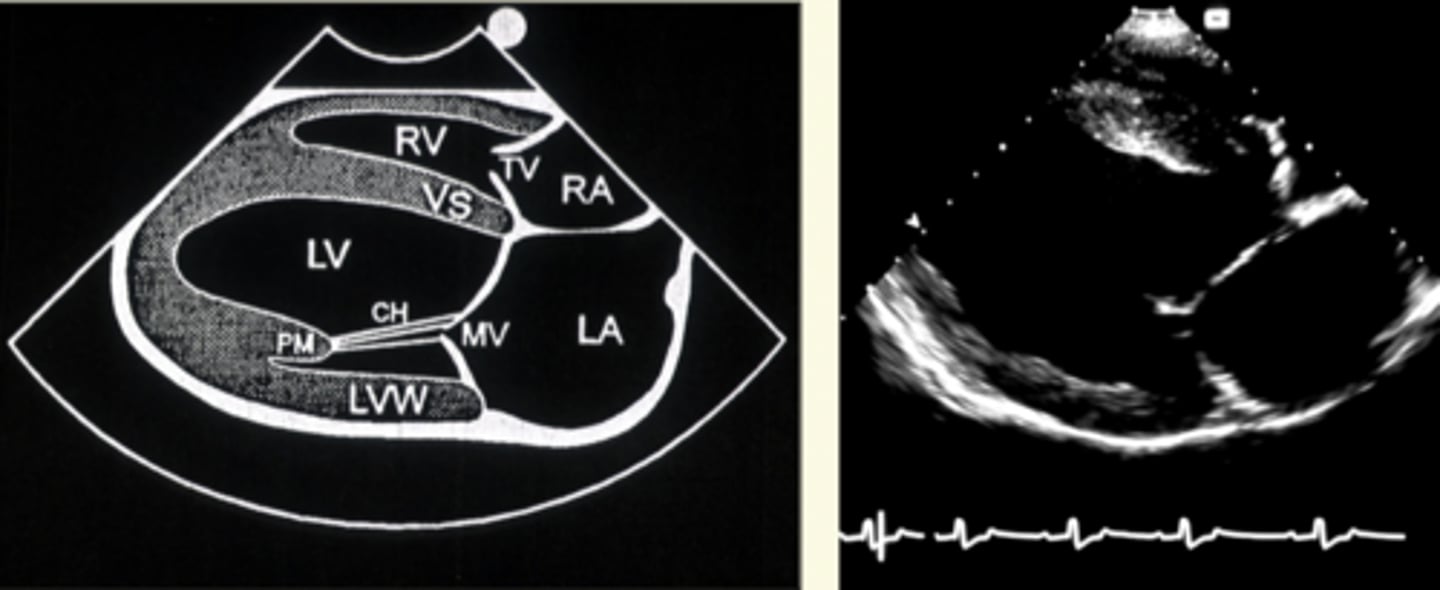
what is the right parasternal long axis view used to evaluate?
LV outflow, systolic function, and valve function
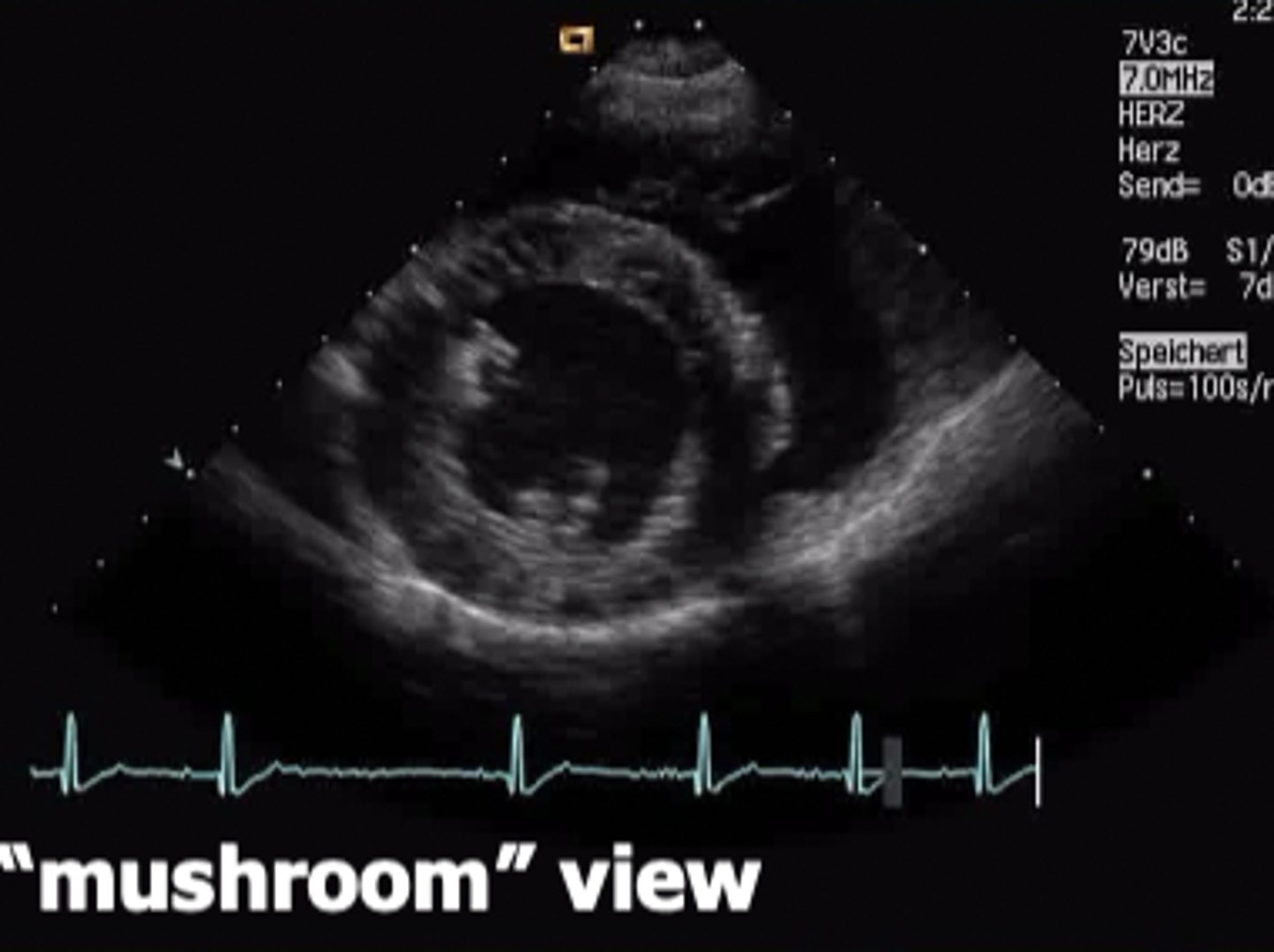
right parasternal short axis view
view that slices the heart in different crossections at several different levels (from apex to base)
What does the parasternal short axis view look like at the level of papillary muscle?
mushroom
What does the parasternal short axis view look like at the level of the mitral valve?
fish mouth
What does the parasternal short axis view look like at the level of the aortic valve?
mercedes benz logo
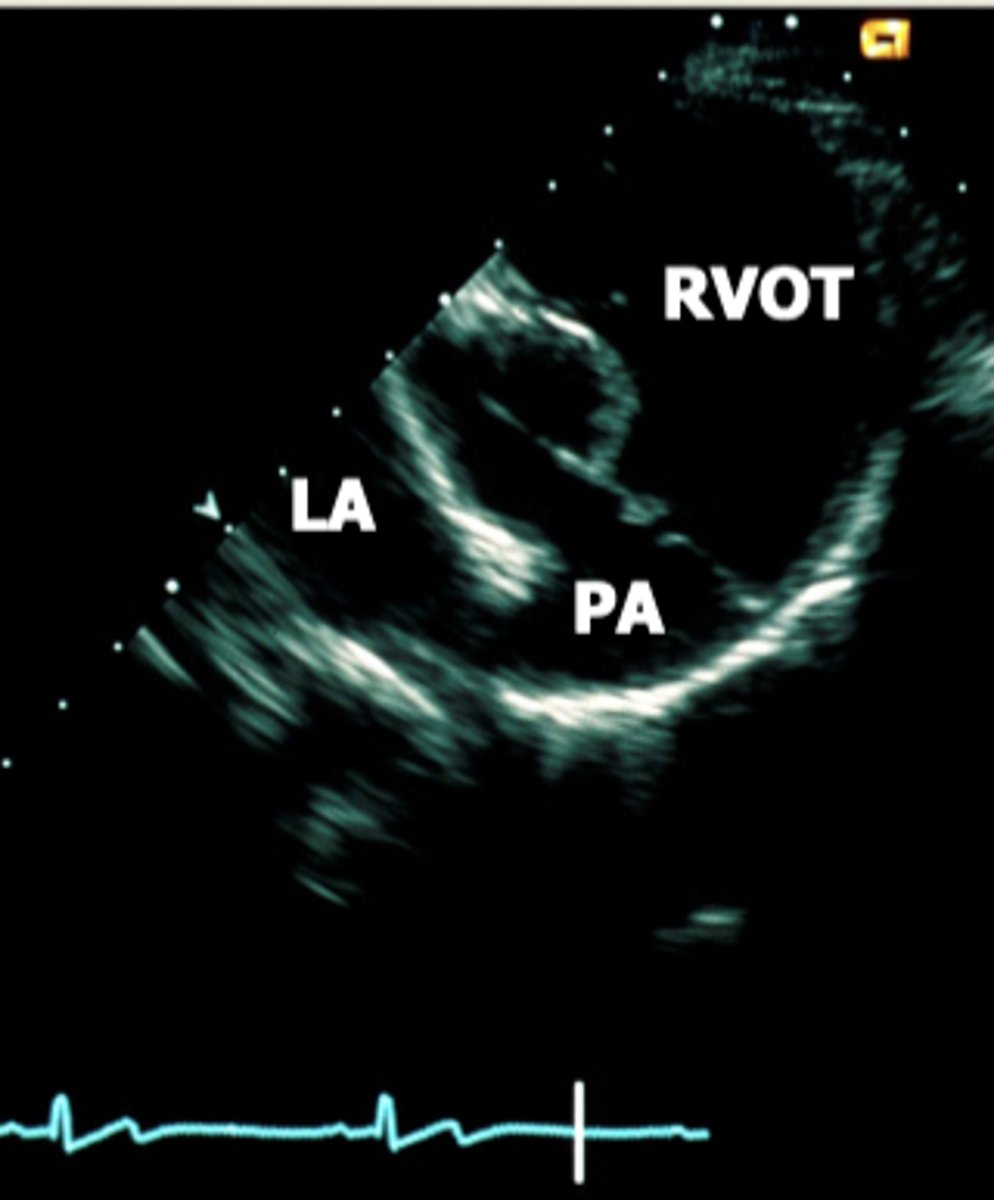
right parasternal subcostal view
view that best aligns with direction of the blood flow; used to truly measure velocity
left parasternal apical view
used for four chamber or five chamber view when the dog in on their left side
For left parasternal apical view, what can be evaluated in the four chamber view?
tricupsid and mitral valve
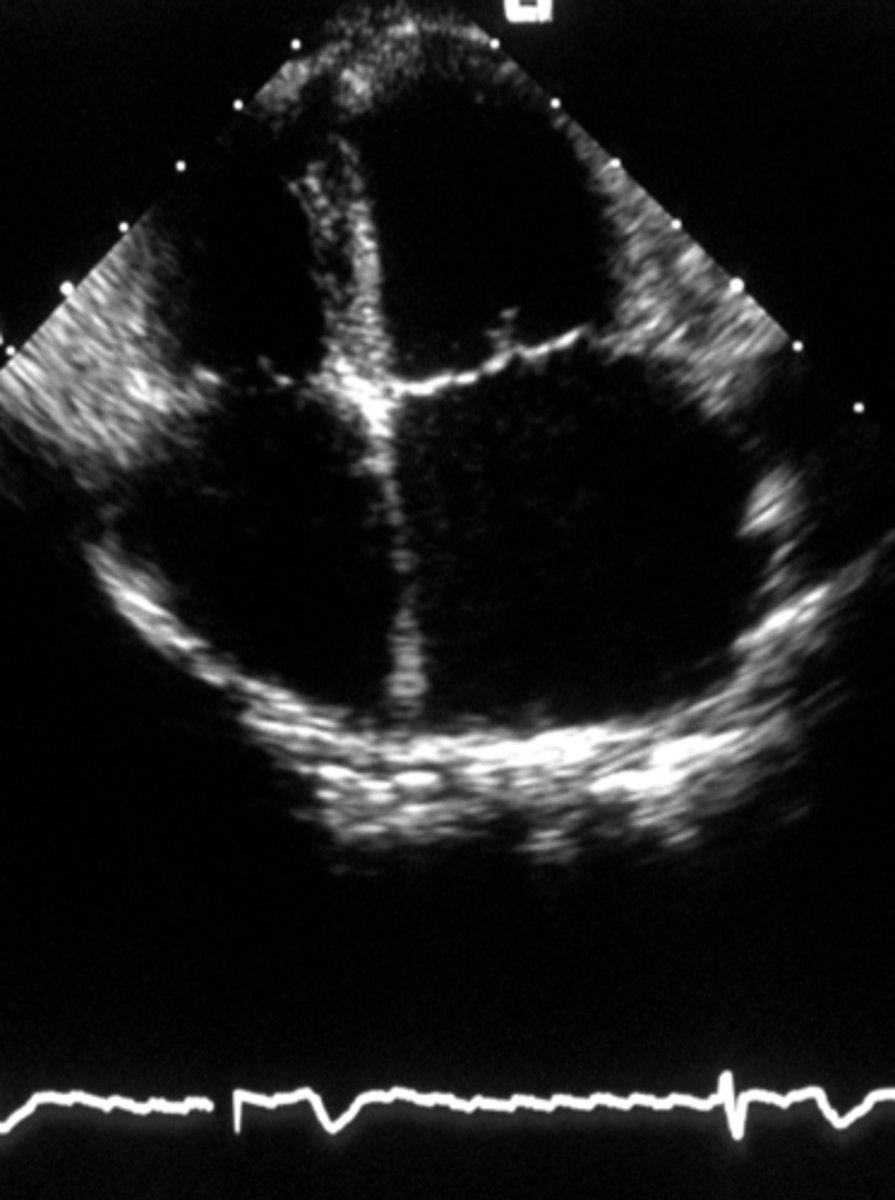
For left parasternal apical view, what can be evaluated in the five chamber view?
aortic valve
M-mode echocardiography
one-dimensional imaging used to display motion of certain parts along a single ultrasound line
M-mode echocardiography is applied during assessment of what?
Left ventricular systolic function
How is left ventricular systolic function measured using M-mode echocardiography?
a single ultrasound line is plotted against time so that you can visualize the widening (diastole) and narrowing (systole) of the ventricle as it contracts
Shortening fraction
percent change in ventricular diameter during diastole and systole; measured using M-mode echocardiography
Ideal shortening fraction in dogs
25-45%
Ideal shortening fraction in cats
35-55%
Doppler echocardiography
used to determine blood flow
Doppler principle
when ultrasound waves hit moving objects they change their reflected frequency, which is proportional to the velocity of the object
Doppler frequency shift
the difference between the frequencies of emitted and reflected waves
The Doppler frequency shift is ________
audible
Three qualities of blood flow doppler can identify:
1.) direction
2.) velocity
3.) quality of flow
Two flow qualities
laminar and turbulent
_________ is normal blood flow while __________ is abnormal blood flow
laminar; turbulent
What can turbulent blood flow be caused by?
valve stenosis, valve insufficiency, shunt flow
Two types of doppler echocardiography
1.) spectral
2.) color
spectral doppler
displays blood flow as a spectrum of velocities
color doppler
displays blood flow as red (toward the transducer) and blue (away from transducer)
What color will turbulent blood flow appear using color doppler?
mixed colors including green and yellow
How is left ventricular diastolic function assessed?
using pulsed wave doppler (type of spectral doppler)
pulsed wave doppler
uses pulses of sound to obtain Doppler signals from a user-specified depth
To assess left ventricular diastolic function, pulse wave inflow signals are recorded at the level of the opened _______ or _______ valves
mitral; tricupsid
How is valve competence assessed?
using color doppler
Which of the following statements regarding echocardiography is CORRECT?
a. Echocardiography uses ultrasound frequencies between 100Hz and 20,000 Hz.
b. The transducer frequency is equivalent to the number of updated images/sec.
c. Low frequency transducers have high penetration but low resolution.
d. The frequency range used in Doppler ultrasound is between 18 and 32 MHz.
e. Doppler echocardiography is used to estimate blood volume in cardiac chambers.
c. Low frequency transducers have high penetration but low resolution.
M-mode echocardiography is preferentially used to estimate LV systolic function via left ventricular shortening fraction?
a. True
b. False
a. True
Which statement regarding Doppler ultrasound is CORRECT?
a. This method is used to measure systolic function of the right ventricle and the left atrium.
b. The Doppler principle states that ultrasound waves are reflected twice ('double') if stationary organs are hit (e.g., theliver).
c. The Doppler shift is used to generate high contrast black and white images.
d. The Doppler shift can easily be displayed on the Doppler echocardiogram; however, it is not audible.
e. The Doppler shift is the difference between emitted and reflected (received) ultrasound.
e. The Doppler shift is the difference between emitted and reflected (received) ultrasound.
All statements regarding color flow Doppler (CFD) echocardiography are correct, EXCEPT:
a. CFD is used to identify direction of blood flow
b. CFD is used to estimate velocity of blood flow
c. Red color indicates flow away from the transducer
d. Green-yellow color indicates flow turbulence
e. Laminar flow is displayed in monochromatic red or blue color
c. Red color indicates flow away from the transducer