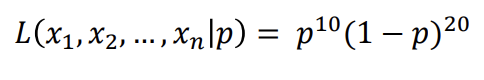Likelihood and Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE)
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to likelihood, probability, and maximum likelihood estimation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Likelihood
Tells us how likely different parameter values are, given the observed data.
Bernoulli likelihood
Gives the relative likelihood of what the true value of p could be given a particular outcome (data).
Bayesian approach
Uses the whole likelihood function along with a prior distribution to produce the posterior distribution using Bayes theorem.
Frequentist approach
Finds the most likely value of the parameter and uses this value as a point estimate for the parameter.
Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE)
The frequentist approach of finding the most likely value of a parameter as a point estimate.
Finding the MLE
Differentiate the likelihood function with respect to the parameter, equate it to 0, and solve for the value of the parameter that will maximize it.
Log-likelihood
Log transformation of the likelihood function, used since it is easier to differentiate and solve.
Probability
Tells us the chance of observing certain data, given that the parameters of the model are known.
In Probability, what is fixed and what is unknown?
Parameters are fixed (known), data is unknown.
In Likelihood, what is fixed and what is unknown?
Data is fixed (observed), parameters are unknown.
If we observe 10 heads out of 30 trials, what is the Bernoulli Likelihood function?