Physics P5-P8
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
How do you find amplitude on a wave diagram?
Distance from centre line to peak or trough.
1/2 of distance from peak to trough.
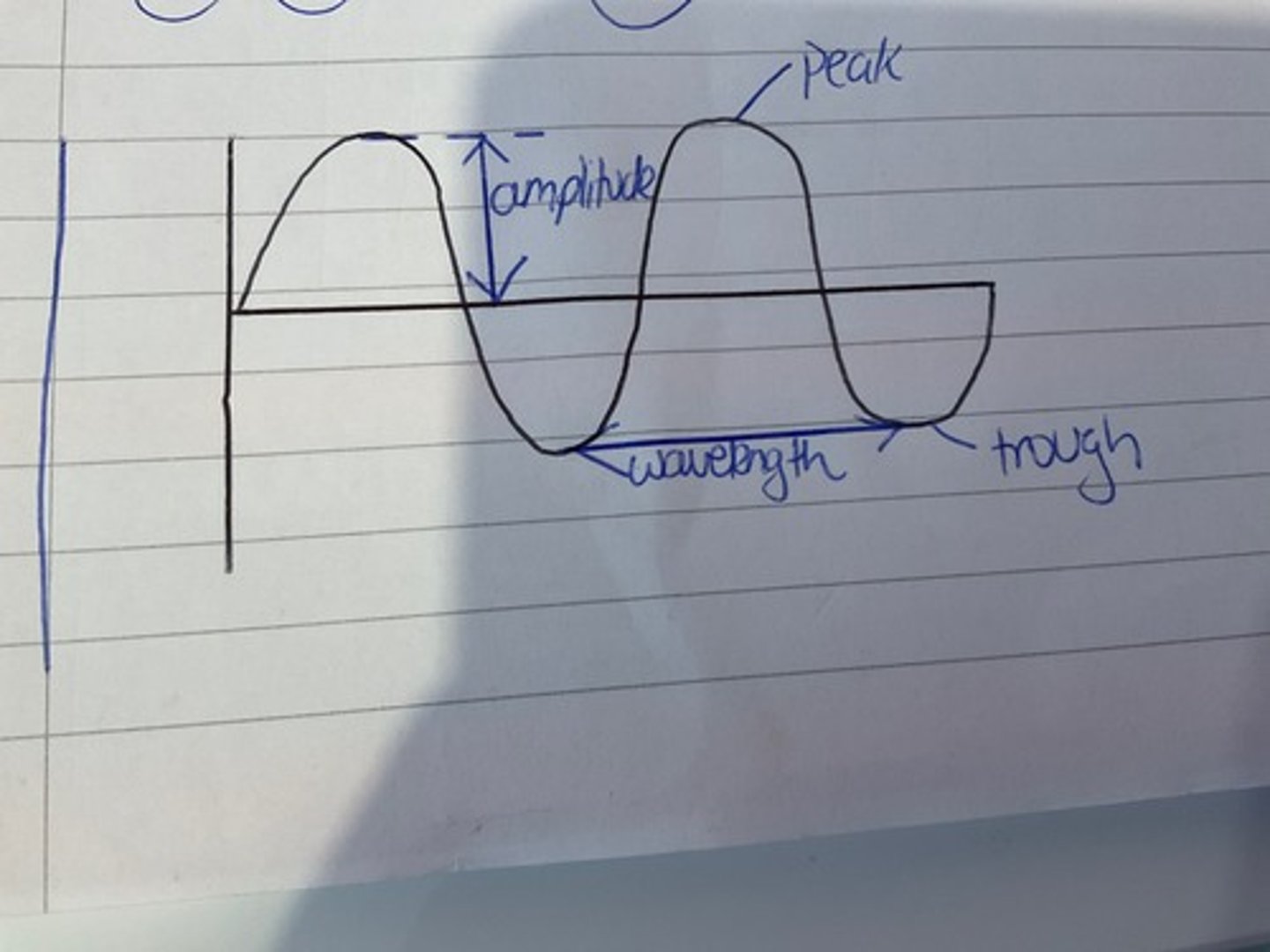
How do you find wavelength from a transverse wave graph?
Distance from trough to trough, or from peak to peak.
Double distance from peak to trough.
What is the difference between a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave?
Transverse: oscillations are perpendicular to direction of energy transfer. eg water waves, light waves.
Longitudinal: oscillations parallel to direction of energy transfer. eg Sound waves
What is a compression?
-Region of high pressure where particles have moved close together.
What is a rarefaction?
-Low pressure where particles have moved further apart.
How do you find wavelength on a longitudinal wave graph.
Distance from compression to compression, or rarefaction to rarefaction.
What is time period?
The time taken for one complete oscillation
What is frequency?
Number of waves per second past a given point.
What is the relationship between time period and frequency?
T = 1/f
f = 1/T
What is the equation for wavespeed?
wavespeed = frequency x wavelength
What is a ripple tank?
-Shallow glass tank filled with water and contains an oscillating paddle. The paddle produces waves at a constant frequency.
How do you measure wavespeed using a ripple tank?
Calculate wavelength:
-Place ruler on white paper underneath the ripple tank.
-Take a picture of shadow cast onto paper.
Using a ruler, measure a distance between centres of 11 crests(dark patches).
-Divide by 10 to measure wavelength.
Calculate Frequency:
-Mark fixed point on paper.
-Using a stopwatch record the number of dark lines(peaks) that pass the marker in 60s. Divide this by 60 to get frequency.
Use V = frequency x wavelength to calculate wavespeed.
How do you measure the speed of sound in air w/out an oscilloscope?
-Measure distance of 100m with a trundle wheel.
-With one person at one end, clap using cymbals.
-Other person 100m away would start the stopwatch when they see the cymbals connect, and stop it when they hear the cymbals.
-Use equation s = d/t to calculate wavespeed..
How do you measure the speed of sound in air w/ an oscilloscope?
Determine wavelength:
-Start with the 2 microphones connected to an oscilloscope next to eachother. Generate a known frequency with a speaker and a signal generator.
-Move one microphone until the 2 traces(waves) on the oscilloscope are in phase (aligned with eachother)
-Measure the distance between the microphones with a ruler: this is the wavelength of the sound wave.
To calculate wave speed:
-use V = frequency x wavelength.
Why isn't a bell in a vaccum heard when hit?
-No particles next to bell for energy to be transferred to.
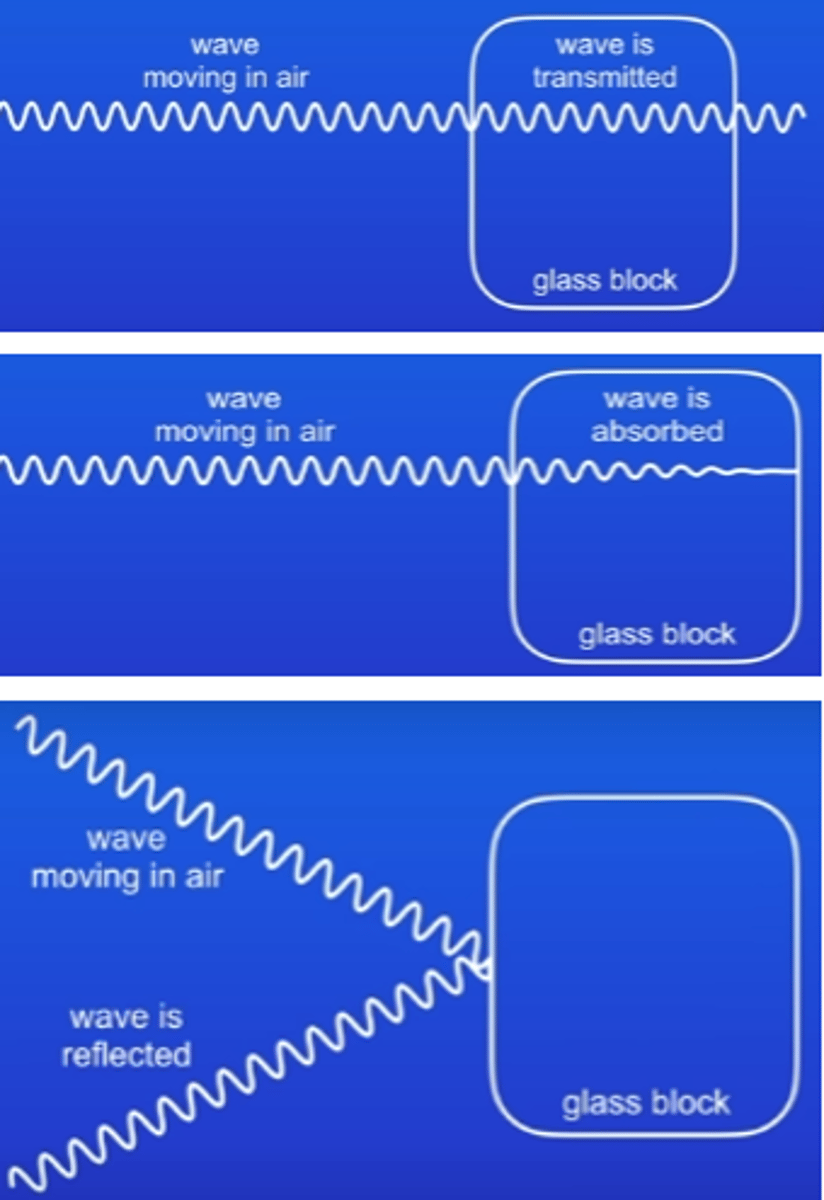
What 3 things can happen when a wave hits a boundary between 2 media?
Reflection: bounces off of boundary.
Transmission(and possible refraction) travels through boundary.
Absorption wave stopped by boundary.
How does the ear hear?
-Sound waves collected by pinna (outer ear). These waves travel along the ear canal.
-The waves reach the eardrum and make it vibrate. The ossicles amplify the vibrations.
-The cochlea contains fluid which transmits the movement from the oval window to small hairs called cilia on the inside wall of the cochlea.
-Hairs are attached to sound-detecting cells which release chemical substances. These substances make nerves send a signal down the auditory nerve to the brain.
What range of sound can humans hear?
-Frequencies between 20Hz- 20 kHz.
-Sound above 20kHz is ultrasound.
Name 3 uses of ultrasound.
-Body scanning
-Echolocation
-Finding and treating kidney stones.
Describe how an ultrasound body scan works.
-Apply gel to skin to prevent air gaps- the change of density between air and the skin is so great, most the waves would reflect back.
-Press transducer against body- it emits ultrasound waves which are transmitted into the body.
-The ultrasound waves are partially reflected every time they travel into a tissue with a slightly different density.
-The transducer detects the reflected ultrasound waves and produces a live image on a computer screen.
What properties do all EM waves share?
-are transverse waves.
-Can travel through vacuums.
-Travel at the speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s)
-oscillations of electric and magnetic fields.
What is the order of the EM spectrum?
Radio, Micro, infra-red, visible light, ultra violet, x-rays, gamma rays
-Order of increasing frequency and energy.
-Order of decreasing wavelength.
How are radio waves produced?
-AC in the transmitter produces radiowaves with the same frequency, and induces a matching AC in the receiver.
What is diffraction?
-When a wave passes through a gap or round an obstacle, it spreads out.
-Diffraction is greater when the wavelength of the wave passing through is similar to that of the gap size.
Compare radio and microwaves for use in communication.
Radiowaves:
-Diffract around hills and buildings due to large wavelength: this is an advantage, as a direct line of sight isn't needed between transmitter and receiver.
-A disadvantage is that the signal weakens as the radio wave diffracts.
-Some radio waves pass through the atmosphere bust most are reflected off of the ionosphere.
Microwaves:
-Micro waves can travel through Earth's atmosphere to get to satellites.
-Signal receives and re-transmitted by orbiting satellites.
-A disadvantage is that they need a direct line of sight between retriever and transmitter.
What may cause signal losses in microwaves?
-poor weather
-large areas of water causing scattering(water tends to absorb micro waves)
Describe heating with EM waves.
Infrared(normal oven)
-Heats all particles on surface of food- IR is absorbed by all objects.
-These particles gain ke.
-Heat is transferred to the centre of the food by convection in a liquid and conduction in solid.
Microwaves
-Causes only water of fat molecules to gain ke-penetrates up to 1cm below surface of food.
-Heat transferred through the food via convection in a liquid or conduction in a solid.
Both infrared and microwaves reflect off shiny surfaces.
What emits infra red radiation?
Everything above absolute zero.
What is the range of coloured light.
Red orange yellow, green and blue, indigo and violet (incrreasing frequency and energy.)
What are the 3 primary colours? How do these combine?
red + green = yellow
red + blue = magenta
blue + green = cyan
What is white light
-all wavelengths of visible light.
Specular reflection vs diffuse scattering
Specular reflection: reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction- an image can be seen in the reflection.
Diffuse scattering: reflection from rough surface, causes scattering in various directions: reflected image cannot be seen.
Opaque, translucent andd transparent
Opaque: transmits no light: absorbs some wavelengths of light, and reflects others.
Translucent: transmits most wavelengths of light, absorbs and reflects others.
Transparent: transmits all wavelengths of light: absorbs and reflects some.
What determines the colour of an opaque object?
-Wavelength of light they reflect eg red object reflects red light, and absorbs all other wavelengths.
What is a filter?
A translucent that trnsmits some wavelengths of light, and absorbs the others- used to produce coloured lighting.
Explain what is seen through a red filter.
-White light, containing all wavelengths of light hits the filter- only red light is transmitted, all other wavelengths of light are absorbed.
Explain what is seen through a red and blue filter
-red filter: only lets red light.
-blue: only lets blue light. No light reaches eye- eye perceives as black.
What EM waves are ionising?
UV, X-rays, Gamma rays.
How do ionising EM waves damage cells?
-damaged DNA could mutate leading to uncontrollable division(tumour)
-damage more likely to actively dividing cells.
What can overexposure to UV lead to?
Sunburn, skin cancer, cataracts, premature skin aging.
Benefits of UV light
-stimulates body to produce vitamin D: esssential to absorption of calcium. Diets lacking in vitamin D/calcium can lead to defiency diseases, like rickets.
Natural protection against UV
Darker skin and eye colour caused by chemical called melanin: absorbs more UV radiation, so less reaches underlying body tissues.
Describe how X-rays are formed.
Point transmitter at area of body being X-rayed.
-Place detector, eg film paper, behind body.
-X-rays transmit through patient's body and onto film paper. Film changes from white to black where X-rays hit.
-Dense substances like bone absorb X-rays: film stays white where bones prevent X-rays from hitting film paper.
What is a CCD?
charge coupled device: alternative to film, a digital image is produced which can be stored/ shared more easily than photographic film.
What is a CT scan? What are the advantages vs a normal X-ray?
CT scans involve taking a range of X-ray images from various positions: processed by computer to build a 3D image from cross sections.
-Traditional X-rays give a 2D view from 1 angle can cause detail to be obscured by other body structures.
Medical Tracer
Another scanning technique using x-rays and gamma rays.
How does sterilisation involve gamma rays? What are the advantages?
-Food can be irradiated with high doses of gamma rays to kill bacteria. Keeps them fresh without contaminating them.
-Medical equipment sterilised the same way.
What are 2 uses of gamma rays?
-Sterilisation
-Gamma knife.
Gamma knife
-used to fire a narrow beam of low intensity gamma rays to treat diseases/ lesions.
What is the law of reflection?
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
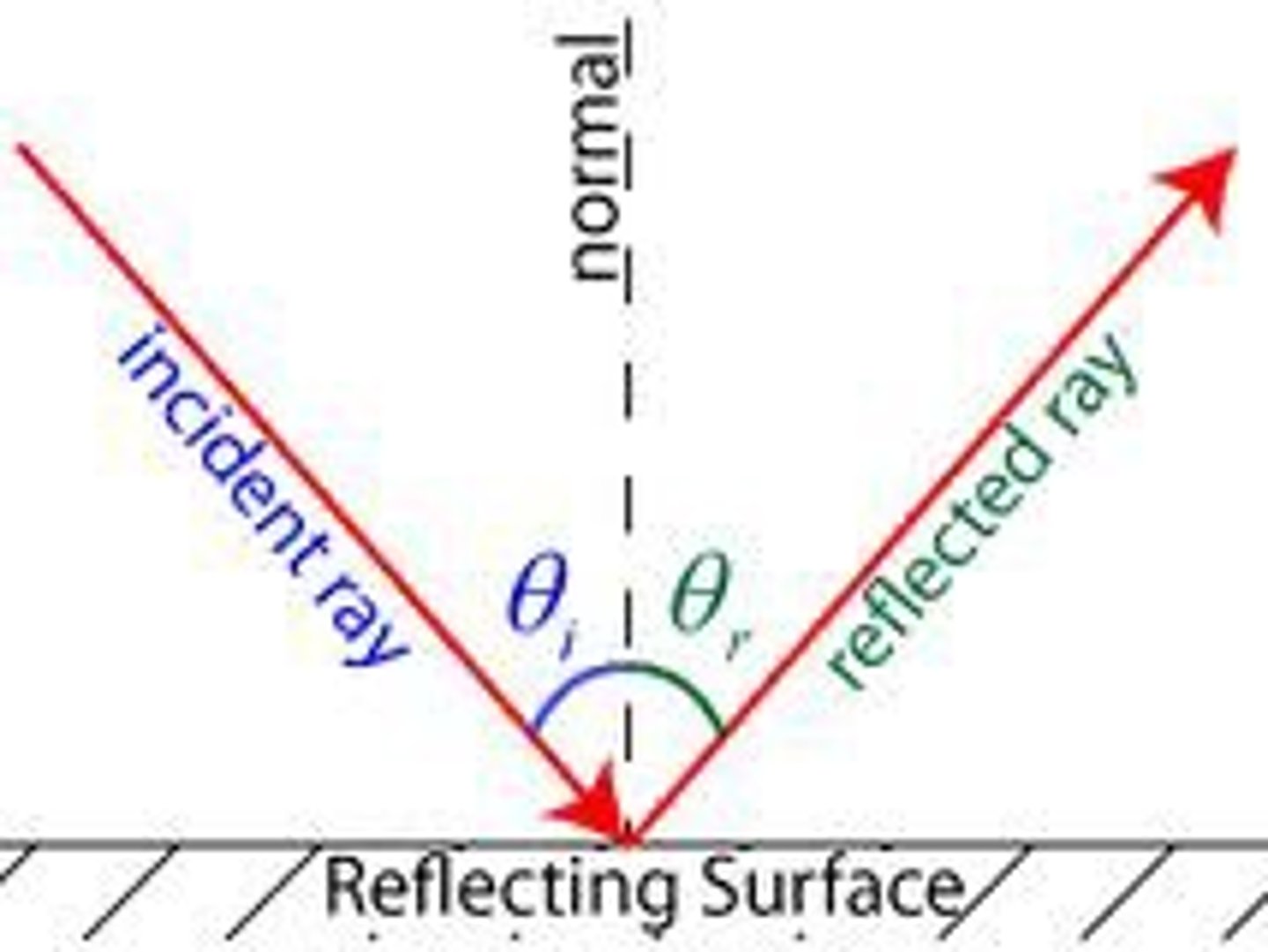
What is the normal?
Imaginary line drawn as a dotted line: angle of incidence/reflection measured from this.
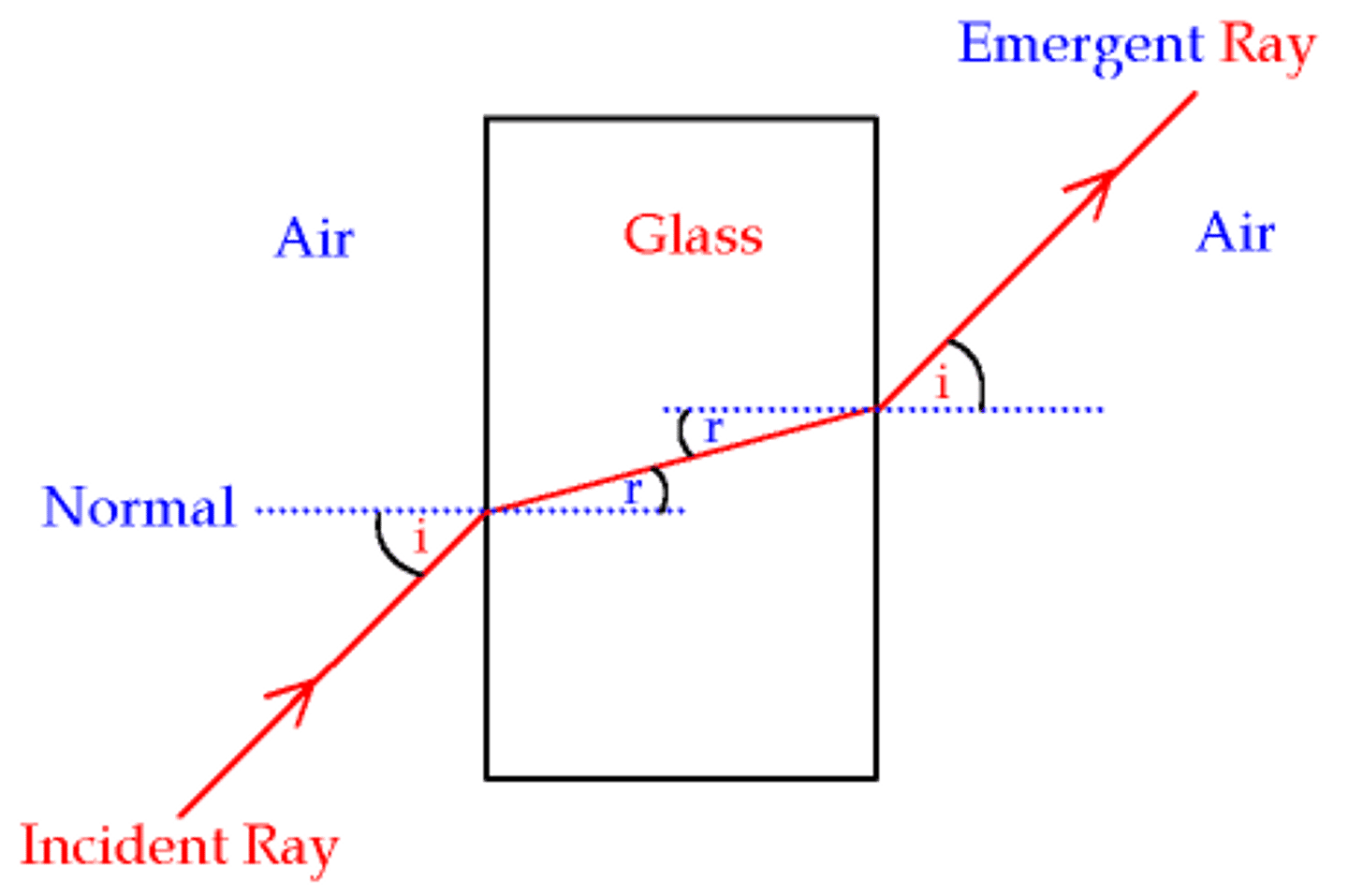
Refraction
What light enters a desner medium, it slows down an bends towards the normal.
-when light enters a less dense medium, it speeds up and bends away from the normal.
Dispeersion
Seprating white light into spectral colours.
-White light contains all wavelengths of light: violet light bends towards the normal the most.
Refractive index
higher refractive index: light is slowed down more.
Violet travels slowest: highest index
Red travels fastest: smallest index
How do you do the refraction practical?
Place perspex block on the white paper, trace outline with pencil.
Draw the normal at right angles to surface of one long side of the outline, passing through to middle of block.
Use a protractor to measure and draw incident rays at 20 40 and 60 degrees from normal.
Place the block back. Shine a single incident ray nto block along first incident ray line.
Mark with dots where it leaves the the block,and where it reaches the edge of the paper.
-Remove the block and ray box, and join up the dots with a pencil and ruler.
What is a len?
-Lens refract light and are usually used to form images.
2 types of lens?
Convex: thicker at centre than edge.
Concave: thicker at edges than centre.
What are the symbols for concave and convex lenses?
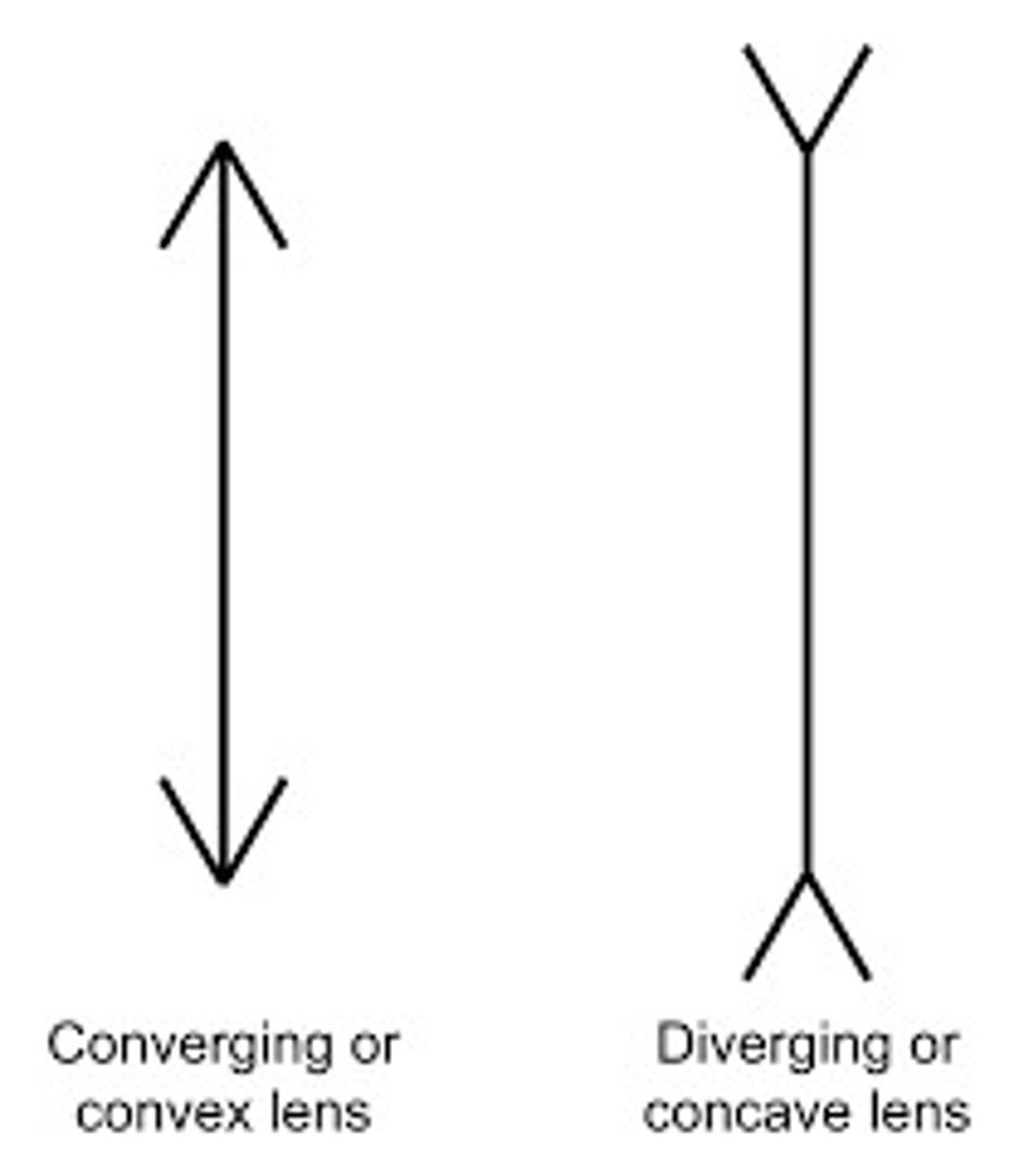
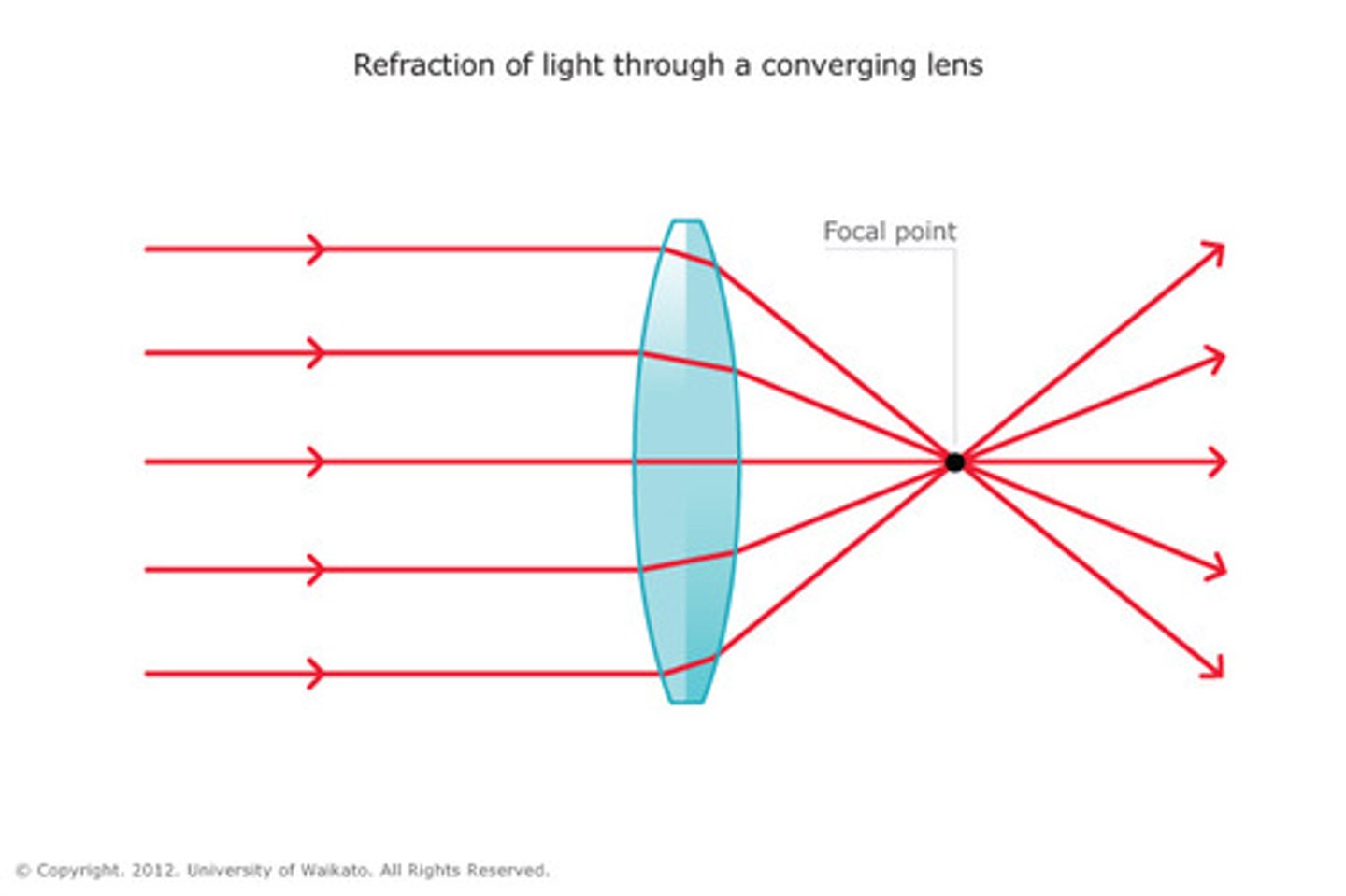
Draw a ray diagram for a conex lens.
-Rays hit lens perpendicular, pass through far focal point.
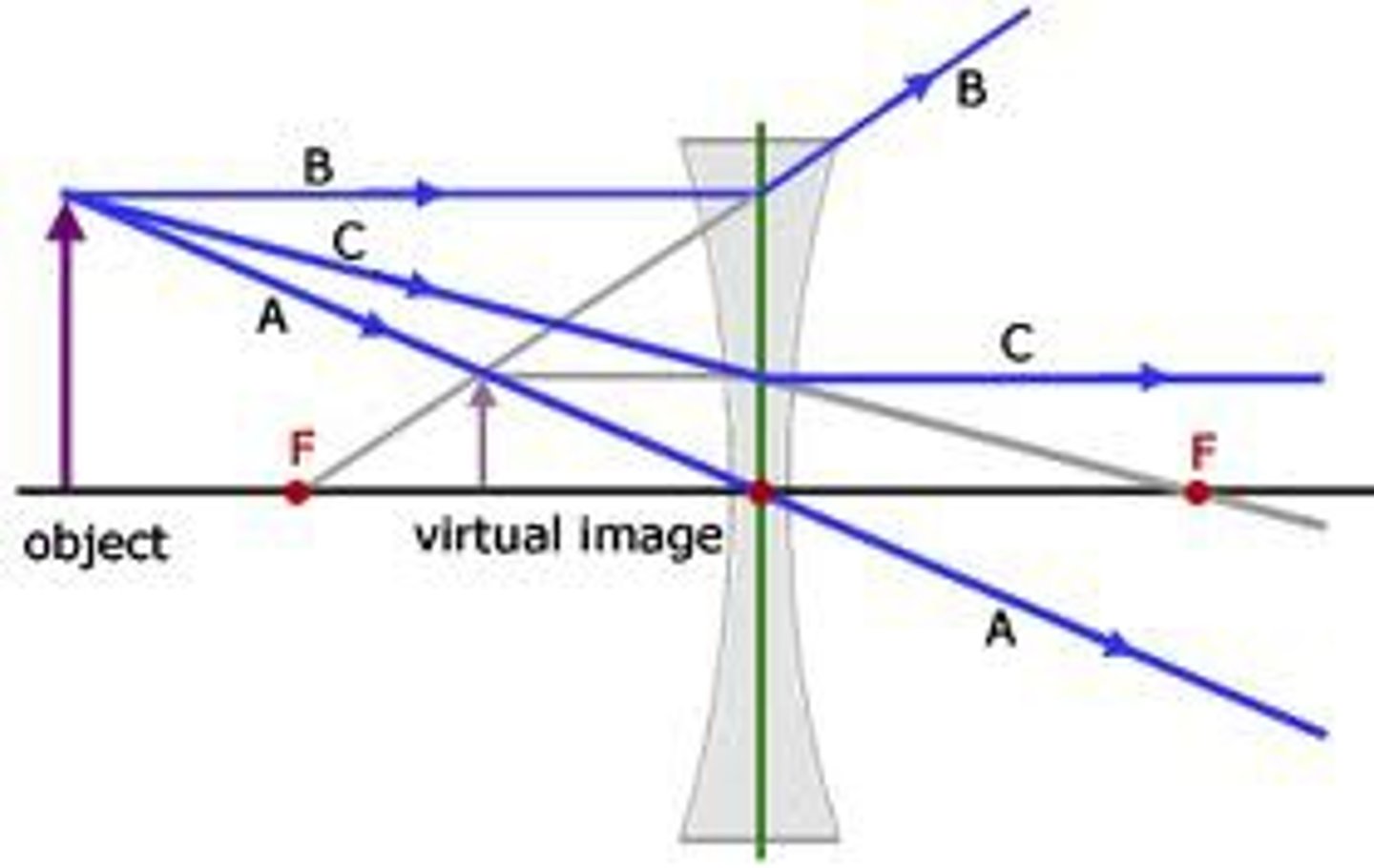
Draw a ray diagram for a concave lens.
-Rays hitting perpendicular to lens axis pass through lens as if they were travelling straight from near focal point.
Rules for ray diagrams(convex)
-Any ray that hits the lens axis at 90 degrees will pass through the far focal point.
-Any ray that hits the centre of the lens will pass through without changing direction.
-Any ray that passes through the near focal point and then hits the lens wlll leave the lens perpendicular to lens axis.
Define real vs virtual image.
Real: rays converge on other side of lens. Can be projected onto screen.
Virtual: rays, if traced backwards, converge on same side they came from.
What kind of image is formed by a convex lens if the object was placed outside of 2 focal points? What uses does this have?
Image position:
between 1 and 2 focal points
Diminished
Real
Inverted
Cameras and eyes use this lens.
What kind of image is formed by a convex lens if the object was placed at 2 focal points? What uses does this have?
Image position:
at 2F
same size
Real
Inverted
copying camera, where image has to be to same scale, photocopiers.
Image formed if object between F-2F + uses.
Image position:
outside 2F
Magnified
Real
Inverted
Projectors
Image formed at F + uses
no image. searchlight: perfectly straight beam of light that doesnt get weaker with distance.
Image formed inside F + uses
inside 2 near focal points, magnified, virtual magnifying glass. upright
What lens is used to correct myopia?
Focal point is in front of retina: concave lens diverges light to bring image formed into focus.
What lens is used to correct hyperopia?
Focal point of rays behind retina: ocvex lens converge light rays to bring image back into focus.
Why is violet light refracted more than red light in a prism?
-violet light has a higher frequency than red light and higher refractive index: bends away from normal more after leaving denser medium.
What is an isotope of an element?
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons
What is a nucleon?
Particle found in the nucleus of atom (protons and neutrons)
What characteristics do all radioactive atoms share?
-They all have unstable nuclei: decay is a product of the atom's attempt to become stable.
5 types of radiation
Alpha, beta, gamma, proton, neutron
Alpha Radiation and characteristics. How fast does it move? What is its charge? Why is it emiited?
-Comprised of a helium nucleus(2 protons and 2 neutrons)
-moves at 10% speed of light. Charge of 2+
-Emitted from a too large nucleus.
Beta Radiation and characteristics
-Comprised of a fast-moving electron at 90% speed of light.
1- charge.
-Emitted when ratio of neutrons: protons is too large.
Gamma Radiation and characteristics
Comprised of a gamma ray, a high energy electromagnetic wave(not a particle) that moves at the speed of light..
-No mass and no charge.
-Emitted when nucleus of the atom has too much energy.
Neutron decay and characteristics
-Fast moving neutron released from nucleus.
-Hard to detect as it isn't ionising.(lacks charge)
Proton decay and characteristics
Fast moving proton released from nucleus, ionising as it has a charge.
Compare alpha, beta and gamma radiation
Alpha: largest mass, slowest speed, most ionising
Beta: smaller, faster, harder to stop than alpha.
Gamma: Fastest, least ionising, unstoppable
What is a nuclear equation?
Explain what changes occur in an atom when undergoing radioactive decay
symbol for alpha particle, mass and atomic number
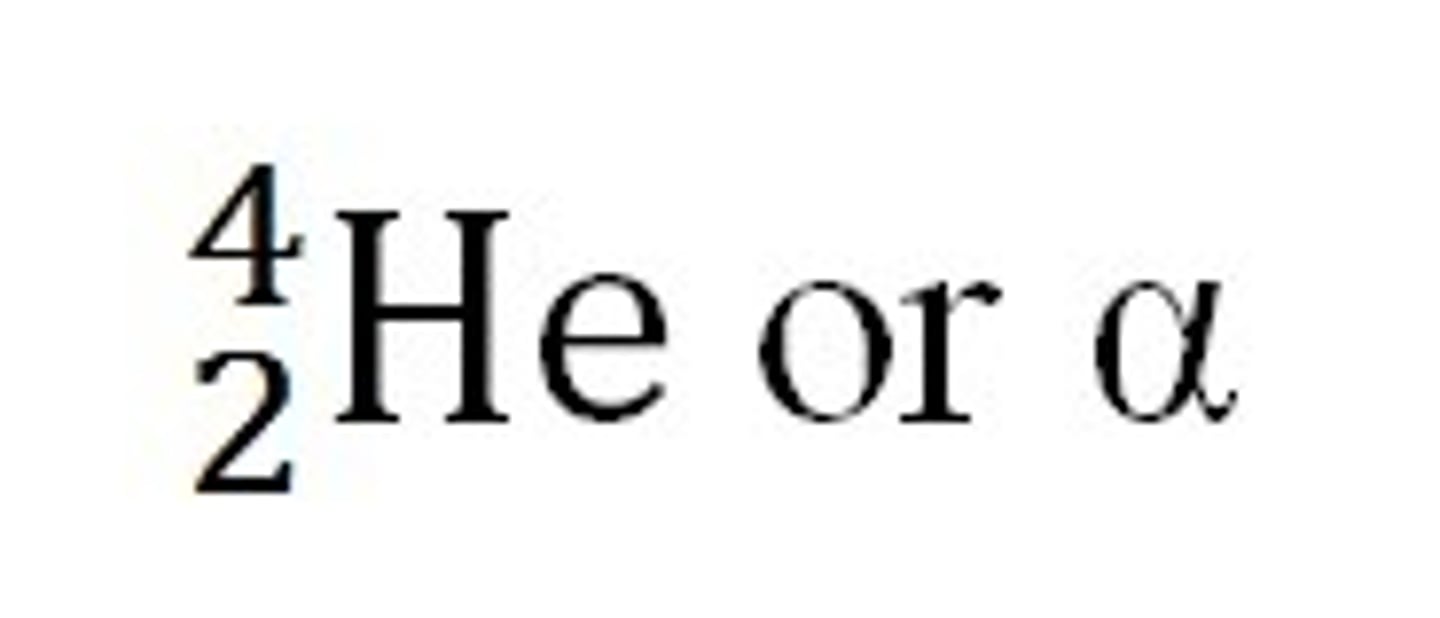
symbol for beta particle, mass and atomic number
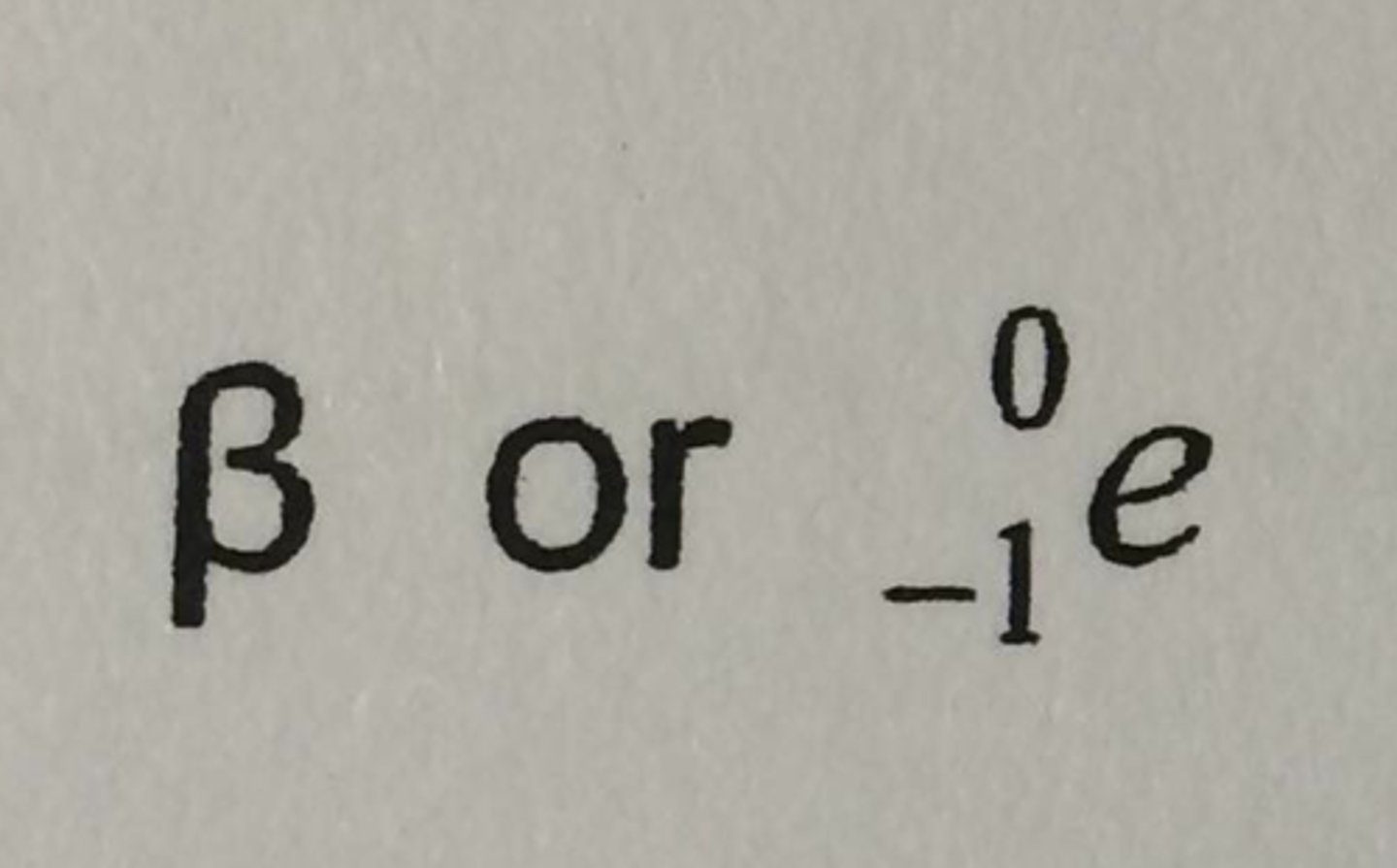
symbol for gamma ray, mass and atomic number
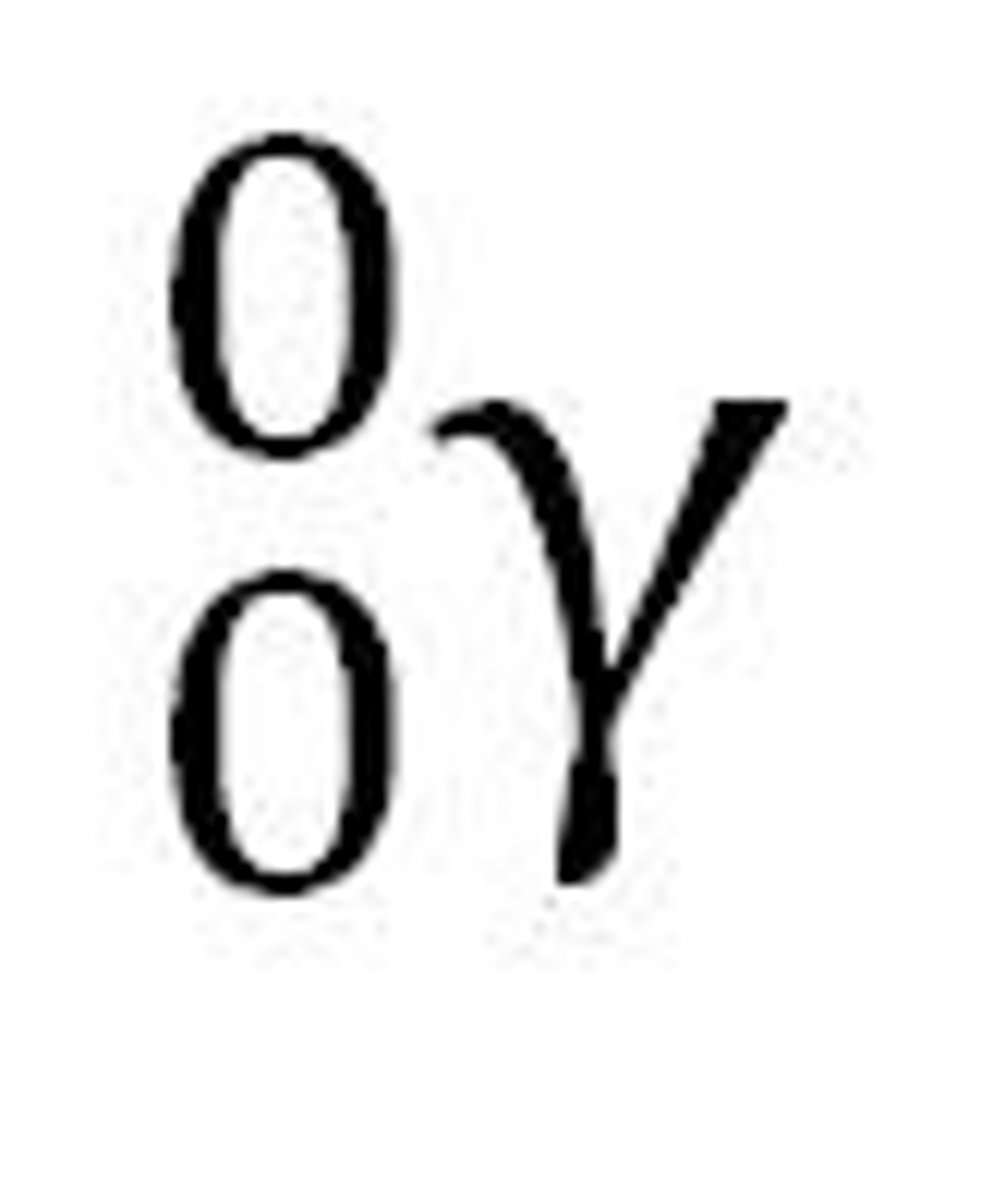
Give the formula for alpha decay.
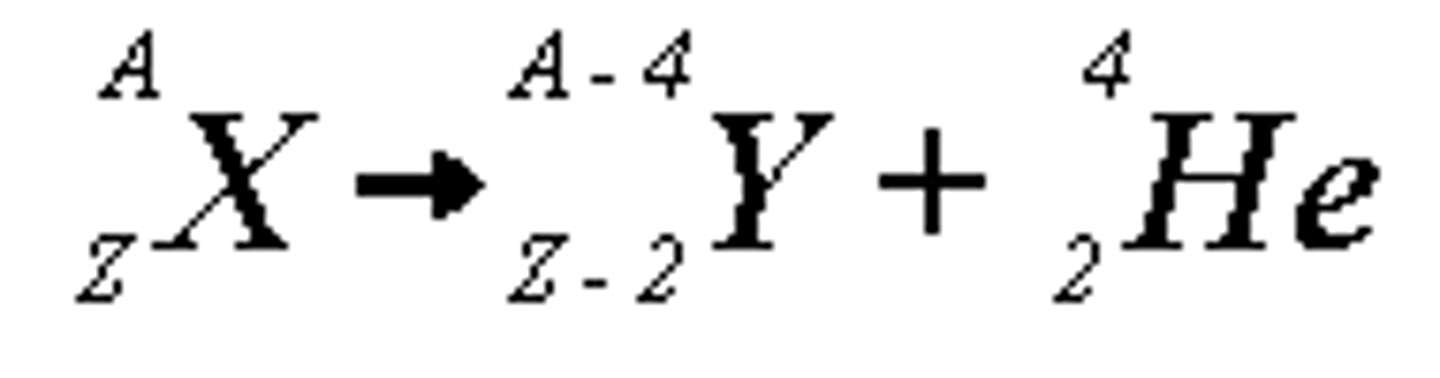
Give the formula for beta decay.
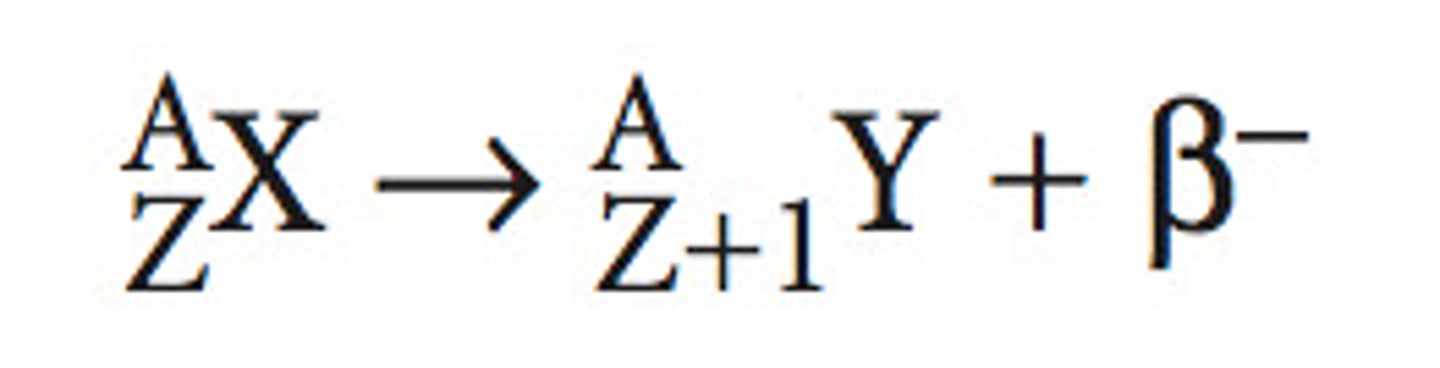
Give the formula for gamma decay
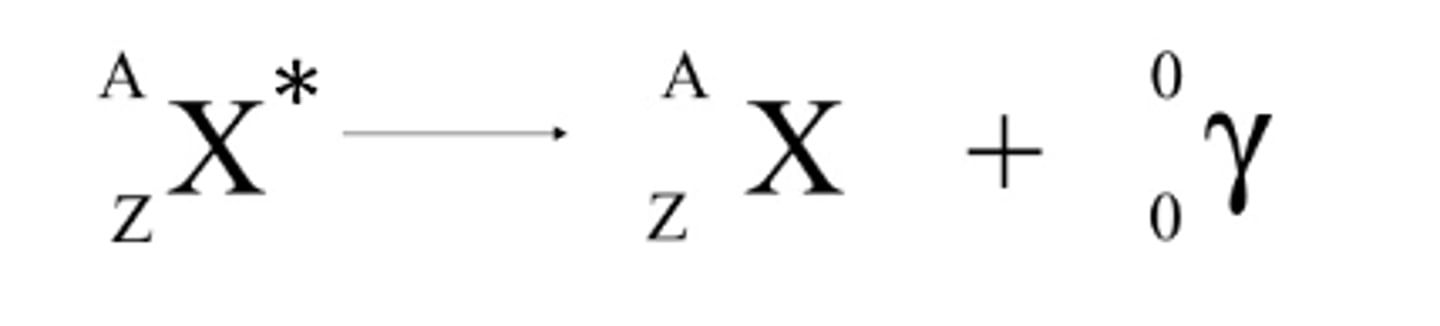
Give the formula for neutron decay
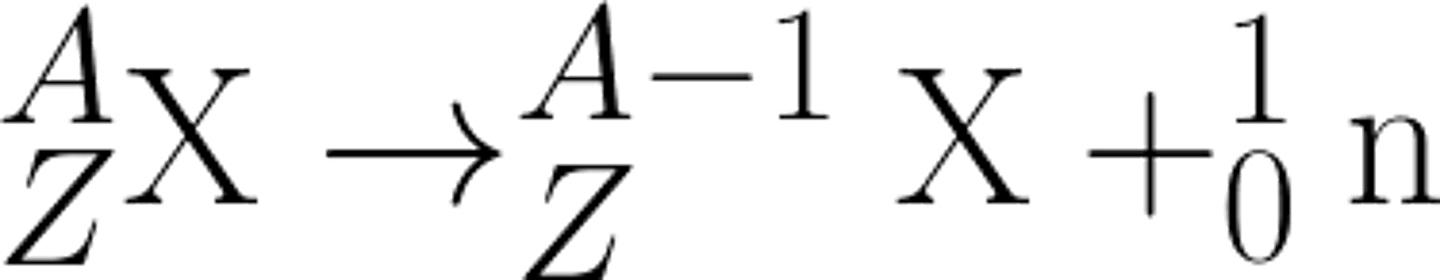
Give the formula for proton decay
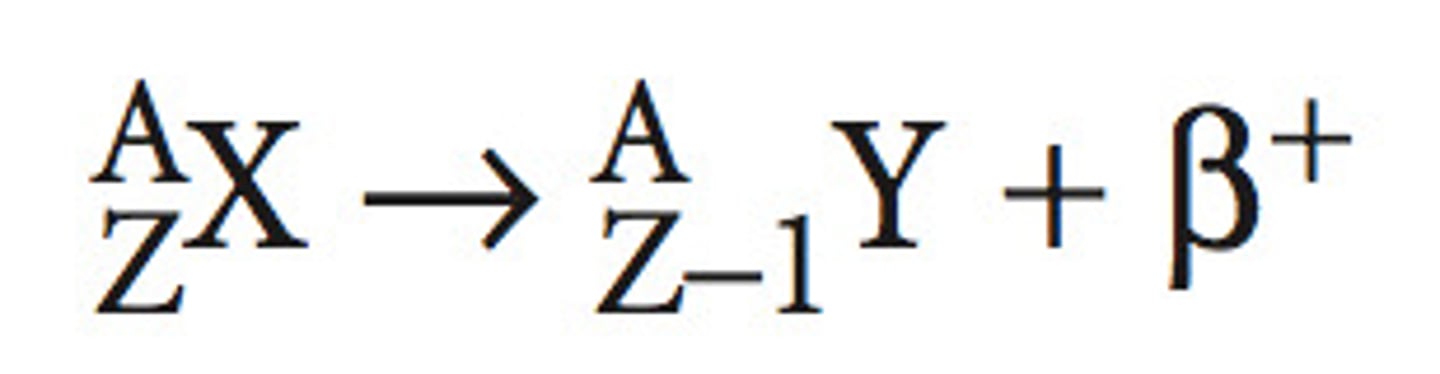
Count Rate/Activity
Decays per second tetected by a GM Tube in a substance.
How would you detect ionising radiation?
Measure count rate or activity of a sample with a GM Tube.
Penetrating Power of Alpha Particles
-Can be stopped by 3-5cm of air, paper or skin. Least PP
Penetrating Power of Beta Particles
Can be stopped by 30-50 cm of air or 3mm of aluminium (NOT ALUMINIUM FOIL)
Penetrating Power of Gamma Radiation
Can only be reduced by several cm of lead or several metres of concrete: most penetrating.
Why may it be difficult to measure the penetrating power of alpha radiation in a liquid?
container would absorb the alpha particles
Irradiation vs Contamination
Irradiation- exposing something to ionising radiation.
Contamination- radioactive substance itself has been transferred to object in question e.g radioactive steam into atmosphere.
Name natural and man made sources of background radiation
Natural: Carbon-14 in atmosphere, Rocks
Man-made: nuclear weapons, nuclear power plants, nuclear waste.
What 2 qualities does radioactive decay have?
RANDOM- in a substance, cannot predict which nucleus will decay.
SPONTANEOUS- Cannot predict when a nucleus will decay?
Half Life
Time taken for half of a radioactive substance to decay, OR
Time taken for activity to fall to half of its original value.w
-Each radioactive substance has a constant half life.
Uses of radioactive substances
Smoke detectors
Carbon dating
Medical tracers