examination of heart
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
through palpation what can we determine
Temperature
Pain
Tremors
Heartbeats
how to carry out palpation
We press on the intercostal spaces
We place the hand flat
heart beat best felt in horse
5 intercostal space on the left side
4 intercostal space on the right side
heart beat best felt in cattle/small ru
4 intercostal space on the left side
heart beat best felt in dogs,cat,foxes
4-5 intercostal space on the left side
is the shifting of heart beats pathological or physiological
pathological
shifting heartbeat- up
enlarged hear
shifting heartbeat- back
enlarged left ventricle, whole heart, mediastinal lymph nodes, mediastinal tumors
Cardiac enlargement is
enlargement of the area where the heartbeat is felt and increased force of the beat
causes of increased heartbeat
• Fever
• Stress
• Second half of pregnancy
• Hypertension
• Cushing's disease
cause of weakened heart beat
• Significant weakening of the heart
• Fluid in the pericardial sac (hydropericardium)
• Fluid in the pleural cavity (hydropneumothorax)
• Advanced pulmonary emphysema
Cardiac dullness area:- Enlarged
Cardiac dilatation and hypertrophy
Hydroendocardia
Leftward displacement of the heart
Pseudoenlargement of cardiac dullness
pseudoenlargment = false enlargement, is an increase in the size of an organ due to infiltration of a tissue not normally found in that organ
Hydrothorax
Hepatomegaly (carnivorous)
Lung tumors
Fibrinous pleuris
Cardiac dullness area: Reduced
Pulmonary emphysema
Pneumothorax
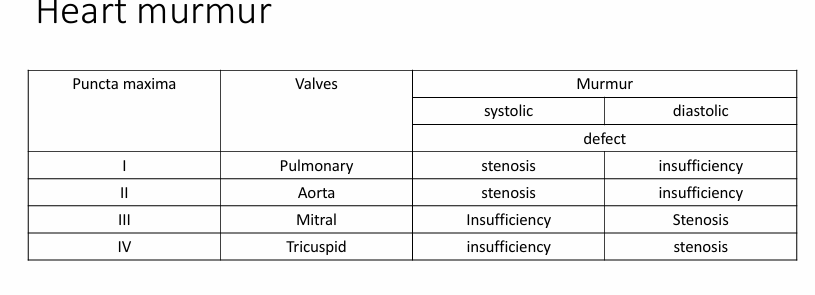
systolic tone
systolic
diastolic tone
diasoltic
Systolic period
time between I and II tone
Diastolic period
time between II and I tone
tone I- muscular
Lower sound than tone II
Quieter
Less resonant
how is tone I created
created as a result of the tremors of closing valves and the muscular-fibrous apparatus of the valves
tone II- valvular
Higher and shorter than I
Louder
cause of tone II
caused by the tremors of the closing valves of the aorta and pulmonary artery
tone II in horse (pm) left side
I – 3 i.c.s just behind the sternum – projection of the pulmonary valve
II – 4 i.c.s 2 fingers' width below the shoulder joint line - projection of the aortic valve
III – 5 i.c.s. A hand's width below the shoulder joint line - projection of the mitral valve
valves of heart present on left side
pulmonary
aortic
mitral
projection of pulmonary valve in horse/ cattle
LEFT SIDE
I – 3 i.c.s just behind the sternum
projection of aortic valve in horse/ cattle
LEFT SIDE
II – 4 i.c.s 2 fingers' width below the shoulder joint line
projection of mitral valve in horse/ cattle
LEFT SIDE
III – 5 i.c.s. A hand's width below the shoulder joint line
what valve is present on right side
trispid
projection of the tricuspid valve in horse/ cattle
RIGHT SIDE
3 i.c.s. Just above the sternum
projection of the pulmonary valve dog and cats
LEFT SIDE
I – 3rd p.m. of the heart just behind the sternum
projection of the aortic valve dog and cats
LEFT SIDE
II – 4th p.m. of the heart just below the shoulder joint line
projection of the mitralvalve dog and cats
LEFT SIDE
III – 5th p.m. of the heart in the upper half of the 1/3 of the ches
projection of the tricuspid valve dog and cats
IV - 4th p.m. of the heart Just above the sternum
Auscultatio
Rate – number of beats per minute
Intensity – strength of heart sounds
Rhythm – regularity Intervals between beats
Additional sounds
physiological cause of tachycardia
young age, high ambient temperature, excitement
pathological cause of tachycardia
circulatory failure, anemia, adrenal hyperfunction, hyperthyroidism
Physiological cause of bradycardia
sleep, anesthesia, trained animals
pathological cause of bradycardia
arrhythmias, hypothermia, uremia
Arrhythmia
different time interval between individual heartbeats
the interval between the first and second tone is shorter
Splitting and splitting of the tone – physiologically at the peak of inspiration, pathologically with some arrhythmias and increased pressure
rythm resembles what
galloping horse
how many tones dose rhythm consist of
It consists of 3 tones
An additional tone in the diastolic phas
persistant arrythmia is longer than
2 days
Parcotic arrythmia
sudden onset and end, periodic
dull heart tone caused by
fur, pleural fluid
heart murmur
Additional examination of heart
• ECG
• X-ray
• Cardiac ultrasonography
• Phonologic cardiology
• Magnetic resonance imaging
• scintigraphy
Clinical signs of heart disease that you may see at home
• weakness
• lethargy
• exercise intolerance
• shortness of breath
• Coughing
More clinical signs of heart diease from clinical examination
• an irregular heartbeat
• a heart murmur (which indicates turbulent blood flow over a valve within the heart)
• irregular pulses
• abnormal lung sound
in ECG what axis volatge on
Y
in ECG what axis time on
Time on X axis
P wave
atrial muscle depolarization
QRS complex
ventricular muscle depola
T wave
ventricular muscle repolarization
artefacts during ECG
• Motion
• Breathing
• purring
cause of artefacts
• Movement
• Poor contact between the electrodes and the patient
• Electrical items (e.g. clippers, imaging equipment, warming equipment, other monitoring equipment)
position of animals during ecg
lying in right lateral recumbency
gently restrain limbs
electrodes/pads should be placed on the limbs appropriately
right forelimb
left forelimb
left hind limb
ecg on respiratory patients
should have their ECG performed in sternal
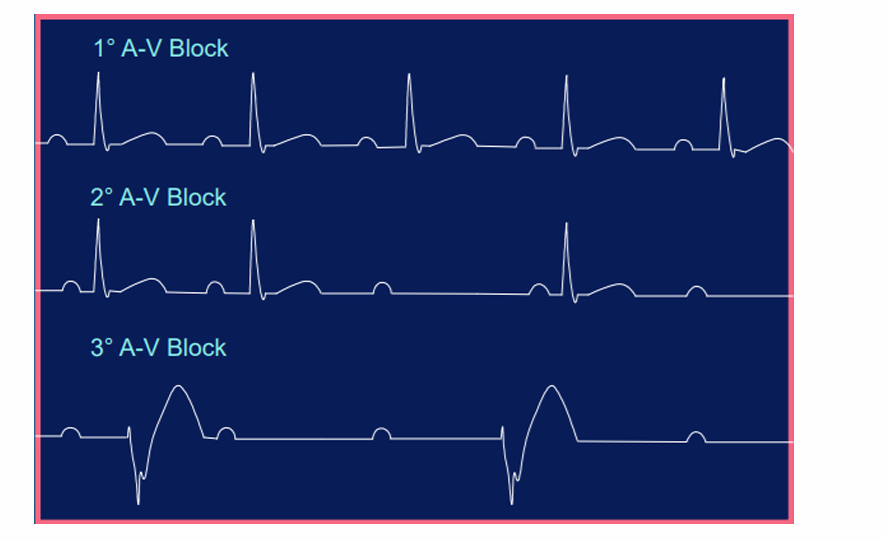
AV block
a disorder in the heart's rhythm due to a fault in the natural pacemaker
types of heart blocks
Sinoatrial nodal blokcs (SA)
Atrioventricular blocks (AV)
SA block- I degree
a lag between the time that the SA node fires and actual depolarization of the atria.
Not recognized by ECG
SA- II degree type 1
aka Wenckebach block
rhythm is irregular
R-R interval gets progressively smaller, while the P-R interval remains constant, until a QRS segment is dropped.
SA- II degree type 2
aka sinus exit block
regular rhythm that may be normal or slow.
It is followed by a pause that is a multiple of the P-P interval usually (2-4).
R-R interval gets progressively smaller, while the P-R interval remains constant, until a QRS segment is dropped
is charc for what heart block
SA- II degree type 1
SA block- III degree
caused by failure to conduct them.
rhythm is irregular and either normal or slow
followed by a long pause that is not a multiple of the P-R interval.
The pause ends with a P wave, instead of a junctional escape beat the way a sinus arrest would.
what SA block is not recog by ECG
SA I degree
difference btwn SA block- III degree and sinus arrest
The pause ends with a P wave, instead of a junctional escape beat the way a sinus arrest would.
AV block- I degree
occurs when there is a delay, but not disruption, as the electrical signal moves between the atrium and the ventricles through the AV node.
AV block- II degree
occurs when the electrical signal between the atria and ventricles is even more impaired than in a first-degree AV block. In a second-degree AV block, the impairment results in a failure to conduct an impulse, which causes a skipped beat.
AV block- III degree
occurs when the signal between the atria and ventricles is completely blocked
there is no communication between the two.
None of the signals from the upper chambers make it to the lower chambers.
On ECG, there is no relationship between P waves and QRS complexes, meaning the P waves and QRS complexes are not in a 1:1 ratio.
what is the most sevre of the AV blocks
Third-degree AV block is the most severe of the AV blocks
in what heart block is no relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
AV block- III degree
what ratio should P waves and QRS complex be in
1:1
AV block- Mobitz I
characterized by a progressive yet reversible block of the AV node.
defined by progressive prolongation of the PR interval, with a resulting dropped beat (the PR interval gets longer and longer until a beat is finally dropped, or skipped)
AV block- Mobitz II
caused by a sudden, unexpected failure of the His-Purkinje cells to conduct the electrical impulse
the PR interval is unchanged from beat to beat, but there is a sudden failure to conduct the signal to the ventricles, and resulting in random skipped beat
progressive prolongation of the PR interval is characteristic of
AV block- mobitz I
position of large animal during X ray
Lateral projection, animal standing
position of small animal during X ray
Lateral and dorsoventral projection, animal lying down – small animals
what dose x ray allow acess to
assess the condition of the heart and blood vessels inside the chest
what can be determined in x ray
• Enlargement of the heart
• Tightening/weakening of the blood vessel pattern
• Displacement of the heart
Scyntygraphy
Heart activity registration after administration of radioactively labeled contrast
The distribution and saturation of the organ by contrast are assessed