Head and Neck
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
neurocranium
calvarium- frontal, occipital, and parietal
cervical plexus: accessory nerve
trapezius and SCM
cervical plexus: hypoglossal nerve
tongue muscles
cervical plexus: lesser occipital nerve
sides of posterior scalp and outer ear
cervical plexus: greater auricular nerve
skin of the ear, mastoid process, and parotid gland
Ansa cervicalis
motor to infrahyoid muscles, move larynx and hyoid
cervical plexus: transverse cervical
skin of anterior and lateral neck
cervical plexus: supraclavicular nerves
skin over clavicle, anteromedial shoulder, proximal chest
cervical plexus: phrenic nerves
motor innervation to diaphragm
base
frontal, occipital, temporal, ethmoid, sphenoid
cranial fossae
brain case; contains and protects brain
complex and varying depths
openings for cranial nerves, blood vessels, spinal cord
anterior cranial fossa, middle CF, posterior CF
foramen magnum
spinal cord passes through
foramen rotundum
maxillary nerve, maxillary artery, and emissary veins pass through
foramen ovale
mandibular nerve, accessory meningeal artery, lesser superficial petrosal nerve, and emissary veins pass through
external auditory meatus
connects outer ear to eardrum (ear canal)
stylomastoid foramen
in temporal bone between styloid and mastoid processes; facial nerve and styloid-mastoid artery pass through
supraorbital foramen
lateral branch of the supraorbital nerve passes through
infraorbital foramen
infraorbital nerve and vessels to the face pass through
division of trigeminal nerve
mental foramen
mental nerve passes through
key landmark for dental and facial surgeries
viscerocranium
skeleton part of the phase; 14 bones
zygomatic
lacrimal
nasal
inferior nasal concha
maxilla
palatine
vomer
mandible
sagittal suture
coronal sutures
lambdoid suture
squamous suture
metopic suture
mandibular condyle
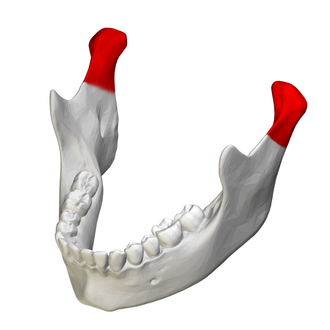
coronoid process
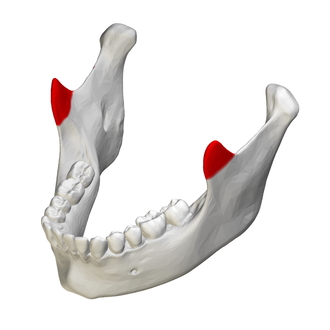
body of mandible
contains lower teeth sockets
base of mandible
sharp inferior edge of body (jawline)
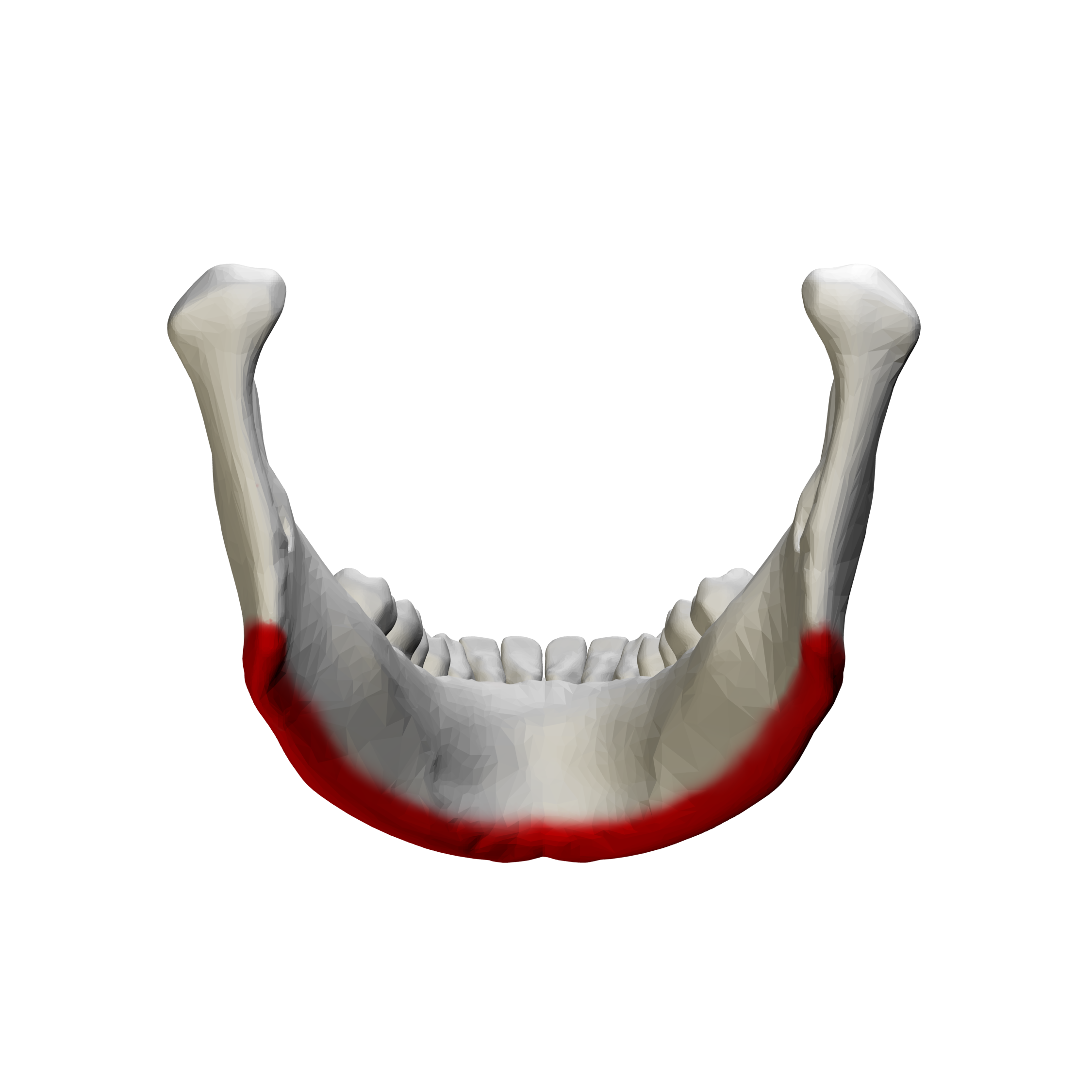
submandibular fossa
interior aspect of mandible; submandibular gland rests here
temporomandibular joint
where the mandibular process joins with the temporal bone
hyoid
U-shaped; serves as an attachment for muscles involved in speech and swallowing
Larynx
formed by arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform cartilage (paired) and thyroid, cricoid, epiglottic cartilage (unpaired)
cervical spine
most mobile segment of spinal column
upper cervical spine- interface between skull and spinal column
C1- atlas
C2- axis
lower cervical spine- C3-C7
nuchal ligament- extends inferiorly from external occipital protuberance to cervical spine; holds areas together
Axis
C2; uniquely designed with DENS- projects upward into atlas
allows for rotation of the skull
atlantooccipital joint
interface between skull and vertebral column
yes joint- flexion and extension of head
convex occipital condyle and conclave atlas facet
atlantoaxial joint
most mobile portion formed by odontoid process
pivot for rotation
no joint
Muscles of Facial Expression
attach to underlying fascia and face to express emotion
Mneumonic- Beavers Don’t Date Llamas, LLamas Make Overly Picky Roomates
Muscles of mastication and speech
movement of the mandible
Muscles of Swallowing
voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions, phases of swallowing, movements of tongue
Muscles for eye movement
extraocular muscles that move eyes and elevate eyelid
Buccinator muscle
facial expression- contracts cheek, narrows mouth
kiss
depressor anguli oris
facial expression- pulls corners of mouth down
frown
depressor labii inferioris
facial expression- depresses, protrudes and pulls the lips
levator anguli oris
facial expression- elevates angles of the mouth
levator labii superioris
facial expresion- elevates and protrudes upper lip
mentalis
facial expression- elevated median skin of chin
orbicularis oris
closes and shapes the lips
platysma
facial expression- tightens the neck
risorus
facial expression- retracts corners of mouth
zygomaticus major
pulls up the corners of the mouth
zygomaticus minor
elevates and protrudes upper lip
levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
flares nostrils
nasalis
controls and regulates airflow
procerus
pulls skin between eyebrows together
corrugator supercilia
depresses and pulls eyebrow medially
orbicularis oculi
closes eyelid
occipitofrontalis
elevates both eyelids
auricularis
wiggles ears
masseter
elevates and protrudes mandible for speech and chewing
bite force of up to 150 lbs
temporalis
elevates and retracts mandible for speech and chewing
medial and lateral pterygoids
protrude mandible; laterally and medially deviate to grind food
extrinsic tongue muscles
protrude, retract, depress, and elevate the sides of the tongue to assist with swallowing
intrinsic tongue muscles
elevate and depress the tip of the tongue; flatten, widen, narrow, and protrude the tongue
suprahyoids
elevate hyoid and tongue, depresses mandible
digastric
depresses mandible, elevate hyoid, retract mandible
infrahyoid
depress hyoid and thyroid cartilage
levator palpebrae
elevates eyelid
extraocular mucles
move eye up, down, lateral, and medial to scan environment
superior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, inferior rectus, superior oblique, inferior oblique
Movement of Temperomandibular Joint
elevates, depresses, protracts, retracts
essential for speech, feeding, swallowing
synovial joint
muscles of the neck
around 30 muscles that extend from the base of the skull and jaw to the shoulder blades and collar bones
support and move head, neck, and spine
chewing, swallowing, breathing
Anterior muscles of the neck
superficial, suprahyoid, infrahyoid, scalene
posterior muscles of the neck
superficial, suboccipital, transversospinalis
Neck flexion
sternocleidomastoid, anterior scalens, longus capitis, longus colli
neck extension
trapezius, levator scapulae, splenius capitus, splenius cervicis, rectus capitis posterior major/minor, oblique capitis superior, semispinalis capitis
ipsilateral rotation
levator scapulae, splenius capitis, spenius cervicis, rectus capiris posterior major, oblique capitis interior, longus colli, longus capti
contralateral rotation
trapezius (upper fibers), sternocleidomastoid, anterior/middle/posterior scalene, mutifidi, rotatores
lateral flexion
trapezius (upper fibers), sternocleidomastoid, levator scapulae, scalenes, splenius capitis, splenius cervicus, longus capitis, longus coli
Trigeminal Nerve (CN 5)
ophthalmic branch- supplies forehead, scalp, frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses, epper eyelid and conjunctiva, cornea, dorsum of nose, and lacrimal gland
maxillary branch- supplies lower eyelid, conjunctiva, cheeks, maxillary sinus, lateral nose, upper lip, teeth, and superior palate
mandibular branch- supplies lower 1/3 of face, lower teeth, anterior 2/3 of tongue, chewing
review cranial nerves
Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet Ah Heaven
Some Say Money Matters But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter Most
Major nerves of neck
C1-C7- exit superior to corresponding vertebra
C8- emerges inferior to C7
cervical plexus- C1-C4
memorize cervical plexus
Arteries of head and neck
internal and external carotid arteries, vertebral arteries, thyrocervical trunk
veins of head and neck
fascial vein, inferior/middle/superior thyroid veins, jugular veins, vertebral veins
Functions of Face
communication (verbal and non-verbal)
feeding, eating, swallowing
vision
reaching
listening
posture
Infant and Early Childhood
large head compared to rest of their body
paraspinal cervical muscles are relatively weak at birth
head lag should be absent by 3-4 months
full control by 6 months
face has to catch up to head size; growth is significant during this stage
adenoids and tonsils are largest in relation to surrounding structures between 4-6 years
Adolescence/Puberty
female facial maturation- 12-15 years
male facial maturation- 15-18 years
airway length increases significantly in boys after puberty
males experience enlarged vocal cords—> deep voice
facial fat and overall body fat change
Adult
neck muscles weaken
fat distribution shifts
reduced collagen and elastin production—> thinning and sagging skin
loss of bone mass in haw; reduced lower face size
nose and ears appear to lengthen
eyes change with wrinkles, sunken appearance, drooping eyelids
swallowing changes- decreases sensitivity, weakened muscles
hunch back