term 2 science 2 finals
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
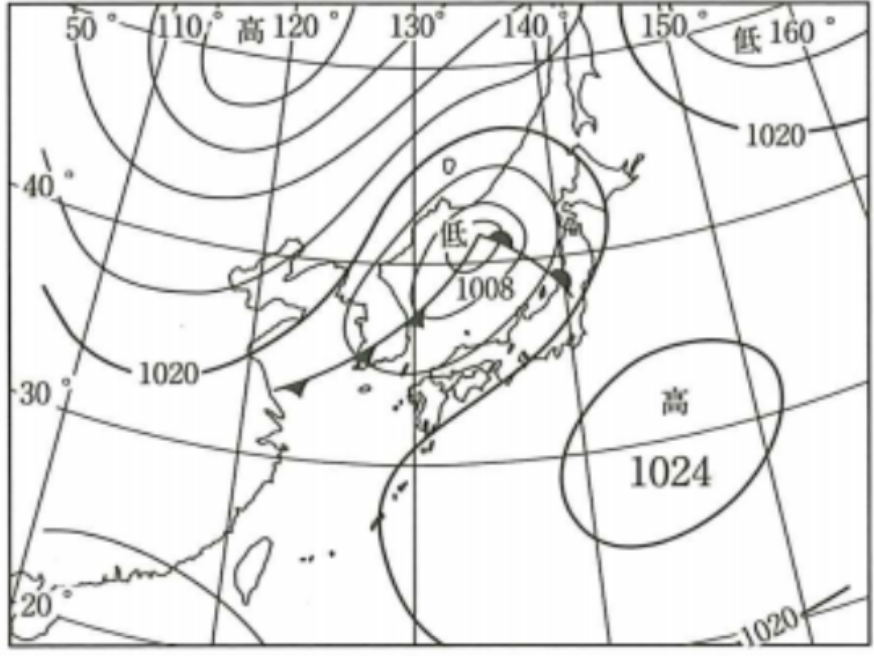
spring extratropical&migratory cyclone
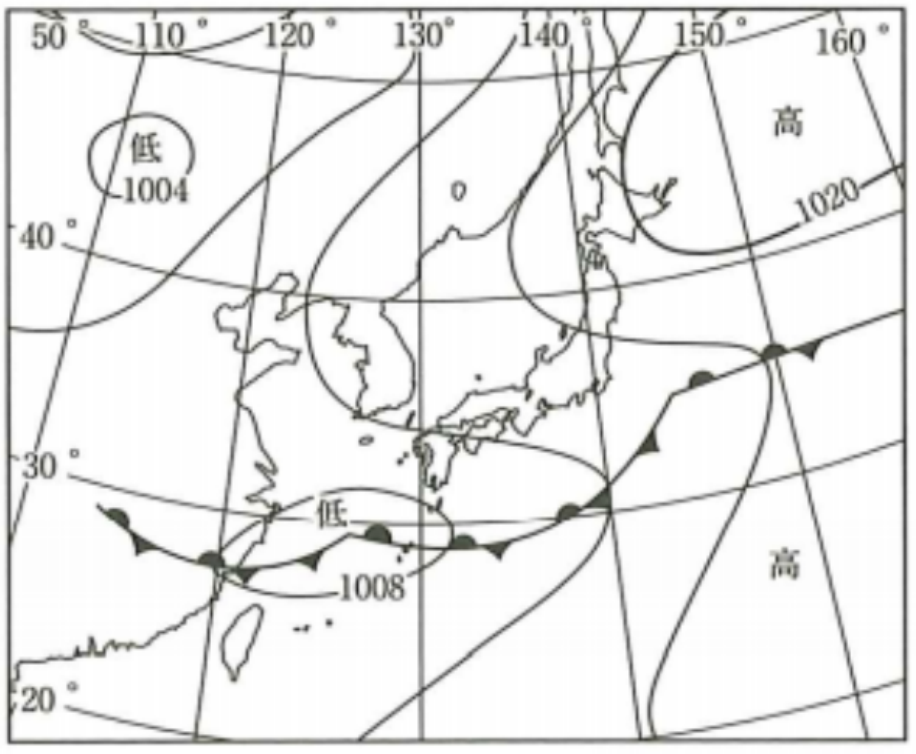
tsuyu okhotsk high&ogasawara high forms baiu front
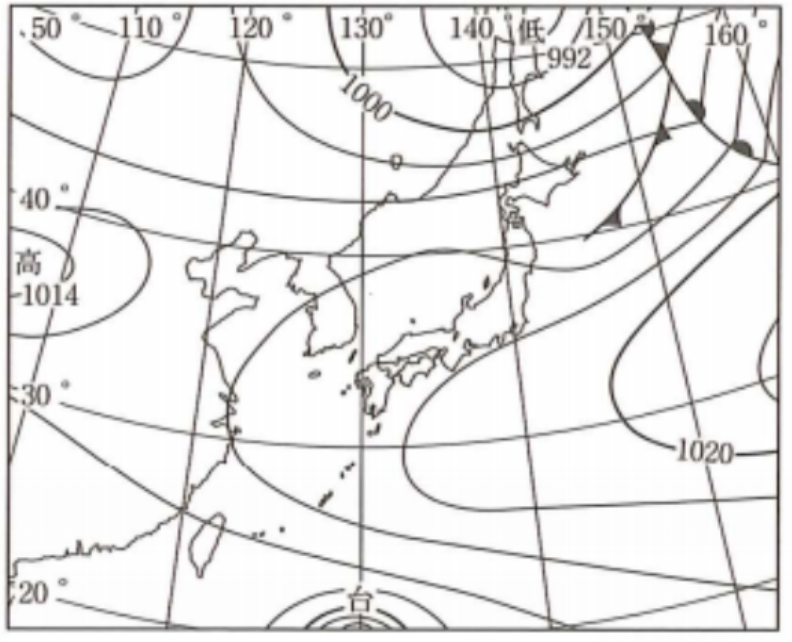
summer
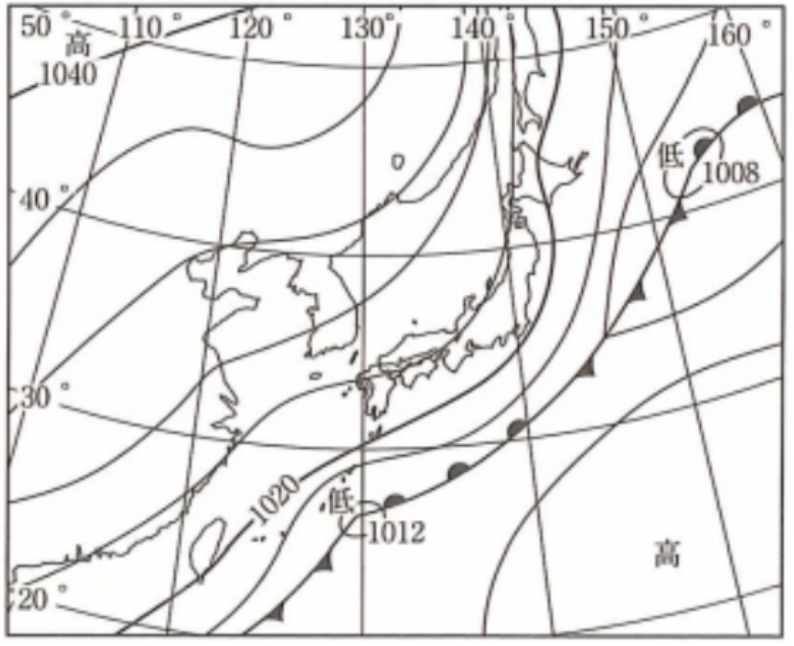
akisame
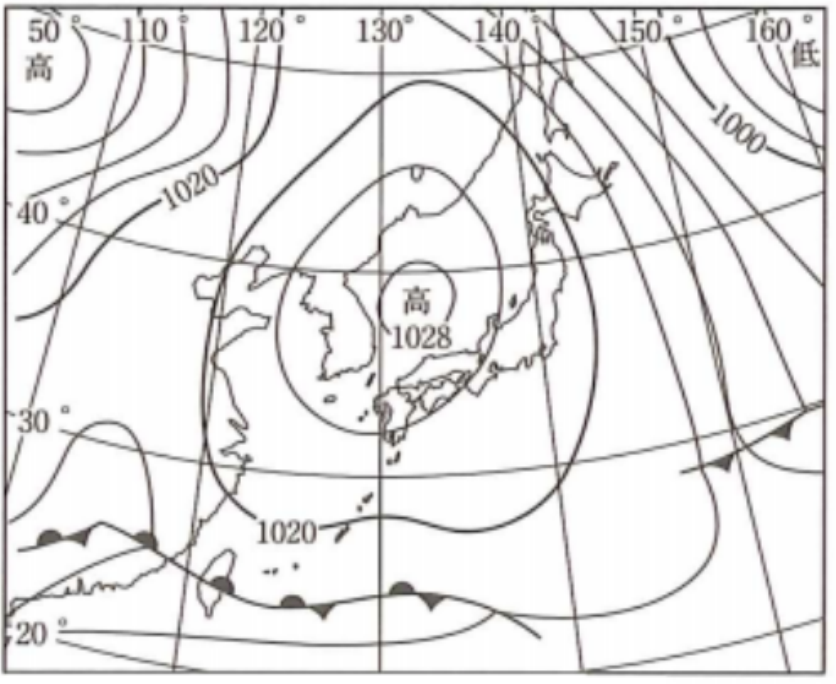
autumn
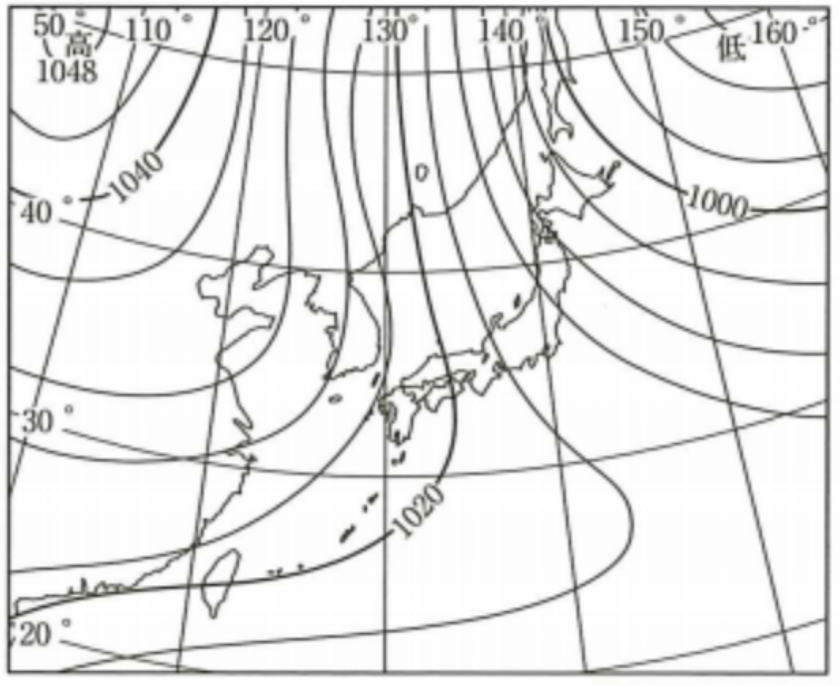
winter siberian high (west-high east-low pressure distribution
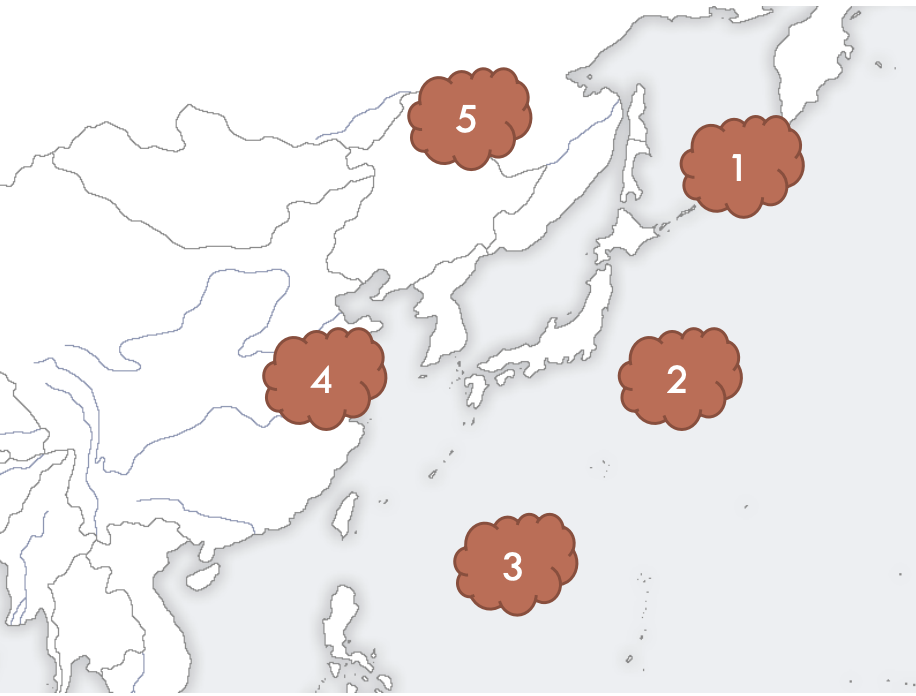
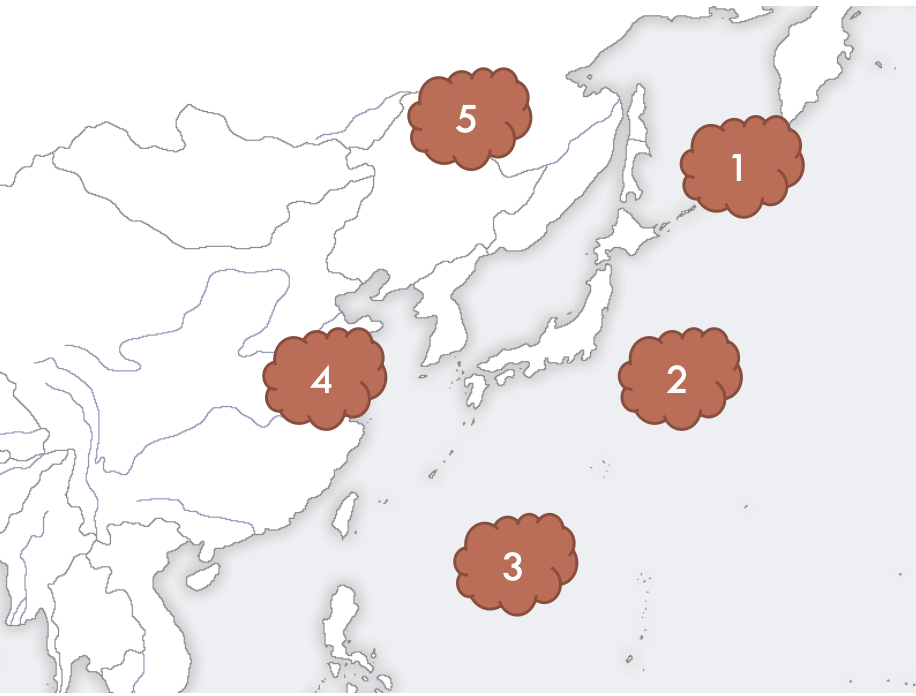
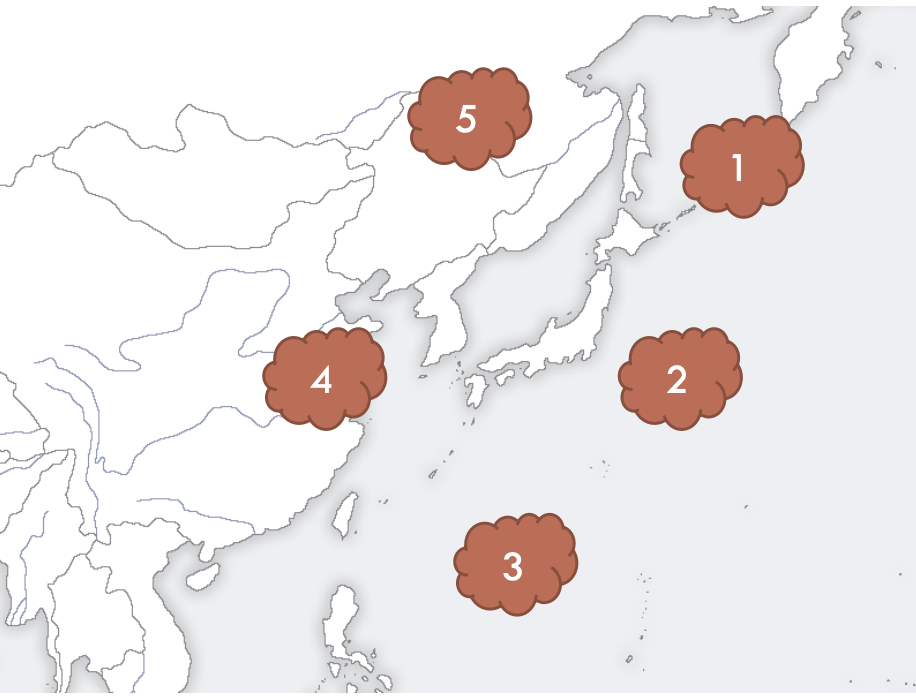
what affects the weather in japan and where is it located?
polar jet stream, N30~N60
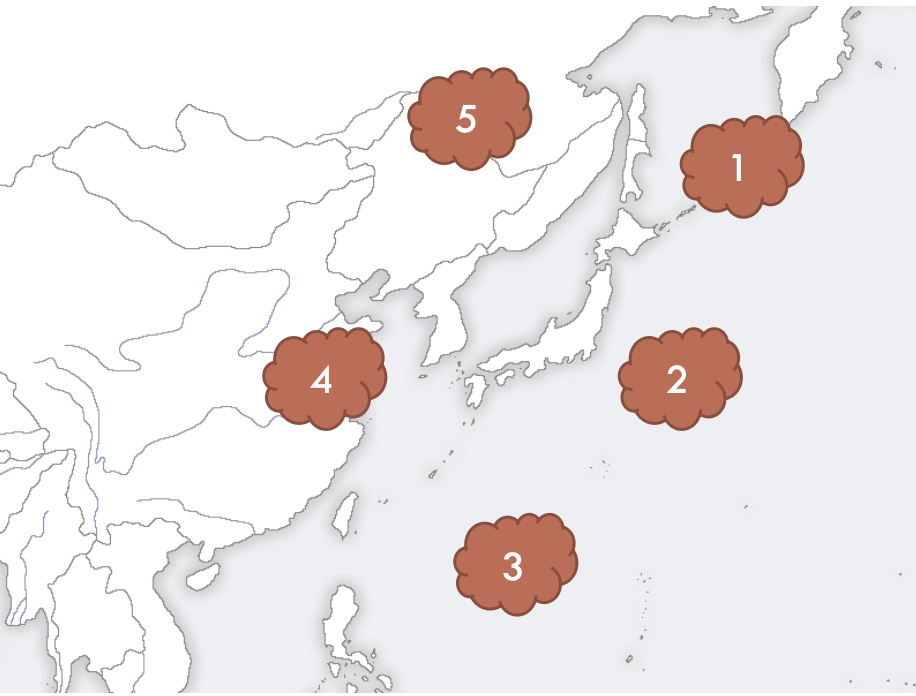
1
Okhotsk air mass (marine cold)
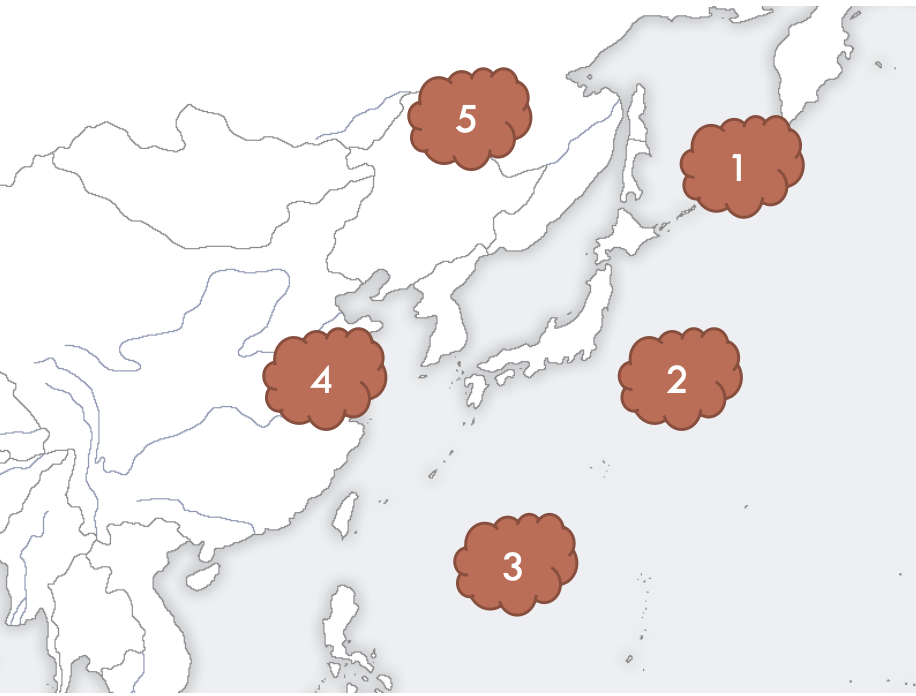
2
Ogasawara (marine tropical)
3
Equatorial (marine tropical)
4
Yangtze river (continental cold)
5
Siberian (continental cold)
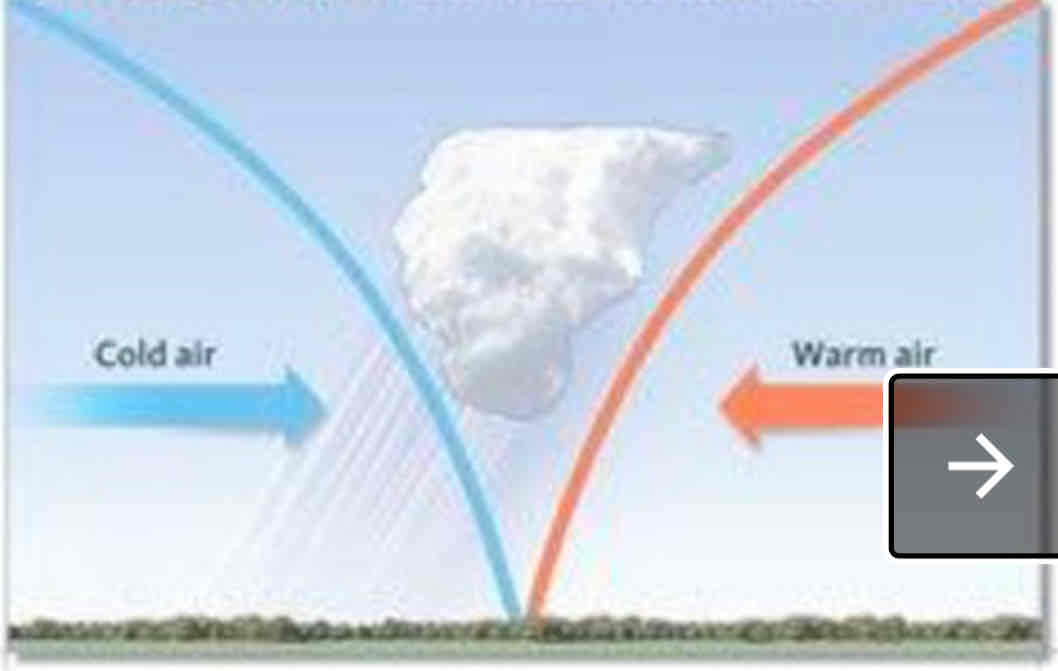
Cold front
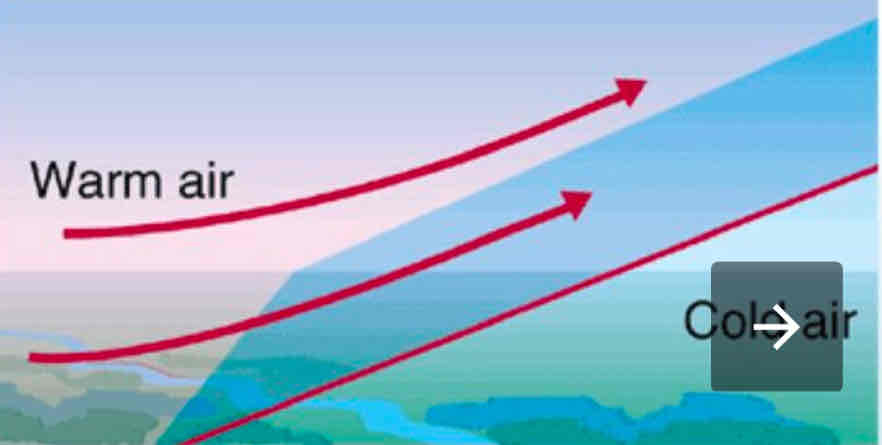
Warm front
Stationary front
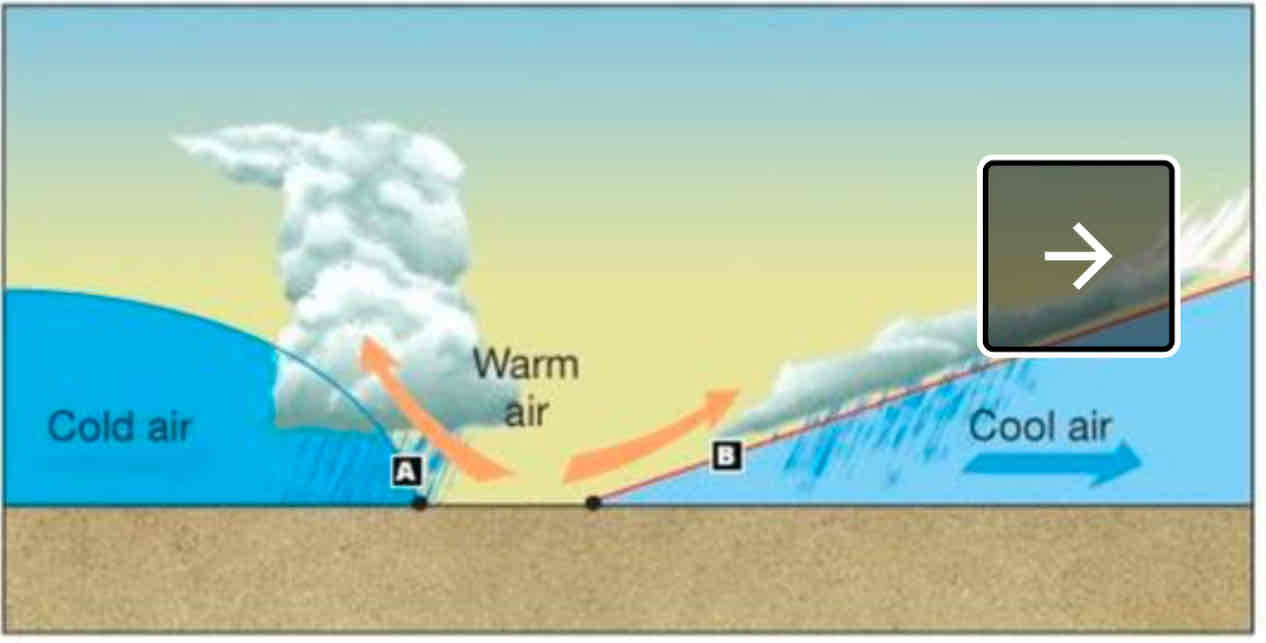
occluded front
Wind blows from… to… high/low
High to low
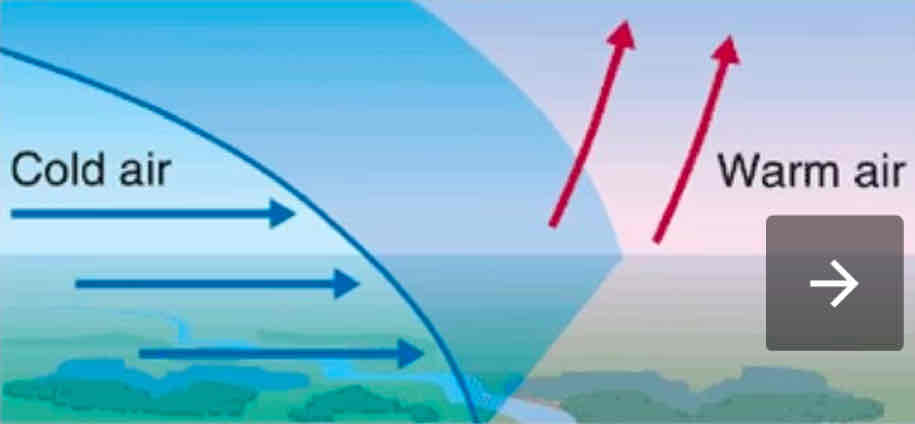
What’s a weather front?
transition zone between two air masses on the surface of Earth.
Stevenson screen
a box used to store various instruments to measure various weather factors
Thermometer
Measures temperature. It needs to be:
1. In a well ventilated area
2. 1.5m above ground
3. Without direct sunlight.
Hydrometer
measure amount of water vapour in air
Psychrometer
hygrometer consisting a dry-bulb thermometer and a wet-bulb thermometer; their difference indicates the dryness of the surrounding air.
Barometer
Measures air pressure. Unit is hectopascals(hPa)
Pressure at sea level is 1013hPa
Low pressure..bad weather
High pressure… good weather
Thermo hygrograph
chart recorder that measures/records both temperature and humidity
Wind vane
direction of wind
anemometer
measure speed of wind
Beaufort scale
13 scales(0-12)
weather scale
0~1=clear, 2~8=sunny, 9~10=cloudy
Rain gauge
tool that measures rain.
1 mm of precipitation
→1L of rain fell over an area of 1 m^2
Isobars
Drawn every 4hPa
High pressure… H
Low pressure…
Isobars are close
pressure is strong⇨wind is strong in that region.
Earth rotates at an angle of
23.4
japan stretches from
N20 to N45
Extratropical cyclone
at the edge of atmospheric cells and its caused by ascending hot air. When warm and cold air collide in the mid latitude region which then forms an updraft.
Hurricane
tropical cyclone that occurs in North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific oceans
Typhoon
tropical cyclone that occurs in Northwest Pacific Ocean
tropical cyclones
storms in south pacific/indian ocean
at what sea surface temperature does typhoons form?
27C or higher
Adiabatic Cooling
air rises then the pressure decreases to the air expands and cools
When water vapour condenses, it loses heat energy to surroundings causing air to rise again.
what happens to the air inside the typhoon when adiabatic cooling occurs?
It is heated, causing the air to expand causing atmospheric pressure at center to decrease
What cause wind to rotate and create typhoons?
corriolis effect
when does the typhoon disappear?
if it moves over land or reaches colder oceans
what causes movement of cyclones?
CORIOLIS EFFECT, TRADE WINDS, JET STREAM, OGASAWARA HIGH
which cloud does a typhoon look like?
cumulonimbus
which way does the wind in a typhoon blow? Inwards or outwards?
anticlockwise towards centre(inwards)
what is it like in the Eye of the typhoon?
calm and clear
which side of the typhoon is the dangerous semicircle? why?
right hand side, because the direction of the wind in the right hand side is the same direction as the traveling direction of the typhoon.
which side is the navigable semicircle? why?
left side, since the wind circling and the wind coming from the traveling direction cancel each other.
describe the traveling route of a cyclone.
form over tropical oceans, blown northwest by trade winds, break away and wanders, blown northeast by jetstreams
how does the ogasawara high affect typhoons during summer? before/after summer?
block japan from typhoons during summer, brings typhoons along the rim towards japan before/after summer
Planet
steady light, orbits around a star and they don't produce light
Star
flickering light, any object that create their own energy and light
Solar Systems
our neighbourhood of the universe
name the 8 planets in order.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Natural satellite
anything that orbits around a planet (ex. moon)
Star cluster
assembly of stars
Open cluster
young blue white light scattered in milky way
Globular cluster
large cluster, red orange and old, not inside of milky way
Nebula
star factory, clouds of dust and gas where concentration is high
Diffuse nebulae
Nebula reflecting light(eg: Orion Nebula)
Planetary Nebula
end of a star, exploited star
Supernova remnant
after explosion of a star
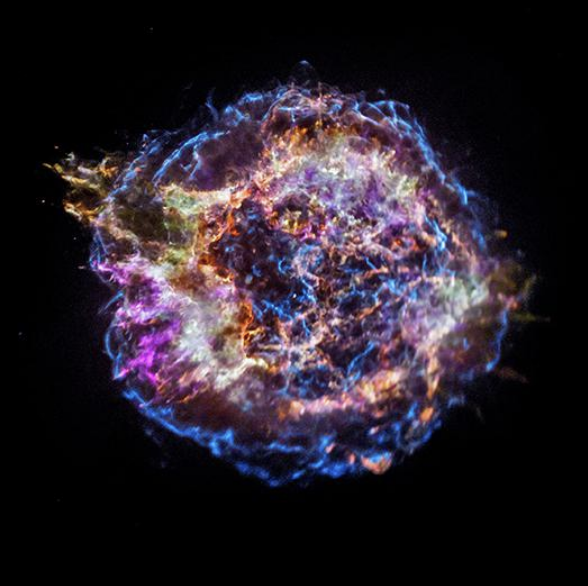

Dark Nebula
blocks all light that tries to pass it
Galaxy
Astronomical objects which contains many things(stars, planets, etc) (ex.MILKY WAY)
External galaxy
not our galaxy
Spiral galaxy
middle of it is spinning
Astronomical Units (AU)
length between earth and sun, used for objects within the solar system
Light years(ly)
how much light travels in a year, used for objects outside solar system
apparent magnitude
scale from 1 ~ 6=bright ~ faint, ✖2.5 for each stage up
Absolute magnitude scale
uses Alpha Centauri 32.6 ly as the standard, shows how bright the star would be if it was at the same distance as Alpha Centauri
Red stars
low temperature(ex:Antares, Betelguese, Aldebaran)
Blue stars
high temperature(ex:Rigel, Sirius)
Main sequence stars
most stars
Red giants
bright but low temperature
White dwarves
faint but high temperature