5 - Early Childhood Interventions
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Economic Arguments for early childhood interventions (3)
Credit Constraints, Externalities, Information Problems
When do gaps in skill accumulation start
Early on
How can early gaps in skill accumulation be prevented
Early investments
What efficiency-equity trade-off exists with early childhood interventions
There is no efficiency-equity trade off
What age range does current policy focus on
Key stage 12 and Higher education
What logical inconsistency exists with current policy focus
If you accept the paternalistic logic that the state knows best in Key stage 12 years, it should also apply even more strongle to early childhood which is arguably more influential
Examples of Early Interventions (6)
Cash subsidies to the poor
Formal Child-Care Centers
Home visits
Individual or Group Parenting Programs
Nutrition Supplements/Health Checks
Incentives for Prenatal Care
Who investigated gaps in test scores in early years (3)
Carneiro-Heckman (2003)
Cunha-Heckman (2010)
Schady et al (2014)
What did Carneiro-Heckman (2003) and Cunha-Heckman (2010) find regarding gaps in early test scores
Big gaps stay persistent over later years
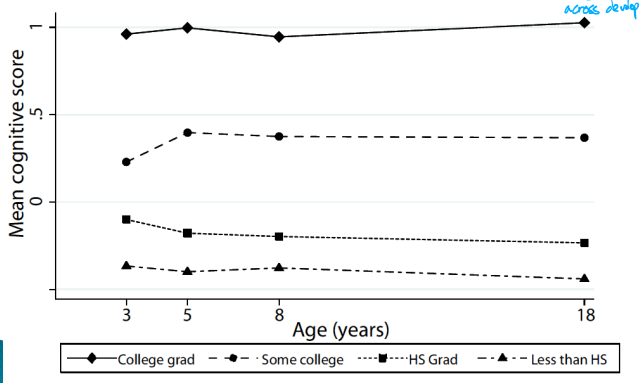
What did Schady et al. (2014) find
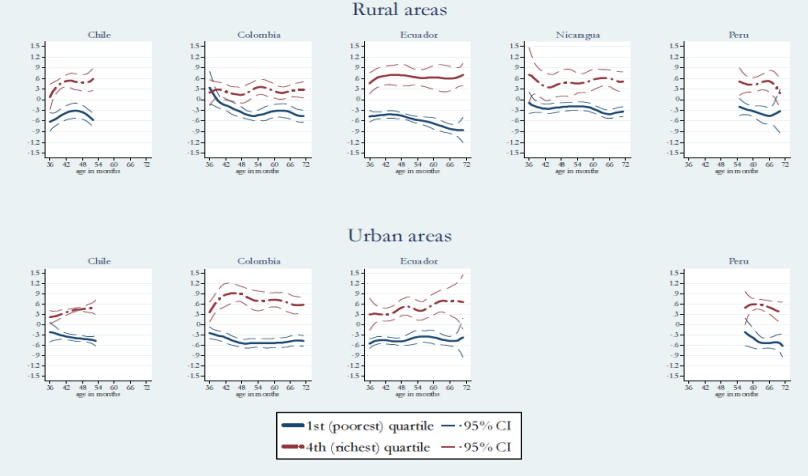
Gaps between the poorest and richest quartiles for very young people are similar between rural and urban areas and also persistent over later years
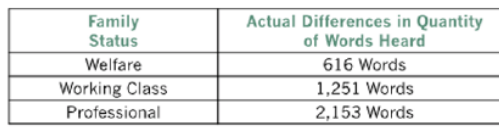
Who investigated differences in heard vocabulary between family status
Hart and Risley, 1995
What did Hart and Risley (1995) find regarding the number of words an average child hears in an hour
Children in professional families hear more than 3x of words that those in welfare families do
What did Hart and Risley (1995) find regarding the quality of words an average child hears in an hour
Those in professional families hear a lot more affirmatives (Encouragements) compared to prohibitions (e.g. No!, Shut up!)
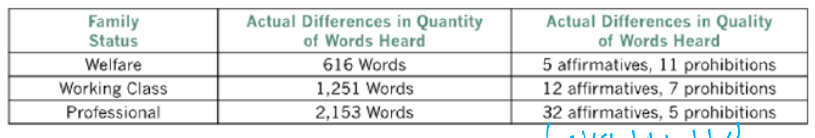
What did Hart and Risley (1995) find regarding cumulative vocabulary at age 3
Children from professional families had a cumulatiev vocabulary around double that of those from welfare families

Who investigated how in-uteral interventions impact outcomes for children
Carneiro et al (2021)
What did Carneiro et al (2021) find regarding how in-uteral interventions impact outcomes for children
In-uteral interventions which are not that hard still have a big impact on outcomes
Who investigated famous early childhood interventions
Barnett (2003)
Which early childhood interventions did Barnett (2003) evaluate (3)
Perry Pre-School Program
Chicago Parent-Child Centers
Abecederian
Was Perry Pre-School Program a randomised program
Yes - The treatment group was selected at random
Were the Chicago Parent-Child Centers randomised programs
No
What did Barnett (2003) find regarding the effects of early childhood intervention programs on IQ
Effects on IQ are small and basically nonexistent
Abecedarian program
An educational child care full-day year-round program in Chapel Hill, NC
What was the Maternal high school graduation rate in the Abecedarian program
Around 33% (2/3 are highschool dropouts)
What results did the Chicago Parent-Child Centers program produce regarding high school graduation
High school graduation increased by around 10%

What results did the Chicago Parent-Child Centers program produce regarding special education
Only 14% of those in the program required special education compared to 25% not in the program
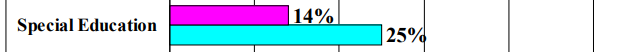
What results did the Chicago Parent-Child Centers program produce regarding grade repeating
Only 23% in the program needed to repeat their grade compared to 40% of those not in the program

What results did the Chicago Parent-Child Centers program produce regarding juvenile arrest
Less of those in the program experienced juvenile arrest

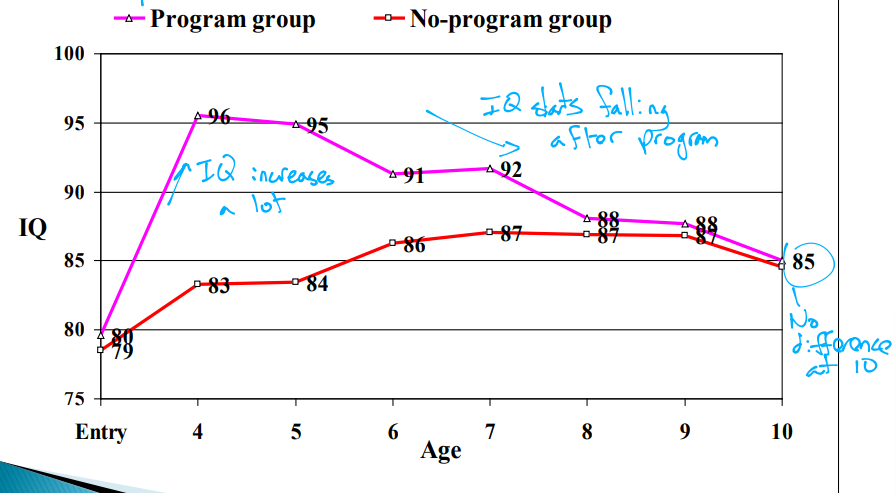
How did IQ differ between the program and no-program group in the Perry Pre-School study
IQ increases a lot at first but after the program IQ starts falling and by age 10, there is no difference in IQ
How did Education (Special Education, 14yrs Achievement, Graduation) differ between the program and no-program group in the Perry Pre-School study
Special Education - The program reduced those who needed special education by ½
Age 14 Achievement at higher than the 10th%ile - A lot more people achieved higher than the 10th %ile in the program
High school graduation - 20% more people from the program graduated
How did Earnings, ‘Own a home’, ‘Never on Welfare as an adult’ differ between the program and no-program group in the Perry Pre-School study
Earnings - The program increased those who earn $2000 monthly by 4 times
Own home - The program increased those who own a home by 3 times
Never on welfare as an adult - Increased by double
How did arrests differ between the program and no-program group in the Perry Pre-School study
Those who took the program had ½ the arrests and those not on the program had arrests mainly driven by violent crime
What does the Perry Pre-School program indicate
IQ is not very plastic so didn’t have a maintained gain but other things were more plastic and sustained gains were made
How does the Abecedarian program compare to the Perry pre school program
It was more intense with it lasting for a full day, full year, for 5 years
How did IQ scores differ between the control and treated group in the Abecedarian program
The IQ effects remained
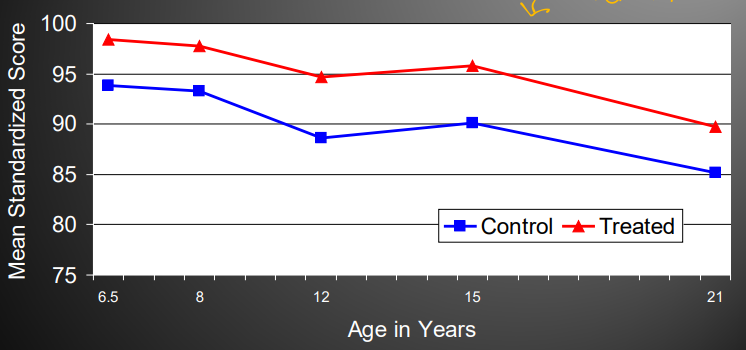
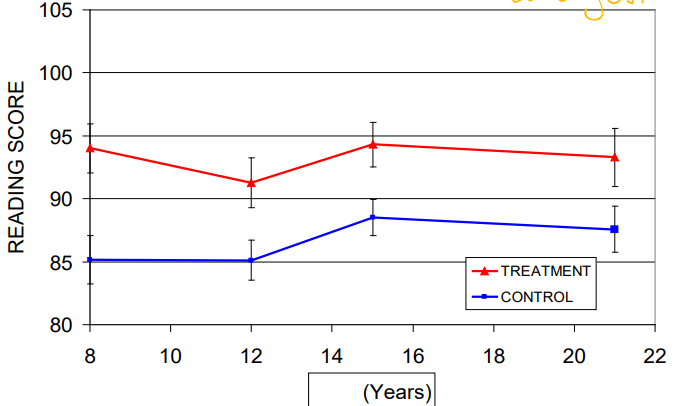
How did the Abecedarian program impact reading scores over time
There were big effects which persisted
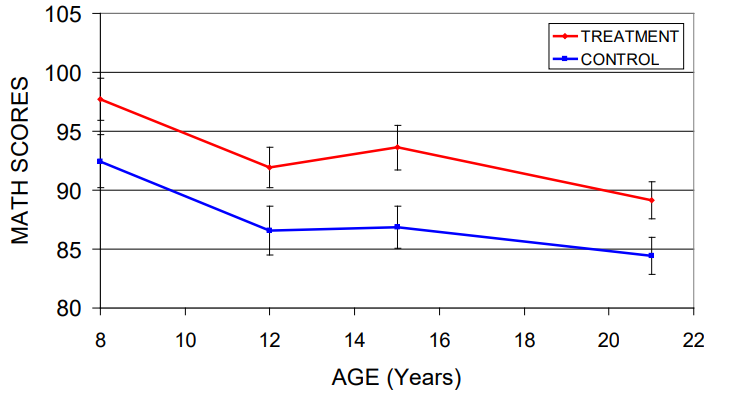
How did the Abecedarian program impact math scores over time
There were big effects which persisted
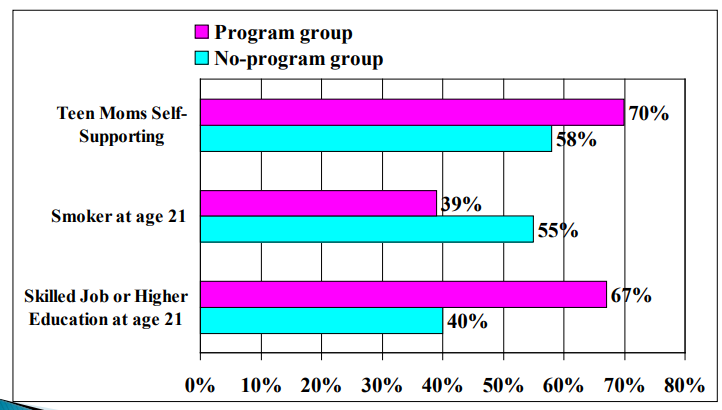
How did the Abecedarian program impact mothers and children (3)
A lot more teen moms were self-supporting
Less smoked at age 21
Around 30% more people had a skilled job or higher education at age 21
What did Carneiro and Heckman find regarding early childhood interventions and their impacts
There are small effects on IQ but large and lasting effects on achievement and noncognitive skills
Who presented a cost benefit analysis of the Perry Pre-School project
Carneiro and Heckman (2003)
What costs did Carneiro and Heckman (2003) measure for the Perry Pre School program
Costs of preschool
What benefits did Carneiro and Heckman (2003) measure for the Perry Pre School program (4)
Decrease in cost to government of K-12 special education
Decrease in criminal justice system costs of child’s criminal activity
Income from child’s employment
Decrease in tangible losses to crime victims
Overall did Carneiro and Heckman (2003) find perry pre school to be benefitting?
They found the benefits to massively outweigh the costs

What effect did Garcia, Heckman, Lead, Prados (2020) find that Perry pre school had on parental labour income
It increased parental labour income
What is the reason behind Garcia, Heckman, Lead, Prados (2020)’s discovery that perry pre-school increased parents labour income
Parents could work because kids went to pre school and didn’t stay at home
What did Barnett (2003) conclude about the programs he studied (2)
They dramatically improved the life outcomes of disadvantaged children
However the interventions were very high quality targeted to a very low number of severely disadvantaged children. Can the results be replicated at a larger scale?
Head Start
A large preschool program in the US serving disadvantaged children
How does Head Start compare to other early interventions in this module
Head Start is a much larger and less well funded program
Who studied the effects on test scores of Head Start
Currie and Thomas (1995)
What did Currie and Thomas (1995) find for effects of Head Start between while and black children (2)
Large effects for white children but very small effects for black children
Black people benefit from the program as much as white people do whilst enrolled but experience much larger fade out effects
What did Currie and Thomas (2000) believe for the reason test score effects of Head Start fade out for black people more
They attend lower quality schools after leaving the program than white people
Who studied the impact of Head Start on adult outcomes
Currie, Duncan and Garces (2000)
What did Currie, Duncan and Garces (2000) find regarding the impact of Head start
There were important effects on school achievement and crime for black people
Sure Start
Similar to head start but like Head Start
Who investigated Sure Start
Carneiro et al (2024)
What did Carneiro et al (2024) find regarding Sure Start (2)
20% higher test scores with 6 years of Sure Start
Effect of Sure Start is biggest at age 11 and 16
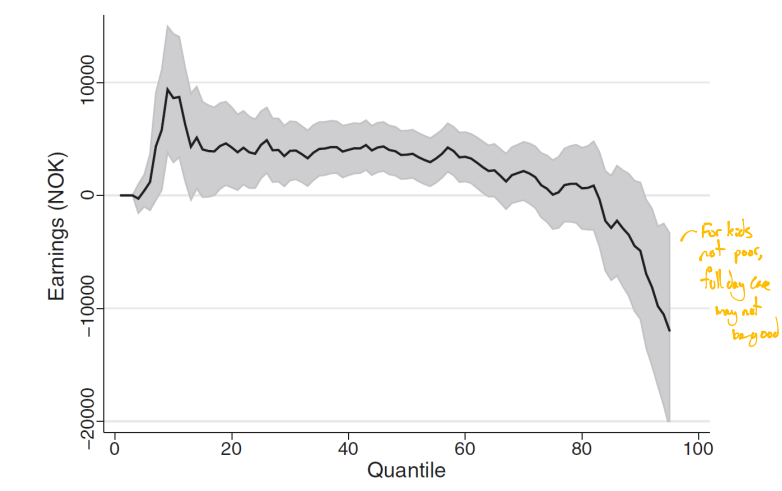
What did Havnes and Mogstad (2015) find regarding full day care on rich kids
For kids who are rich, full day care may have a negative effect on earnings