Micro Econ EXAM 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Economics defintion
The study of how individuals in society allocate their limited resources to satisfy the practically unlimited wants.
Macro
The study of the overall aspects of the working economy
Micro
The study of the individual units that makeup the economy
5 foundations of Economics
1.) Incentives
2.) Trade offs
3.) Opportunity Cost
4.) Marginal Thinking
5.) Trade
Incentives
the factors that motivate you to act or not act
Trade offs
a balance achieved between two desirable but incompatible features; a compromise.
Opportunity Cost
value of the next best alternative not chosen, what is best value
Marginal Thinking
helping optimize choices by comparing incremental changes rather than totals
Trade
the action of buying and selling goods and services (more trade the better for everyone)
Positive Incentives vs Negative Incentives
reward system vs providing undesirable consquences
Direct Investments
obvious and immediate awards or penalties for specific action
Indirect Investments
consequences that are secondary effects or unintened consquences of a direct influence
Circular Flow

Comparative Advantage
where an individual, a business, buisness or a country can produce at a lower opportunity cost than a competitor
Economics is a…
social science
positive statements
something that can be tested and validated Ex. what is the unemployment rate?
normative statement
opinion of what should be
Econ Model definition
a simplified, abstract representation of reality. NOT SUPPOSED TO BE REALISTIC
Assumptions
a simplifying condition or initial premise used to build models, theories, and analyses, helping to make complex systems manageable by isolating key factors, even if they aren't perfectly realistic
Ceteris Peribus
all other things equal, controlling other things by holding a variable constant
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
a model that illustrates a combination of outputs that an economy produces, assumptions made = tech, resources, 2 goods.
endogenous vs exogenous
Inside our model variables vs outside our model variables.
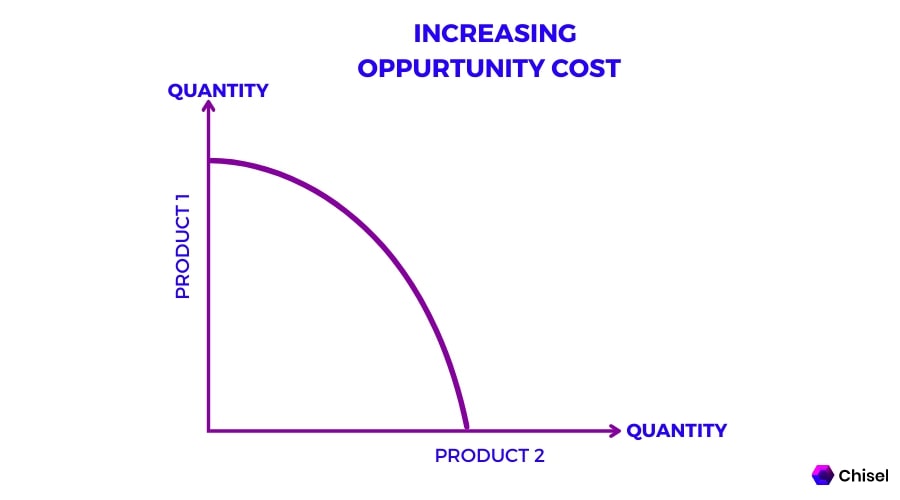
Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs
as you produce more of one good, the cost (in terms of the other good you give up) rises because resources aren't perfectly adaptable
Specialization
limiting ones work to a particular area or areas
Absolute Advantage
When someone can produce more of something than someone else
Market Place
Consumers + firms
Supply
How many units (price) and Quantity Supply (qs) so if price goes up than products go up
Qs greater than Qd
surplus
Qd greater than Qs
shortage
Change in Supply
1.) Cost of inputs (amount of products produce)
2.) Tech (tech you pay once, people $$$)
3.) # of suppliers
4.) Price Expectations (the price you can get day by day)
Law of Supply
holding other factors constant, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers also increases, and as the price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases
Demand
Consumers and relationships between 2 particular variables.
Change in Demand
1.) Income
2.) price of other goods (substitute and complement)
3.) taste
4.) price expectations
5.) # of buyers
Law of Demand
Price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions. Inverse relationships
What way does supply and demand move
right to left