5.3, 5.4 Energy / nutrient cycles
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
How to extract photosynthetic pigments and separate them using chromatography
Add leaf to pestle and mortar. Add low boiling point, polar solvent a few drops at a time and crush into a slurry.
Add chlorophyll solution using capillary tube to chromatography paper with origin drawn with a ruler and pencil.
Place paper in solvent
Leave for solvent to travel paper
Rf Value
Retention factor
(Distance pigment travelled from origin / distance solvent front travelled from origin)
Producers
Plants and algae that access sunlight energy directly
Consumers
Animals obtain the energy indirectly from the consumption of plants
Decomposers
Bacteria and fungi obtain the energy from the decomposition of dead plants and animals
aka saprabionts
feed on dead organic matter
secrete digestive enzymes out of their cells
extra cellular enzymes hydrolyse large, insoluble organic molecules into small, soluble molecules
small, soluble molecules are absorbed into cells
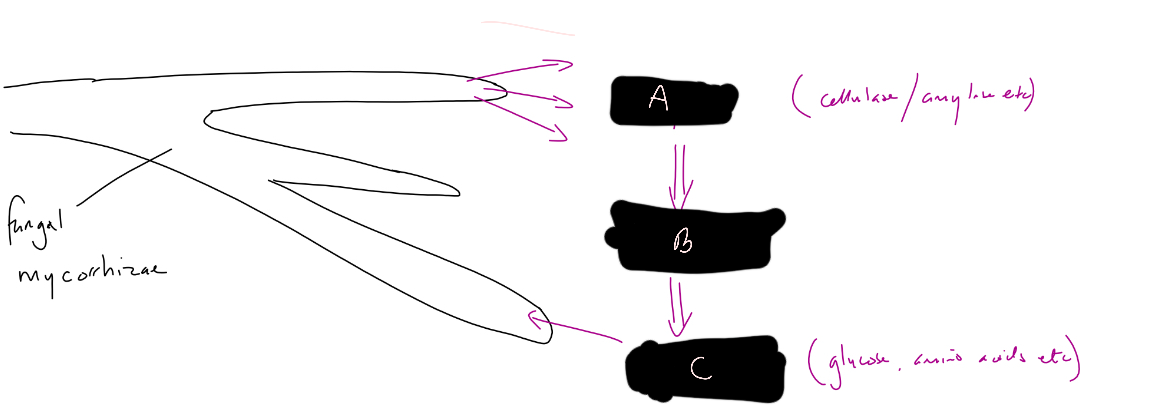
A: extra cellular enzymes
B: extracellular digestion
C: small, soluble molecules
How 99% of energy is lost from the sun
Some light is reflected off the surface of the leaf
Some light is transmitted through the leaf without hitting the chloroplasts
Not all wavelengths of light absorbed are used in photosynthesis
GPP
gross primary production
total mass glucose produced in photosynthesis by producers
NPP
net primary production
total mass of glucose remaining after glucose used in respiration is removed (lost as heat)
biomass
total mass of living material / organic molecules in organism
what % of energy is passed to the next energy flow stage
10%
How is 90% of energy lost through the energy cycle stages (5)
Not all biomass is eaten
Not all biomass is digested
Dead tissue
Faeces and urine
Some biomass used in respiration to provide ATP for metabolism, lost as heat
N = I - ( R + F)
N = net secondary production
I = biomass ingested
R = Respiratory losses
F = energy lost as faeces and urine
Organic forms in phosphorous cycle (4)
phospholipids
ATP / adp
dna / rna
nadp
inorganic forms in phosphorous cycle
Phosphate
Draw the phosphorous cycle
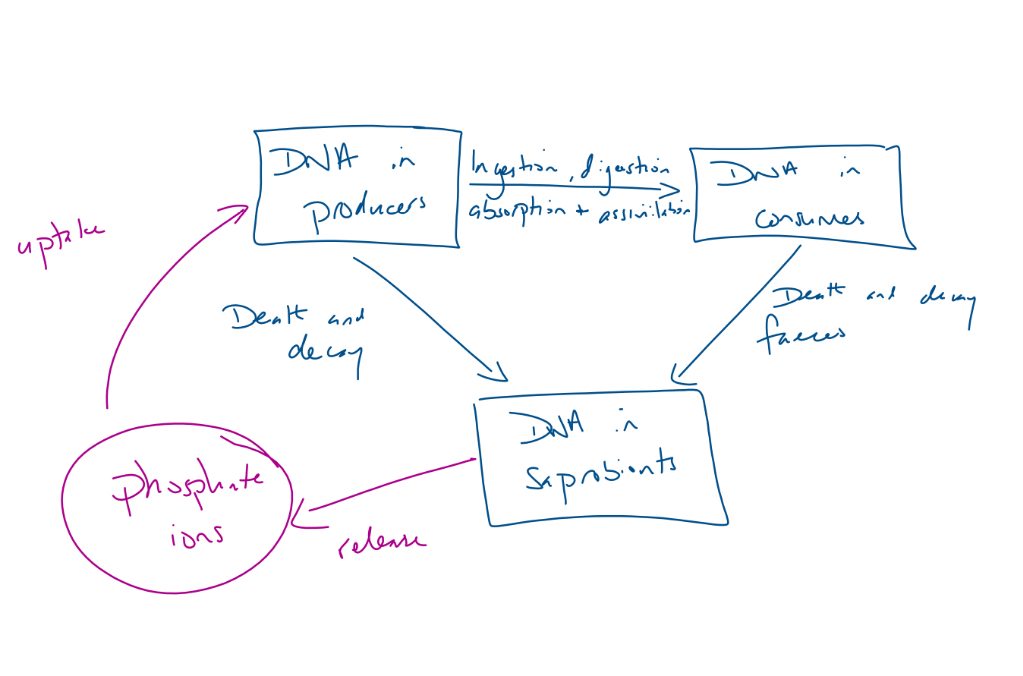
How does DNA in consumers come from DNA in producers?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation
Proteins in saprabionts from proteins in consumers
Death and decay
Urine and faeces
Proteins in saprabionts from proteins in producers?
Death and decay
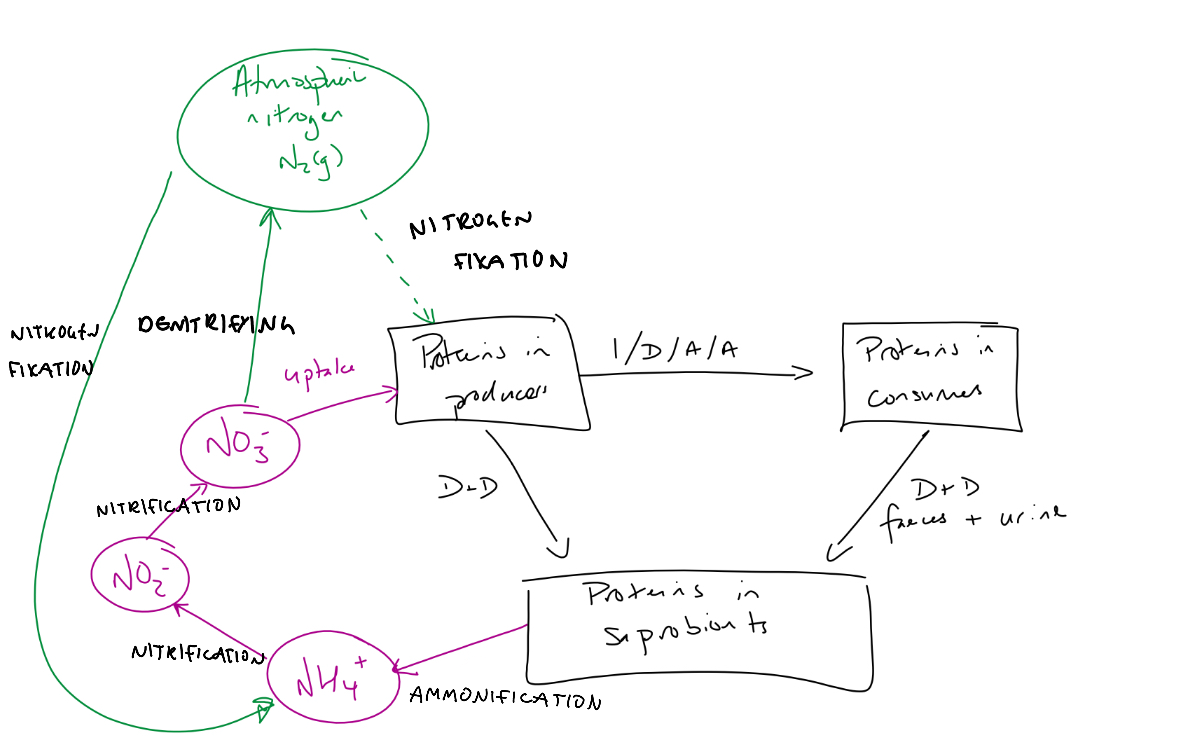
Draw the nitrogen cycle
Organic forms in the nitrogen cycle (5)
Amino acids / proteins
DNA/RNA
ATP
NADP/NAD/FAD
urea
Inorganic forms in nitrogen cycle (4)
Ammonium ions (NH4+)
Nitrite ions (NO2-)
Nitrate ions (NO3-)
Atmospheric nitrogen (N2 gas)
Ammonification
Saprobiotic bacteria convert amino acids (and urea)
Into ammonium ions (NH3 from amino acid to NH4+)
phosphate ions from saprabionts to DNA in producers?
Phosphate ions are released from the DNA of saprabionts to soil
Are uptaken and incorporated into the DNA of producers
Nitrification
Nitrifying, aerobic bacteria convert
Ammonium ions to nitrites to nitrates
Denitrification
Denitrifying, anaerobic bacteria convert nitrates to atmospheric nitrogen
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonium ions
Nitrogen fixing bacteria (4)
some are free living in soil
Others have a mutualistic relationship with plants
Eg legumes (peas, beans, clover)
Found in root nodules
Mutualistic relationship between nitrogen fixation bacteria and legumes
plant uses NH4 to synthesise amino acids
bacteria obtains sucrose to be used as respiratory substitute
Eutrophication
inorganic fertilisers contain NH4+ and PO4 3-
highly soluble, ions are leeched into aquatic ecosystems
increase in NH4+ and PO4 3- leads to algal bloom
prevents light getting to plants, they can’t photosynthesise
saprabionts decompose dead plant material, their population increases
bacterial respiration leads to deoxygenating of water
oxygen sensitive species die