Biomolecules
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
macromolecule
large molecule formed by joining smaller organic molecules together, usually by dehydration synthesis reaction
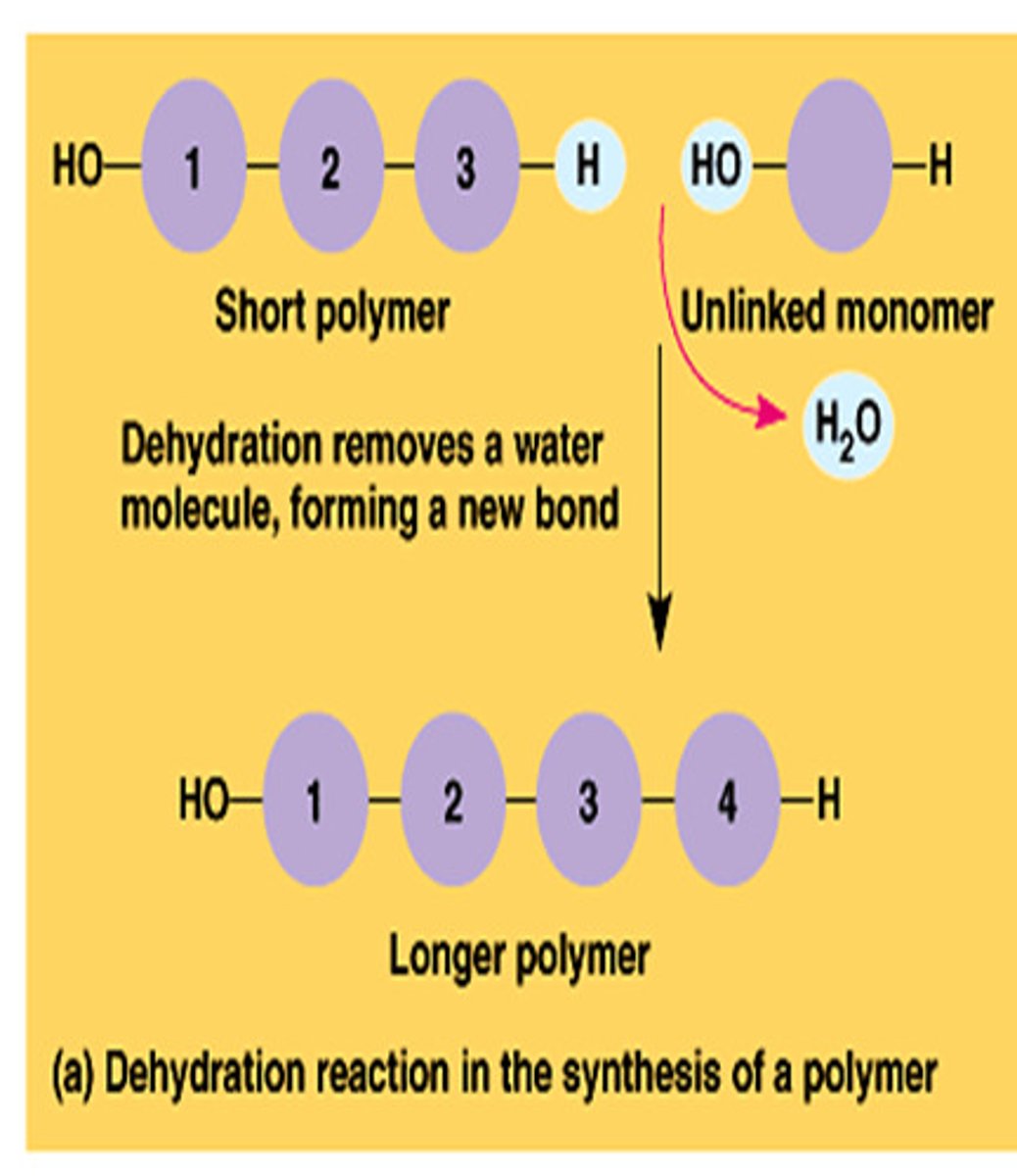
monomer
small molecular unit that is the building block of a larger molecule
polymer
large molecule formed when many smaller molecules bond together
carbohydrate
a class of biomolecules that includes sugars, starches, and fiber; contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; key source of energy
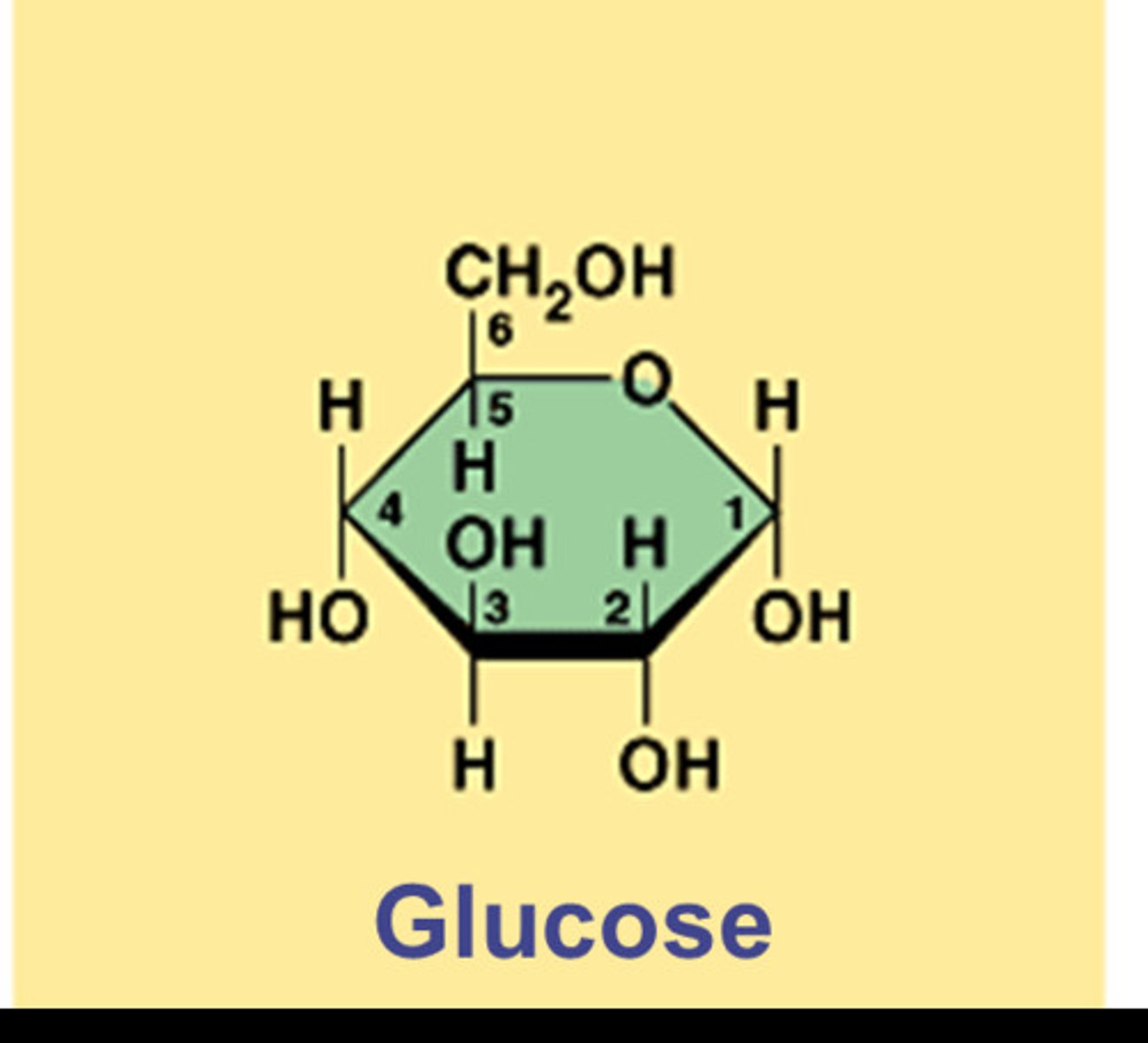
monosaccharide
A single sugar molecule such as glucose or fructose, the simplest type of sugar; monomer of complex carbohydrates
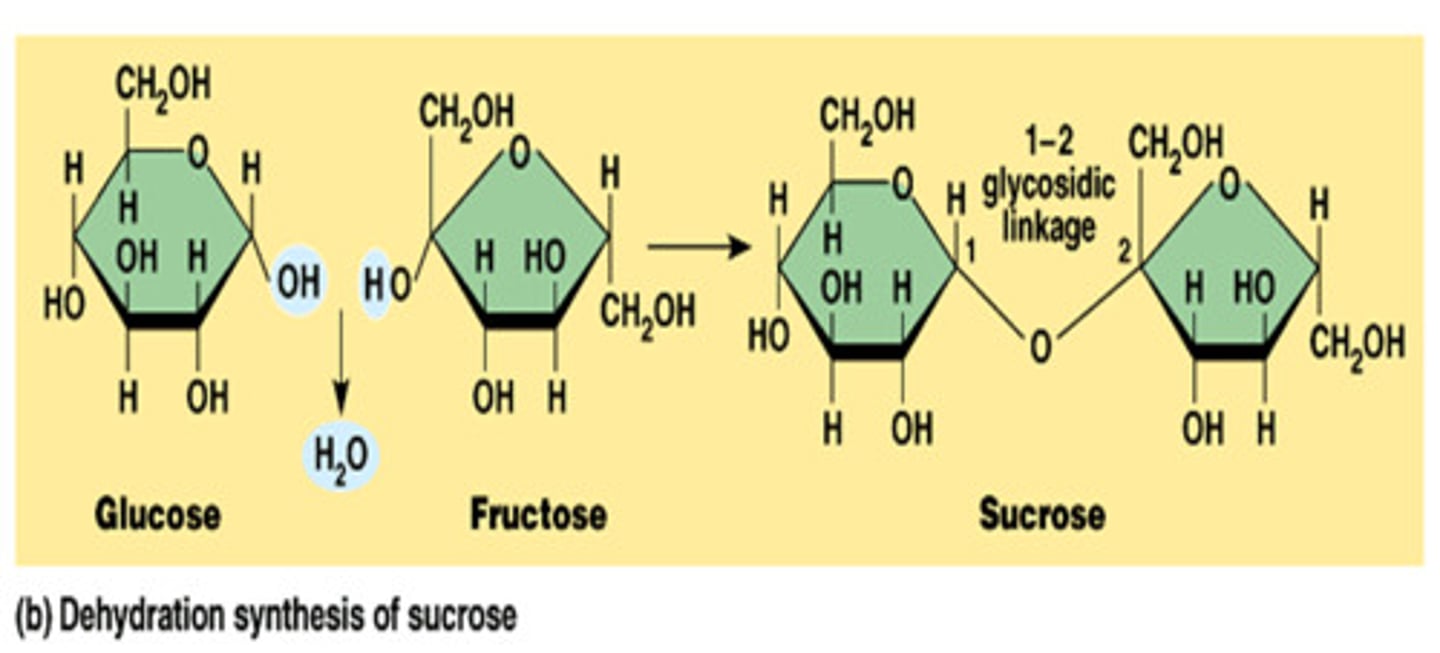
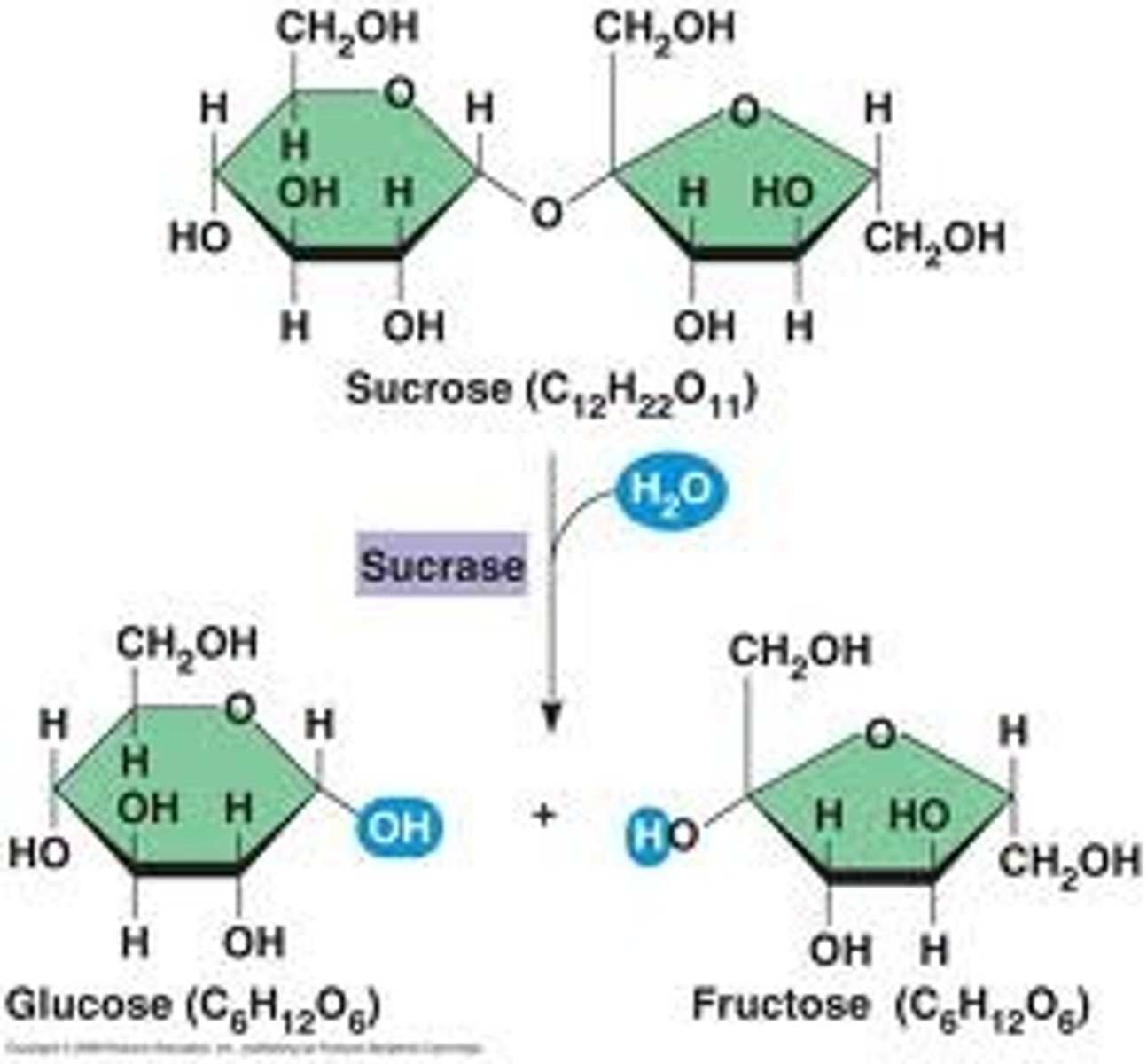
disaccharide
A sugar formed from two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis
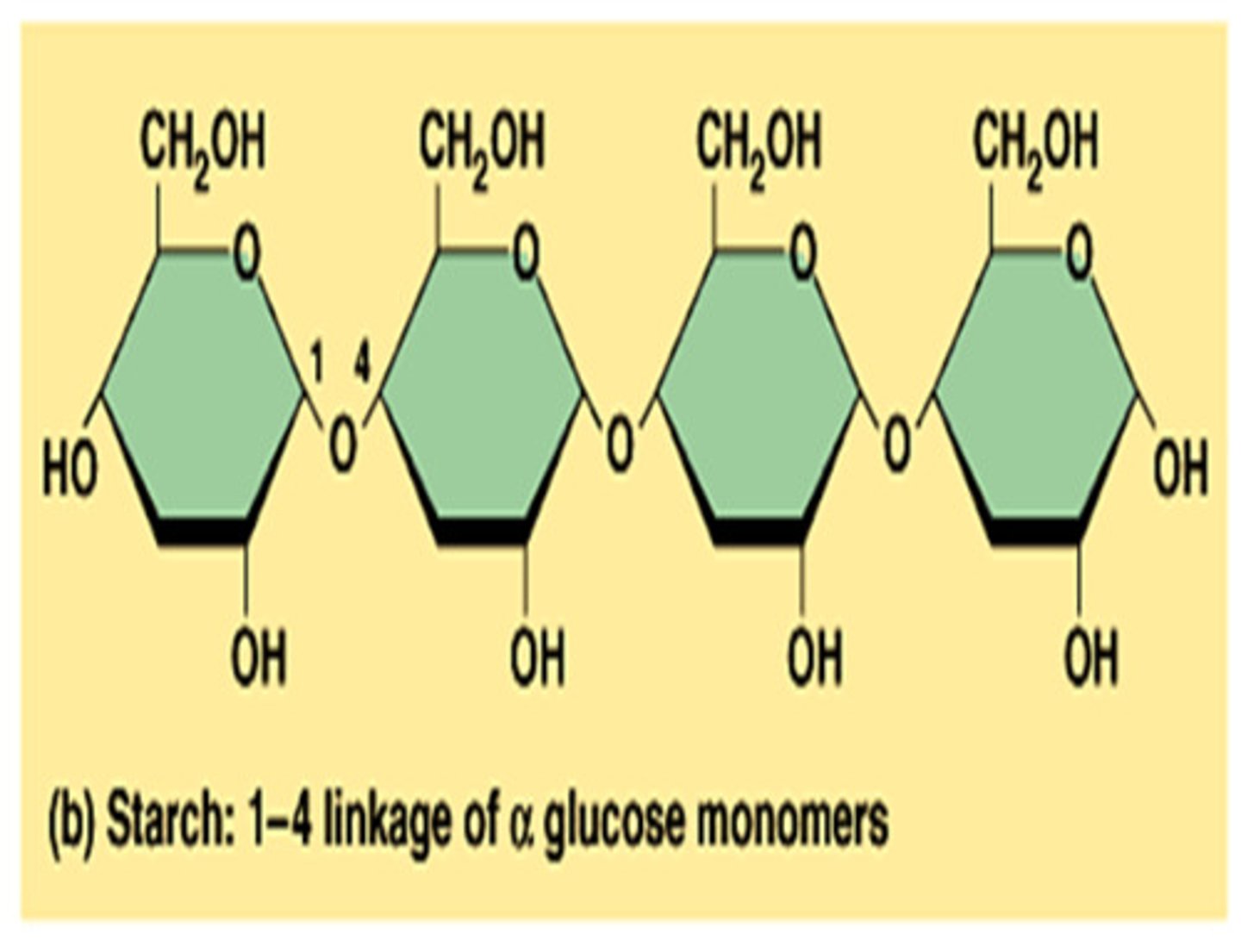
polysaccharide
large macromolecule formed from a long chain of monosaccharides
proteins
a class of biomolecules that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; made up of amino acids; make structure of cell membranes, needed for repair and growth; includes enzymes

amino acid
monomer that makes up proteins; contains carboxyl and amino functional groups
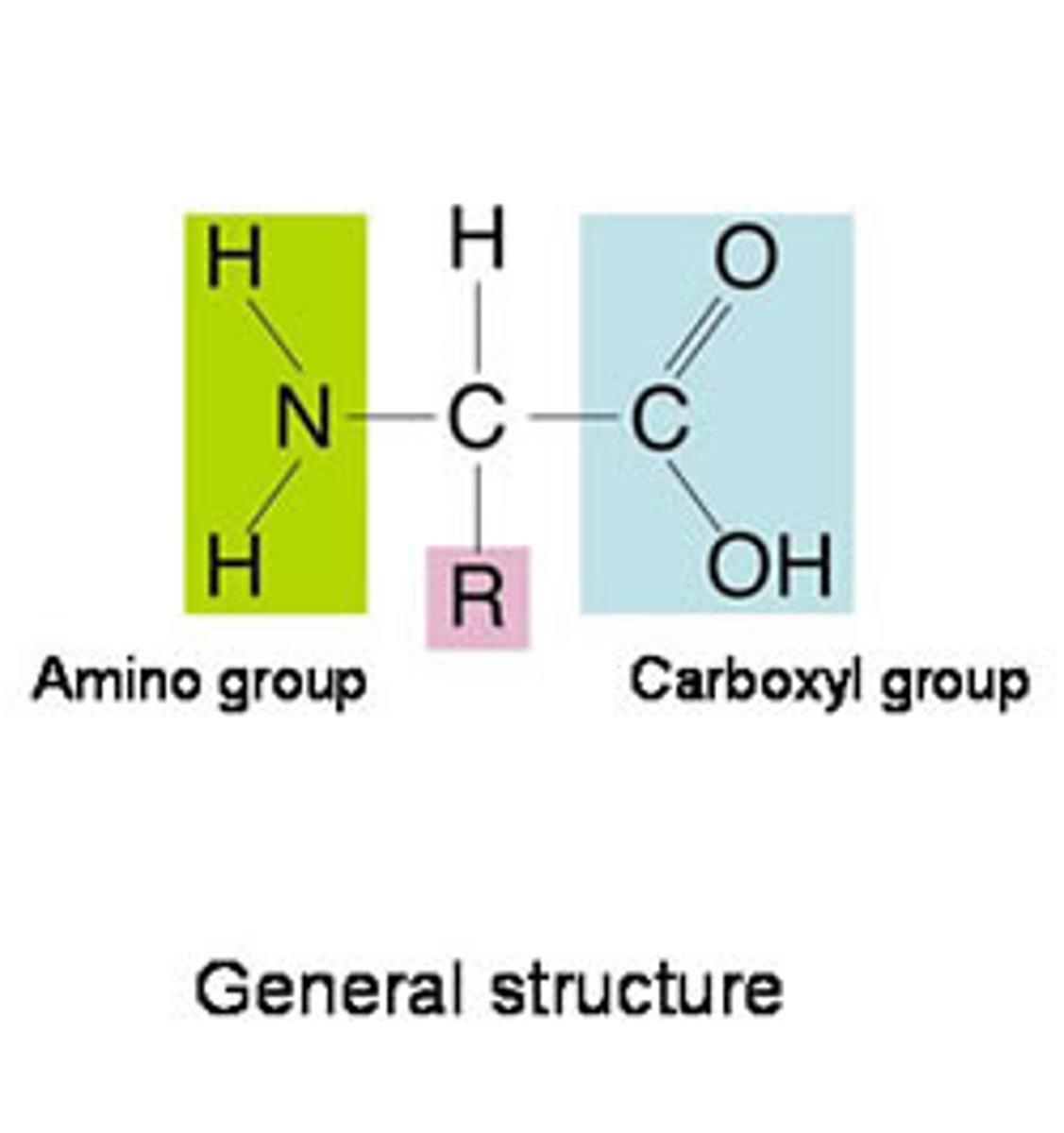
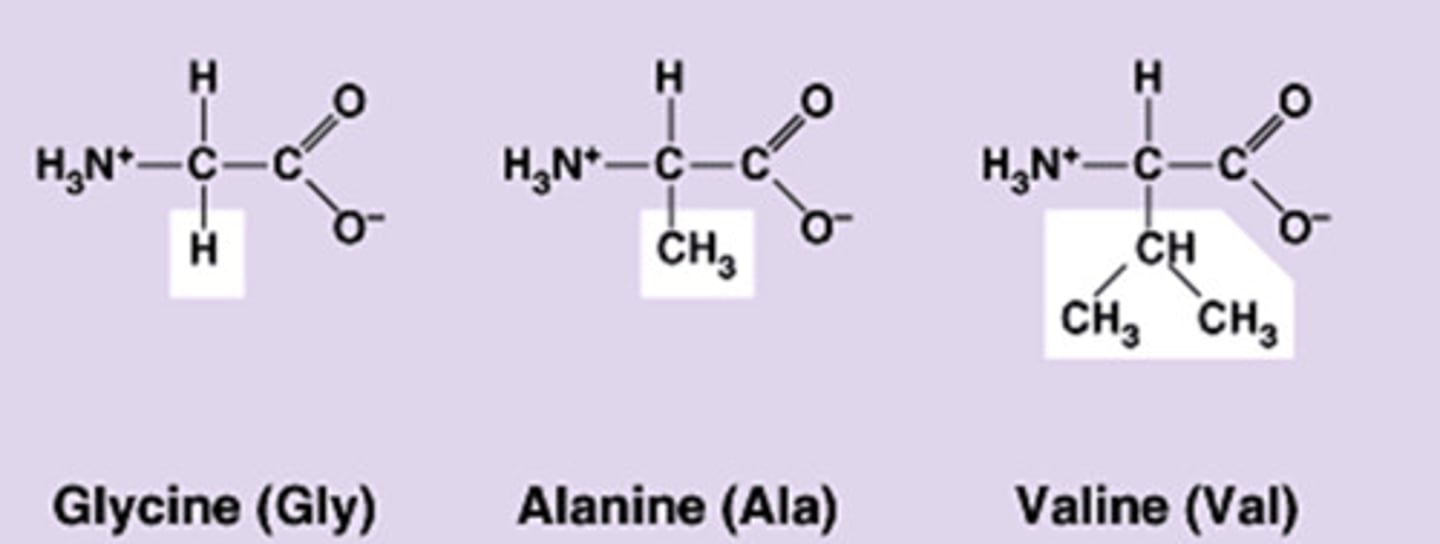
R groups
groups that give different amino acids different properties
lipid
a class of biomolecules insoluble in water and usually made up of fatty acids; make up cell membranes; used by cells for long-term energy storage; examples are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids
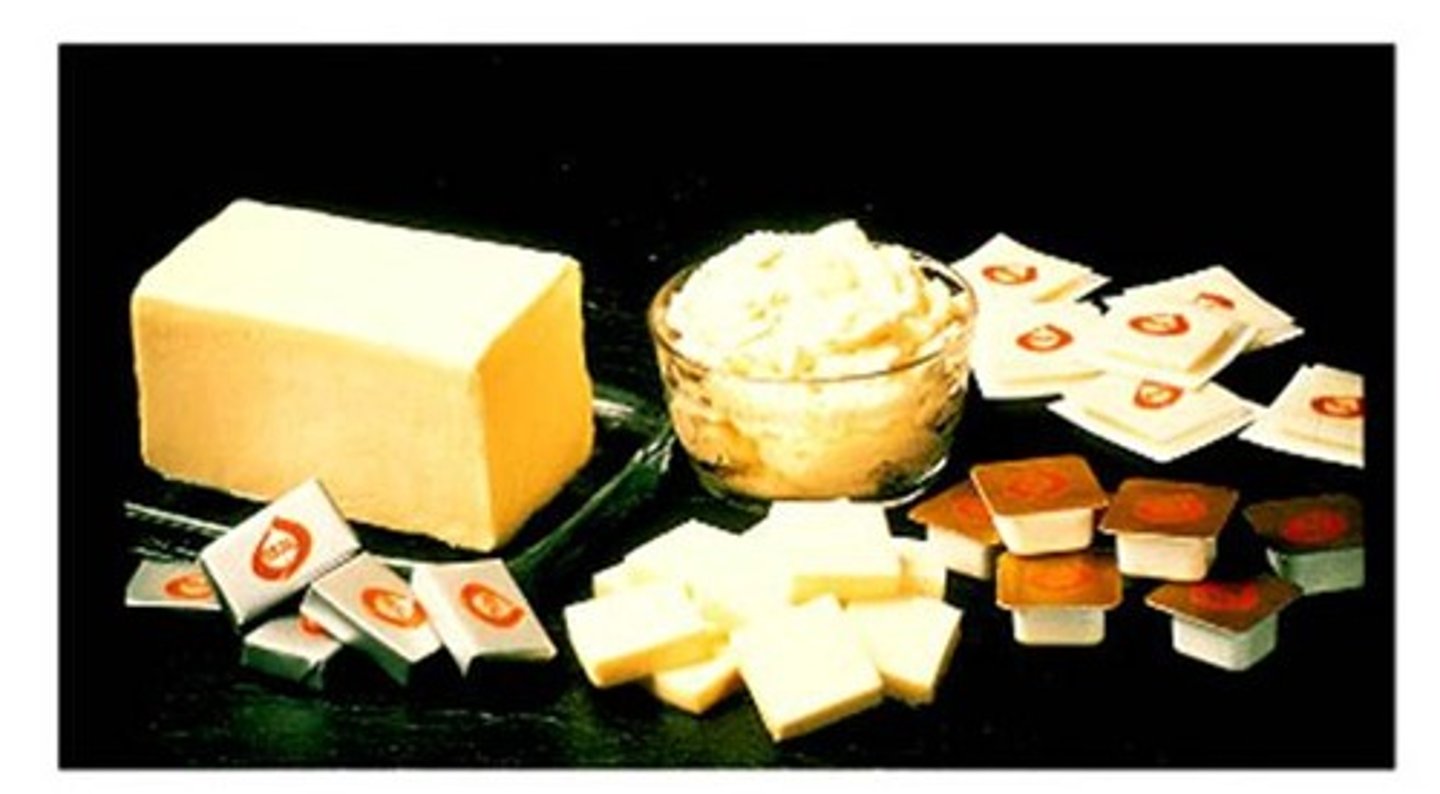

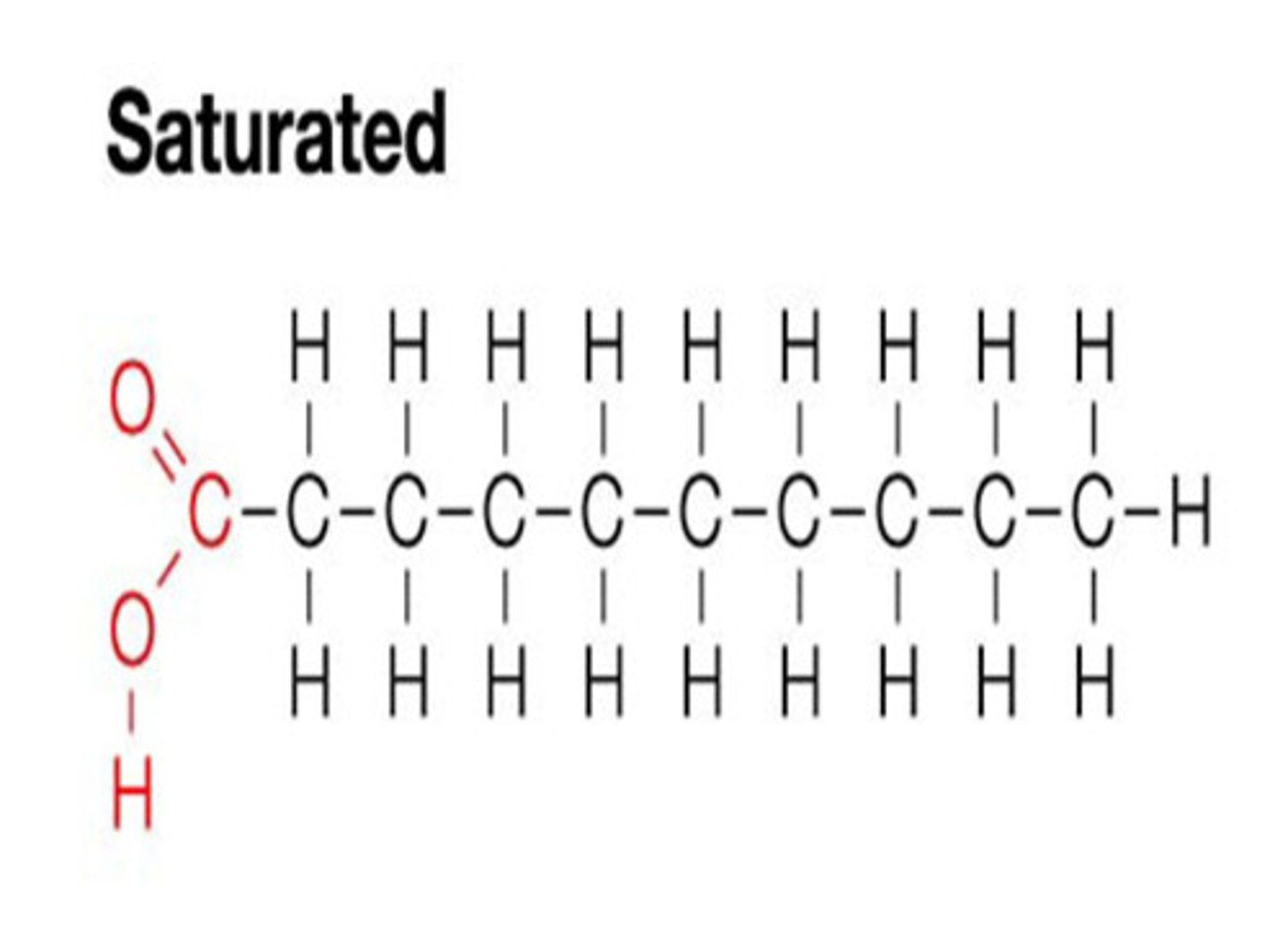
saturated fat
a lipid made from fatty acids that have no double bonds between carbon atoms; solid at room temperature; examples are butter, and animal fat
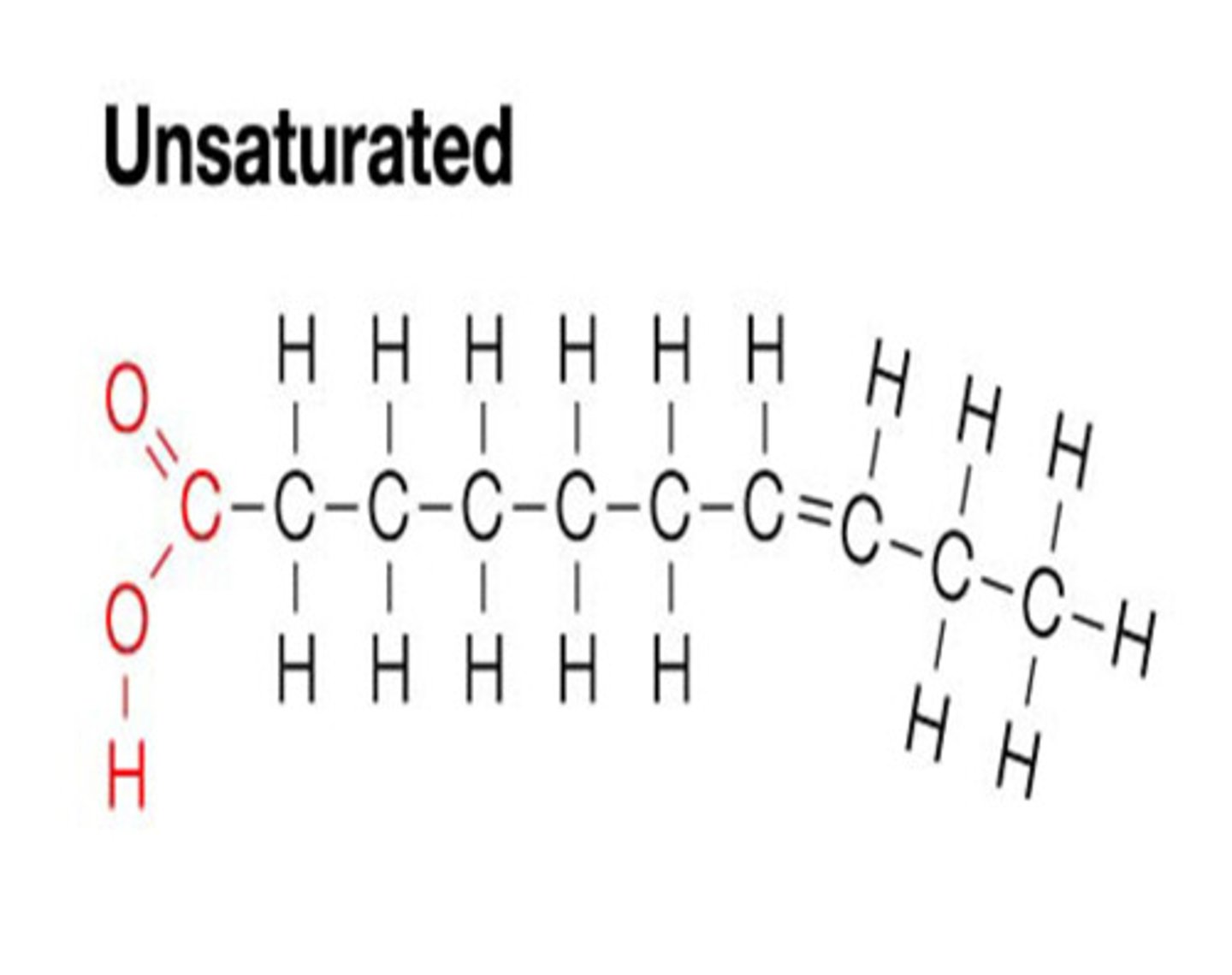
unsaturated fat
A lipid made from fatty acids that have at least one double bond between carbon atoms; liquid at room temperature; examples are vegetable oils
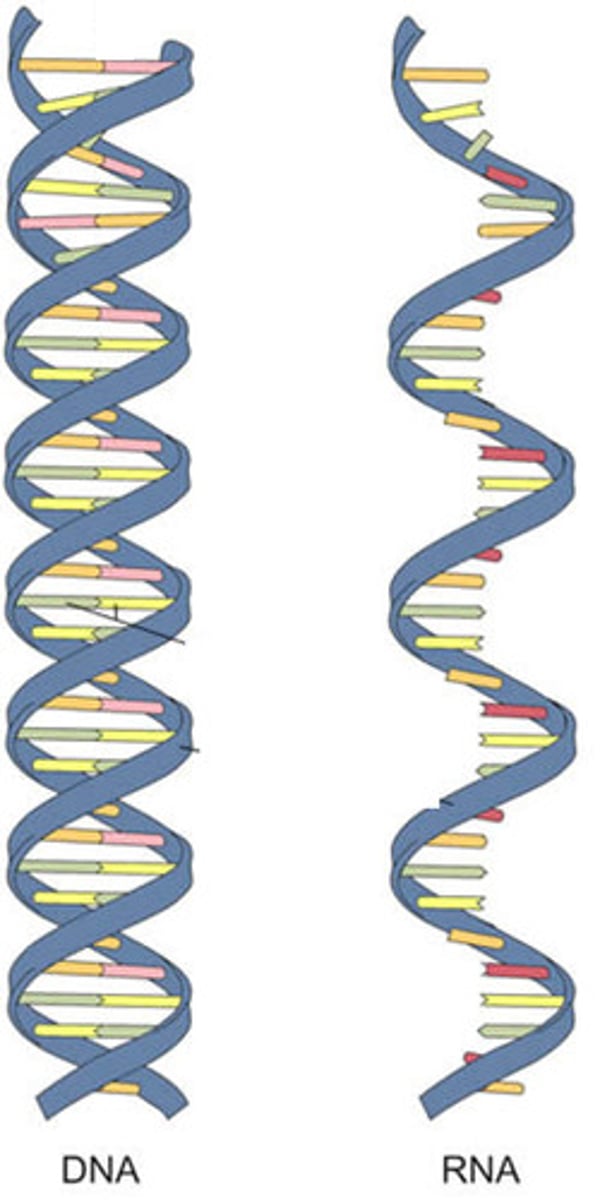
nucleic acid
a class of biomolecles made up of one or two chains of nucleotides; includes either RNA or DNA that carry genetic information
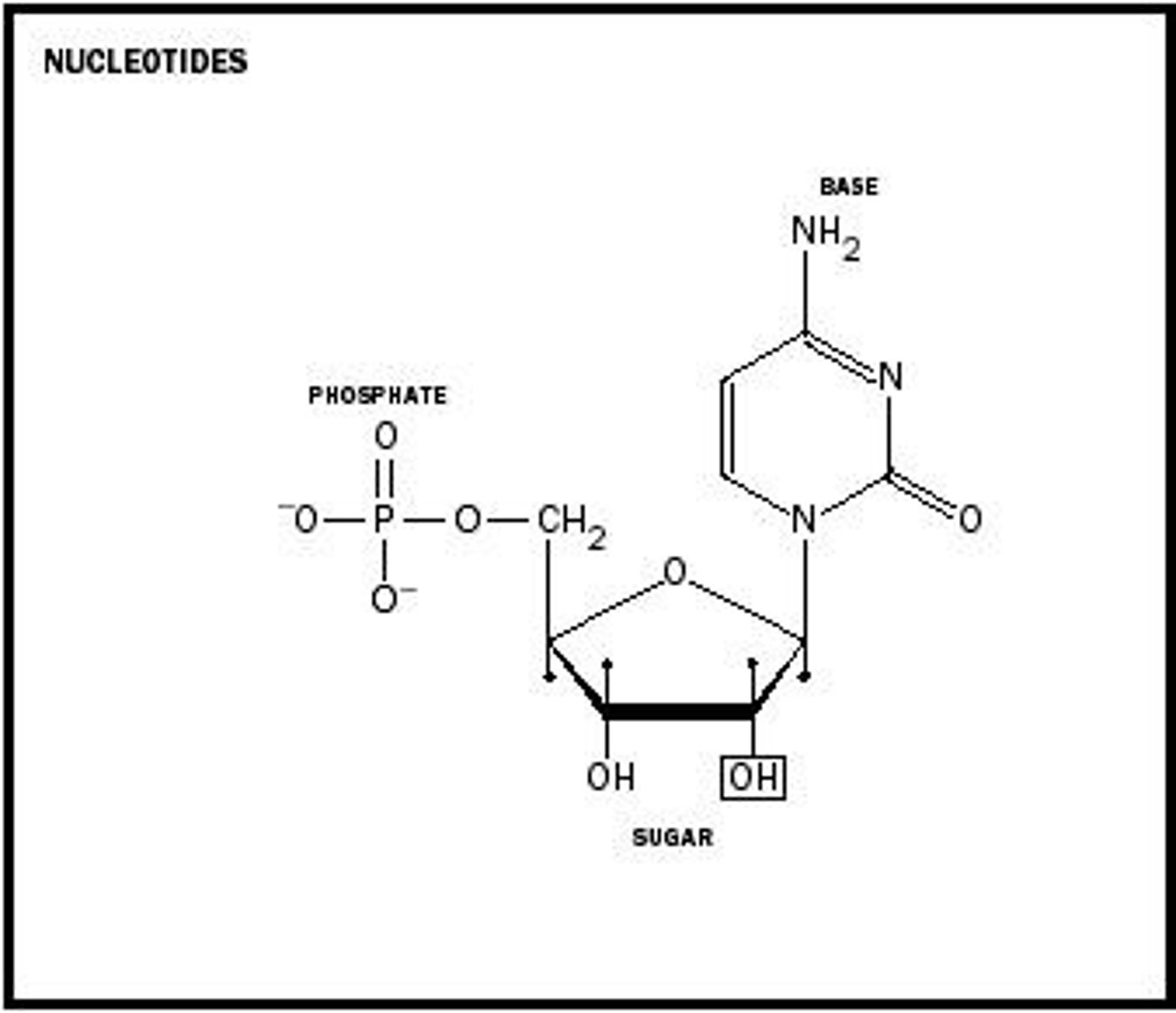
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
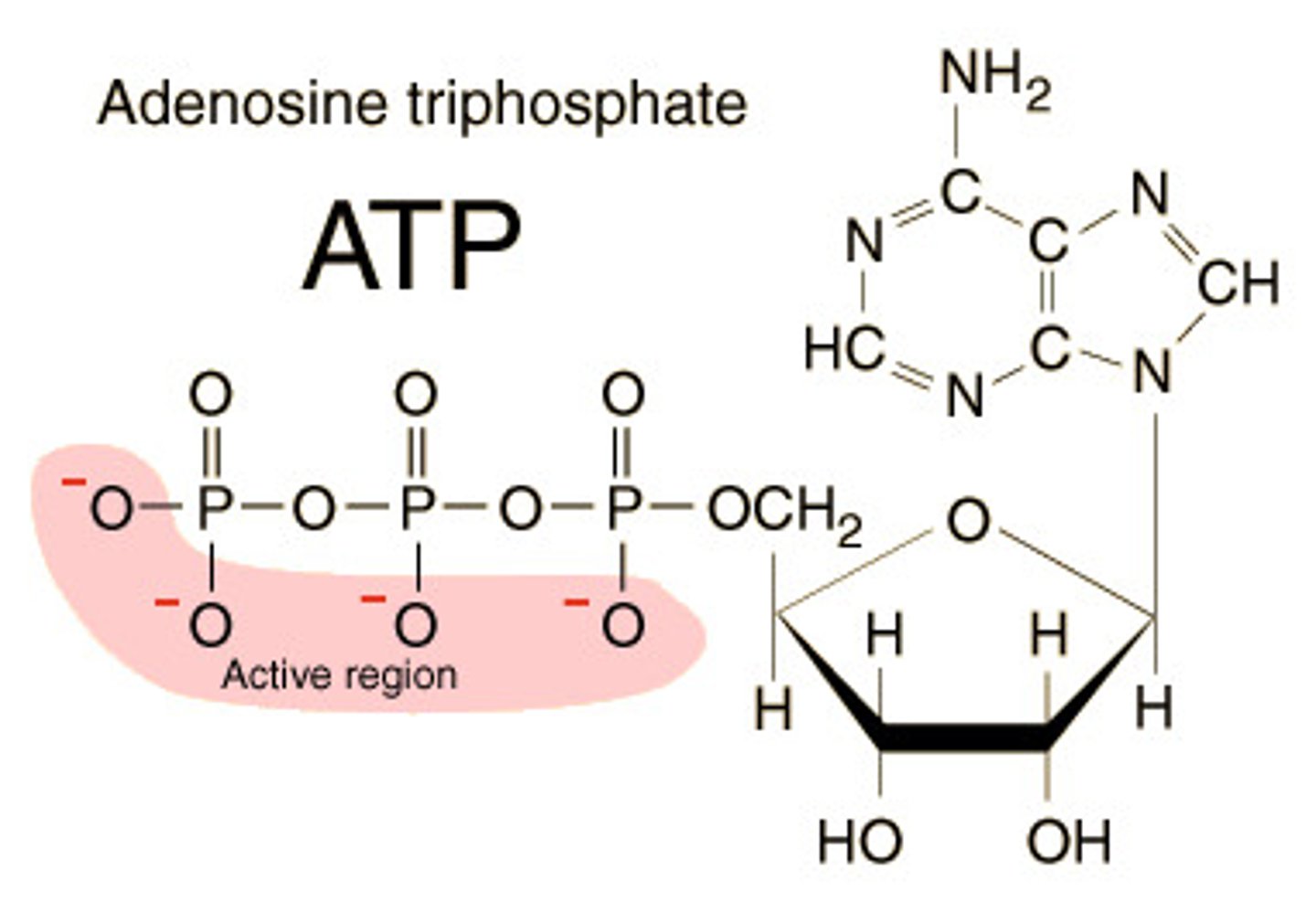
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
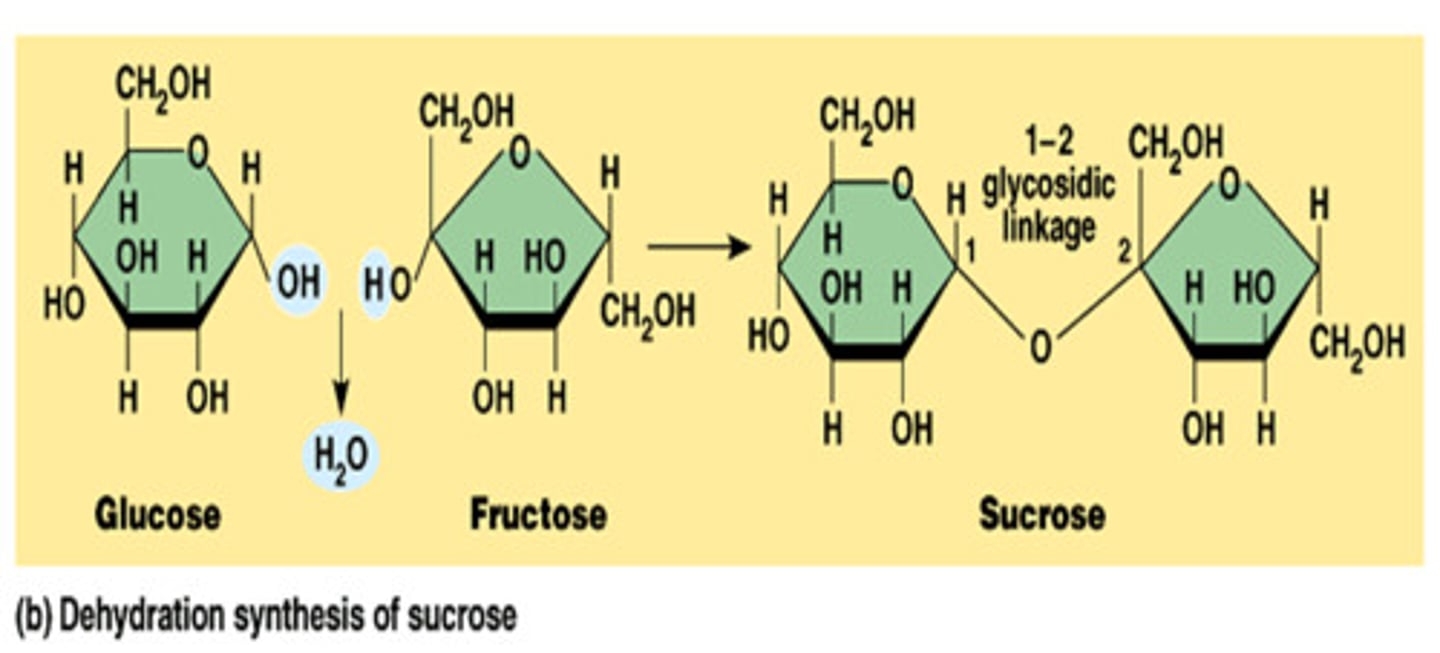
Dehydration synthesis
process where water is removed to put 2 smaller molecules together
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the addition of water; it is essential for digestion
steroid
Lipid with a backbone of four fused carbon rings. Ex. Cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen.
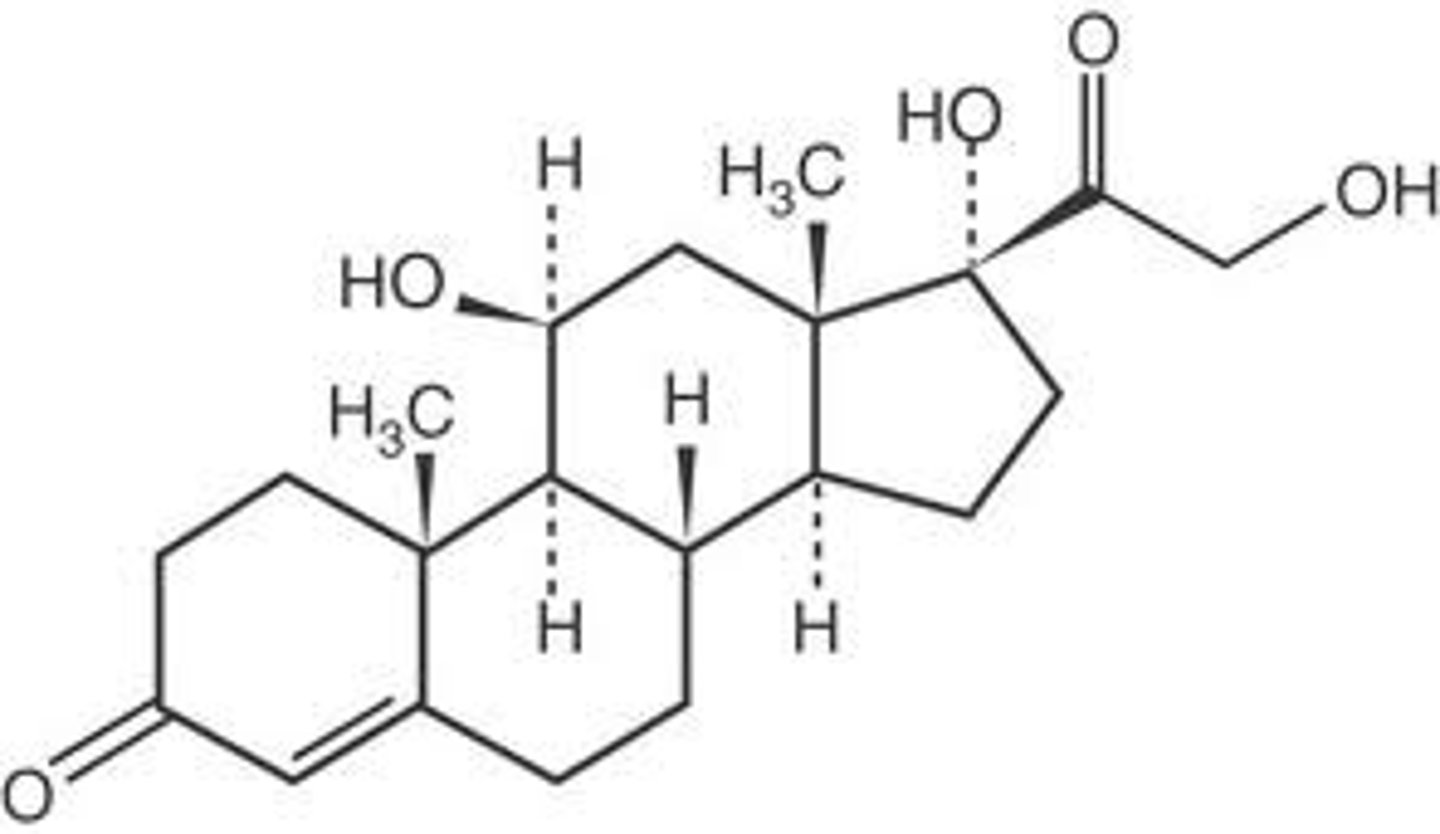
cholesterol
steroid molecule present in the plasma membrane of animal cells. It may clog the arteries causing arteriosclerosis and heart disease