AP BIO FINAL
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Anterior Vena Cava
The large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart.
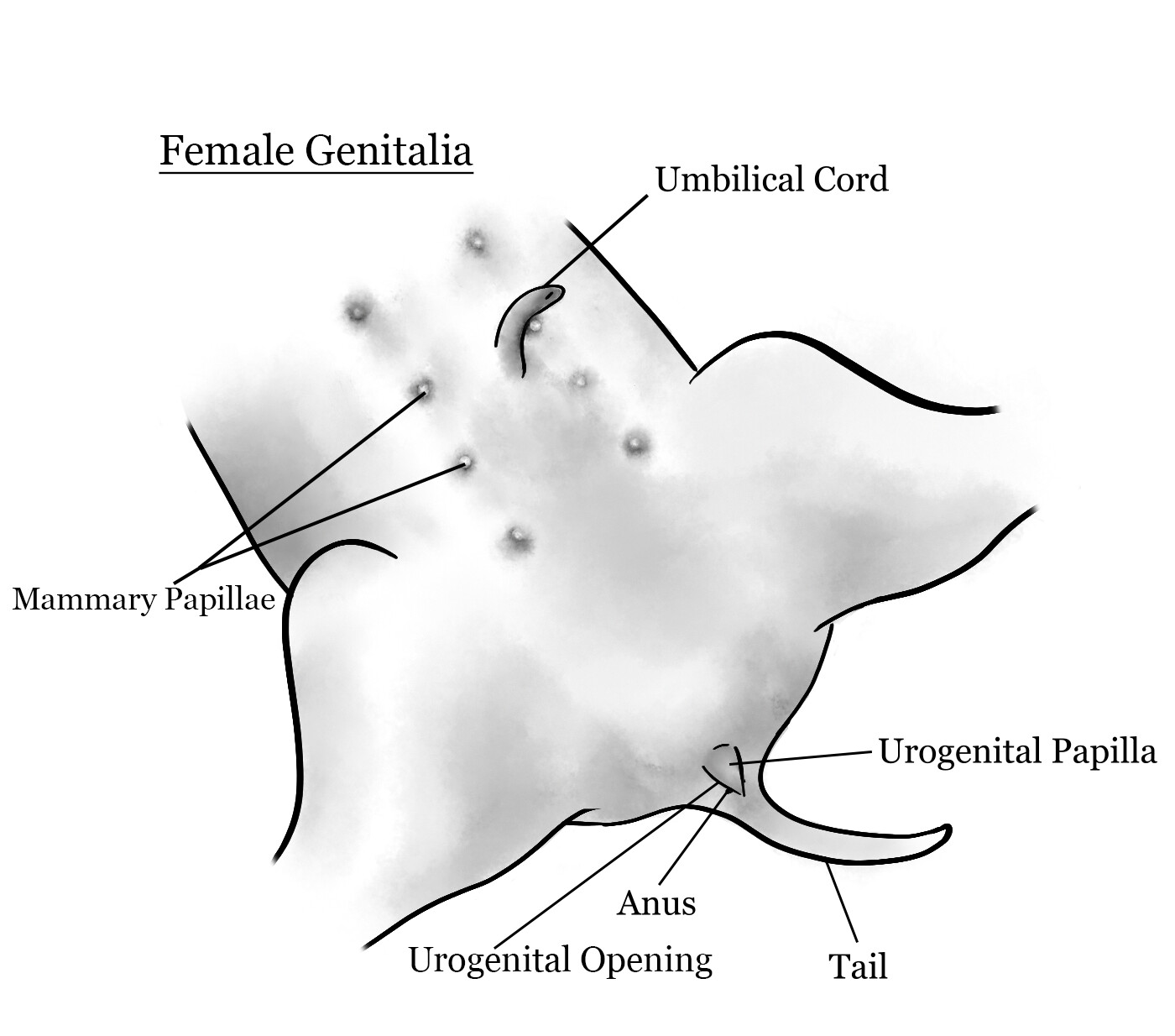
Anus
The opening at the end of the digestive tract through which waste leaves the body.
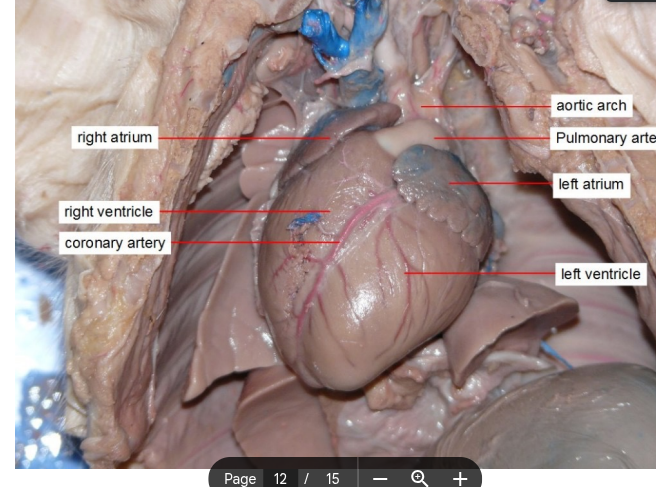
Aortic arch
The curved portion of the aorta that gives rise to the major arteries supplying blood to the head, neck, and arms.
Aortic valve
The valve located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta, which prevents backflow of blood into the ventricle after contraction.
Bicuspid valve/ Mitral valve
A heart valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle, allowing blood to flow in one direction.
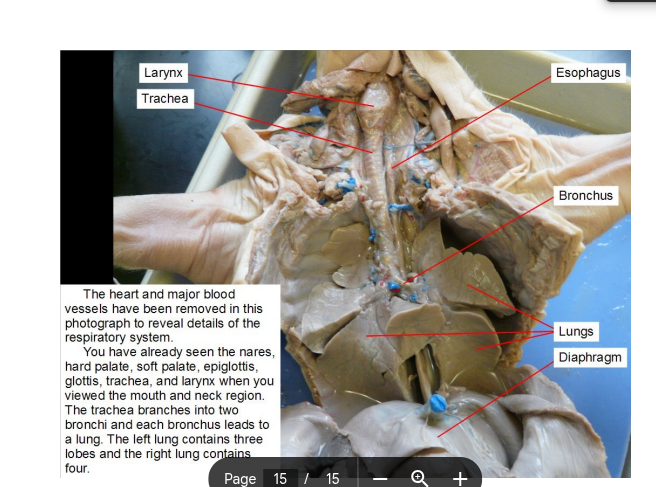
Bronchus
The main airway that branches from the trachea and leads into each lung, facilitating air passage for respiration.
Caecum
It is a pouch connected to the junction of the small and large intestines, playing a role in the absorption of fluids and salts and plays a role in fermentation; acts as a bacterial fermentation chamber for cellulose breakdown
Cardiac sphincter
A ring of muscle at the end of the esophagus and entrance to stomach that regulates the passage of food and prevents reflux.
Carotid artery
The major blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the head and neck, branching from the aorta.
Diaphragm
A dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, playing a crucial role in respiration by contracting and relaxing to facilitate breathing.
Ductus arteriosus
Carries oxygenated blood from pulmonary artery to Aorta, allowing blood to bypass the lungs in the womb
Ductus venosus
Carries oxygenated blood from the umbilical vein to the inferior/posterior vena cava. This allows blood to bypass the liver in the fetus.
Duodenum
The first part of the small intestine, where most of digestion occurs.
Epididymis
A coiled tube located at the back of each testis where sperm mature and are stored.
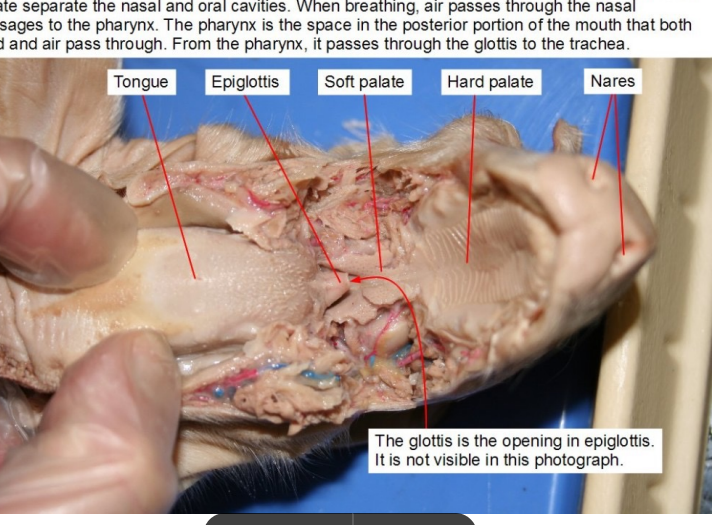
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that covers the trachea during swallowing, preventing food from entering the airway.
Esophagus
The muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) with the stomach, facilitating the movement of food and liquids to the stomach.
External nares
Nostrils
Eyes
Organs that detect light and enable vision.
Foramen ovale
Hole between the atrium which allows blood to flow from the right to left atrium. Allows blood to bypass the lungs in a fetus.
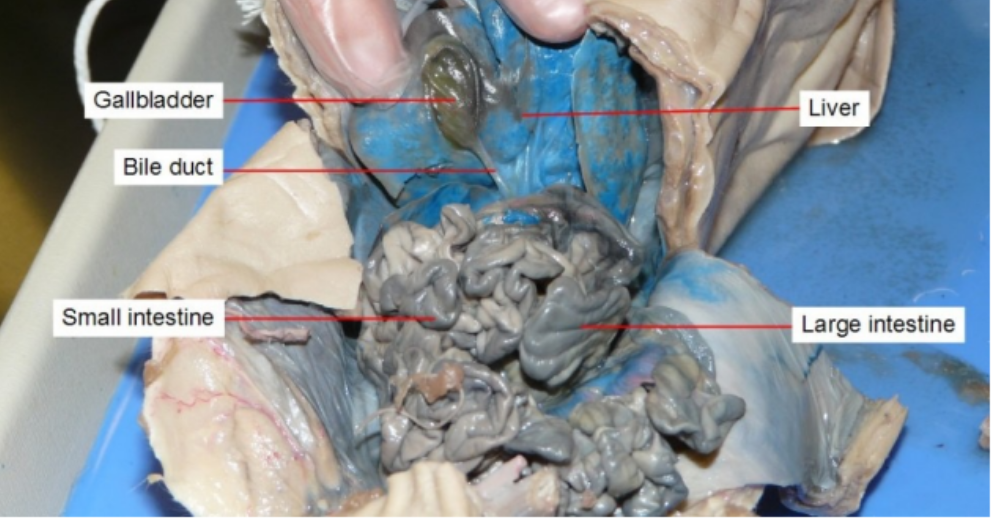
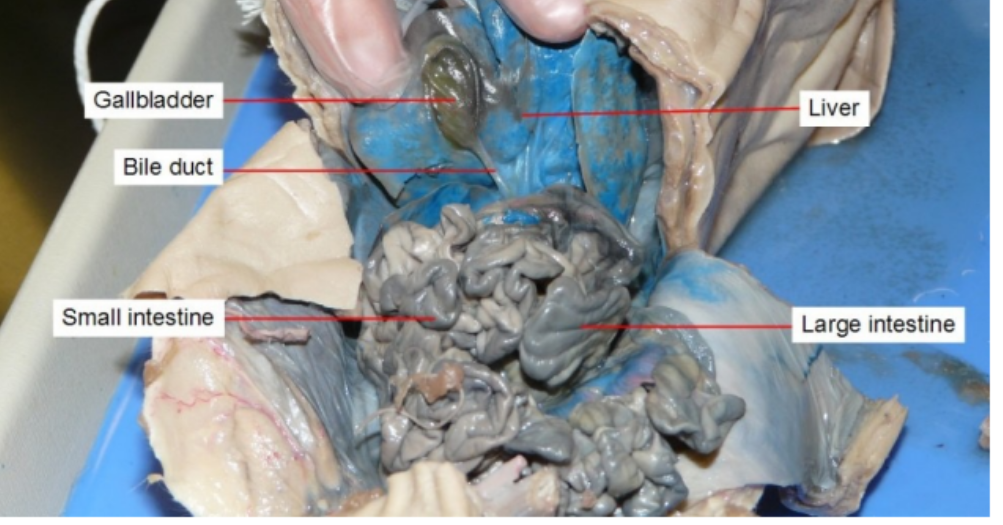
Gall bladder
stores and releases bile to help your digestive system break down fats.
Hard palate
the bony, anterior portion of the roof of the mouth, separating the oral and nasal cavities
Heart
The hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body of a vertebrate animal by contracting and relaxing.
Jejunum
The middle part of the small intestine, helps to further digest food coming from the stomach.
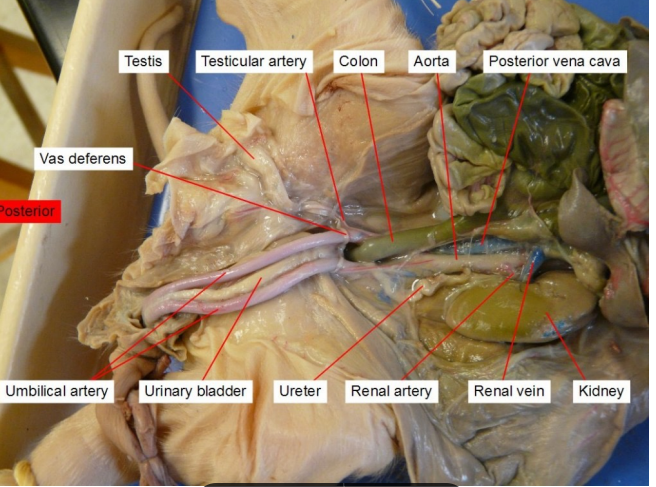
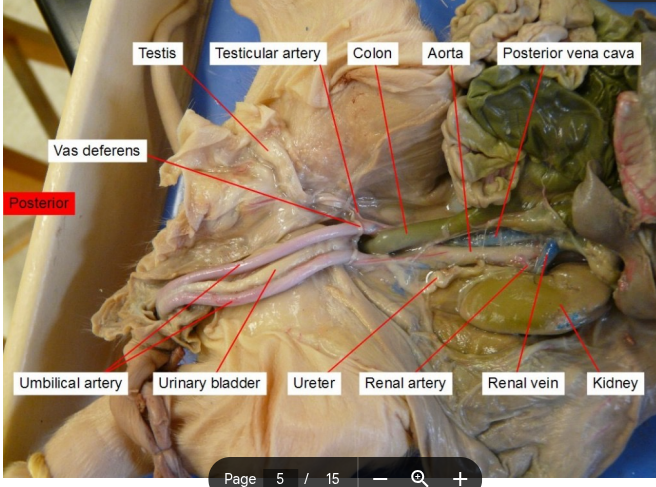
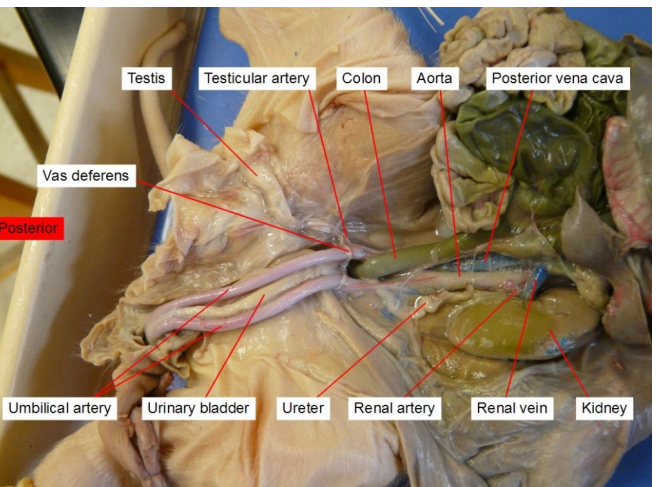
Kidney
filters your blood and removes nitrogenous waste, and is involved in osmoregulation
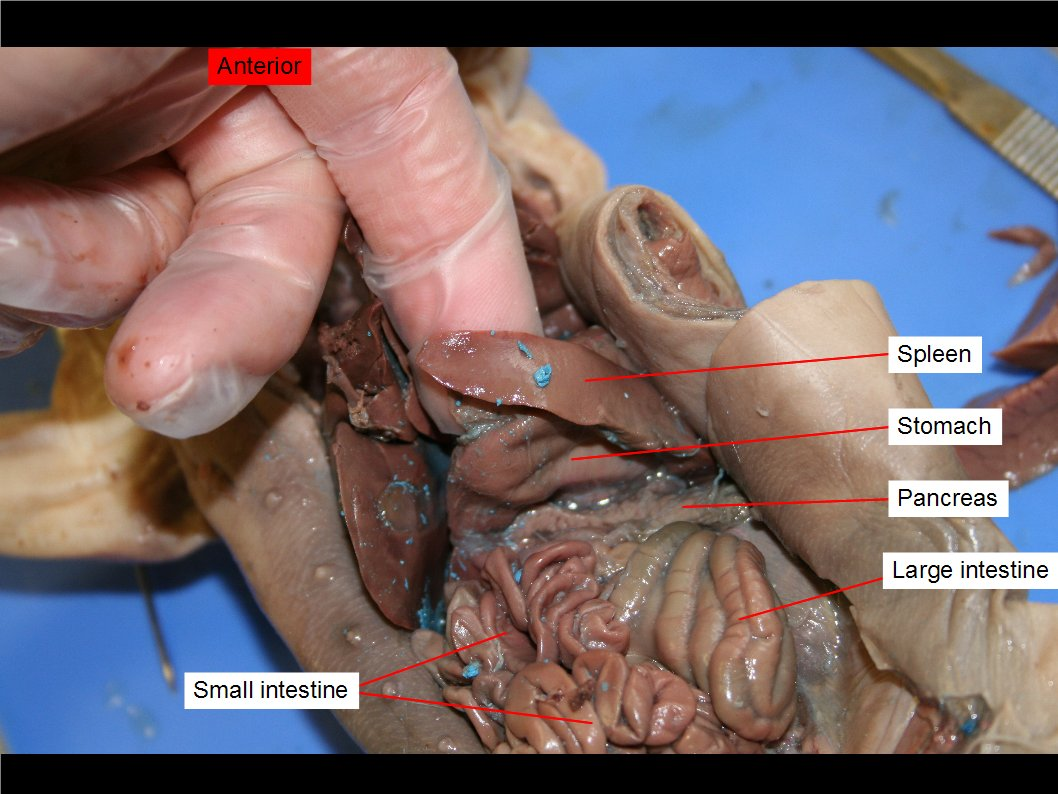
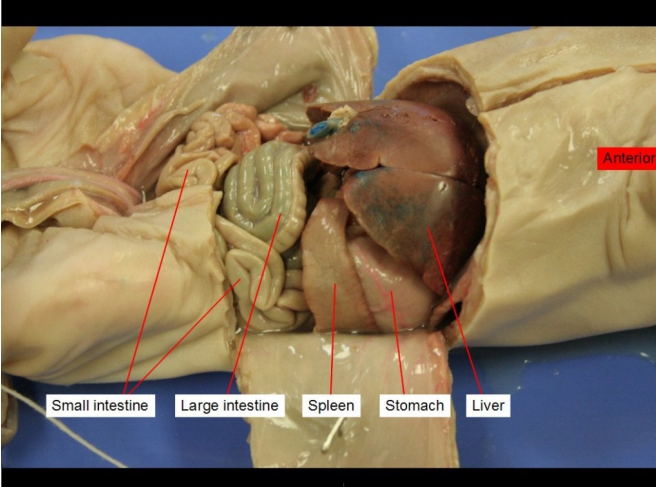
Large Intestine
re-absorb water, vitamins and electrolytes from undigested food
Larynx
where the voice box is.
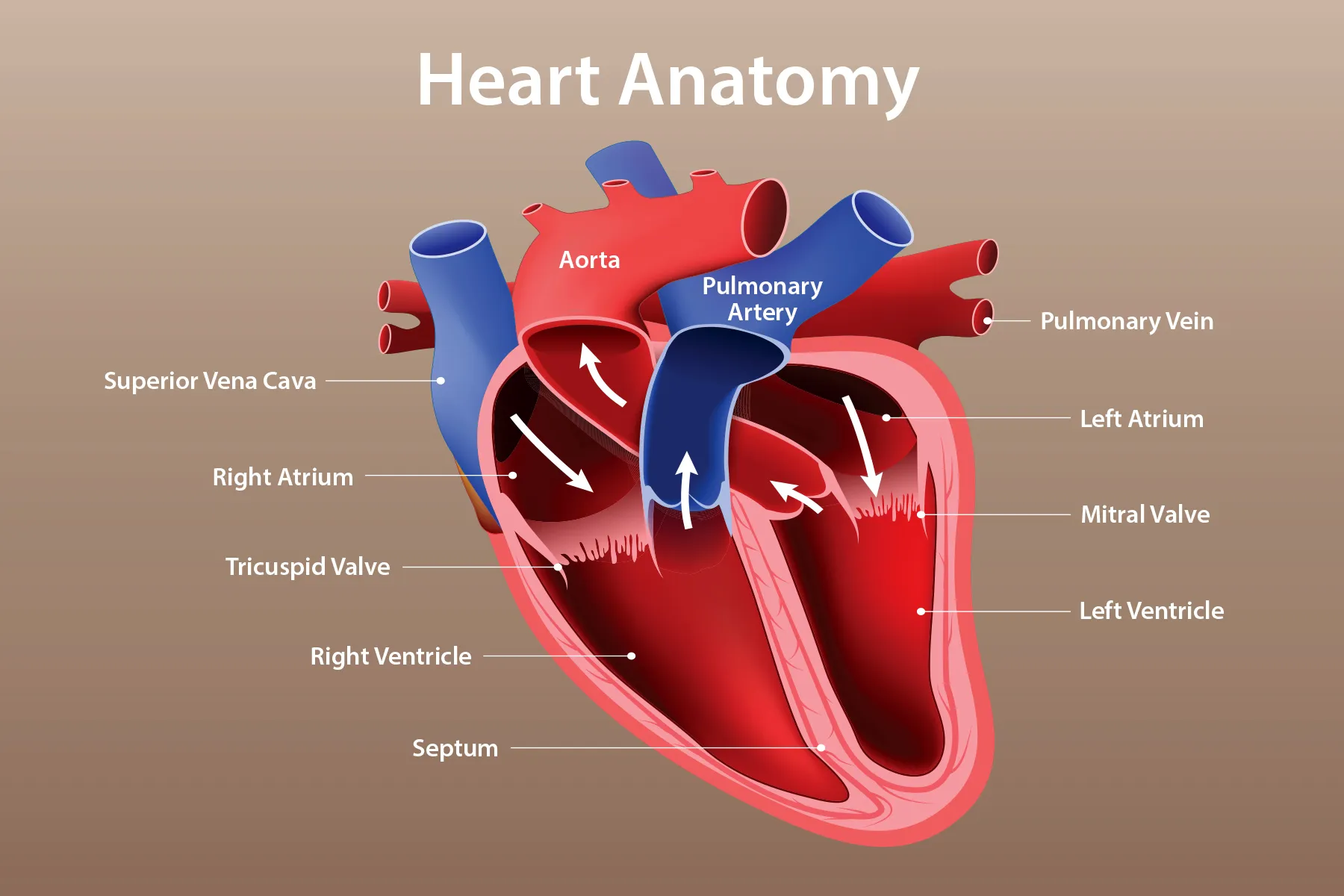
Left Atrium
receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs from pulmonary vein
Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta.
Liver
Produces bile
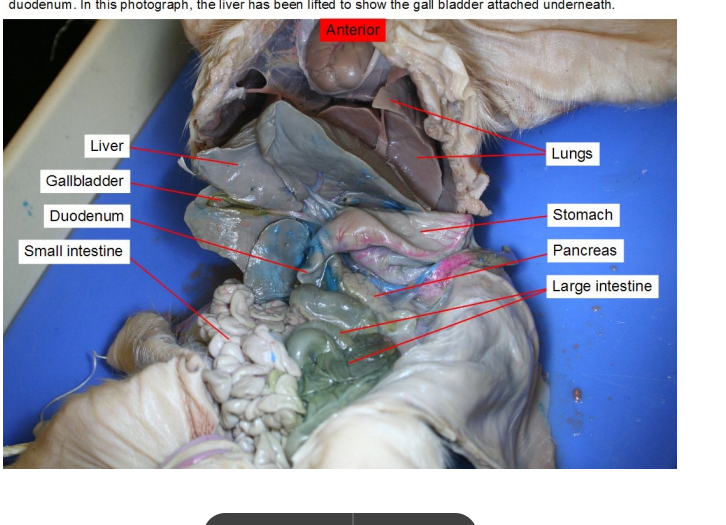
Lungs
They bring oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide, a waste gas. This all occurs in the alveoli —> Air sacs where gas exchange occurs between lungs and its capillaries.
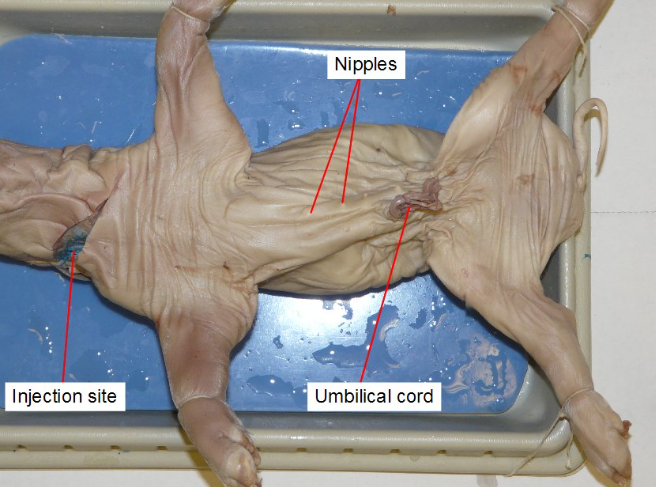
Mammary Papillae
Small, nipple-like structures present on the ventral (underside) surface of fetal pigs
Will turn into the teats of female pigs.
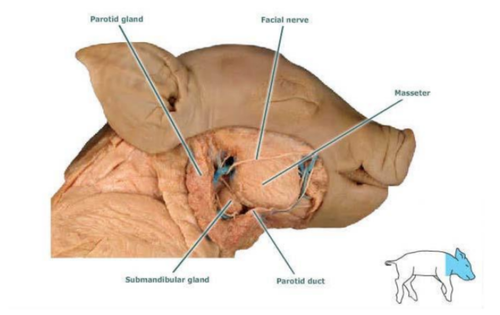
Masseter
responsible for the action of mastication (chewing)
Mesentery
suspend and hold the intestines in place within the abdominal cavity (suspend and hold the intestines in place within the abdominal cavity).

Mitral valve
controls blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle
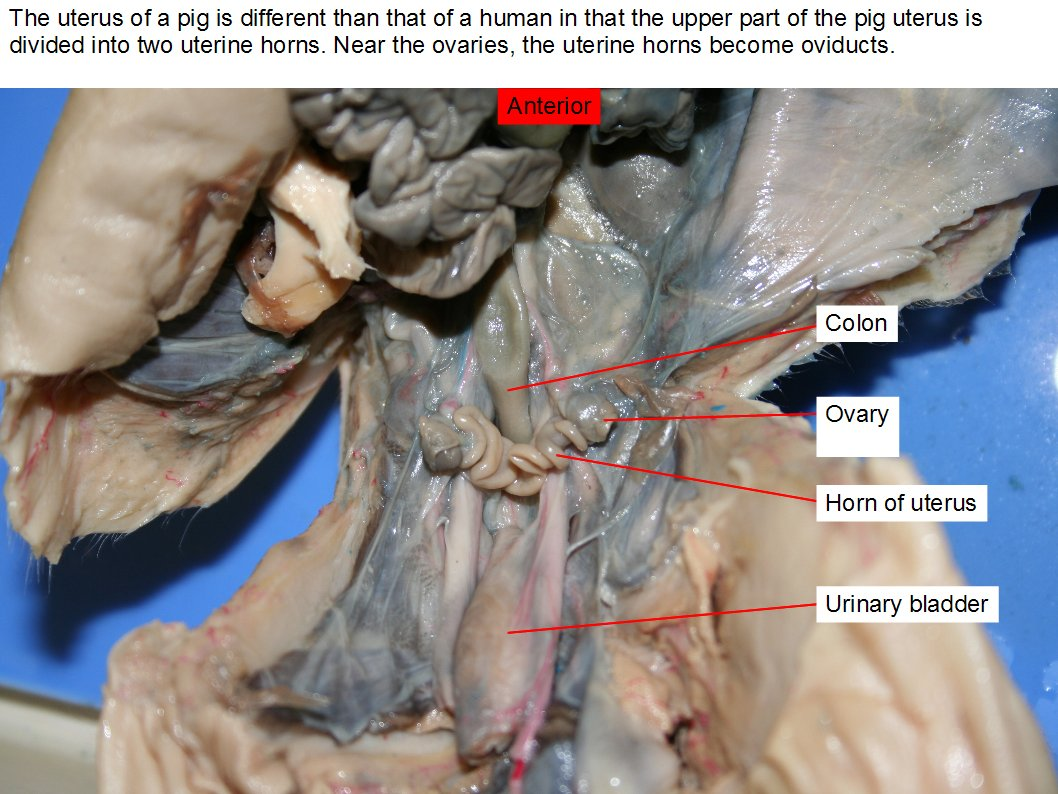
Ovary
produce eggs
Pancreas
produces digestive enzyme
Peptidase —> break down protein
Lipase —> bread fats
Produces buffers to reduce acidity
Parietal peritoneum
serous membrane that lines the internal surface of the abdominal wall and pelvic cavity
Parietal pleura
is the outer layer of the pleura, a double-layered membrane surrounding the lungs. Attaches to the chest wall.
Penis
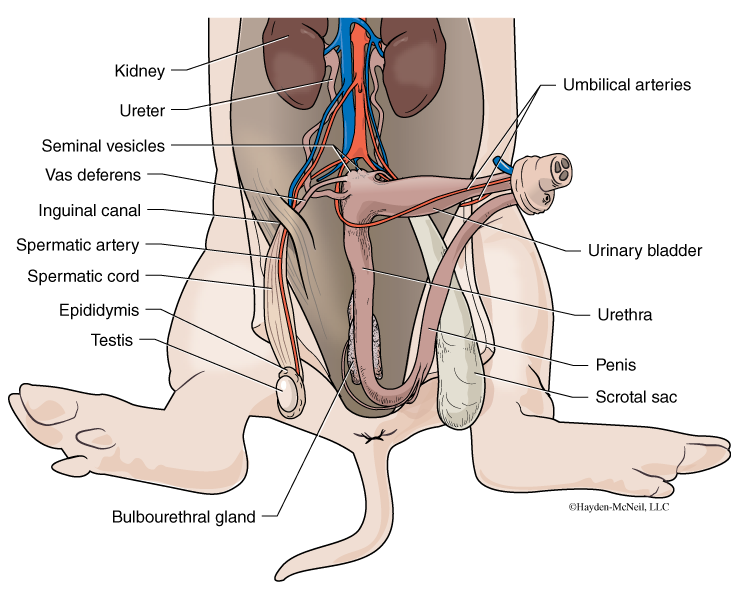
male reproductive organ that contains the urethra which carries urine and semen.
Pericardium
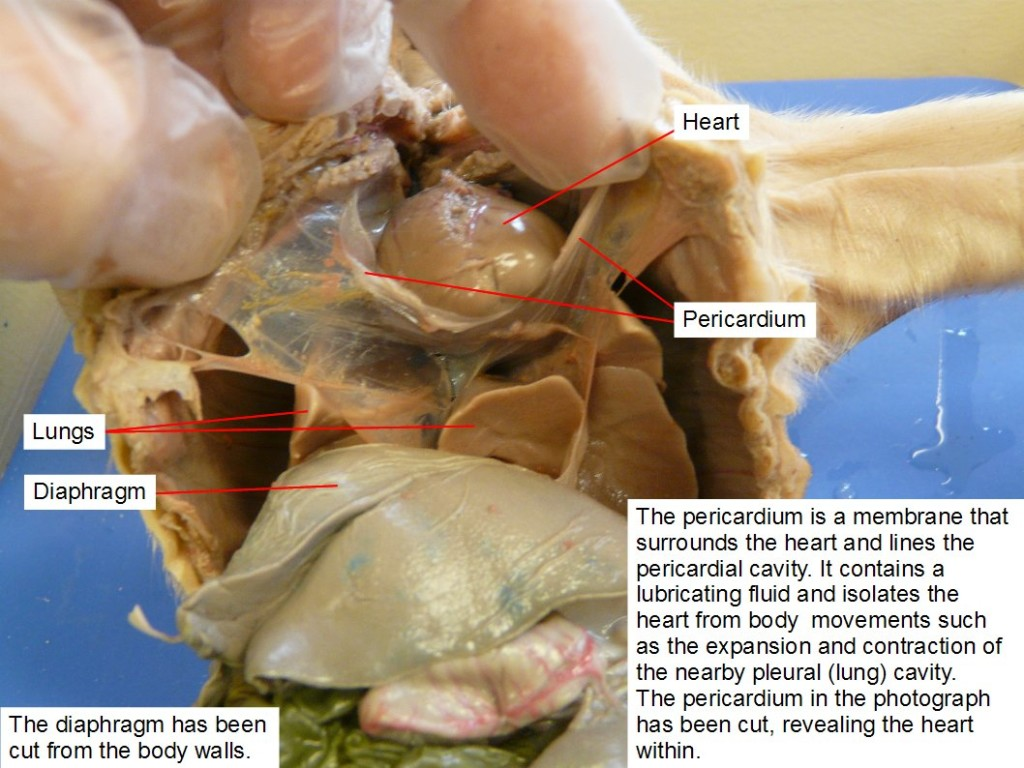
a double-walled sac that surrounds the heart, composed of a fibrous outer layer and a serous inner layer
Pinnae
Ears
Posterior vena cava
Inferior Vena Cava
Pulmonary artery
carry oxygen-poor blood from your heart to your lungs
Pulmonary valve
one of the four valves in the heart, located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Pyloric sphincter
governs the passage of food out of the stomach into the small intestine, muscle
Rectum

the final section of the digestive tract, end of the large intestine.
Right Atria
Right atrium of the heart, carries deoxygenated blood.
Salivary glands
produces saliva
Scrotum
Sack of skin that protects the testes (balls)
Semilunar valve
prevents flow of blood back into the heart
pulmonary valve
aortic valve
Sensory papillae
basically taste buds
Small intestine
digest food and absorb nutrients into the bloodstream
Snout
the nose basically
Soft palate
acts as a barrier to prevent food from entering the nasal cavity during swallowing
Spleen
filtering the blood, storing blood cells, and producing and releasing immune cells to fight infections
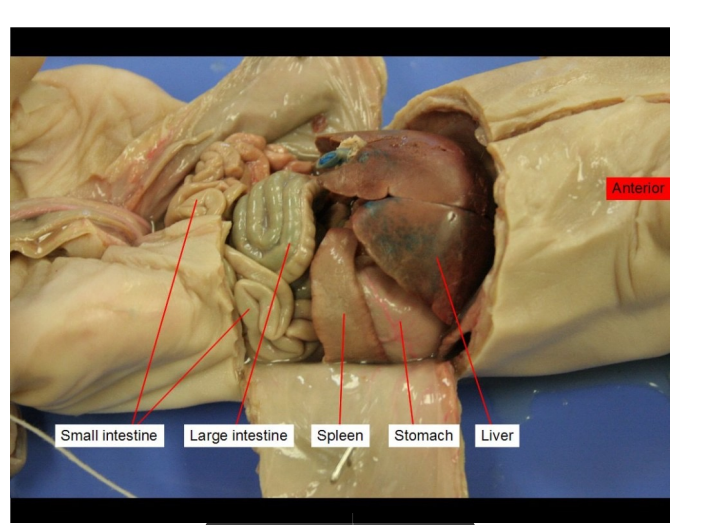
Stomach
Forms chyme, which is partially digested food
Stores ~2L of food
Disinfects food
Does chemical digestion
Tail
self explanatory
Testes
sperm production (spermatogenesis) and the secretion of male sex hormones, primarily testosterone
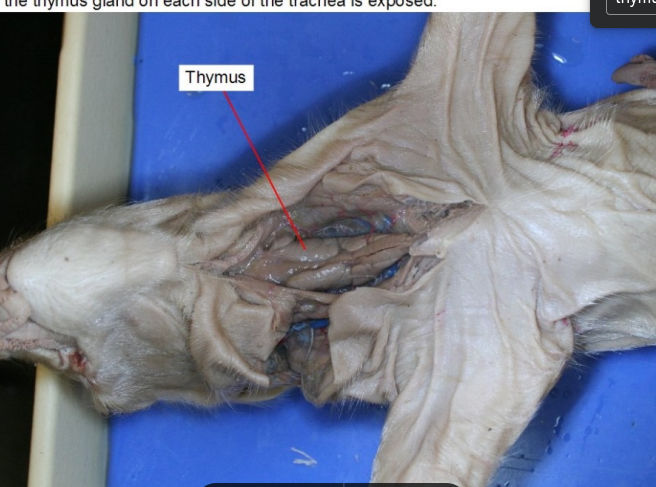
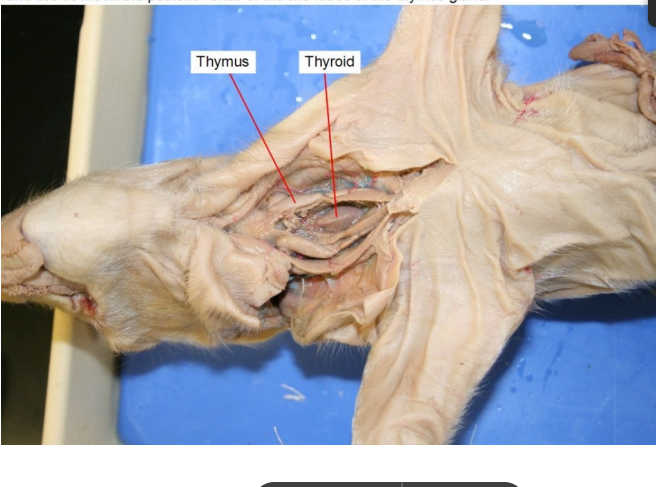
Thymus
producing and maturing T cells, which are essential for fighting infections and maintaining immune function
Thyroid
gland responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development
Tongue
tongue
Tooth
tooth
Trachea
allow passage of inspired and expired air into and out of the lung
Tricuspid Valve
between right atrium and ventricle
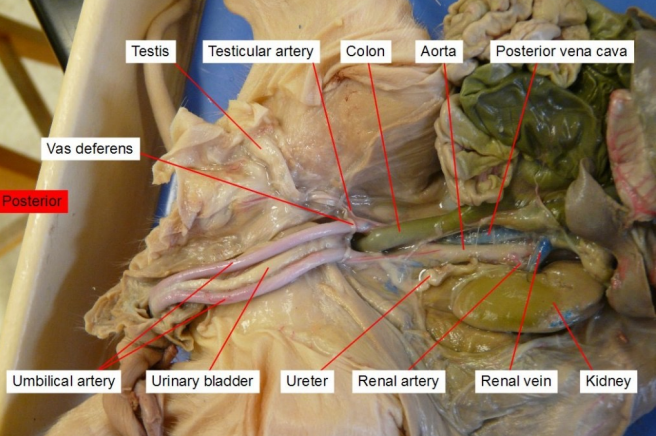
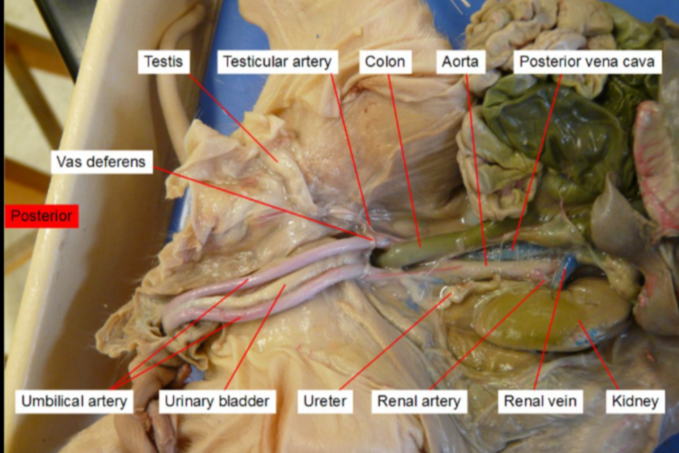
Umbilical artery
paired blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood and waste products from the developing fetus to the placenta
Umbilical cord
a lifeline for a developing fetus, connecting it to the placenta and providing nutrients and oxygen.
Umbilical veins
Carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus
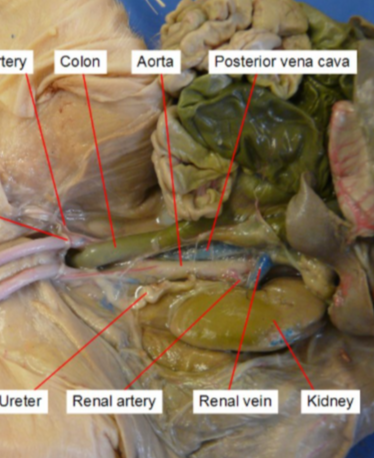
Ureter
transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Urethra
This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra.
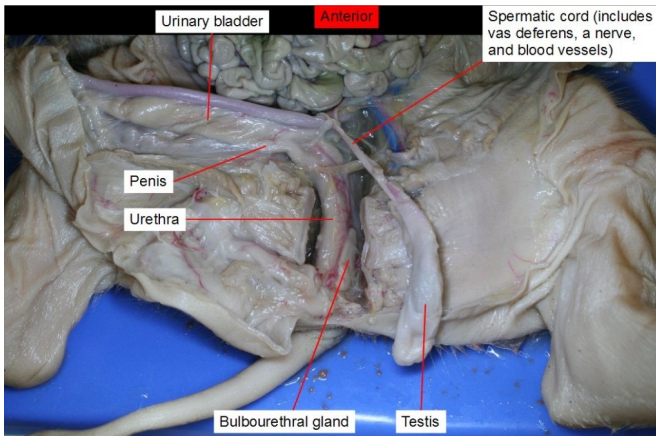
Urinary bladder
a hollow, stretchy organ in the lower part of your abdomen that stores urine before it leaves your body through your urethra.
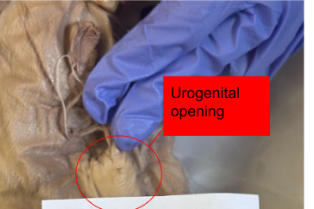
Urogenital opening
where bodily waste and reproductive fluids are expelled to the environment outside of the body cavity.
Urogenital papillae
fleshy protrusions located near the anus of certain fish species, particularly in males, where they serve as a structure for delivering sperm into the female reproductive tract
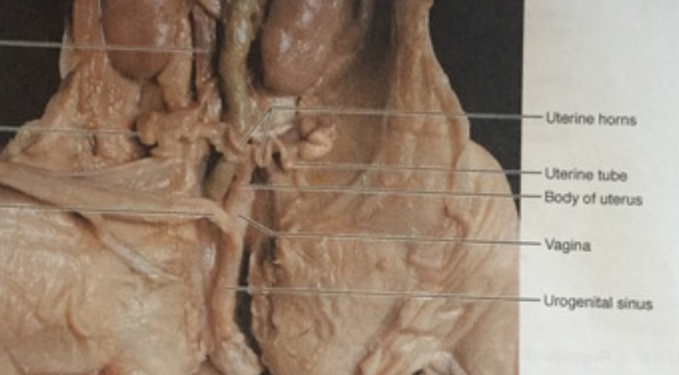
Urogenital sinus
serves as the embryonic origin for both the urinary and reproductive system
Uterine horns
provide the environment for the developing fetuses to grow and mature.
And is a passageway for sperm
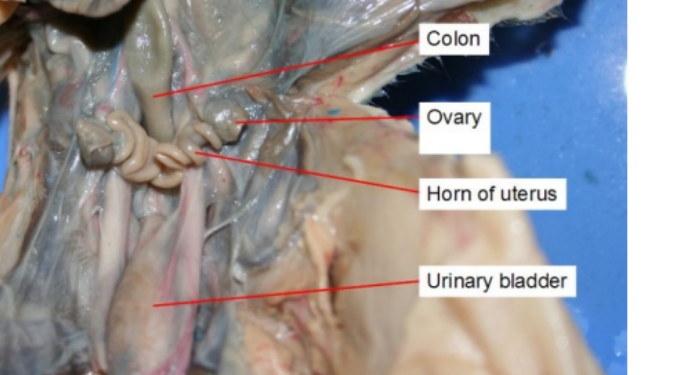
Uterus
a bicornuate structure, meaning it consists of two separate horns that join at the cervix.
function: nurture a fertilized egg and develop a fetus until birth
Vagina
muscular canal that connects the cervix (the lower part of the uterus) to the outside of the body, serving as the birth canal and the pathway for menstrual flow.
Vas deferens
A coiled tube that carries the sperm out of the testes.
Vena Cava
transport deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart.
Villi
facilitating efficient absorption of nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream.
contain capillaries which help transport and absorb
Visceral peritoneum
the layer of tissue that directly covers the organs within the abdominal cavity, including the intestines and stomach.
The inner layer that directly covers the organs, providing a smooth surface for them to move and interact.
one of two layers of the peritoneum in the abdomen
Visceral pleura
a thin membrane that covers the lungs and extends into the fissures between the lobes
the inner membrane of the pleura, the outer membrane is called parietal pleura