Anatomy & Phsiology (15%)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
endocrine system
organs that excrete hormones to control the body’s responses to stimuli and functions
2
New cards
what does the endocrine system include?
pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pancreas
3
New cards
pituitary gland
produces growth hormones and prolactin
4
New cards
thyroid
regulates rate of metabolism
5
New cards
parathyroid
maintains calcium levels
6
New cards
adrenal
release hormones in response to stress and excitement
7
New cards
pancreas
secretes insulin
8
New cards
immune system
identifies and kills pathogens
9
New cards
two categories of immune system?
innate and adaptive
10
New cards
innate immune system
first line of defense, nonspecific, nonadaptive AKA no memory. (skin, fur, saliva, stomach acid)
11
New cards
adaptive immune system
attacks specific threats, adaptive AKA has memory. (spleen and lymph nodes)
12
New cards
kidneys
filter blood to form and excrete urine as well as regulate fluid and electrolyte balance
13
New cards
bladder
hollow muscular organ that stores urine
14
New cards
urethra
excretes urine from body
15
New cards
ovaries
located right behind kidneys. contain eggs to be fertilized. produce reproductive hormones.
16
New cards
uterus
site of implantation of fertilized eggs and fetal development. top two sections called uterine hornes
17
New cards
vagina
site where males deposit semen. passageway between uterus and outside the body
18
New cards
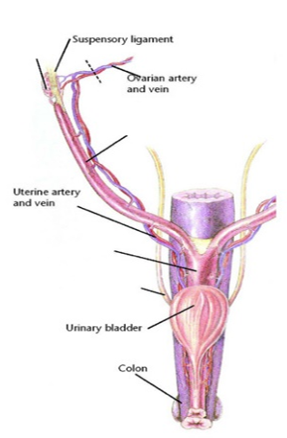
reproductive tract
female
19
New cards
scrotum
houses testicles
20
New cards
testicles
produce reproductive hormones
21
New cards
epididymides
store sperm before ejaculation
22
New cards
deferent ducts
transport sperm from the epididymides to the urethra
23
New cards
penis
acts as male sexual organ
24
New cards
dorsal
back (highest part of four legged animal)
25
New cards
caudal
tail
26
New cards
cranial
head
27
New cards
ventral
stomach
28
New cards
proximal
close to body
29
New cards
distal
away from body
30
New cards
skin
largest organ on the body
31
New cards
epidermis
outermost layer of skin
32
New cards
dermis
connective tissue which provides the body with cushioning from stress and strain. houses sweat glands, hair follices, and nerve endings
33
New cards
subcutaneous tissue
provides insulation and nutrient storage
34
New cards
keratin
chemical component of epidermal tissues. (hair, hooves, horns, and nails)
35
New cards
horns
consist of a bone core, attached to the animal’s skull; used for fighting for dominance of territory, mating/courtship, and defense
36
New cards
auricle
external part of ear where ear tag is attached
37
New cards
nares
nostrils
38
New cards
vibrissae
whiskers
39
New cards
mammary papilla
teat
40
New cards
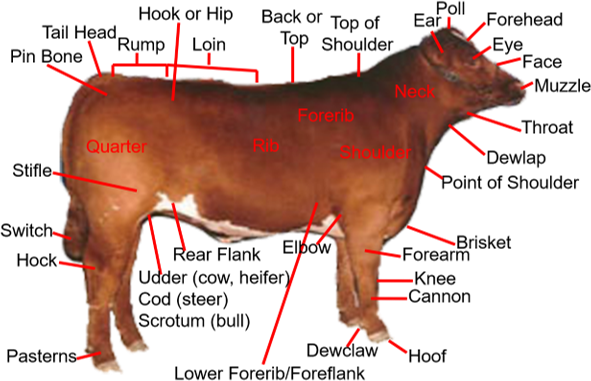
cattle external anatomy
okay
41
New cards
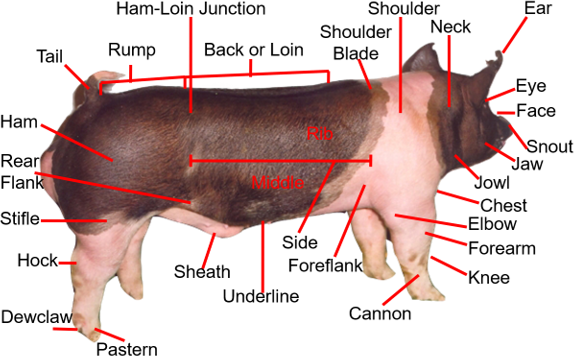
pig external anatomy
okay
42
New cards
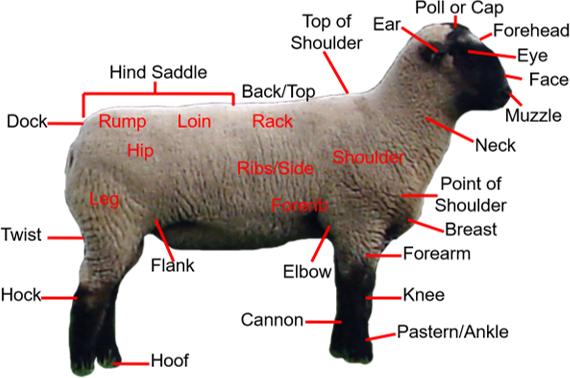
sheep external anatomy
okay
43
New cards
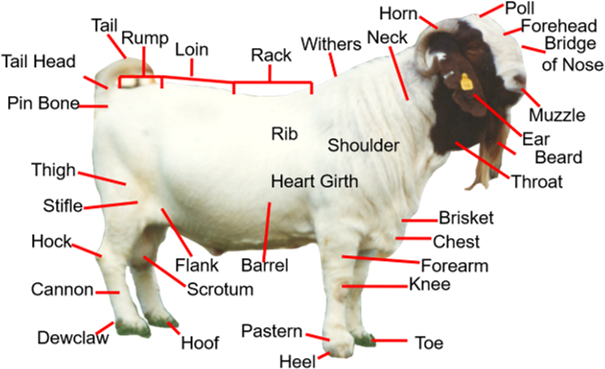
goat external anatomy
okay
44
New cards
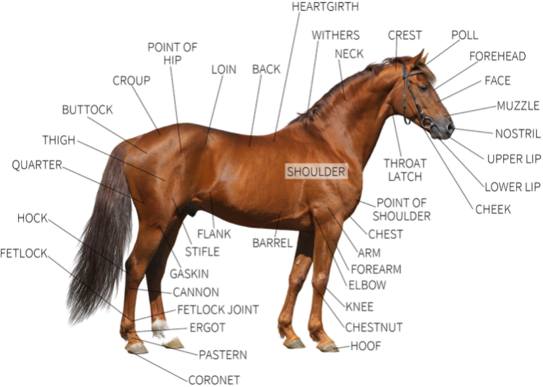
horse external anatomy
okay
45
New cards
circulatory system
transporting oxygen, hormones, and nutrients to body tissues. transport carbon dioxide and waste FROM body tissues. transporting body’s defenses. aid temp regulation
46
New cards
red blood cells
carry oxygen from the lungs to body’s tissues. carry carbon dioxide from the tissues to lungs to be expelled.
47
New cards
arteries
vessels which carry blood away from the heart to body tissues
48
New cards
veins
vessels that carry blood towards the heart from body tissues.
49
New cards
superior and inferior vena cavas (veins)
enter the heart carrying deoxygenated blood
50
New cards
four pulmonary veins
carry oxygenated blood from lungs
51
New cards
pulmonary arteries and pulmonary trunk (artery)
carry deoxygenated blood
52
New cards
pulmonary trunk and aorta
arteries that immediately exit the heart
53
New cards
chambers of the heart
right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. separated by septum
54
New cards
right side of heart
deoxygenated blood to lungs. enters RA, then through tricuspid valve into RV, then blood through pulmonary semilunar valve into pulmonary arteries which transport blood to lobes of the lungs. RV must exert enough pressure to push blood to the lungs and back to left side of the heart.
55
New cards
left side of the heart
blood enters LA though four pulmonary veins, blood propelled through bicuspid valve into LV, LV pushes blood through aortic semilunar valve into aorta which leads to rest of the body. left ventricle (strongest) must push blood through entire body
56
New cards
respiratory system
exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. upper and lower respiratory portions
57
New cards
right lung
three lobes
58
New cards
left lung
two lobes
59
New cards
digestive system
breaking down food in order to absorb nutrients to maintain body function. can be monogastric or ruminant
60
New cards
ingestion
food enters mouth
61
New cards
mechanical processing
food is physically broken down into small pieces
62
New cards
digestion
food is chemically broken down into tiny pieces
63
New cards
secretion
body releases enzyes, water, and acids into food.
64
New cards
salivary glands
release saliva
65
New cards
liver
detoxification. nutrients or toxins collected from digestive system must be processed by liver before going to rest of the body. releases bile.
66
New cards
pancreas
releases enzymes
67
New cards
absorption
movement of molecules into the blood stream
68
New cards
excretion
waste eliminated from the body
69
New cards
prehension
act by which food is grasped and gathered into the mouth
70
New cards
prehension for human
hand
71
New cards
prehension for horse
lips
72
New cards
prehension for cattle
tongue
73
New cards
prehension for goats and sheep
lips and tongue
74
New cards
esophagus
uses a peristaltic wave to move
75
New cards
stomach
churns to mechanically breakdown food and mix food with enzymes to allow chemical breakdown
76
New cards
rumen
holds consmed food and mixes
77
New cards
artieral blood system
takes from from the heart to the organs
78
New cards
venous blood system
takes blood from organs to the heart
79
New cards
hepatic portal vessel
large vessel where all venous blood is collected before traveling throuhg the liver
80
New cards
small intestine
duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
81
New cards
gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile
82
New cards
large intestine
cecum, appendix (humans), ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colons, and rectum
83
New cards
reticulum
holds heavy objects such as metal or wire (honeycomb)
84
New cards
omasum
folds increase length of time food spends in omasum. increasing water absorption (omasum)
85
New cards
abomasum
true stomach
86
New cards
endocrine system
secretes hormones to help integrate and control bodily metabolic activity. includes hypothalamus, pineal body, pituitary, thyroid, thymus, adrenal, and reproductive glands
87
New cards
pituitary gland
master gland at base of brain. secretions affect many body functions
88
New cards
adrenal gland
top of each kidney and divded into two organs: cortex and medulla. helps control heart rate and blood presssure
89
New cards
ovaries
secrete estrogen and progesterone
90
New cards
testis
produce sperm cells and secrete androgens
91
New cards
immune system
protecting body from infection. two types of defense mechanisms.
92
New cards
non specific immune system
skin and mucus, phagocytes, inflammation and fever, and interferons
93
New cards
specific defense mechanisms
antibody mediated immunity (b cells) and cell mediated immunity (t cells)
94
New cards
b cells
developed in bone marrow from lymphocytes
95
New cards
t cells
developed in thymus from lymphocytes
96
New cards
integumentary system
retains body fluids, protects against disease, eliminates waste, and regulates body temperature
97
New cards
accessory structures of integumentary system
hair, nails, exocrine glands (sweat glands and sebaceous glands)
98
New cards
nervous system
regulates body’s response to internal and external stimuli. two parts: central and peripheral nervous systems
99
New cards
central nervous sytem
brain & spinal cord
100
New cards
peripheral nervous system
nerves