ELECTRIC FIELDS TO REMEMBER
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Electric field
The force field around a charged object is an electrical field. A force field is a region where a body will experience a non contact force.
Electric field line
The direction, and relative magnitude, of force on a small positive charge placed in the electric field of a large charge.
Electric field strength
The electric field strength at a point is the force per unit charge on a small positive charge at that point. (The electric field strength is equal to the negative of the potential gradient.)
Coulomb's Law
The force of attraction/repulsion between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation.
Electrical potential energy
The energy of an object due to its position in an electric field (position for zero e.p.e. is at infinity).
Electric potential
The work done per unit positive charge in moving a positive test charge from infinity to that point (i.e. the electric potential energy per unit charge)
Electric potential for a positive charge
- increases when a test charge moves closer (wd to push a +ive charge towards another, point charge typically +ive)
- decreases when a test charge moves away (the test charge would move away from the +ive charge due to repulsion)
Electric potential for a negative charge
- decreases when a test charge moves closer (the test charge would move towards the +ive charge due to attraction)
- increases when a test charge moves away (wd to pull +ive charge & -ive charge away from each other)
Why are gravitational potential energy (Eₚ) values negative (2 marks)
(1) Eₚ is defined as zero at infinity
(2) Because work is done by the field moving the object from infinity
Equipotential
A 2-dimensional surface of constant potential. No work needs to be done to move along an equipotential surface.
Potential gradient
The potential gradient at a point in an electric field is the change of potential per metre at that point.
Uniform field
Electric field strength is the same everywhere. Field lines are parallel and equally spaced.
Radial field
Due to a point charge. Electric field strength follows inverse square law.
Motion of a charged particle in a uniform electric field
If a charged particle is in motion through a uniform electric field it will experience a constant electric force and travel in a parabolic trajectory
- force on the particle is the same at all points and is always in the same direction
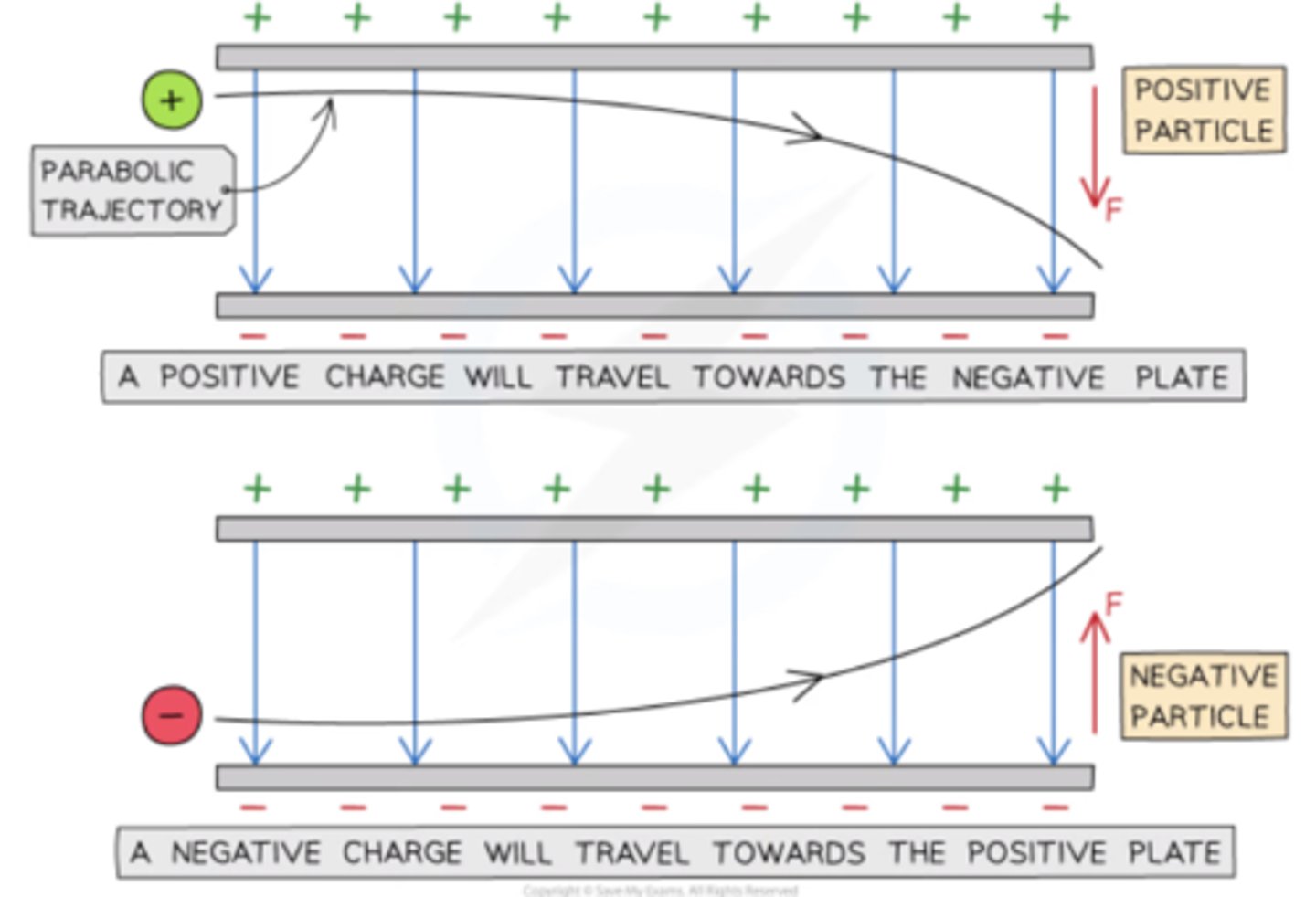
Motion of a neutral particle in a uniform electric field
It experiences no force and will therefore travel straight through the plates undeflected
What does the amount of deflection depend on
Mass - the greater the mass, the smaller the deflection
Charge - the greater the magnitude of the charge of the particle, the greater the deflection
Speed - the greater the speed of the particle, the smaller the deflection
Graph of electric potential and distance
- All values of potential are negative for a negative charge
- All values of potential are positive for a positive charge
- As r increases, V against r follows a 1/r relation for a positive charge and a -1/r relation for a negative charge
- The gradient of the graph at any particular point is equal to the field strength E at that point
- The curve is shallower than the corresponding E-r graph

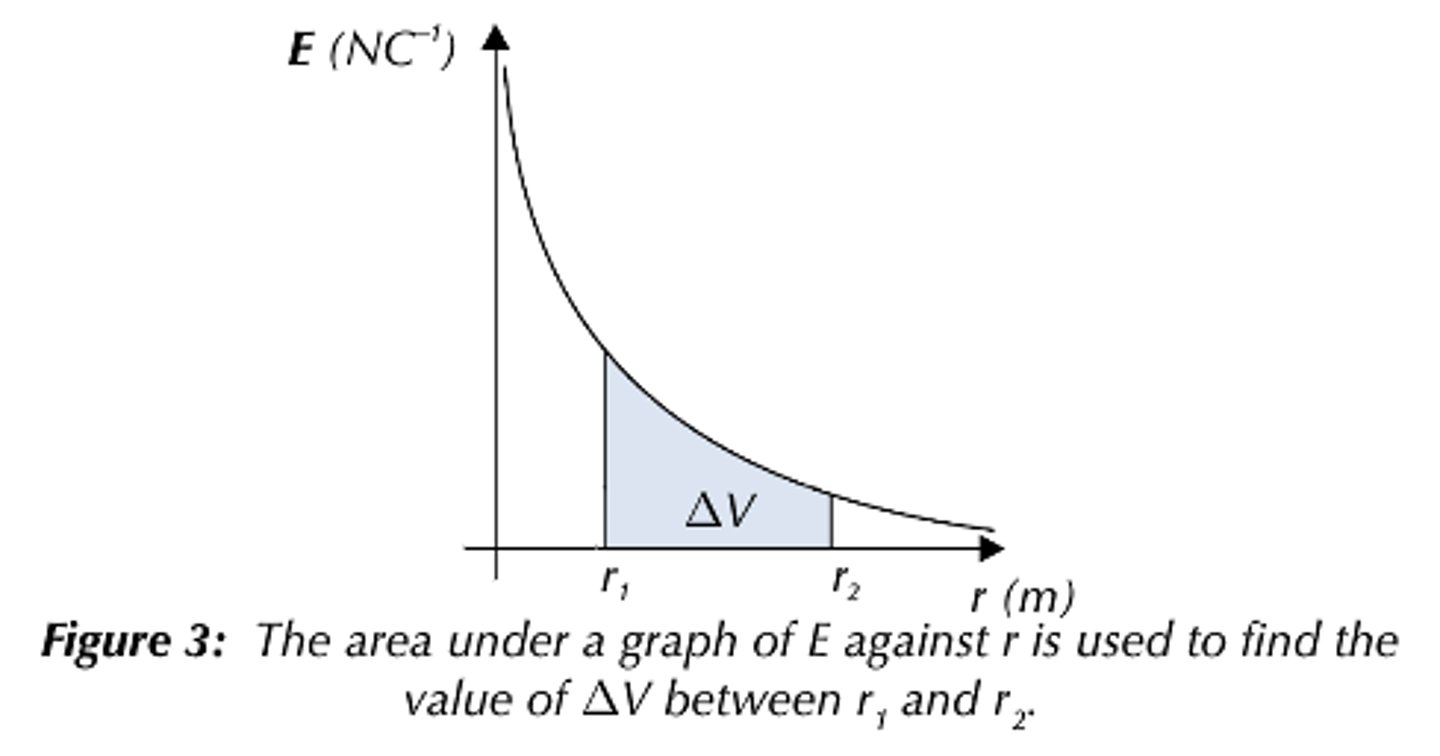
Area under a graph of electric field strength against distance
- All values of field strength are negative for a negative charge
- All values of field strength are positive for a positive charge
-As r increases, E against r follows a 1/r2 relation (inverse square law)
- The area under this graph is the change in electric potential ΔV
- The curve is steeper than the corresponding V-r graph