IOA2 Exam 2 - Vitreous Humor
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
When does the primary vitreous develop?
at the end of the 3rd embryonic week
The primary vitreous is located behind the _______.
lens vesicle
What forms the primary vitreous?
Mesoderm migrating between the optic cup and lens vesicle.
The primary vitreous primarily consists of the:
hyaloid vasculature
Hyaloid artery
An artery that supplies nutrients to the tissue behind the lens and the lens
The secondary vitreous starts to develop by:
the ninth week
What is the secondary vitreous synthesized by?
Primary vitreal cells and retinal glial cells (neuroectoderm origin)
What does the secondary vitreous become?
Mature vitreous
The mature vitreous is mostly ________ and _______.
acellular and fibrous
The secondary vitreous eventually fills the ______ and compacts the primary vitreous.
globe
When does the tertiary vitreous develop?
at 6 months embryonically
What does the tertiary vitreous form?
zonular fibers
The fibrous structure of the secondary vitreous condenses and forms the ______.
zonules
What do the zonules merge with during vitreous development?
Lens capsule and the BM of the ciliary body
What happens to the hyaloid vasculature before birth?
It dissolves through an autolytic process (the vasculature dissolves itself)
The canal that is left after the primary vitreous dissolves is called the
Canal of Cloquet (aka hyaloid canal)
How does the Canal of Cloquet change over time?
At birth, it runs straight; with aging, it becomes serpentine
With liquefaction, the canal of Cloquet becomes more
mobile (ascension phenomenon)
The vitreous chamber is filled with
gel-like vitreous body
The vitreous makes up _____% of the entire volume of the eye.
80%
Volume of the vitreous chamber vs. size of the eye
4 ml (vitreous chamber)
5 ml (size of eye)
Shape of the vitreous humor
Spherical shape except for the center of the anterior surface
Indentation located in the center of the anterior surface of the vitreous chamber, where the lens sits
Patellar fossa
What are the main components of the vitreous chamber (6)?
1) 98.5-99.7% water
2) Collagen
3) GAG substance
4) Hyalocites
5) Vitamin C
6) Amino acids
Type of collagen fibers in the vitreous chamber
Type II collagen fibers
Main type of GAG in the vitreous chamber
Hyaluronic acid
What are hyalocites and where are they located in the vitreous chamber?
vitreous cells located at the cortex near the vitreal surface
Is the concentration of Vitamin C in the vitreous humor higher or lower than in blood plasma?
Higher
Is the concentration of Amino Acids in the vitreous humor higher or lower than in blood plasma?
Lower
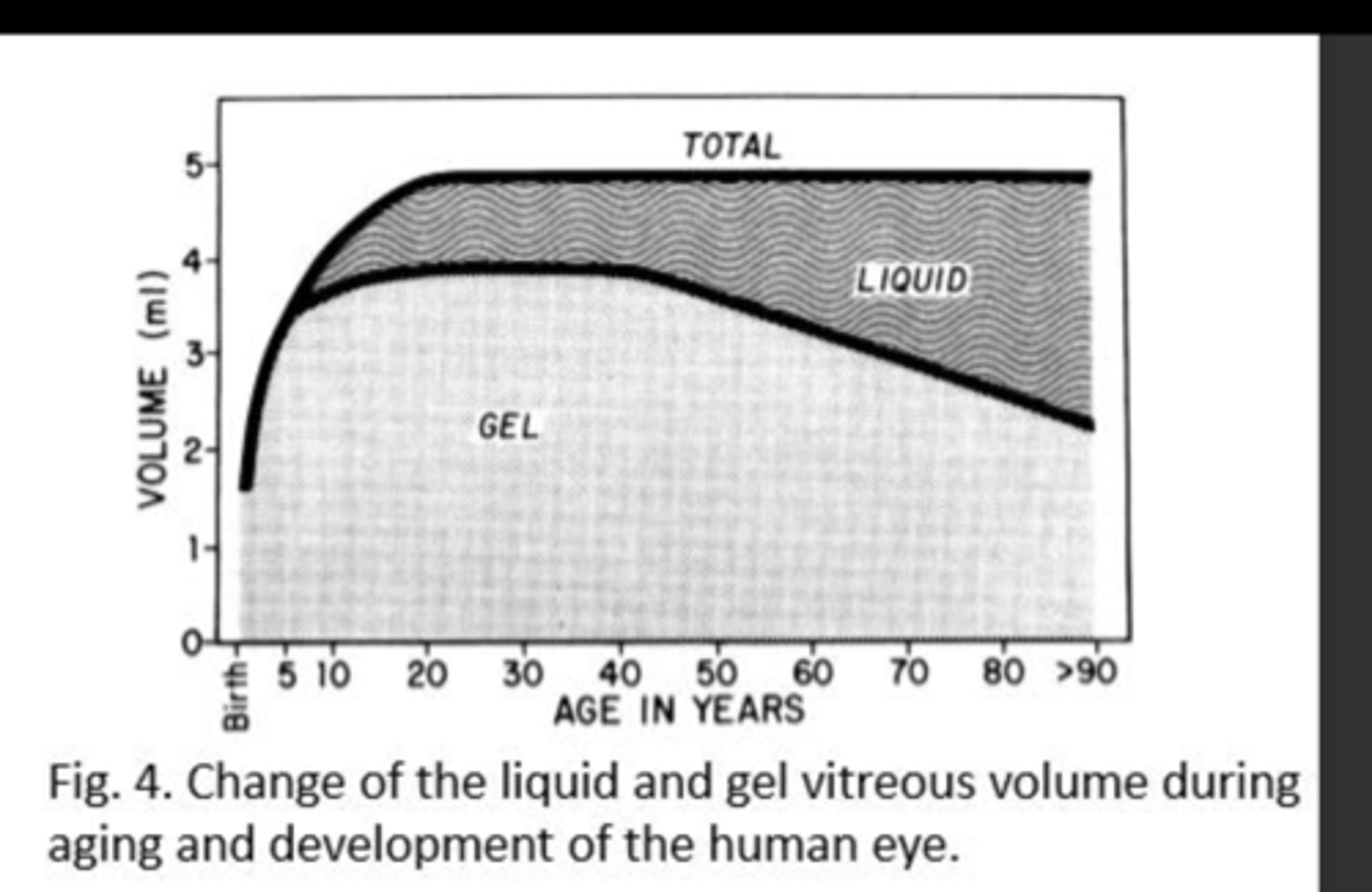
In early life, the vitreous chamber is
gel like (jelly)
What happens to the vitreous as we age (70-80 years)?
Becomes more liquid in the center, forming:
1) pockets of fluid
2) aggregation of collagen fibrils - floaters
5 main attachments to the vitreous (retina and lens)
1) Vitreous base (strongest)
2) Posterior lens
3) Optic disc
4) Macula (annular ring)
5) Retinal vessels
Which vitreous attachment is the strongest and most extensive?
Vitreous base
Where is the vitreous base located?
It extends 1.5 - 2mm anterior to the ora serrata
What is the shape of the vitreous attachment at the macula?
annular ring (ring shaped)
How does the vitreous attach to the retinal vessels?
Fine strands extend through the internal limiting membrane to branch and surround the larger retinal vessels
Which attachments are most likely to cause a retinal tear?
The tightest attachments
Name the 4 vitreous regions
1) Anterior hyaloid
2) Vitreous cortex
3) Intermediate zone
4) Cloquet's Canal
The anterior hyaloid contains the
1) Weiger's ligament (retrolental ligament)
2) Berger's Space
Weiger's ligament
Ring-shaped attachment at the posterior lens capsule in the anterior hyaloid region
Berger's Space
Space between the ligament and the lens
Is considered the outer region of the vitreous
Vitreous cortex
The Vitreous Cortex contains (4):
-Collagen fibrils
-Cells
-Proteins
-Muco-polysaacharides
What are the subdivisions of the vitreous cortex?
1) Anterior vitreous cortex
2) Posterior vitreous cortex
Anterior Vitreous Cortex
Extends to the ora serrata and has a hyaloid surface (hyalocites)
Posterior Vitreous Cortex
Contains transvitreal channels that appear as holes
Types of transvitreal channels (holes) that are in the posterior vitreous cortex
1) Peripapillary hole
2) Premacular hole
3) Prevascular fissures
What is found in the intermediate zone of the vitreous?
Fine, unbranched fibers running antero-posteriorly
Cloquet's Canal is aka
Hyaloid channel
What is Cloquet's Canal
An S-shaped normal remnant of primary vitreous (at the center) that represents the site of the former embryological hyaloid artery
Cloquet's Canal terminates at the ________.
area of Martegiani
Area of Martegiani
Funnel-shaped space at the optic nerve head
Functions of the Vitreous
1) Transparent medium of passage of light
2) UV filter
3) Cushion to the globe
4) Shock absorber
5) Storage of nutrients
Refractive index of the vitreous
1.33
The vitreous acts as a UV filter by decreasing transmission of light at
300-350nm
The vitreous acts as a cushion to the _______.
globe (especially retina and lens)
The vitreous absorbs:
vibrations and external forces during trauma and eye movements
The vitreous acts as a storage area of nutrients for the _______ and _______.
retina and lens
Bleeding into the vitreous cavity
Vitreous hemorrhage
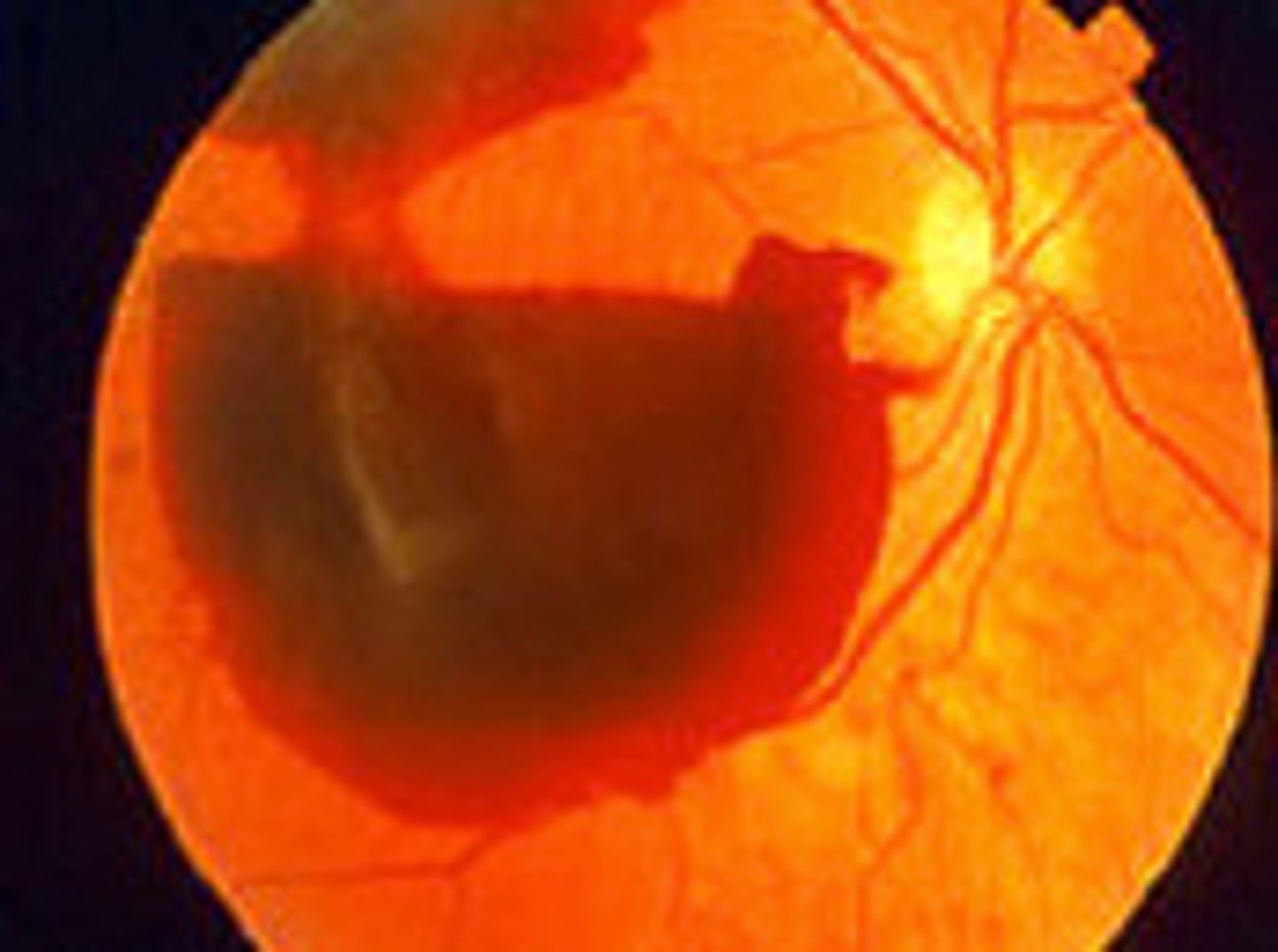
Causes of Vitreous Hemorrhage (2)
-Neovascularization
-Rupture of normal vessels
Causes of vitreous hemorrhage due to Neovascularization
-Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
-Central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO)
Causes of vitreous hemorrhage due to Rupture of normal vessels
-Retinal tear
-Trauma
-Posterior vitreous detachment
-Retinal detachment
Separation of the posterior vitreous cortex from the retina
Vitreous detachment
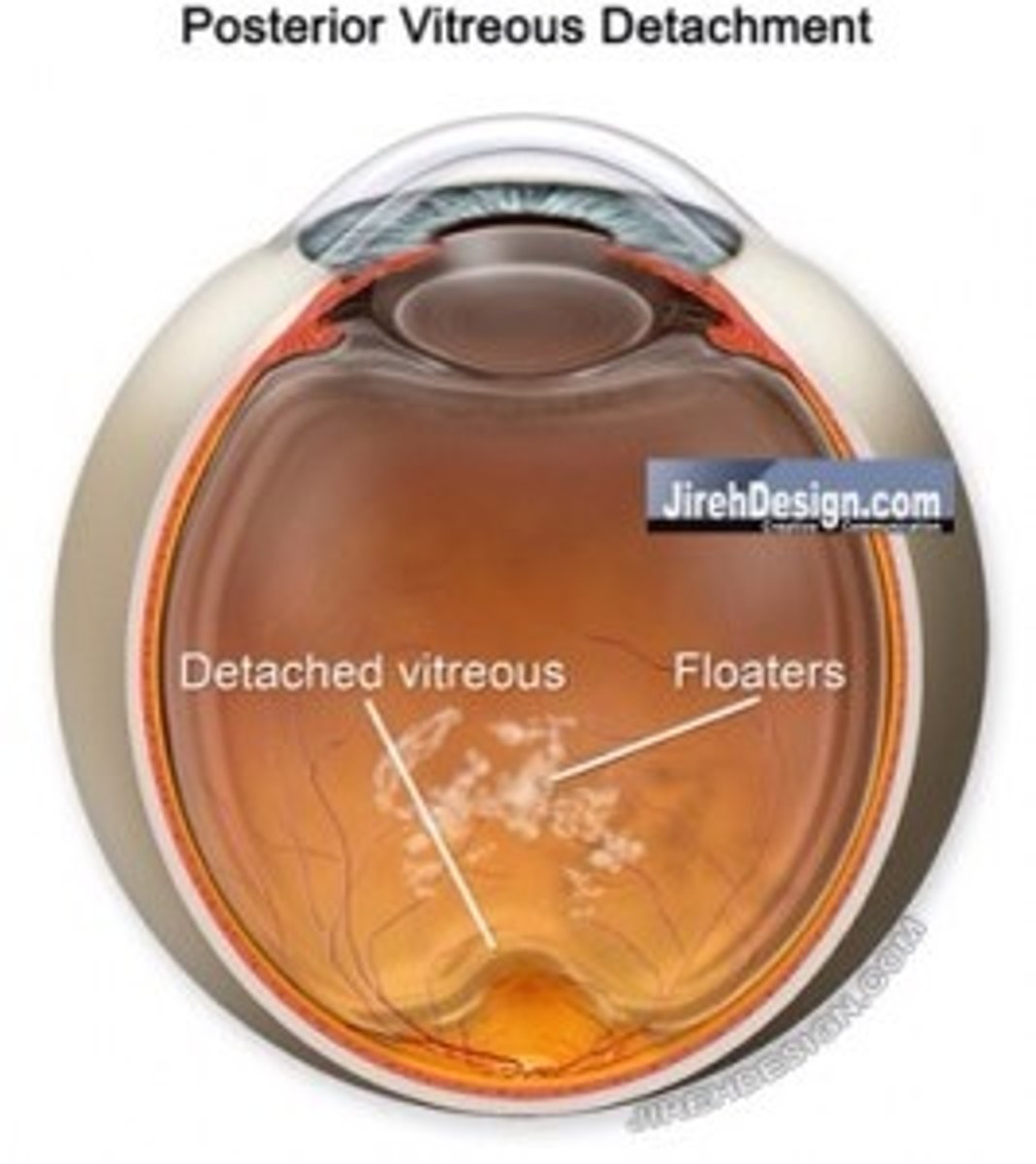
Causes of Vitreous Detachment (2)
-Trauma
-Posterior vitreous detachment
Posterior vitreous detachment usually results from:
normal, age-related changes in the vitreous gel
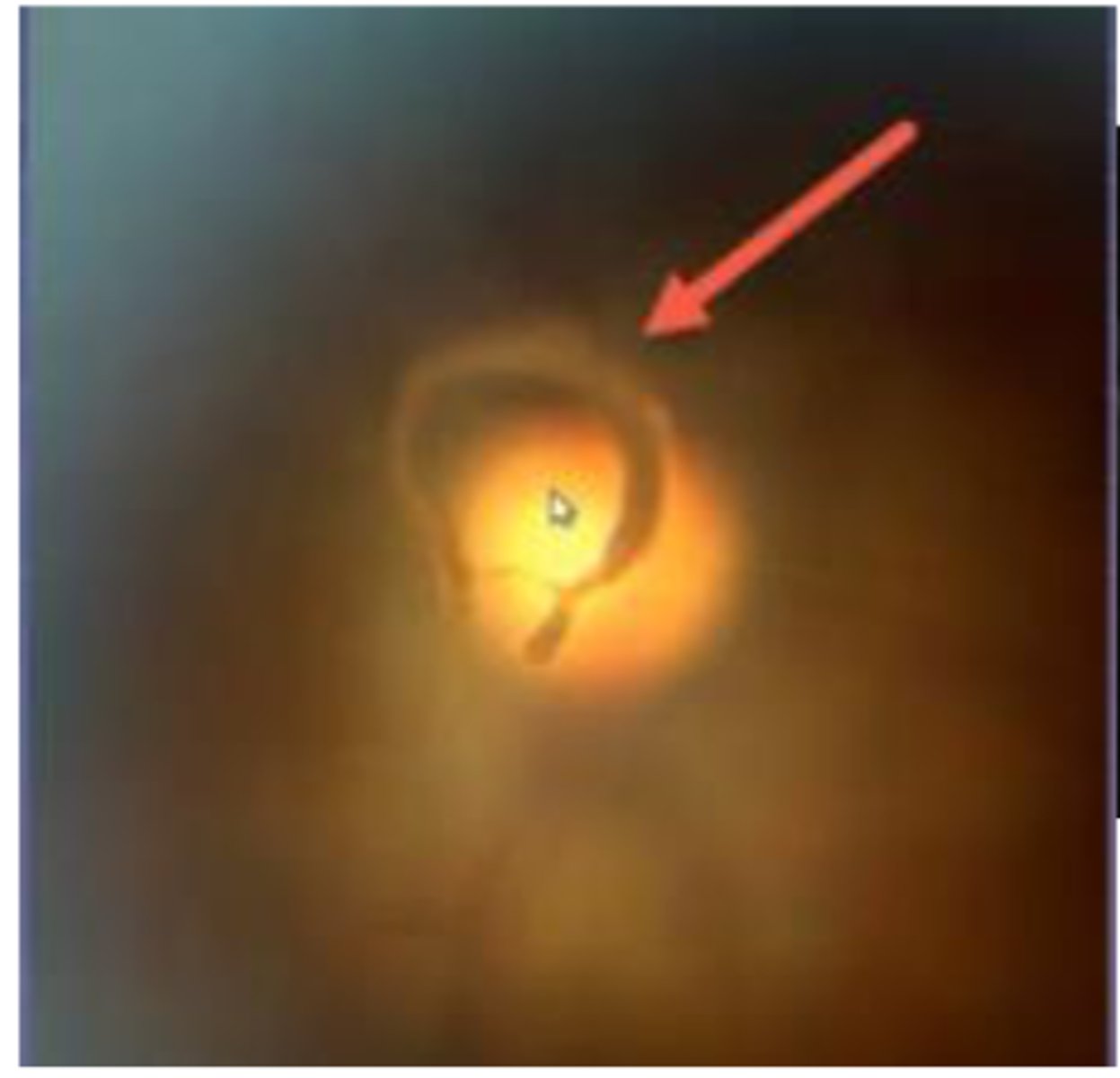
What is Weiss Ring?
A sign of posterior vitreous detachment
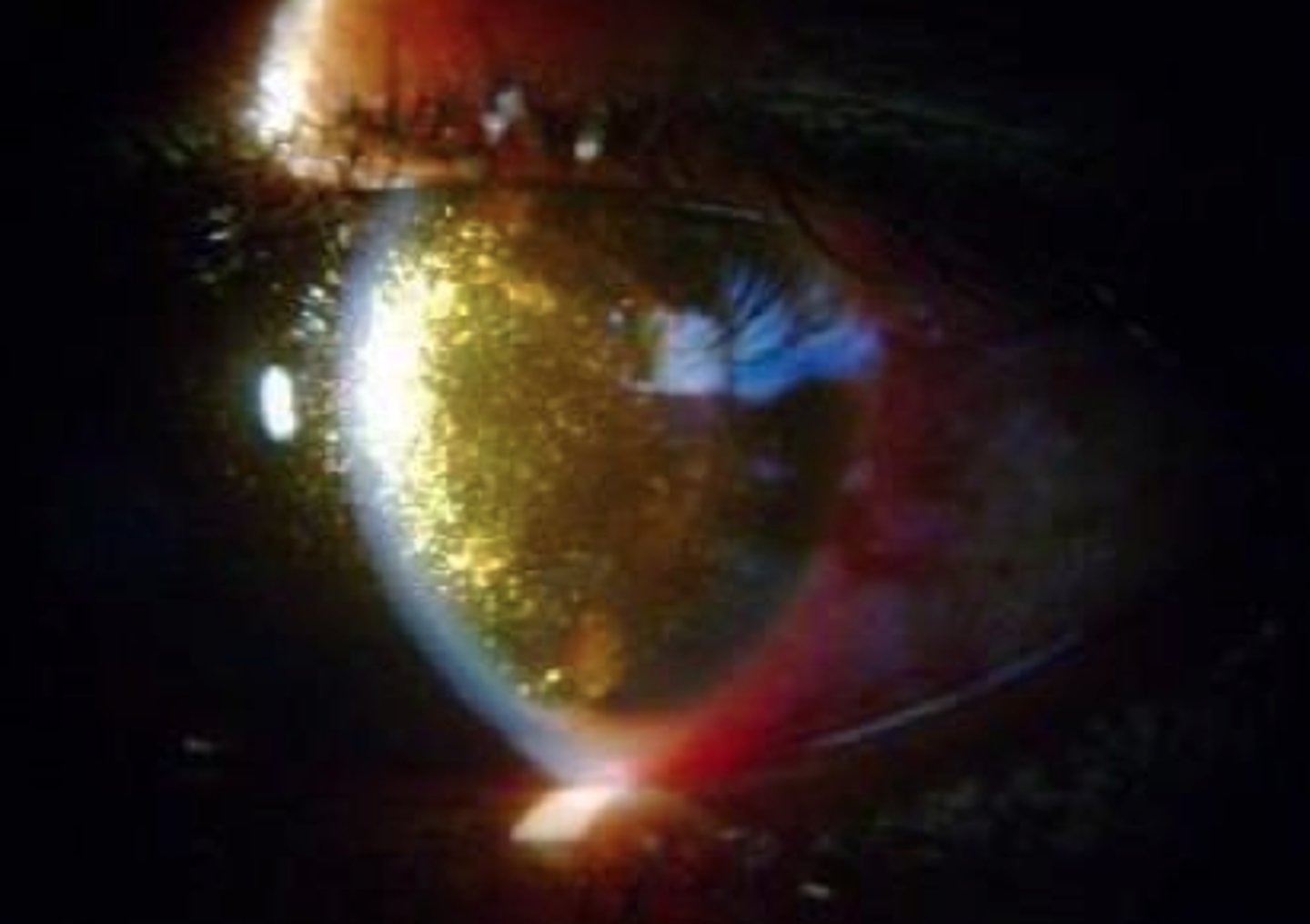
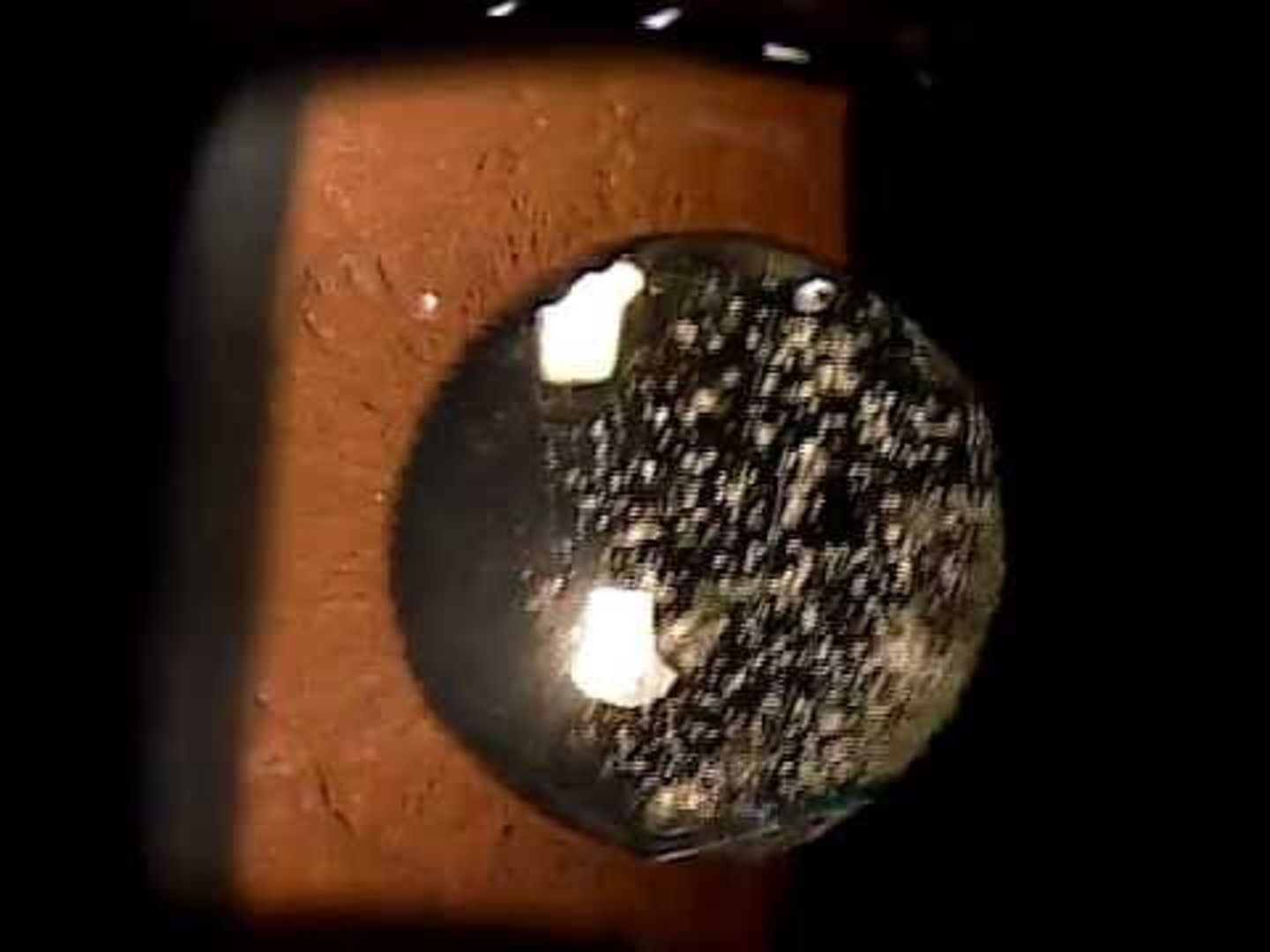
What population does Asteroid Hyalosis present in and what what composition is the vitreous made of?
Elderly population, calcium deposits
Is Asteroid Hyalosis typically unilateral or bilateral?
Unilateral
Describe the typical appearance of asteroid hyalosis in the vitreous.
Spherical, white opacities that move with the vitreous

What population does Synchysis Scintillans present in and what what composition is the vitreous made of?
Young population, cholesterol crystals
Is Synchysis Scintillans typically unilateral or bilateral?
Bilateral
Describe the typical appearance of synchysis scintillans in the vitreous.
Highly refractile, multicolored crystals that move freely and fall to the floor of the vitreous chamber