A&P TEST 4 YAAAAY
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dccc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Sebaceous Glands
Secrete Sebum (oil), Connected to hair follicles
Acne
Inflammation of sebaceous gland in a hair follicle
Sudoriferous glands
Sweat Glands
Eccrine Sudoriferous
Thermoregulation, do not secrete into a hair follicle
Apocrine Sudoriferous
Located in specific regions (axillary, groin, mammary, face), scent glands, secrete into a hair follicle
Ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands in the ear canal, secretes cerumin (wax)
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Stratum Basale cells become cancerous, shiny
Squamous cell carcinoma
Stratum spinosum keratinocytes become cancerous, reddish
Melanoma
Melanocytes become cancerous, rarest form and most deadly, abnormal mole
Melanoma risk factors
Family History, Male, Red hair, severe sunburns in childhood
First degree burn
Only epidermis injured, red, painful, sunburns
Second degree burn
Epidermis and part of dermis injured, blistered, takes weeks to heal and leaves scars (Scalds)
Third degree burn
Epidermis, dermis and deeper tissue injured, cannot heal itself normally
Synarthrosis Joint
No movement
Amphiarthrosis joint
Little bit of movement
Diarthrosis joint
Freely Moveable
Fibrous joint
collagen fibers hold bones together, no joint cavity
Cartilaginous joint
Cartilage holds together, no joint cavity
Synovial joint
Dense regular CT holds together (ligaments, tendons), Has a joint cavity
Suture (Fibrous)
Thin strand of collagen fibers connect them together, synarthrosis
Syndesmoses (Fibrous)
long sheet like collagen fibers connect, amphiarthrosis (ex: distal joint of tibia and fibula)
Gomphoses (Fibrous)
Small ligaments connects bones, synarthrosis
Synchondroses (Cartilaginous)
Hyaline cartilage connects, synarthrosis (Ex: Epiphyseal plate)
Symphyses (Cartilaginous)
Fibrocartilage connects, amphiarthrosis (Ex: intervertebral discs)
Synovial Joint function
Diarthrosis
Synovial joint characteristics
Has a joint cavity (Contains synovial fluid)
Articular (Hyaline) cartilage covers articulating surface
Articular capsule surrounds joint like a sleeve and covers synovial cavity
Synovial fluid: secreted by synovial membrane
Articular capsule layers
Fibrous capsule (outer). Synovial membrane (inner)
Fibrous capsule
Attaches to periosteum, dense irregular CT, strengthen joint, flexibility
Synovial membrane
Areolar CT, lines synovial cavity, secretes synovial fluid, cushions
Tendon
Connects muscle to bone, dense regular CT
Ligament
Connects bone to another bone, Dense regular CT
Articular disc (Menisci)
Pad of fibrocartilage that separates articular surfaces, stabilizes joint
Articular disc location
Knee
Bursa
Fibrous sac like structure, reduces friction, located where skin,bone,muscle,tendons rub together
Tendon sheath
Really long bursa that wraps around a tendon, reduces friction and cushions
Plane (Gliding) Joints (Synovial)
Flat articulating surfaces, gliding (Ex: intercarpal, intertarsal)
Hinge joints (Synovial)
Cylinder and trough articulating surfaces, flexion and extension (Ex; Knee, elbow, ankle)
Pivot joint (synovial)
A round area fits into a ring, rotation (Ex: radioulnar, atlanto-axial joint (neck)
Condyloid joint (synovial)
Complementary oval surfaces, flexion, extension, abduction, adduction (Ex: radiocarpal joint of wrist)
Saddle joints (synovial)
Rider in saddle, flexion, extension, abduction, adduction (Ex: trapeziometacarpal joint of thumb)
Ball and socket joints (Shoulder, hip)
Ball in socket, freely moveable of all synovial joints
Ball and socket movements
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction,rotation, circumduction
Energy muscle cells use
Chemical energy (ATP)
Body obtains energy from
Food (Nutrients)
Chemical energy in food is converted into ATP
Transfer of energy from the chemical bonds of nutrients to the phosphate bonds of ATP
ATP synthesis occurs
When energy is transferred from chemical bonds of nutrients to ATP
Cellular respiration
Chemical breakdown of glucose to form ATP
Cellular respiration equation (Aerobic)
C6H12O6+6O2→H2O+6CO2+36ATP+Heat
Aerobic
Requires O2
Anaerobic
ATP production without O2, uses glycolysis instead
Glycolysis equation
Glucose → Pyruvic acid + 2ATP
What happens to pyruvic acid?
Converted into lactic acid (too much in muscles will cause cramps)
Responsiveness (Muscle tissue property)
Can respond to stimuli
Can contract (Muscle tissue property)
Shorten in length
Extensible (Muscle tissue property)
Stretch without damage
Elasticity (Muscle tissue property)
Return to original shape and length
Each muscle is made of
Thousands of muscle cells, blood vessels, nerve fibers, CT
Epimysium
Outermost layer of connective tissue wrap

Epimysium surrounds
Entire muscle
Epimysium is made of
Dense Irregular CT
Perimysium
Middle layer, surrounds group of muscle fibers
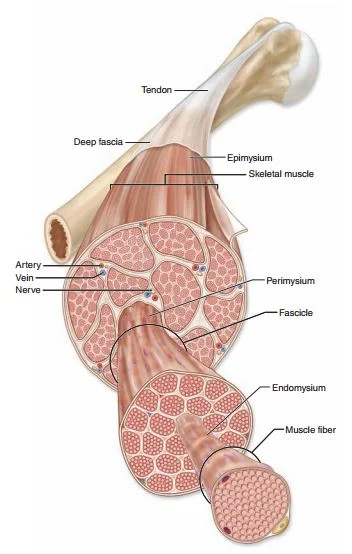
Perimysium is made of
Dense irregular CT, forms fascicles
Fascicles
Bundle of muscle fibers
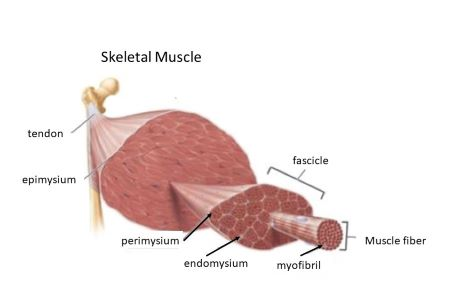
Endomysium
Innermost layer, surrounds individual fibers within fascicle
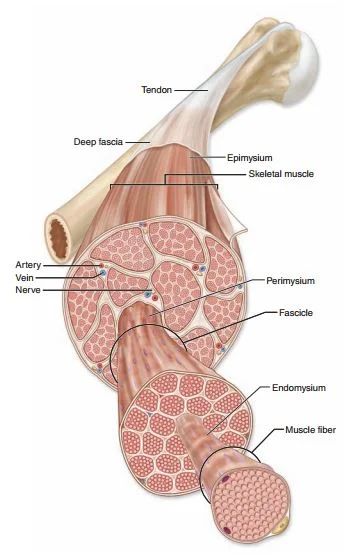
Endomysium is made of
Areolar CT
Direct attachment
Epimysium fused to periosteum of bone
Indirect attachment
Epimysium extends beyond muscle
Aponeurosis
Sheet of dense irregular CT
Tendon (Indirect)
Cord of dense regular CT
Sarcolemma
Cell membrane
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm
Sarcoplasm contains
Glycogen, Myoglobin, Myofibrils, T-tubule, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum, Multinucleate
Glycogen
Energy stored in glycosomes, liver stores glycogen
Myoglobin
Binds O2, Stores O2 in cell, red pigment
Myofibrils
Thread-like fibers, Contractile elements of cell structures that shorten
T-tubule
In pockets of sarcolemma, communication system
Sarcoplasmiic reticulum
Modified smooth ER, Stores and releases Ca
Multinucleate
Muscle cells are formed in embryo and by fusion of many individual stem cells called myoblasts
Satellite cells
Unspecialized unipotent stem cells, located between muscle cell and endomysium
A Band
Dark band of myofibril
I band
Light band of myofibril
H band (A band zone)
Lighter region in center, visible when relaxed
M line (A band zone)
Center of H zone
Z disc (I band zone)
Center region
Sarcomere
Allows for shortening, functional unit of a muscle cell
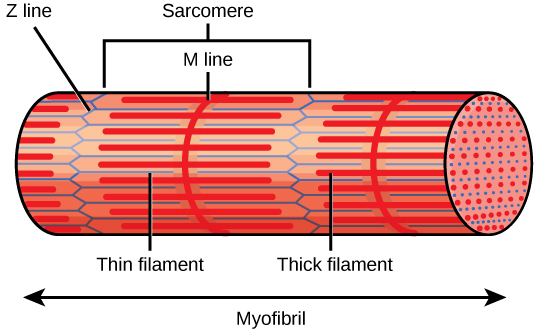
Thick myofilament
made of myosin, 200 myosin = 1 thick filament
Thin myofilament
Made of actin, anchored in Z discs
Elastic filament
Made of elastic fibers, anchors thick filament Z discs and M line, stabilizes thick filament
Myosin Tail
Points toward M line, forms shaft
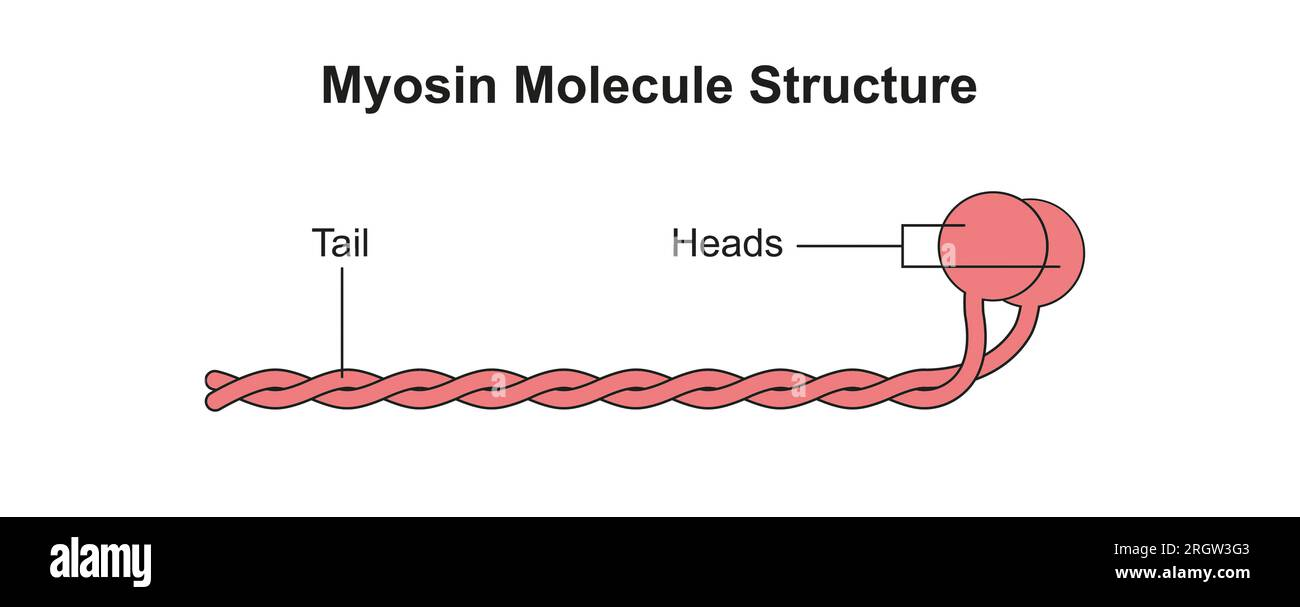
Myosin Head
Extend from shaft, points toward thin filament, can bind actin.

Myosin function
Contractile motor protein that binds actin
Where does myosin get the energy to do work?
PE from myosin phosphorylation
Actin
Contractile protein with a myosin bind site
Regulatory proteins (Troponin, Tropomyosin)
Regulate myosin, binding to actin by blocking the myosin bind site on actin
Dystrophin
Largest protein known, links microfilaments to sarcolemma, needed for muscle contraction
Muscle dystrophy
Genetic disease caused by a mutation in the dystrophin gene
Muscle action
Muscles pull, not push
Prime mover
Muscle that is most responsible for an action
Antagonist
Muscle performing the opposite action as the prime mover
Myosin ATPase
Enzyme on myosin head hydrolyzes ATP ATP→ADP+P