Biology: 2C - Biological Molecules
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the different types of Biomolecules?
water, carbohydrates, lipids/fats, proteins, nucleic acids
Which elements do all carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids contain?
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
What can carbohydrates be broken down into?
monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
What are monosaccarides?
simple sugars. They are most basic units or monomers of carbohydrates (meaning can't be broken down further).
What are monosaccharides function?
1. Fast-acting source of energy during respiration
2. Building blocks of complex sugars.
What monosaccharide has 6 carbon atoms, and some examples?
Hexose, eg Glucose, Galactose, Fructose.
What are disaccharides?
A disaccharide is formed when two monosaccharides are joined together be a covalent bond.
What are some examples of disaccharides?
maltose, sucrose, lactose
What are polysaccharides (complex sugars)?
A polysaccharide is a macromolecule formed of several hundred or thousands of monosaccharides monomers.
What are polysaccharides functions?
polysaccharides are large and insoluble, so they are used for structural purpose (cellulose) and storage (Glycogen, Starch).
What is the function of starch?
Excess glucose from photosynthesis is stored in plants as starch. Can be broken down to glucose to release energy for plants.
What is the function of cellulose?
Provides tensile strength to plant cell wall.
What is the function of glycogen?
Excess glucose from digestion of carbohydrates is stored in liver and muscles of animals as glycogen. Can be broken down to glucose to release energy for plants.
What are lipids/fats?
1 glycerol molecule chemically bonded to up to 3 fatty acid chains.
What are Lipids classified into?
fats (solid at room temp)
oils (liquids at room temp)
What are the functions of lipids?
Long term store of energy.
Cushion vital internal organs
Provide thermal insulation
Forms the cell membrane of cells.
What are proteins?
amino acids.
What are the functions of proteins?
To form enzymes (digestion), antibodies (immunity), haemoglobin (transport oxygen in red blood cells), keratin (hair and nails), actin (muscles).
Which test do you use to test for glucose (a reducing sugar)?
Benedicts test.
What are some examples of reducing sugars?
Glucose, galactose, fructose, maltose, lactose.
How does the Benedict test work?
Add 1cm of Benedict's solution into 1cm sample solution in test tube. Heat at 60-70°C in a hot water bath for 5 minutes. Take test tube out of water bath and observe the colour. If negative result, it remains blue, if positive turns orange or brick-red.

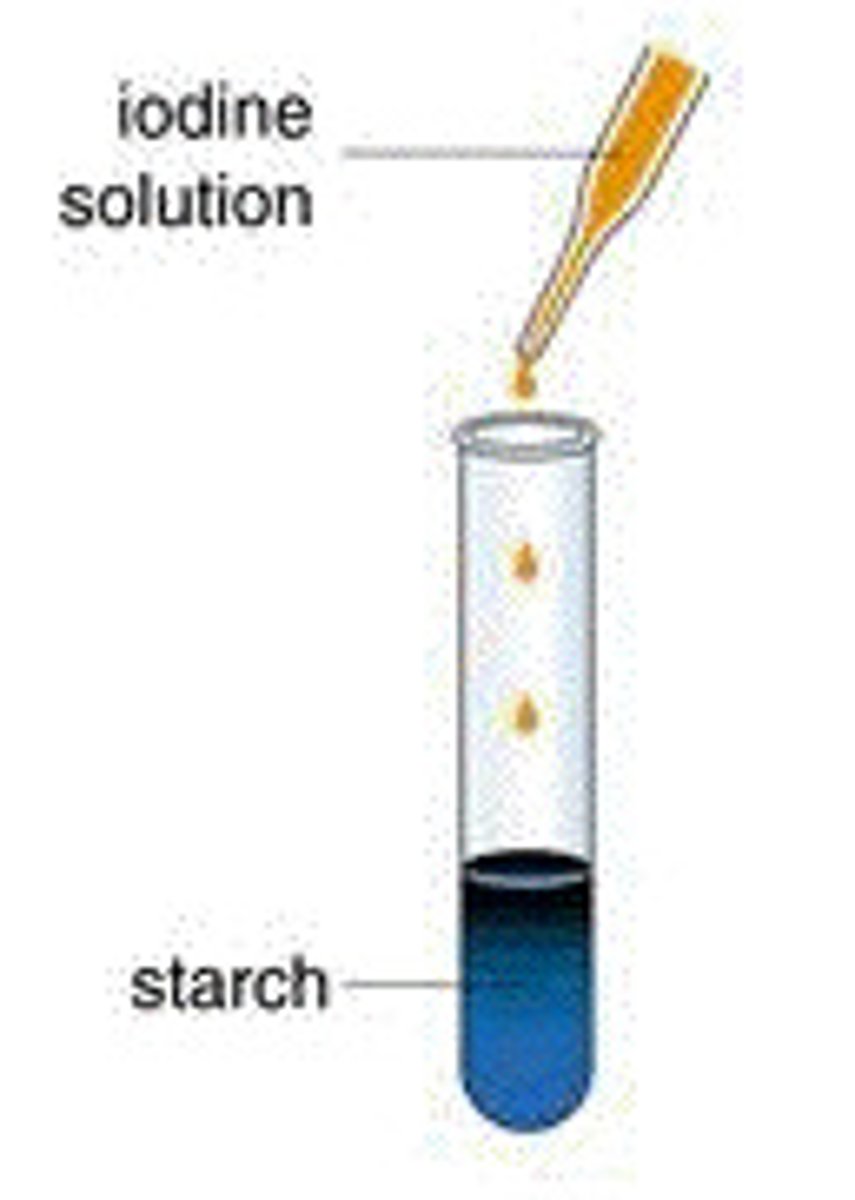
Which test do you use to find starch?
Iodine test.
How does the iodine test work?
Add drops of iodine solution to the food sample. If result is negative, it remains brown, if positive turns blue-black.
Which test do you use to find protein?
Biuret solution
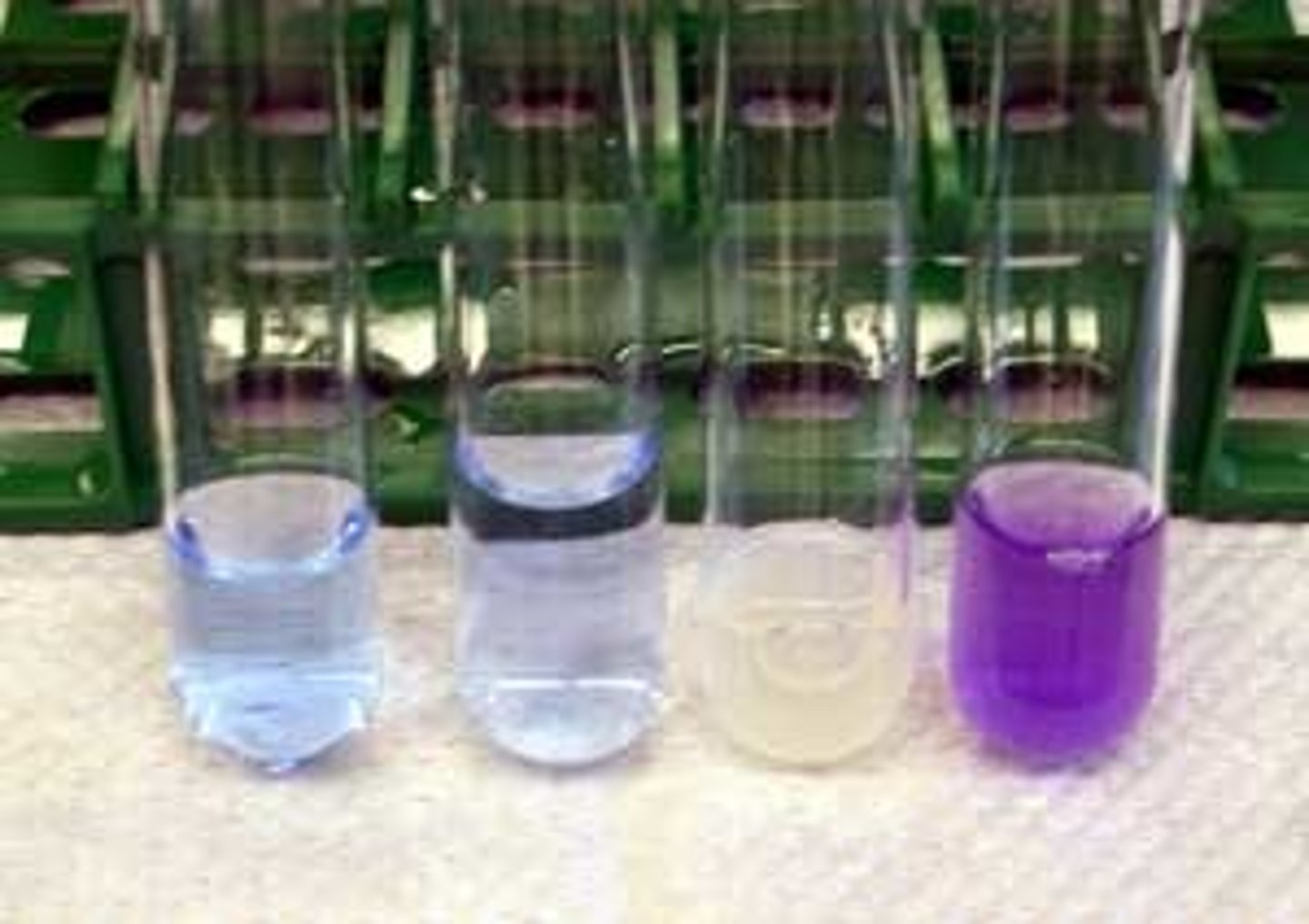
How does the biuret solution work?
Add drops of Biuret solution to the food sample solution. Shake the mixture. If negative result, it remains blue, if positive, it turns violet.

Which test do you use to find lipids/fats?
ethanol emulsion test
How does the ethanol emulsion test work?
Food sample is mixed with 2cm of ethanol and shaken. Add a few drops of distilled water. If negative result, it remains clear, if positive, a white emulsion is created.
What are enzymes?
Proteins that function as biological catalysts.
Function of enzymes?
Speed up rare of chemical reactions. Remain chemically unchanged at end of reaction.
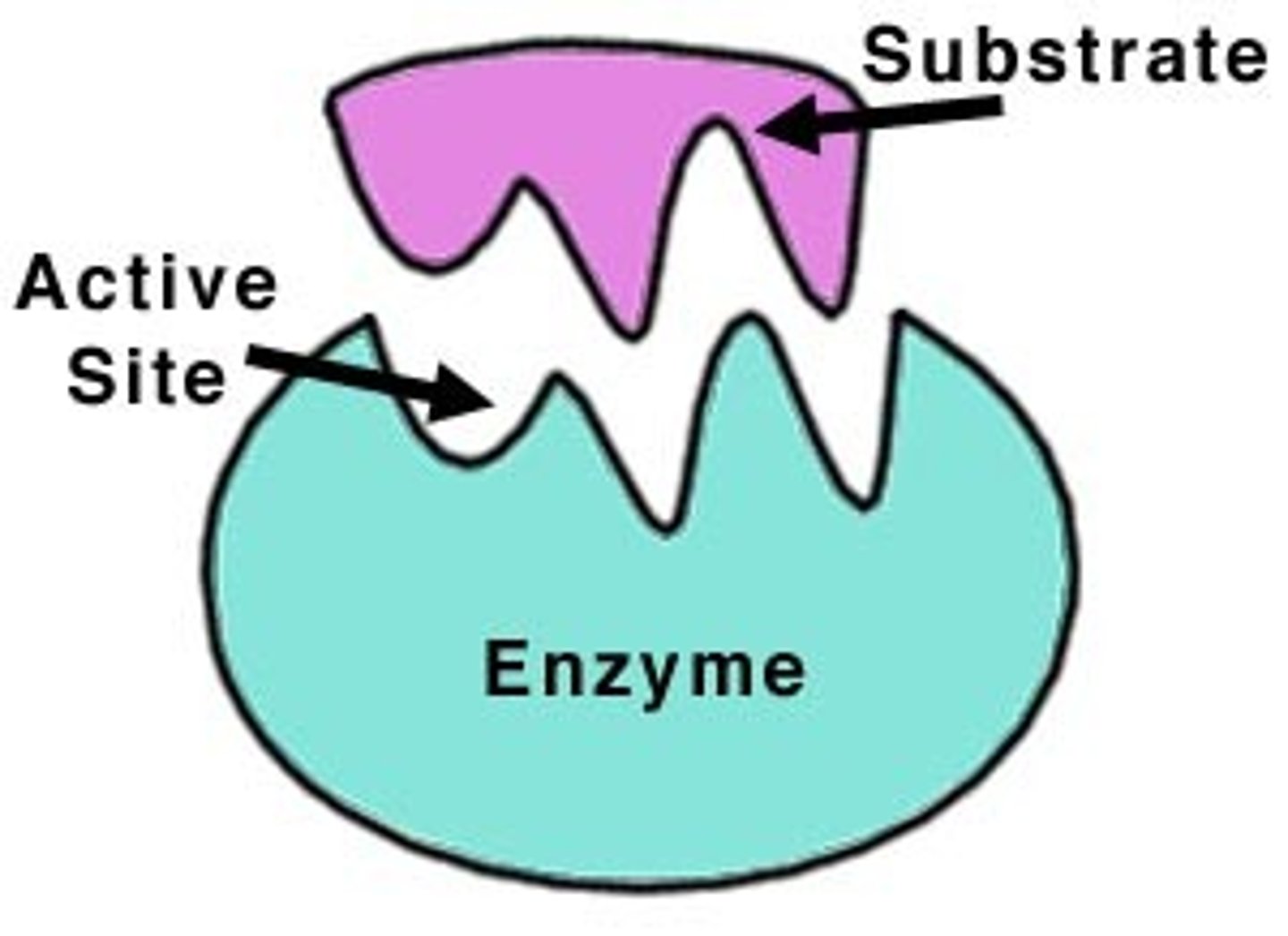
Explain the 'lock and key' mechanism of enzymes.
Each enzyme (lock) has an active site where molecules called substrate (key) binds to. The active site specifically matches the shape of the substrate molecule as substrate has a complementary shape to active site. Enzyme is specific because it only binds to one substrate.
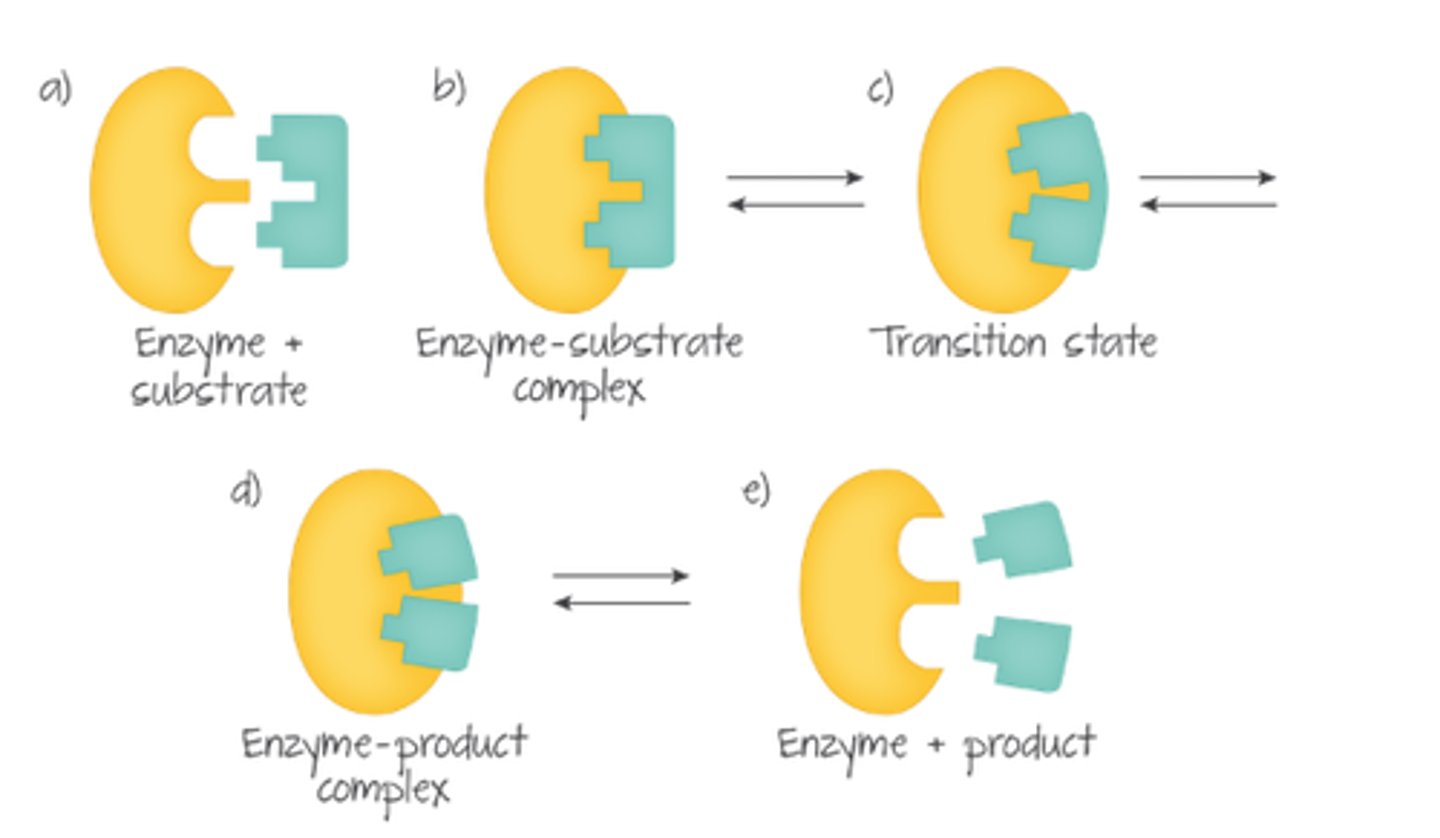
Steps to enzyme-substrate reaction?
1. Substrate randomly collides with active site. Greater kinetic energy = higher probability of collisions.
2. When enzyme and substrate collide at correct orientation and speed, an enzyme-substrate complex is formed.
3. Products is released, enzyme chemically unchanged.
enzyme+substrate -> enzyme-substrate complex -> enzyme+product
What are some factors affecting enzyme controlled reactions?
Temperature and pH.
Description of low temp on enzymes?
Low temp = Low kinetic energy = few collisions = slow rate of reaction,
Description of high temp on enzymes?
Above optimum temp = enzyme becoming denatured (loses 3-dimensional structure) = active site not matching shape of substrate = decreasing enzyme reaction.
Description of above or below optimum pH on enzyme?
enzyme becomes denatured (loses 3-dimensional structure) = active site not matching shape of substrate = decreasing enzyme reaction.