AICE Marine Science: Unit 5: Examples of Marine Ecosystems
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the 5 oceans?
Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, Arctic
Where is the Pacific Ocean located?
between Asia and Australia to the west and the Americas to the east, extending from the Arctic in the north to the Antarctic in the south
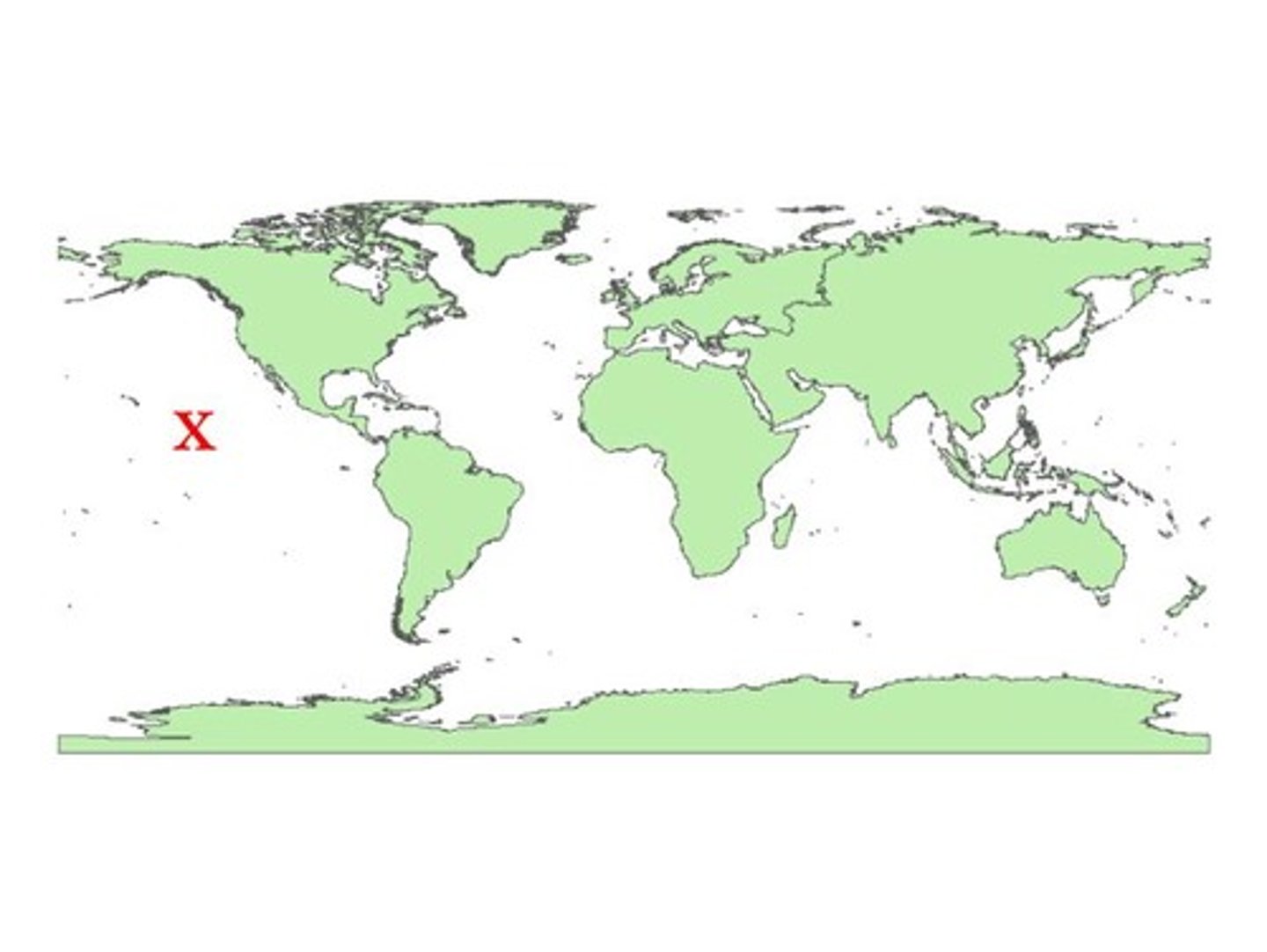
Where is the Atlantic Ocean located?
between the Americas on the west and Europe and Africa on the east
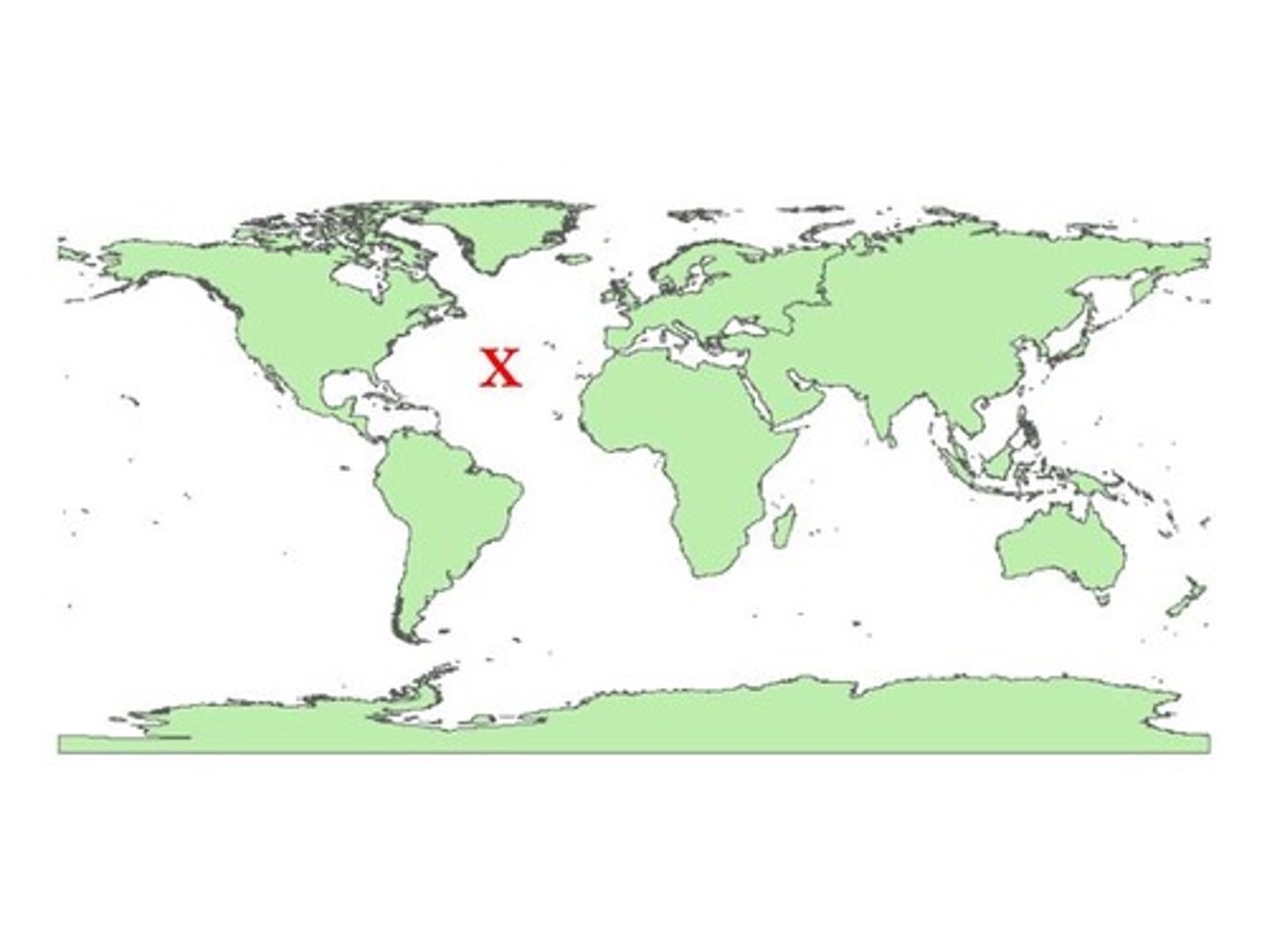
Where is the Indian Ocean located?
between the Americas on the west and Europe and Africa on the east
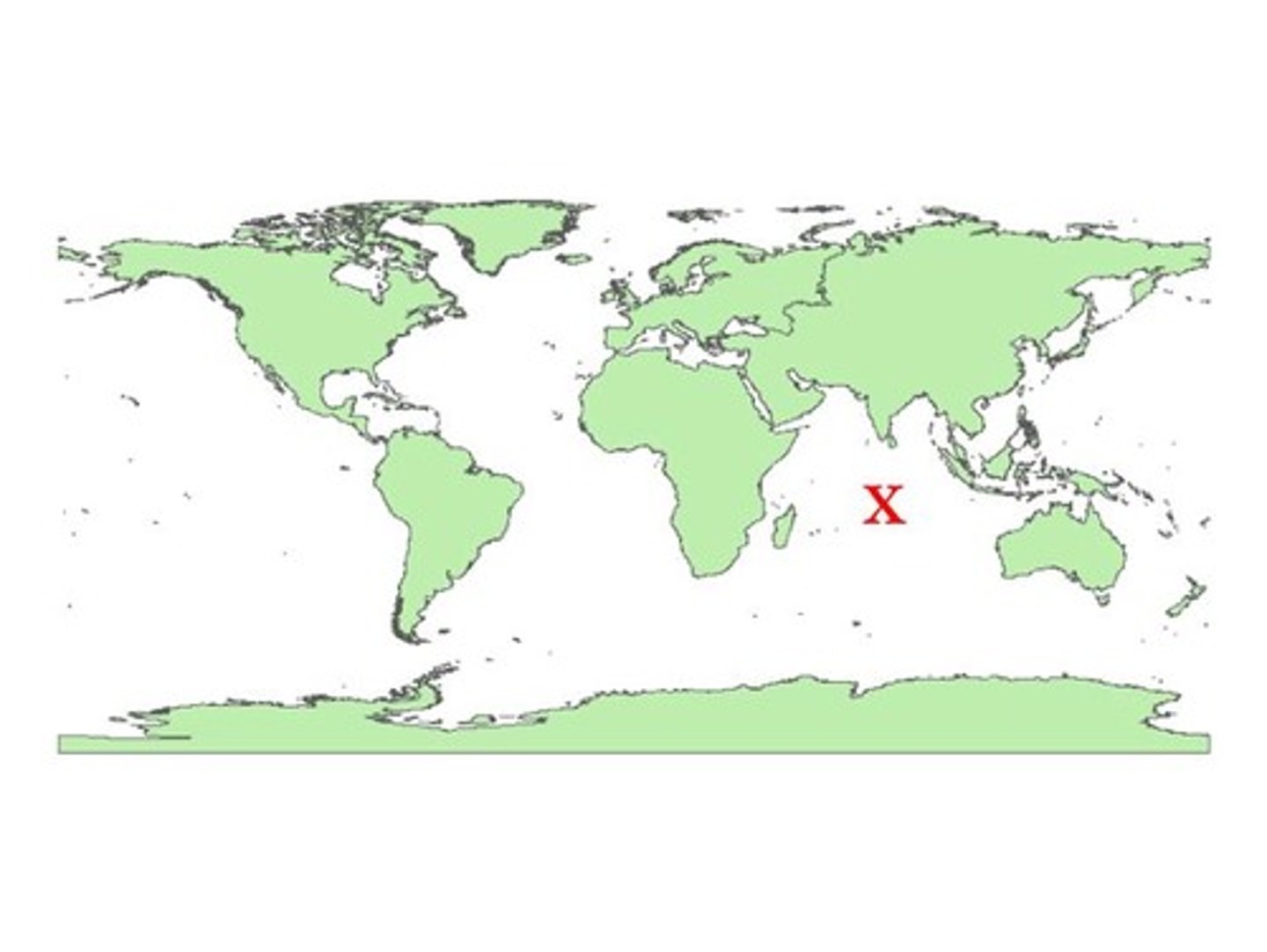
Where is the Southern Ocean located?
in the southernmost waters of the world ocean, encompassing the waters surrounding Antarctica
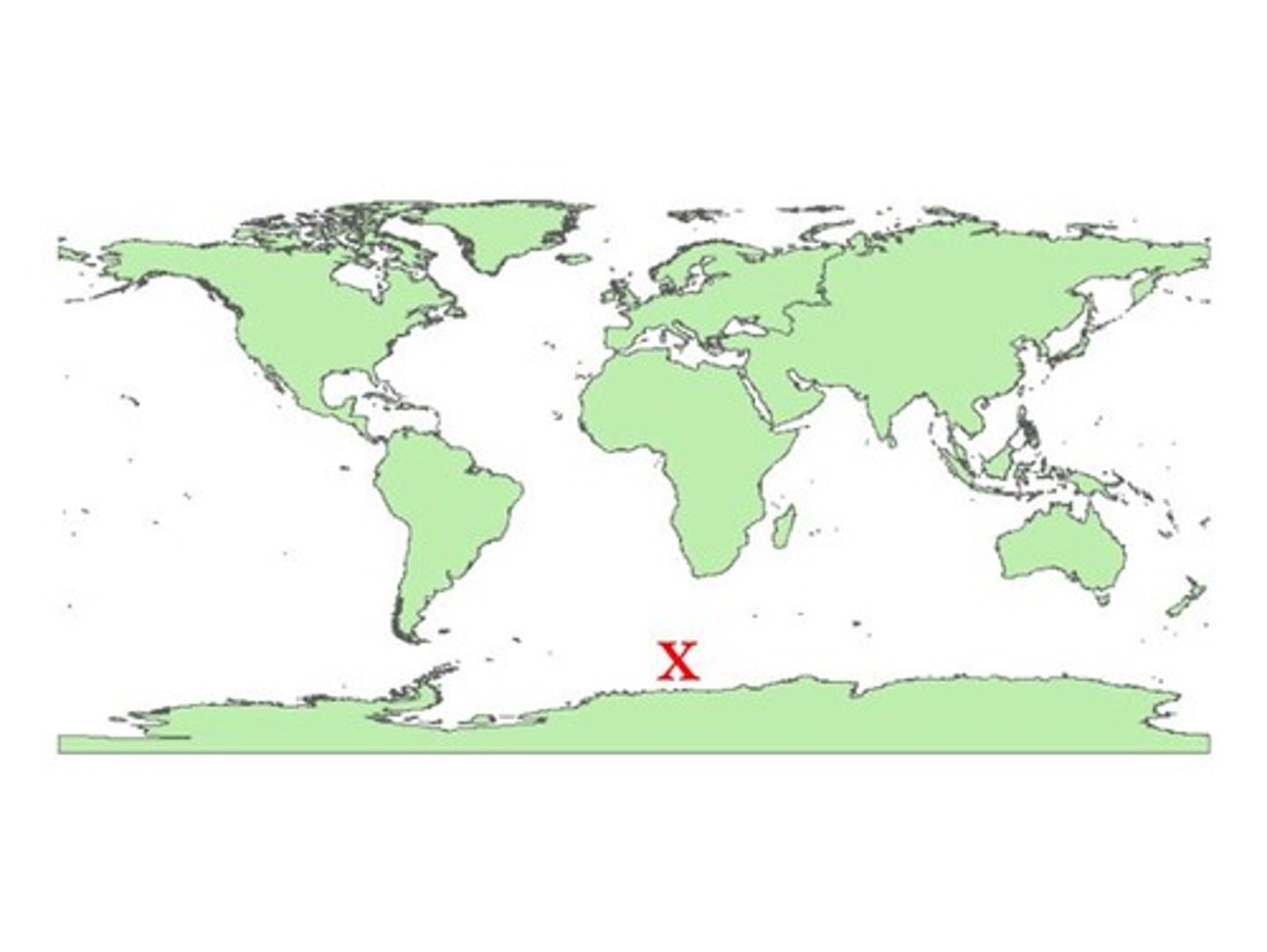
Where is the Arctic Ocean located?
the North Pole, the top of the world
theca
the walls of the calyx
hard corals
stony corals capable of reef-building that have a relationship with zooxanthellae
soft corals
corals that do not build reefs and lack calcification
zooxanthellae
symbiotic, photosynthetic dinoflagellates living within the tissues of many invertebrates
Which zone is located between 0-200m?
epipelagic zone
Which zone is located between 200-1000m?
mesopelagic zone
Which zone is located between 1000-4000m?
bathypelagic zone
Which zone is located between 4000-6000m?
abyssopelagic zone
Which zone is located below 6000m/the seafloor?
benthic zone
this zone receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis and has high productivity levels
epipelagic zone
this zone has enough light for organisms to see but not for photosynthesis, causing organisms to adapt due to the lack of oxygen/nutrients
mesopelagic zone
this zone is completely dark and organisms survive on detrius/marine snow (detrivores) and adapt to be transparent or bioluminescent
bathypelagic zone
this zone is made up of unending darkness and has very high pressure and is very cold (near freezing) with organisms that are blind/colorless
abyssopelagic zone
this zone is completely dark in the open ocean but may receive light in shallower bodies of water like estuaries
benthic zone
What are organisms in the benthic zone called and what do they include?
benthos; crustaceans, echinoderms, polychaetes
What is coral bleaching?
whitening of coral that results from the loss of a coral's symbiotic zooxanthellae -- in essence, it occurs when hard corals become stressed by environmental factors, particularly rising water temperature and reduced pH
What happens if coral bleaching lasts for an extensive period of time?
the coral will die due to a lack of nutrients and poor water condition
What makes rocky shores difficult to live on?
- fluctuating temperatures
- wave action
- exposure to air based on tides
True or False: Rocky shores have significant biodiversity.
true
What do organisms living on rocky shores have to adapt to?
- type of rock making up the substrate
- whether the habitat is temperate or tropical
- how much sunlight is at any time during the year
What are the 4 areas of the intertidal zone of rocky shores?
- splash zone
- upper shore
- middle shore
- lower shore
What makes sandy shores difficult to live on?
- the porous substrate, as they are extremely unstable, a single wave/gust of wind can remove a lot of the fine sand, they do not hold water well, and lack places for attachment
(there is also high competition and predation)
How do organisms living on sandy shores have to adapt?
living in instead of on the substrate by burrowing
Most organisms living on sandy shores are...
detrivores
True or False: Sandy shores have significant biodiversity.
false - low biodiversity
Describe mangrove trees.
salt-tolerant trees that prefer to live in coastal or estuarine environments between latitudes 25N or 25S
adaptations of (red) mangroves to live in seawater
1. prop root structure for stability
2. prop roots for oxygen absorption using lenticels
3. salt exclusion with filtration at the roots and salt sent to leaves and is eliminated from the tree when the leaf dies
4. viviparous reproduction by developing propagules while still attached before releasing them to float in the ocean
What are the conditions needed for the formation of mangrove forests?
- saltwater areas with a large tidal range where deposition is more frequent than erosion due to calmer waters and reduced wave action (so propagules can embed in the sand and take root)
- temperature must be warm year-round (never below a 20C avg)
- preferably areas with healthy coral reefs due to the protection provided
What is the ecological importance of mangroves?
- provide a home for organisms with cage-like roots
- prevent and reduce storm and wave erosion
- cause deposition of sediments protecting buildup in coral reefs and seagrass beds nearby
- help control carbon levels
What is the economic importance of mangroves?
- used for food and timber by island communities
- provide natural protection for coastlines from erosion and storms
- sponge for floodwaters
- purification system for waters
- tourism