Chem Exam 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
cations
formed from METALS because they have lower ionization energies than nonmetals thus like to LOSE electrons (lower i.e makes it easier to remove electrons)
always has positive net charge
*tip: cats are pawsitive
anions
formed from NONMETALS b/c they have higher ionization energies and thus like to gain/accept electrons
always has negative net charge
(high i.e meaning the proton nucleus has a stronger attraction for electrons when we go from left to right across the periodic table)
ionic compound
a bond between metal and nonmetal
formed when a metal LOSES its valence electrons & they’re transferred to a nonmetal; the nonmetal GAINS electrons
metals lose electrons to become cations (and attain the octet rule)
nonmetals gain electrons to become anions
covalent compounds
formed between nonmetals; electrons are shared
octet rule
ionic compounds lose electrons to fulfill this rule, where the outermost energy level acquires 8 electrons
covalent compounds gain electrons to fulfill this rule
ex) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s1 will lose electron in 3s1 so that energy level n=2 has all 8 electrons
overall net charge
when electrons are gained/lost, we add the protons + electrons to find the ___.
It is written as an exponent on an element.
Ex) Na+1 (+1 is overall net charge here)
can be solved using periodic table group # (all p.t. elements have neutral charge, so gaining/removing electrons will decrease/increase the net charge)
Ex) Group 1A metal will LOSE 1 electron, resulting in 1+ net charge
Group 2A metal will LOSE 2 electrons, resulting in 2+ net charge
Ex) Group 6A nonmetal will GAIN 2 electrons, resulting in 2- net charge
Group 7A nonmetal will GAIN 1 electron, resulting in 1- net charge
ionic formula
the total number of positive charges MUST equal the number of negative charges
the sum of ionic charges in the formula should equal 0
transition metals
include elements that can form more than one charge when they combine with anions to produce IONIC compounds
the charge of transition metals in a compound is indicated by roman numerals in parentheses when naming them
polyatomic ions
these are a group of nonmetal atoms bonded together but have a SINGLE CHARGE.
*memorize table and know how to write formulas
molecular compound
formed only by NONMETALS that share electrons
atoms can form these by satisfying the octet rule
(bonus: what is the bond between shared electrons called?)
covalent bond
bcuz the nucleus has protons and the outside of atoms have electrons, there is attraction between atoms. This attraction brings atoms close TOGETHER until they SHARE ELECTRONS, forming __.
the pairing of electrons between NONMETALS
a single line on a lewis dot diagram
(Ex. in the H2 molecule, a __ forms as H atoms move closer together. Each H atom will share its electron to become a stable molecular compound with a DUET configuration)
duet
each H atom is stabilized or surrounded by 2 electrons
(add pic from her notes)
lone pair electrons (nonbonding electrons)
no boron examples
bonding electrons
electronegativity
An atom's ability to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond; higher electronegativity value = the stronger the pull of shared elections by the nucleus.
TREND on periodic table:
going DOWN the periodic table, electronegativity decreases
going ACROSS the periodic table, electronegativity increases
polarity of bonds
in a bond, the atom with a higher electronegativity value will have shared electrons gravitating towards the more electronegative atom. so the shared electrons gravitate more towards the stronger electronegative atom, spending more time there. bc of this , the electron density of a higher electronegative atom is higher
the difference in electronegativity of bonding atoms can be used to predict the ______
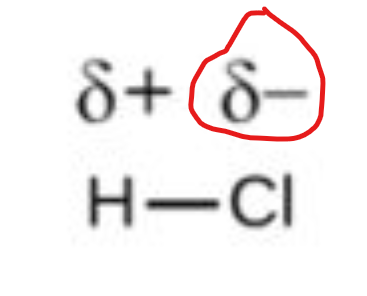
in a bond, this means electrons are spending more time near the more electronegative atom
in this pic, this means chlorine is more electronegative
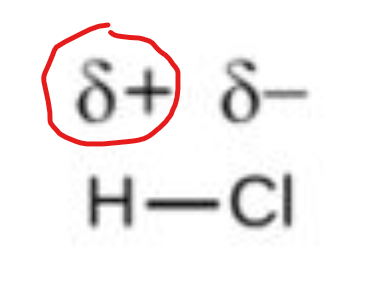
this symbol shows that as electrons move away from the less electronegative atom, the atom gets LESS electronegative (or slightly more positive)
dipole
is created when one end of the bond becomes slightly more positive and the other becomes slightly more negative
polar covalent bond
a bond with dipoles
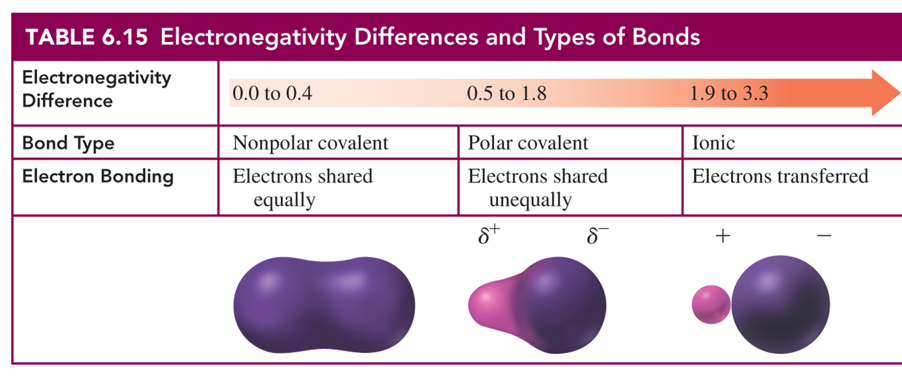
Know Table 6.15 Electronegativity Differences and Types of Bonds
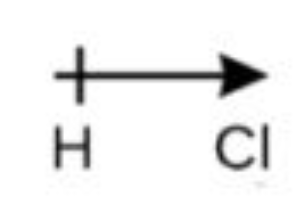
arrow
an arrow can be used to show electrons moving toward the more electronegative atom. There is a line in the arrow, making a positive sign over the less electronegative atom that is more positive
nonpolar covalent bonds are __
atoms are HYDROPHOBIC. DOesnt mix well with water (they are watetr-farin)
polar covalent bonds are ___
atom AS HYDROPHILLIC and interacts with water.
bond in H20 are always polar covalent.
water (charged)
the bonds in water are polar covalent. water has charged bonds; this allows water molecules to interact with charged ends of other polar covalent molecules
water can be interacted with by IONIC AND POLAR COVALENT OUDNS@
Combination reaction
two or more elements form one product.
• simple compounds combine to form one product.
Decomposition reaction
one substance splits into
two or more simpler substances.
Single replacement reaction
one element takes the
place of a different element in another reacting compound.
double replacement reaction
positive ions in the reacts compounds switch places
combustion reaction
oxidation
loss of electrions
In a reaction, a reactant may have its normal charge. but when it becomes a product, that charge “disappears” bcuz the reactants need to cancel each other out right. so if the reactant initially had a positive charge, it will have to LOSE ELECTRONS when it becomes a product
this reactant that is oxidized is called the “reducing agent”
the substance that is oxidized is always the metal, POSITIVE CHARGE
reduction
gain of electrons
a reactant may have a negative charge, but products dont have charges. so, this reactant will have to GAIN electrons to have a chargeless product.
this reactant that got reduced is called the “oxidizing agent”
the substance that is reduced is always the nonmetal, NEGATIVE CHARGE
OIL RIG
Oxidized Is Loss of electrons (
Reduced Is Gain of electrons