Orthodontics - TEST #1
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
orthodontics is
speciality of dentistry with supervision, guidance, and correction of the growing + mature dentofacial structure
facial aesthetics to improve are
appearance
facial profile
occlusion
WHO health definition
state of complete physical, social, and mental well being
treating perio disease is considered
social + mental well being
orthodontics indications
severe malocclusions
large overjet
midline
perio health due to crowed teeth
severe class II
orthodontics contraindications
bone + blood disorders
lack of motivation
successful orthodontic treatment requires
co operation
compliance
who has had high orthodontics discontinuation rates
children + adolescents
orthodontics poor health can result in
decalcification
decay
gingival overgrowth
severe root resorption is
more than 1/3rd of root is lost
severe root resorption occurs between ?? orthodontically treated teeth
1-5%
severe root resorption is seen in the
anterior max
factors for orthodontics potential for relapse
rotated teeth
lower incisor crowding
age related changes
malocclusion is
abnormal / malpositioned relationship of max + mand teeth
etiologic sites of malocclusion
neuromuscular
bones
teeth
neuromuscular system affects occlusion by….?
major muscle groups that affect bone / teeth
strong mentalis
strap like lower lip results in
retroclination of lower incisors
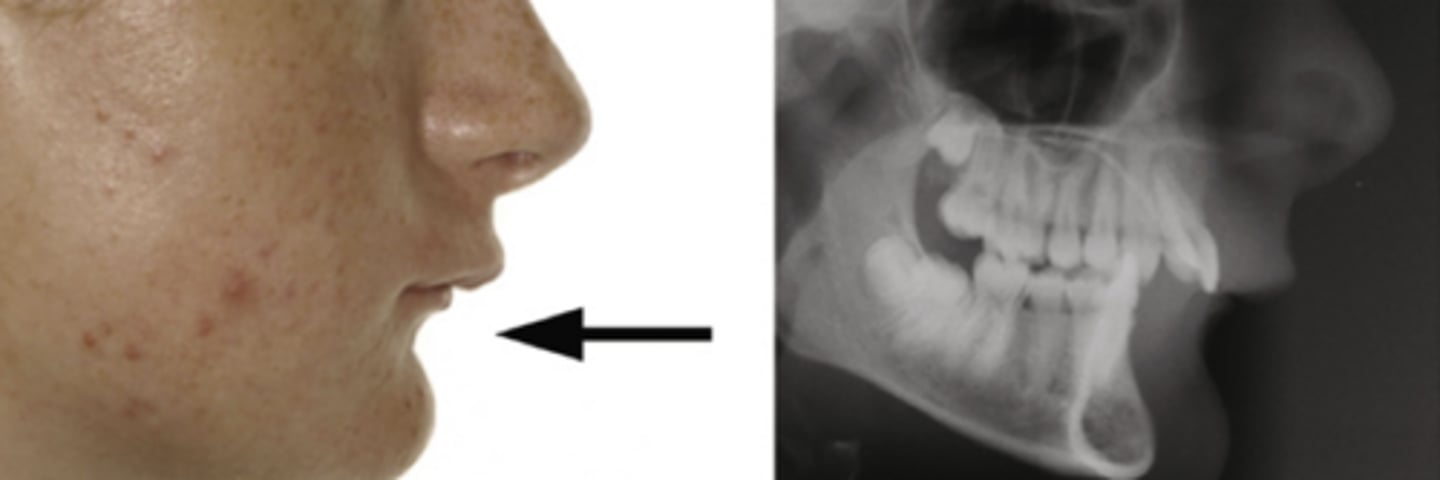
bone etiology is the most
serious malocclusions in skeletal organ
2 stages of treatment of skeletal disharmonies
1. during growth phase (removable/fixed appliances)
2. after growth phase (surgical intervention)
most common site of fracture is
mandible condyle during childhood
= can cause asymmetry
PHOTO = curve of Wilson
juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is
before age 16
results in development of severe class II
teeth etiology developmental causes
eruption sequence
is age or eruption sequence more important
eruption sequence is more important because it will determine occl
congenitally missing teeth is called
anodontia
hypodontia
which teeth are congenitally missing teeth
max laterals
mand 1st pre molars????
8s
small teeth is called
mesoden
what are the two categories of supernumeraries
hyperdontia
mesoden
gemination is
developmental disturbance with single tooth germ trying to divide forming large single-rooted tooth
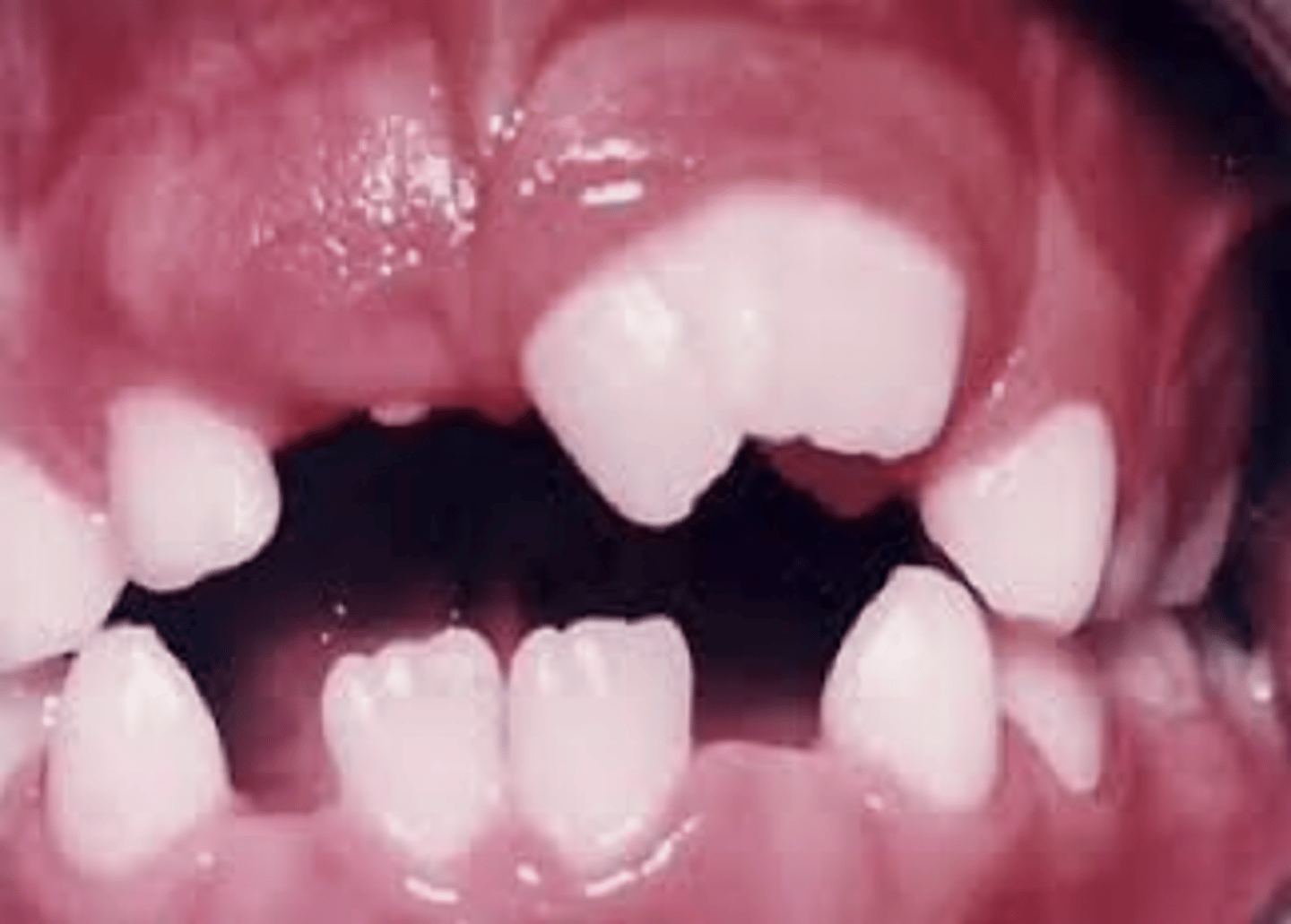
factors related to malocclusion
genetics
environmental
sucking/tongue thrusting/mouth breathing
mouth breathing can lead to
adenoidal face

adenoidal face characteristics
nostrils underdeveloped
upper lip is short
longer faces
minor malocclusion is
slight variations in displaced teeth
major malocclusion is
involves entire dental arches + skeletal bones
class I
medial buccal cusp of max 1st molars occludes with medial buccal groove of mand 1st molar
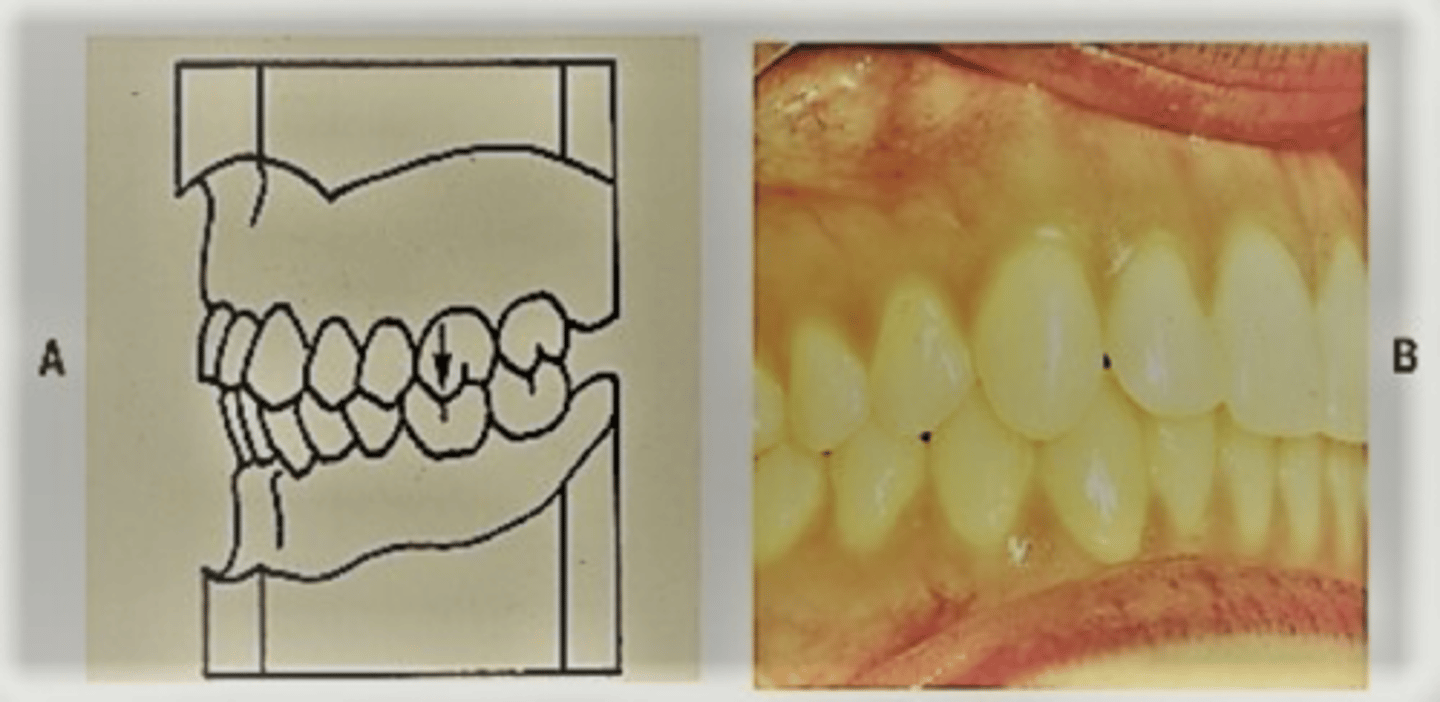
class I malocclusion
deviation from class I
crowding, rotations
class II malocclusion
body of mand is in distal relationship with max
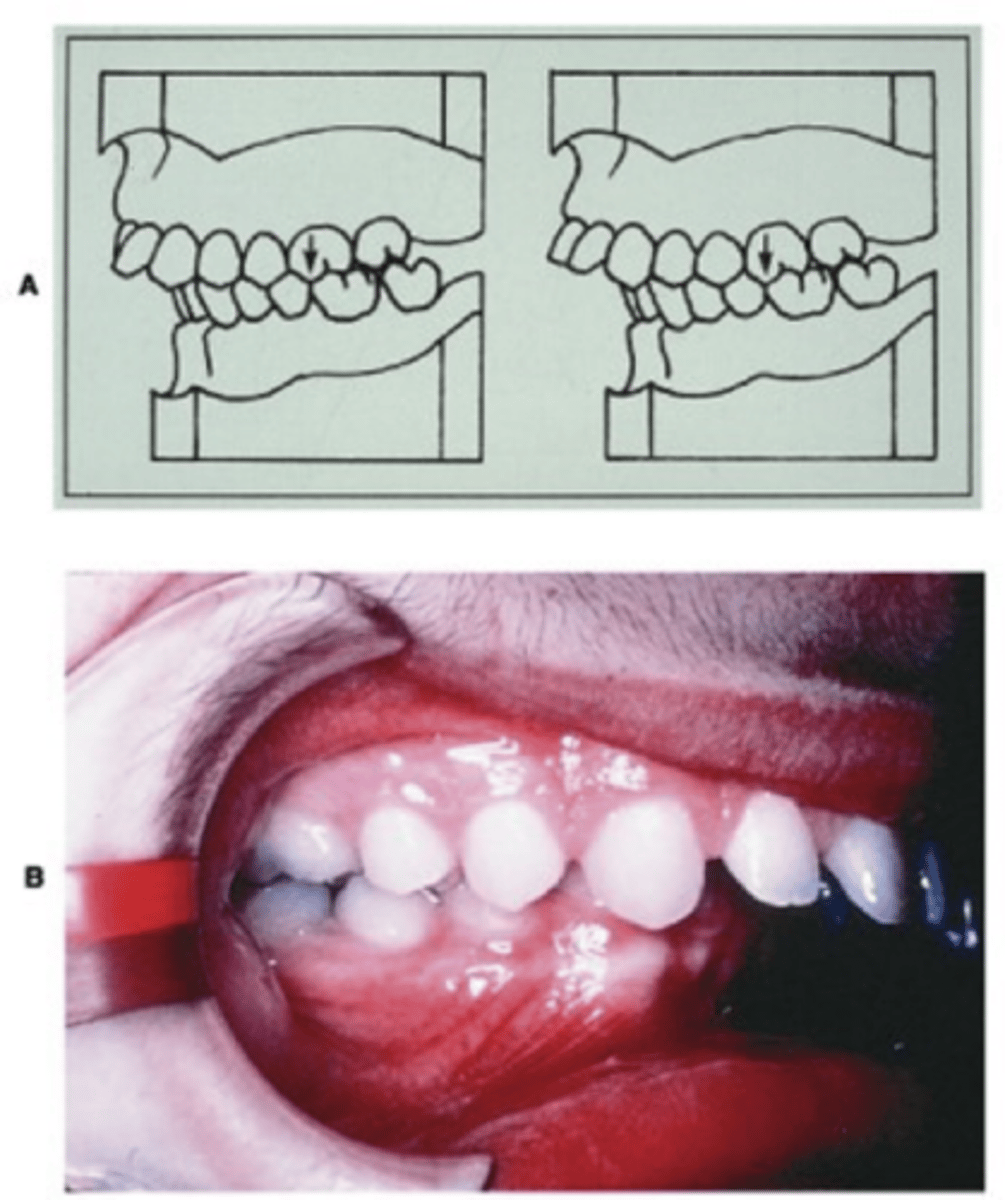
class II malocclusion gives appearance of
max anterior teeth protruding over mand anterior teeth
class II division I malocclusion is
the maxillary incisors are protruded and the mandible is in a retruded position
class II division II malocclusion is
one or more max incisors are retruded and the mandible is in a retruded position to the max
class III malocclusion
body of mand is in abnormal median relationship with max
class III malocclusion gives appearance of
mand teeth protruding in front of max anterior teeth
planes of occlusion is for
primary teeth
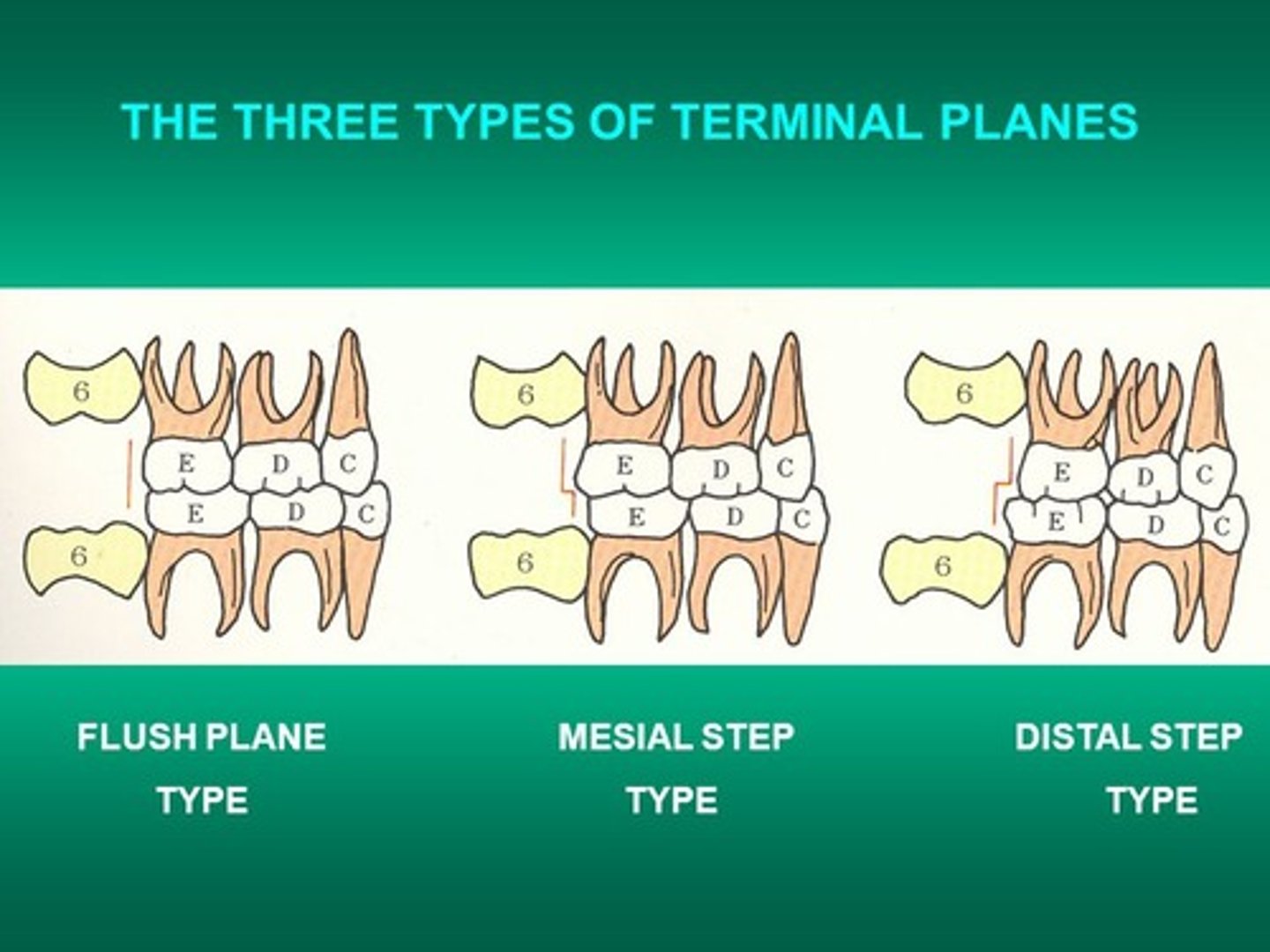
terminal plane is
ideal molar relationship in the primary dentition, when in centric occlusion
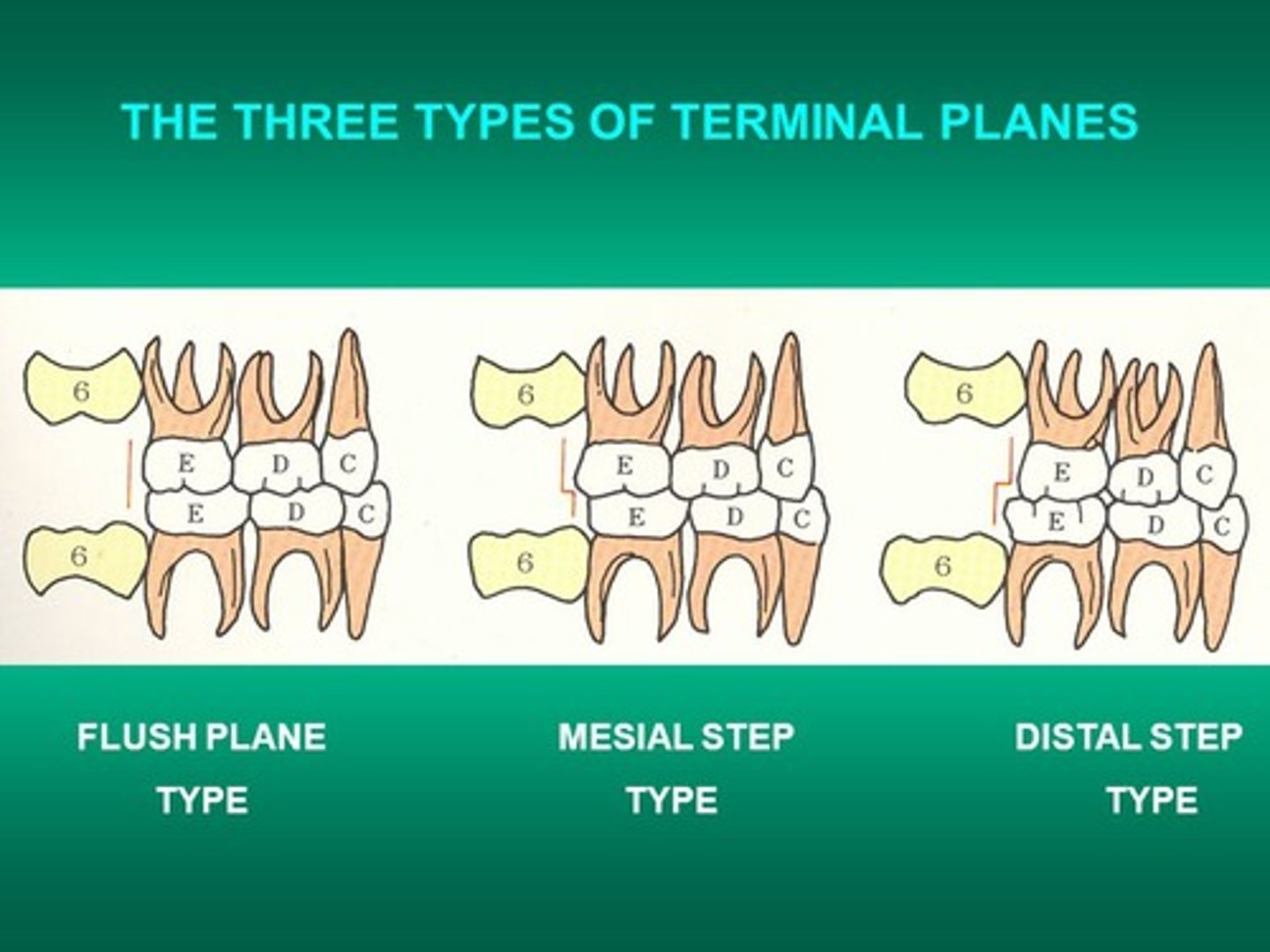
mesial step is
primary mandibular second molar is mesial to the maxillary second molar
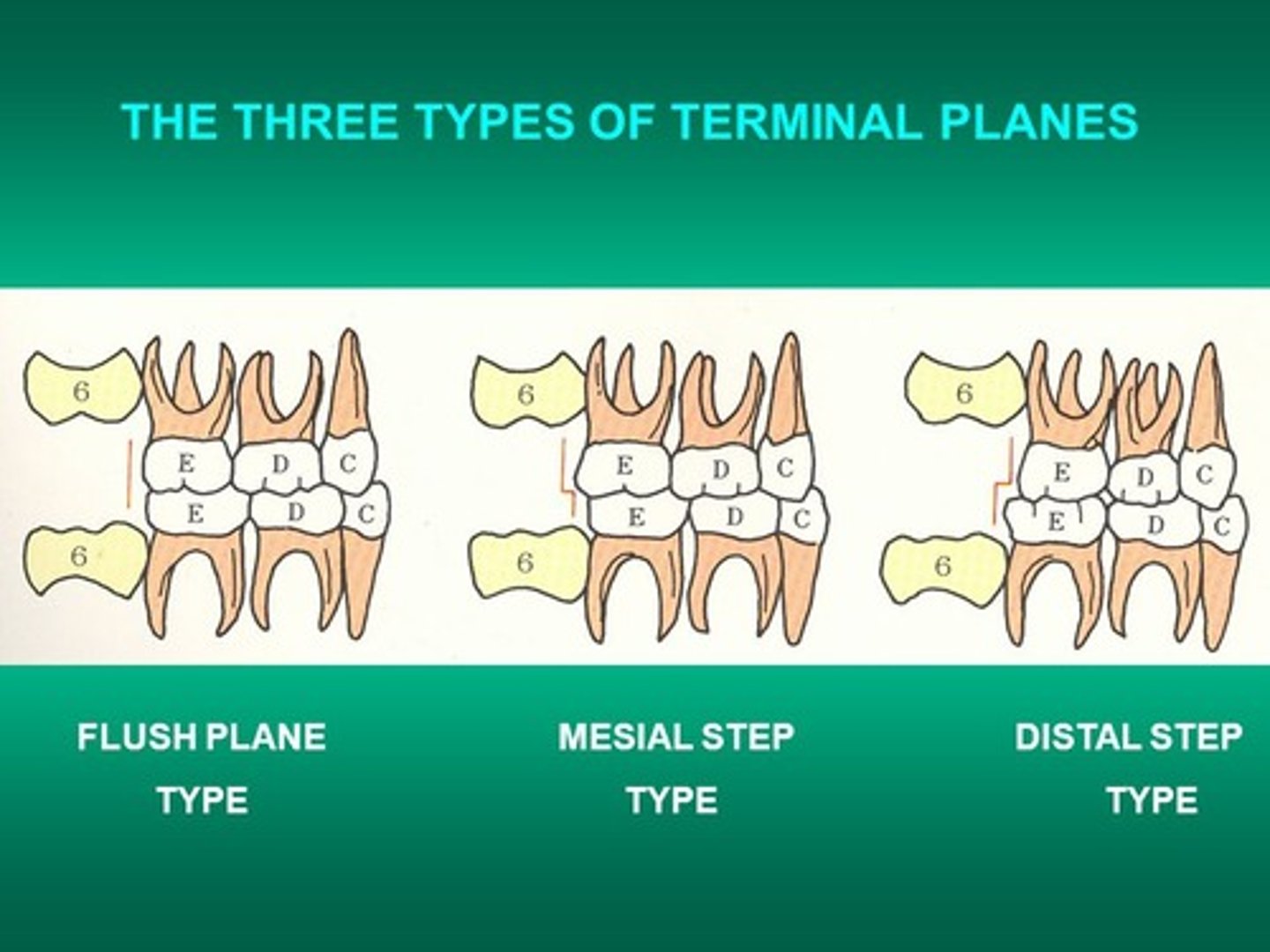
distal step is
primary mandibular second molar is distal to the maxillary second molar
not an ideal molar relationship in the primary dentition
what is the most common contributor to malocclusion
crowding
lower anteriors
overjet is
protrusion of max incisors
expressed in mm
open bite is
lack of vertical overlap of max incisors
causes opening of anterior teeth when posteriors are closed
cross bite is
tooth is not properly aligned with opposing tooth
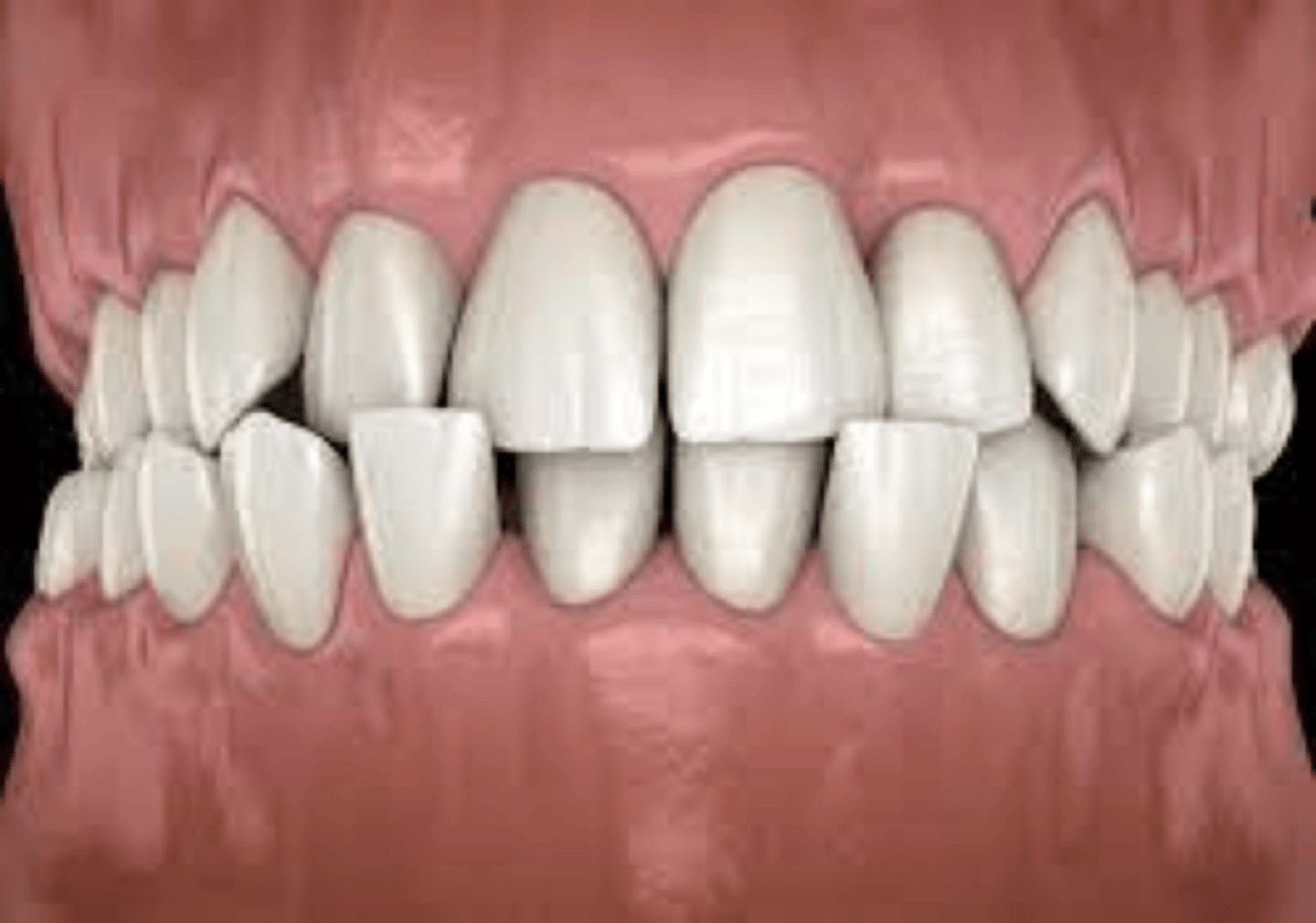
cross bite types
posterior
unilateral
bilateral
anterior
posterior cross bite is
Lingual cusps of maxillary teeth do not occlude in the center of occlusal surface of mandibular tooth
Cusps are located either facial or lingual to their normal position.
unilateral cross bite is
posterior crossbite that affects only one side of the mouth
bilateral cross bite is
posterior crossbite that affects both sides of the mouth.
anterior cross bite is
maxillary incisors are located lingual to the mandibular incisors
overbite is
Increased vertical overlap of the maxillary incisors
expressed in %
slight overbite is
incisal edge of the maxillary central incisors rest in the incisal 1/3 of the mandibular central incisors.
moderate overbite is
incisal edge of the maxillary central incisors rest in the middle 1/3 of the mandibular central incisors.
severe overbite is
incisal edge of the maxillary central incisors rest in the cervical 1/3 of the mandibular central incisors.
orthodontics extra oral exam
soft tissue
facial / profile type
TMJ
lip posture
method of breathing
swallow pattern
musculature - mentalis
soft tissue profile involves
convex
concave
normal
convex soft tissue profile is
upper & lower lips are ahead of a line connecting a point halfway along the lower border of the nose and the most forward point on the chin
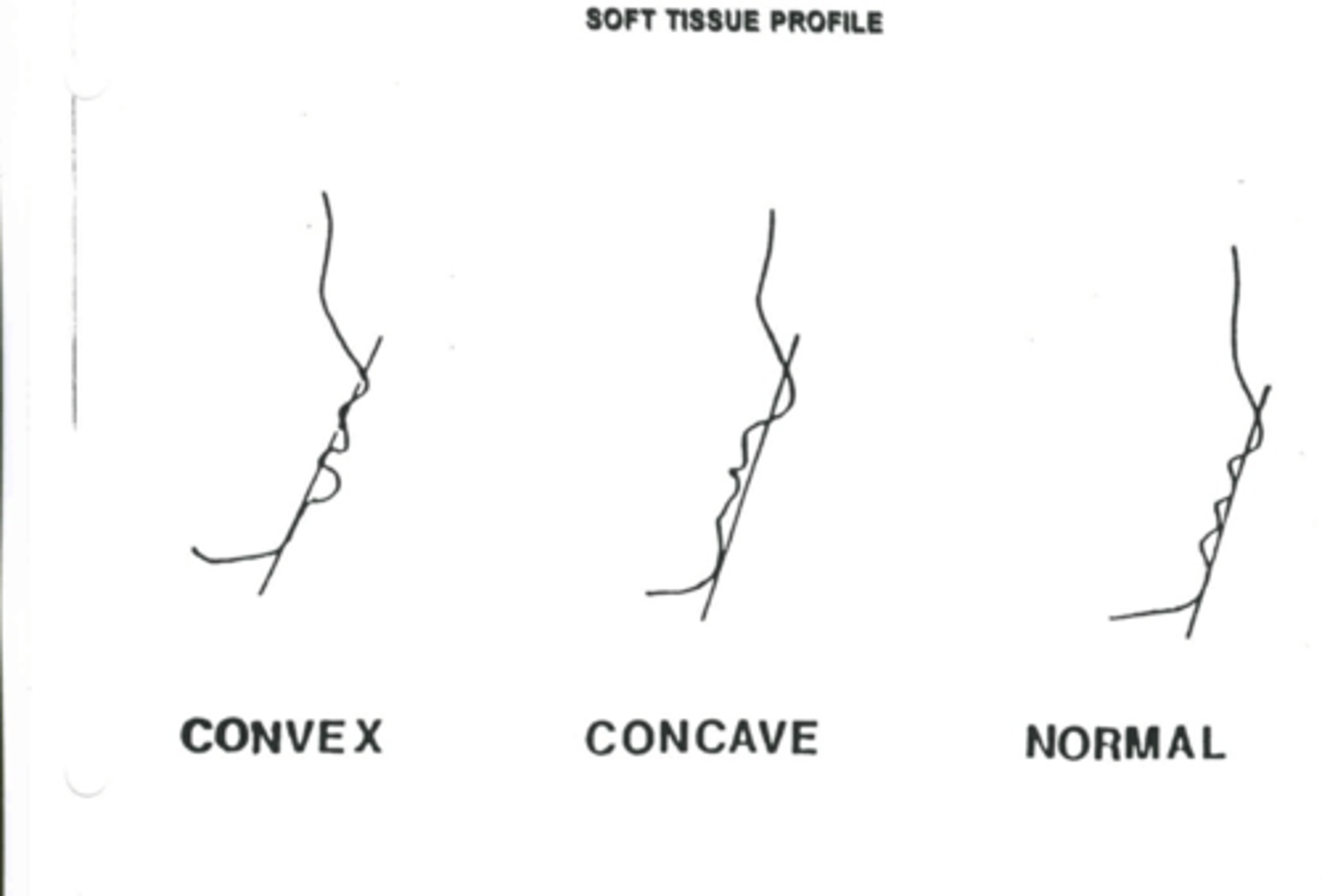
concave soft tissue profile is
upper & lower lips are behind a line connecting a point halfway along the lower border of the nose and the most forward point on the chin
face is divided into
3 horizontal sections
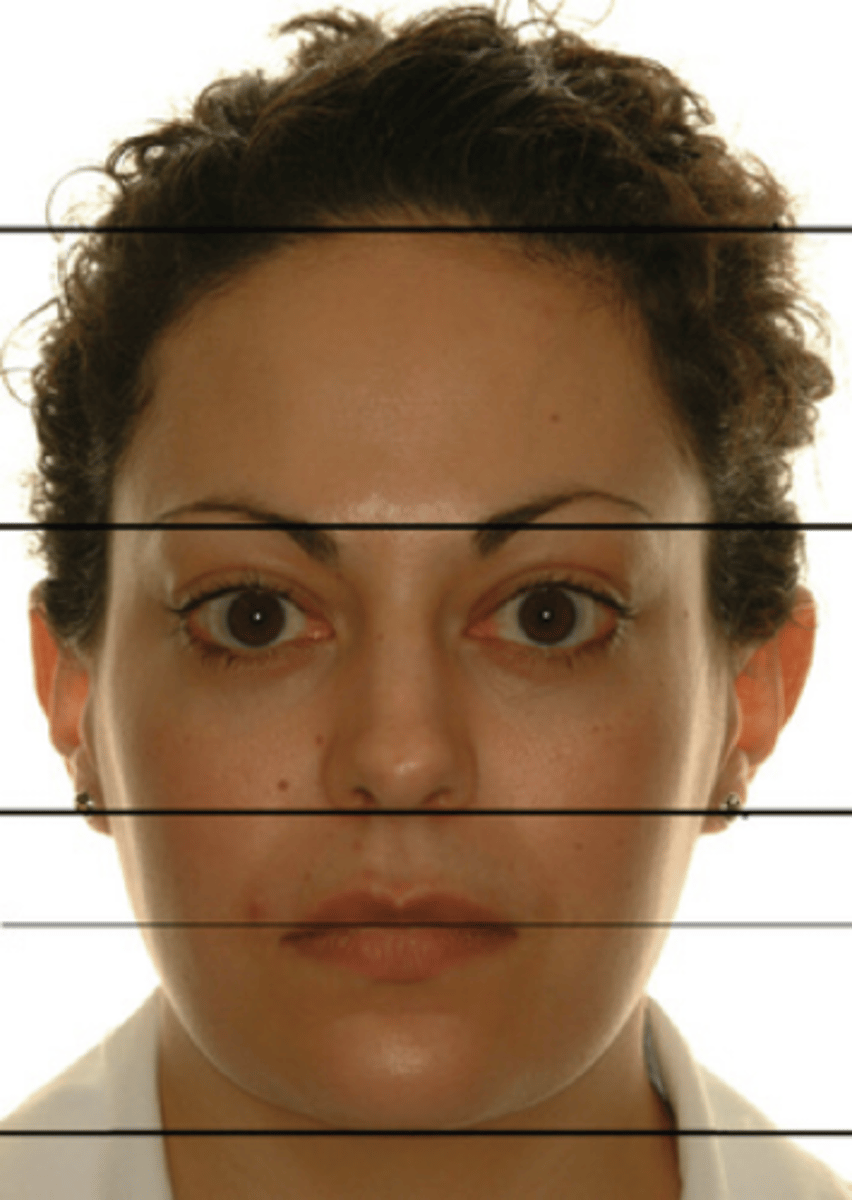
upper face extends from
hairline to base of forehead (trichion) between the eyebrows (glabellar)
midface extends from
base of forehead to base of nose (subnasale)
lower face extends from
base of nose to the bottom of chin (menton)
lower face can be sub divided into
thirds
upper lip is
upper 1/3 rd
lower lip is
lower 2/3rd
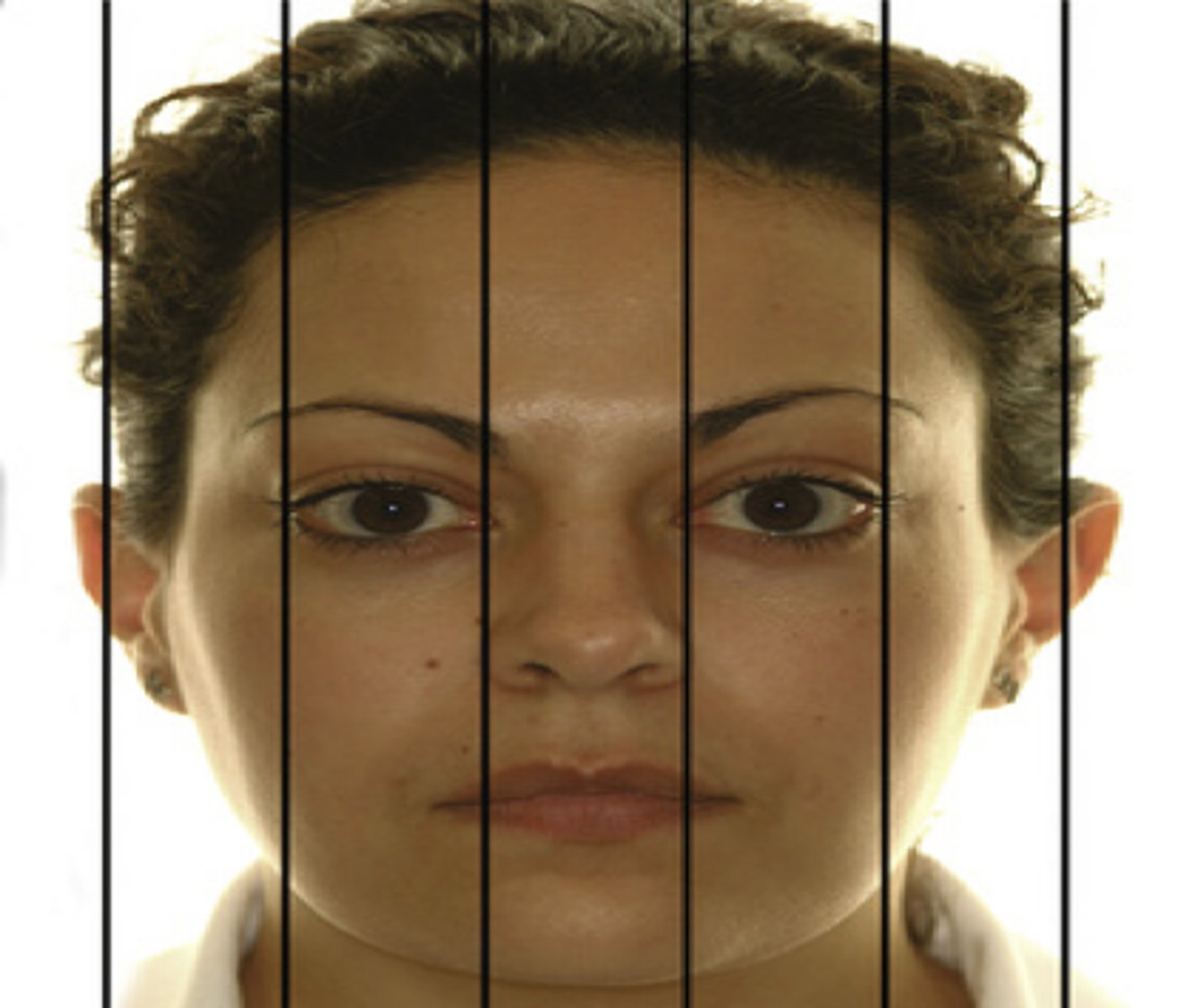
transverse face divided into
5 vertical sections

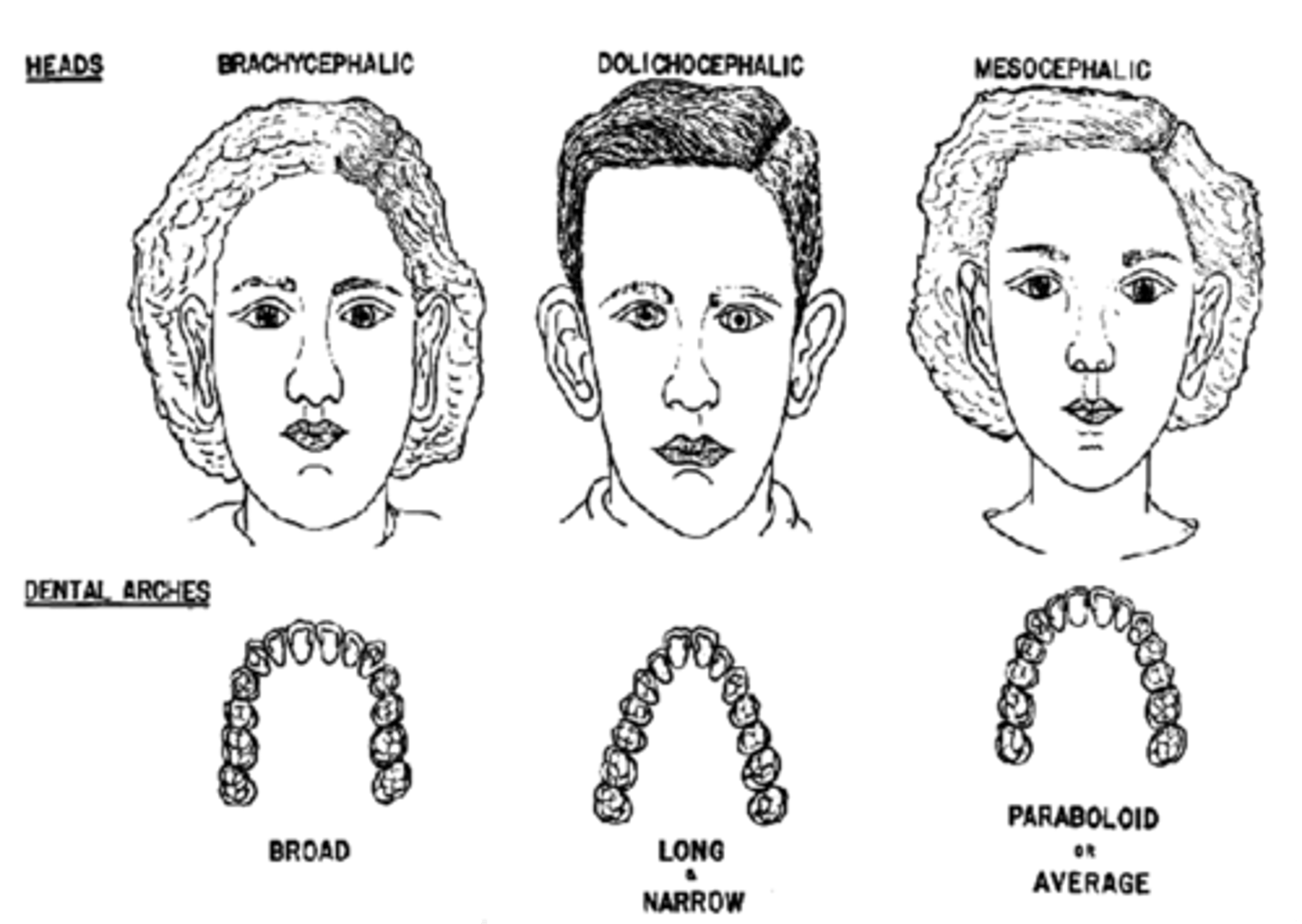
what are the 3 facial types
brachycephalic
dolichocephalic
mesocephalic
brachycephalic is
short wide head
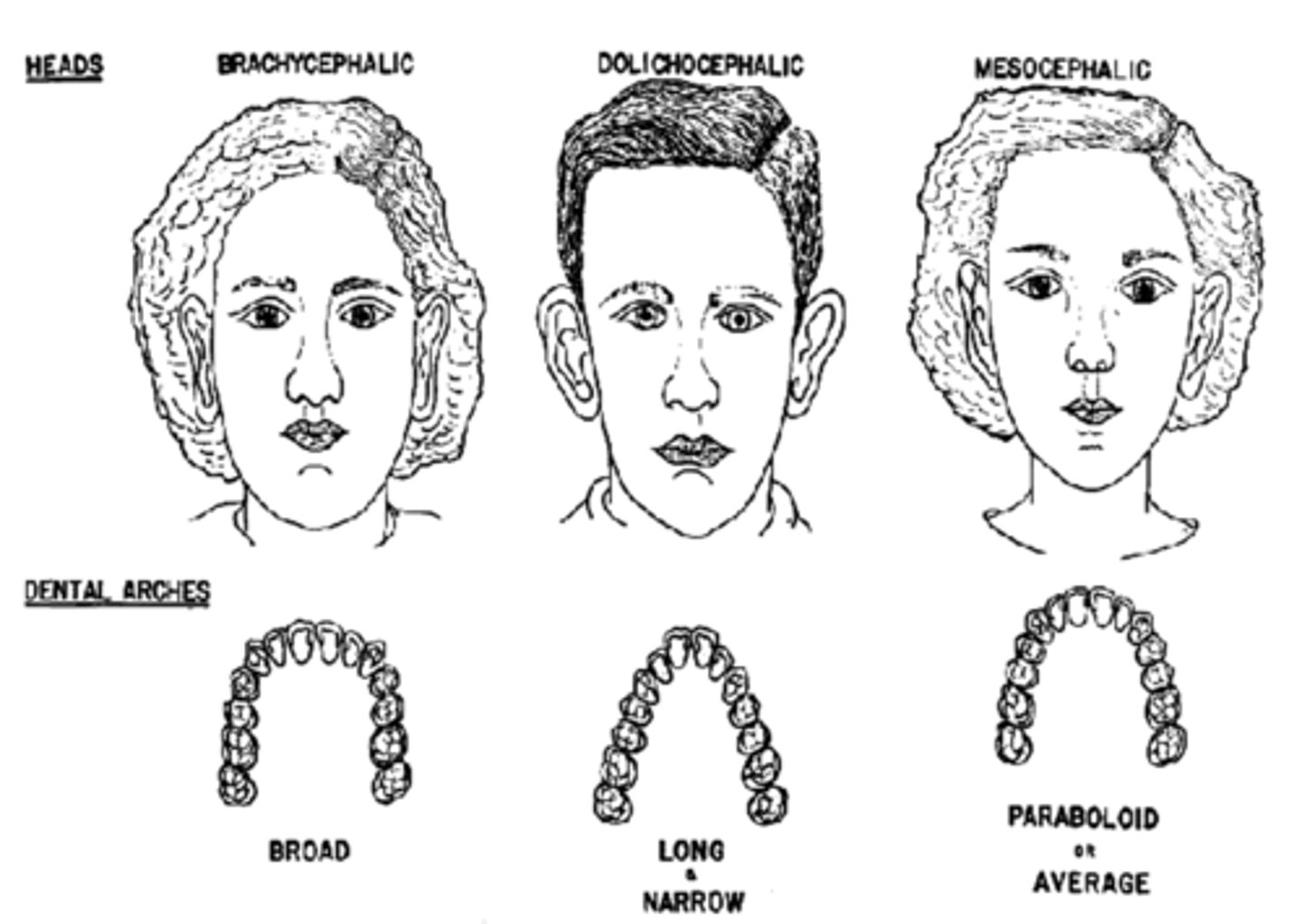
dolichocephalic is
long narrow head
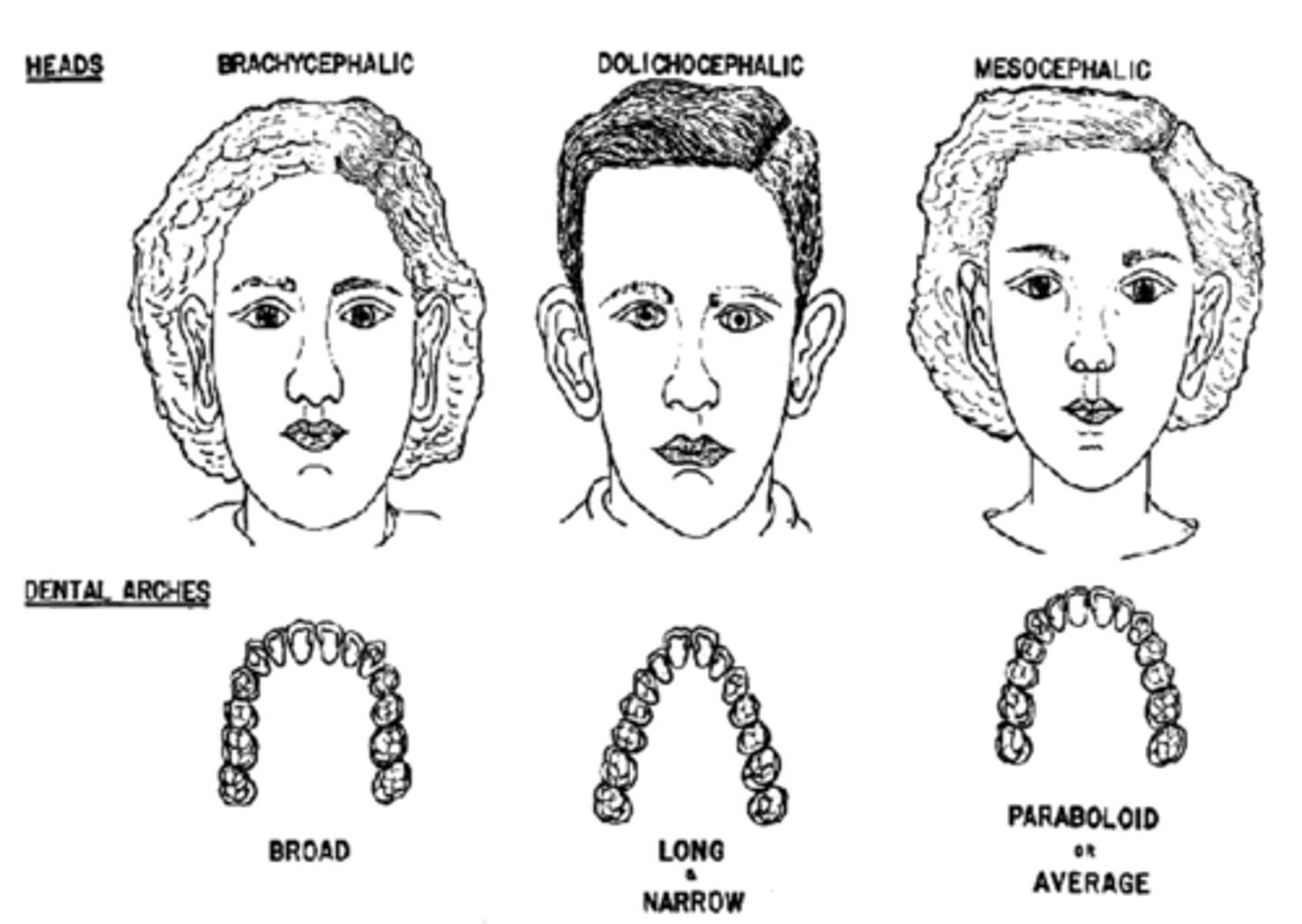
mesocephalic is
average
what are the 3 profile types
retrognathic
prognathic
mesognathic
retrognathic is
prominent maxilla and a mandible posterior to its normal relationship
chin is back
convex
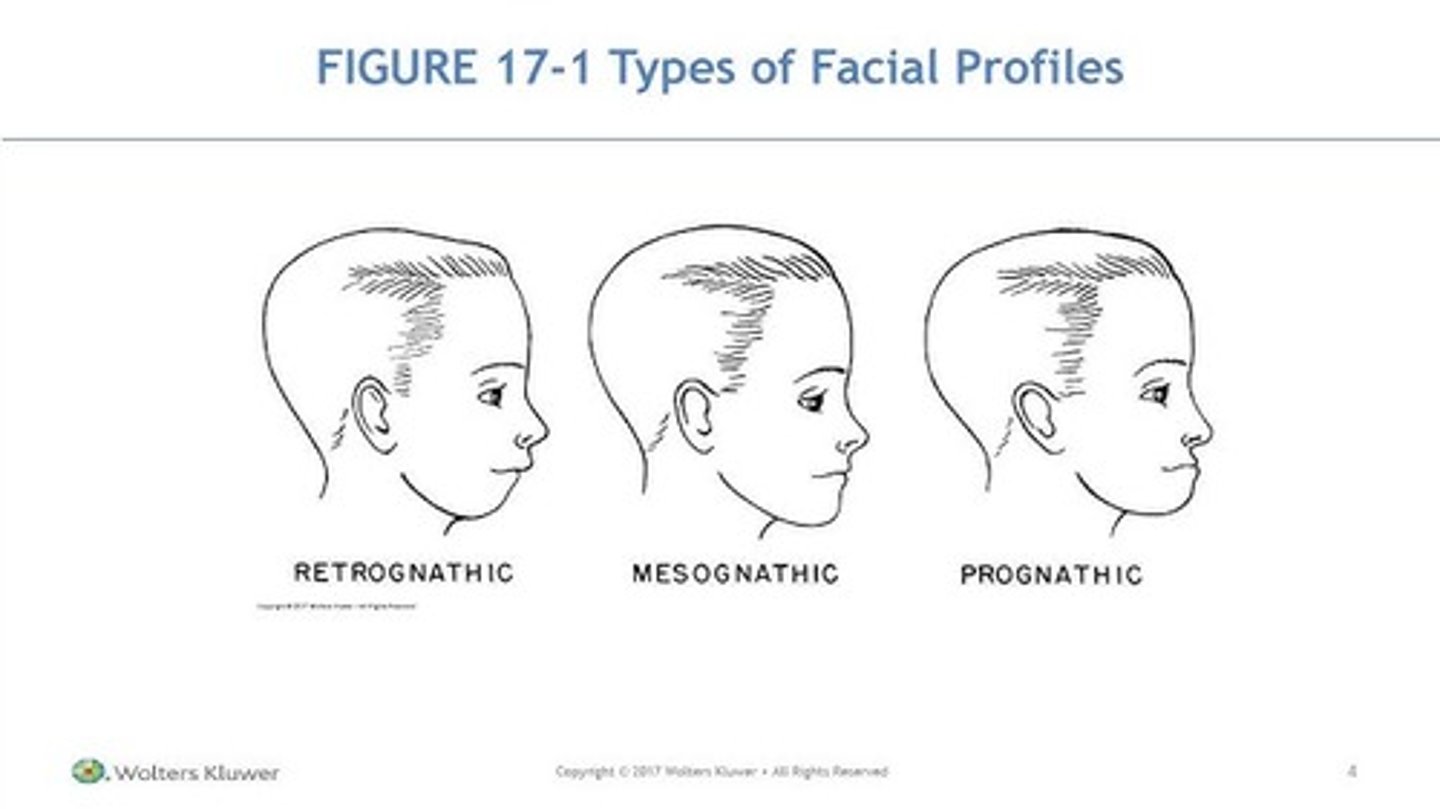
retrognathic leads to what occlusion
class II malocclusion
both divisions
prognathic is
prominent, protruded mandible and normal max
concave
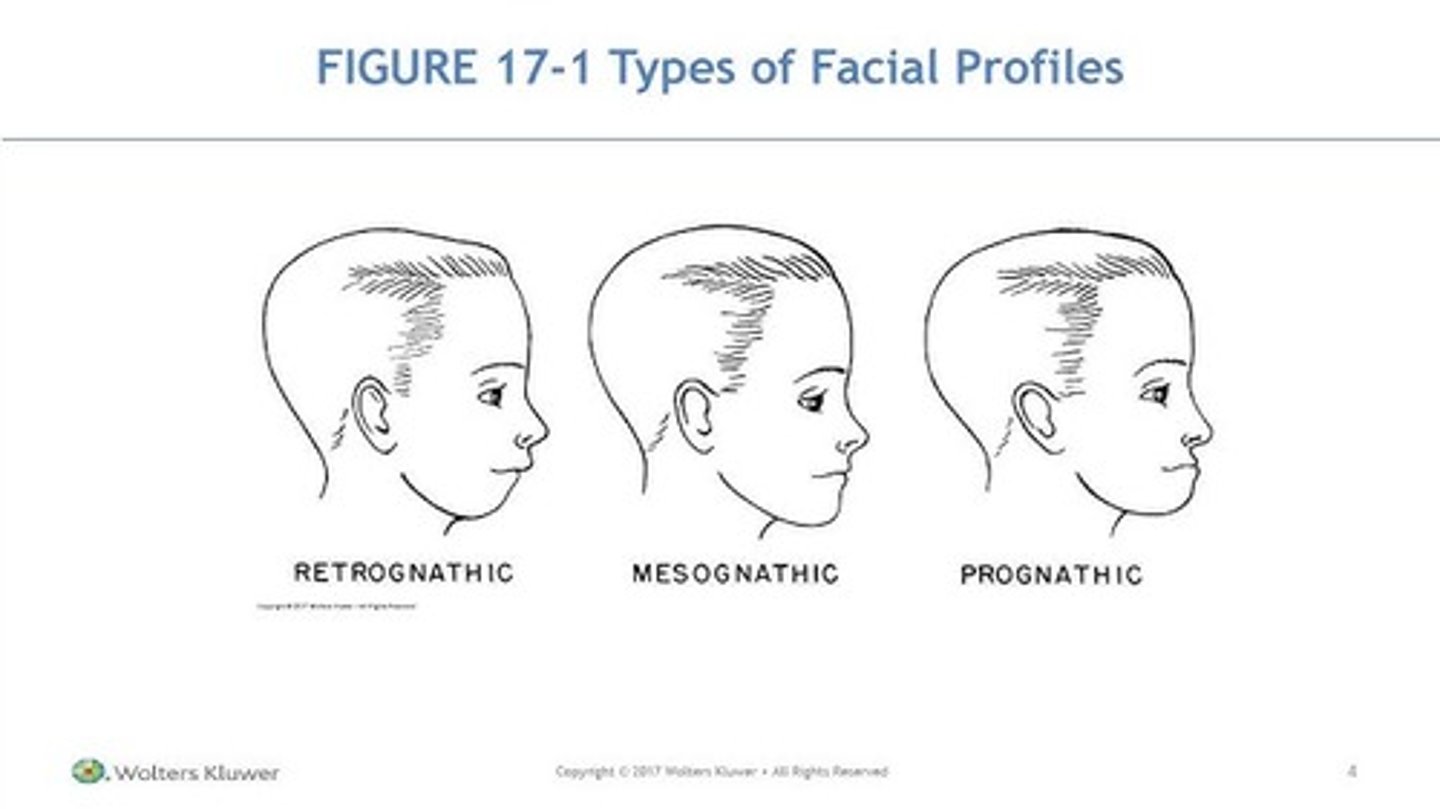
prognathic leads to what occlusion
class III
mesognathic
protruded jaws that gives a flat profile
normal

mesognathic leads to what occlusion
class I
class I malocclusion
nasolabial angle is
formed between upper lip and base of nose
nasolabial angle
90-110
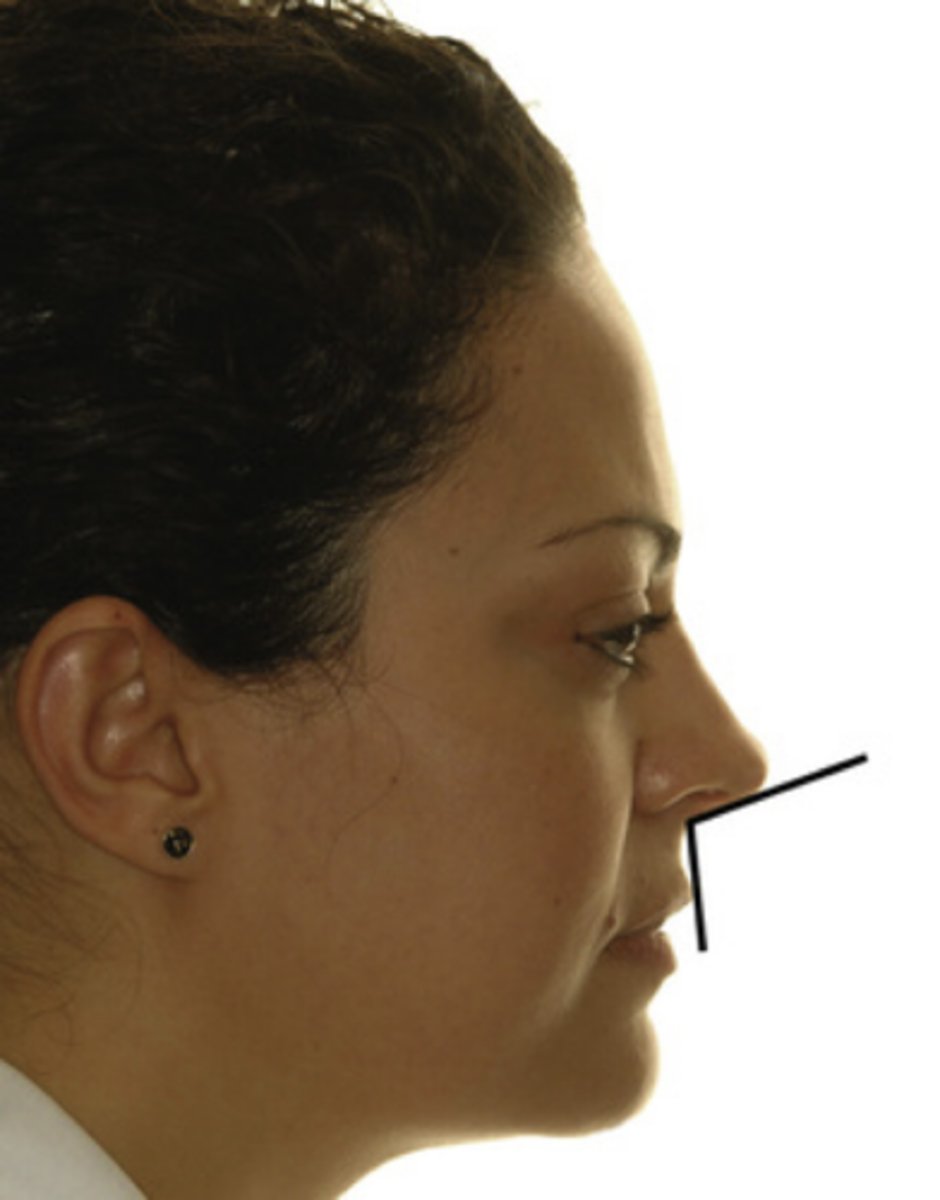
high nasolabial angle implies
retrusive upper lip
low nasolabial angle implies
lip protrusion
lip relationships types
competent
potientally competent
incompetent lips
competent lips
together at rest
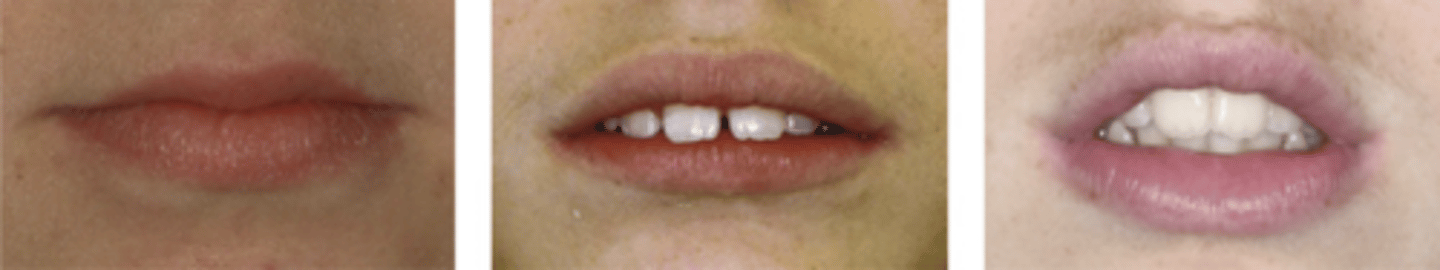
potentially competent lips
apart at rest
due to physical obstruction

incompetent lips
apart at rest
require excessive muscular activity to obtain lip seal
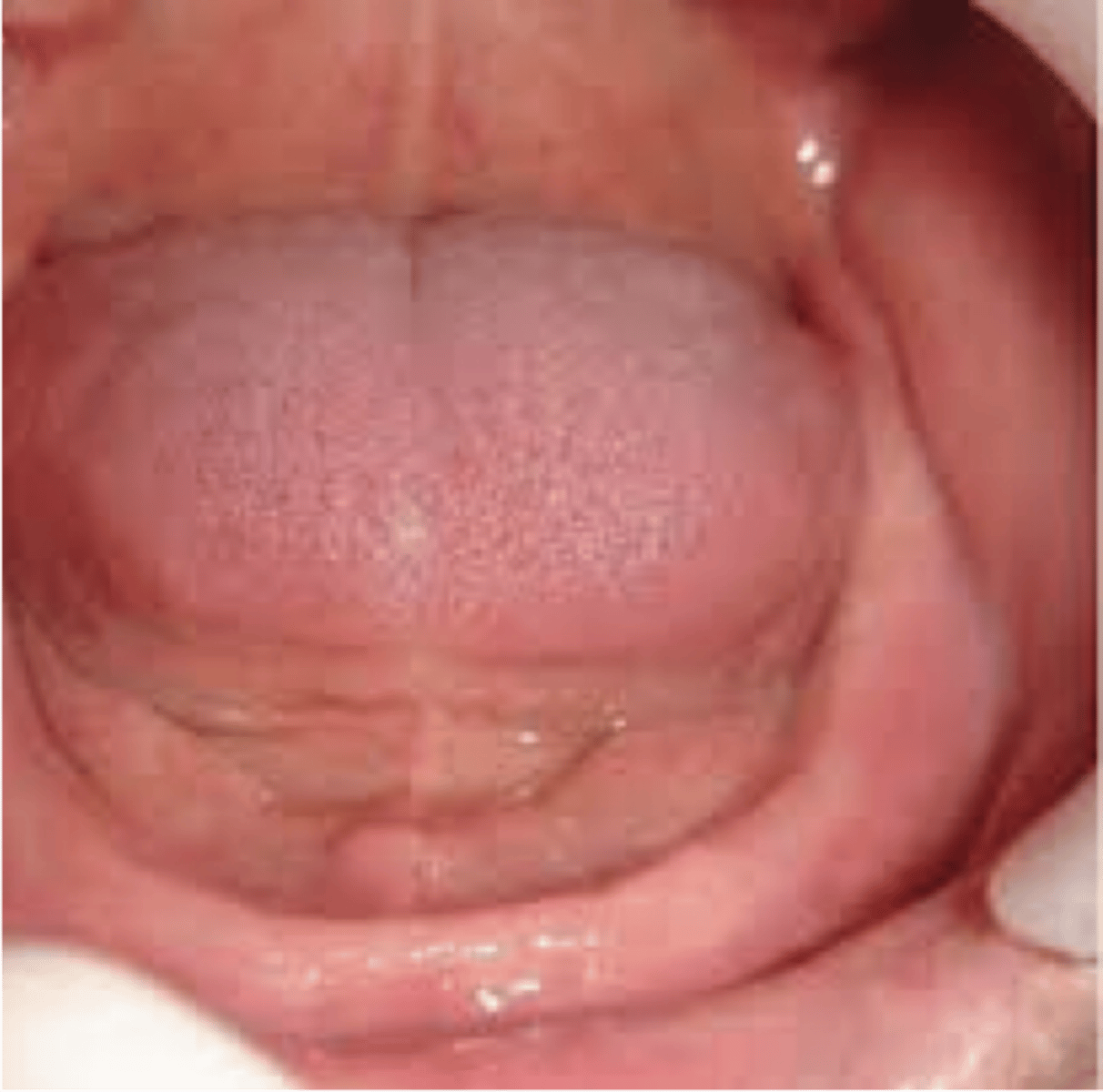
normal tongue position
at rest dorsum touches the palate and tip is lingual to lower incisors
protracted tongue position
tip of tongue rests above lower incisors
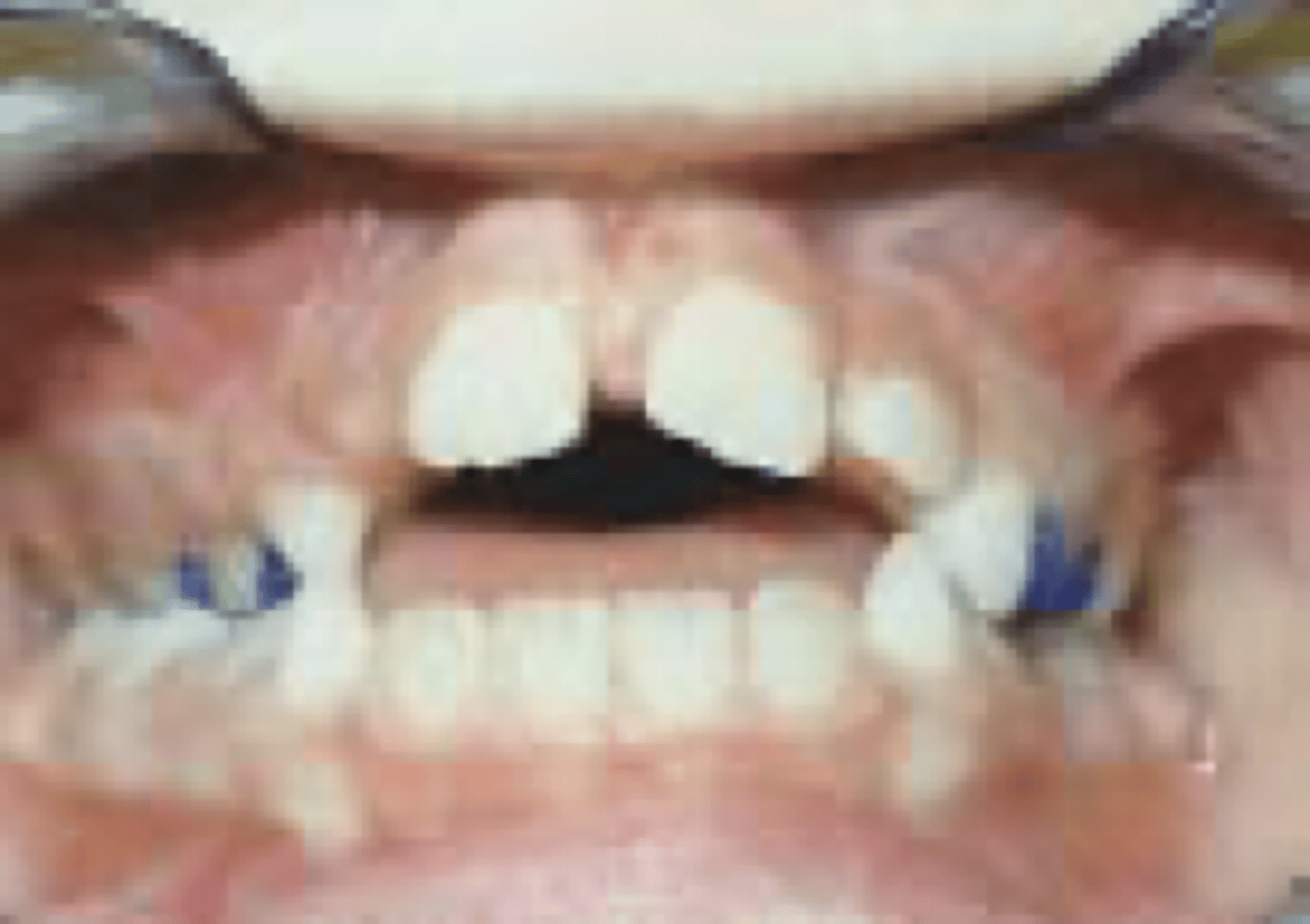
protracted tongue position results in
open bite
protracted tongue caused by
pharyngitis
tonsitilits
retracted tongue position
tip of tongue doesn't touch incisors at all
retracted posteriorly
seen in less than 10%
frequent in edentulous adults
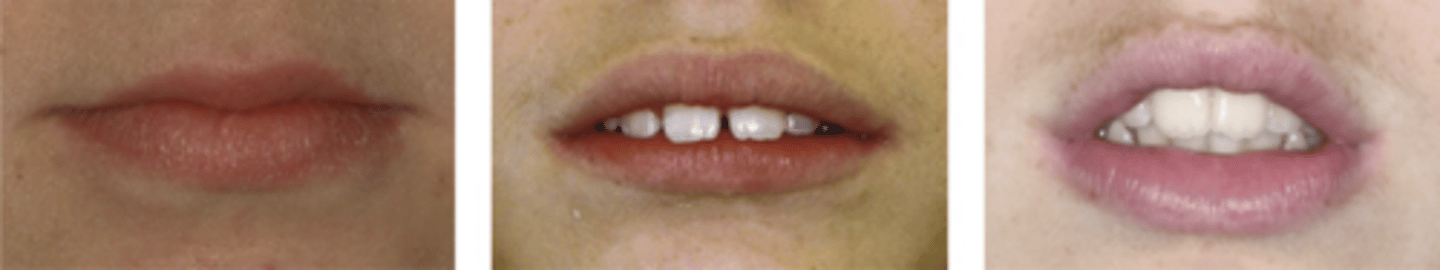
what % of max incisors should show while smiling
75-100%
3 levels of orthodontic treatment are
simple preventive
interceptive
corrective
simple preventive is
easiest type
usually in primary / mixed
involves removable / fixed appliances that will stop a habit
interceptive is
mixed dentition
changes the growth pattern
involves bionators expanders
corrective is
most involved treatment
permanent dentitions (14 or older)
involves full brackets
role of DH in orthodontics
collaboration
recognizing facial profiles / hereditary factors
understanding financial situations
observing cross bites + occlusions
noticing personalities