MCM-SV-Eicosanoids and Lipid Mediators-1 -1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
How many carbon compounds are eicosanoids? What is it derived from? Where do they act out their effects? What are the four classes? How are they different then hormones? What are their secondary messengers?
20, arachidoinic acid; on same cell or close by; protraglandins, leukotreins, thromboxanes, lipoxins;
not transported in blood; cAMP or Ca
Describe the chemical strucutre of Arachidonic Acid. How is AA freed from the cell membrane? How is AA synthesized?
20 carbon omega 6 poly unsaturated acid (PUFA), phospholipase A 2 (PLA2), synthesized from linoleic acid
What is the difference between linolenic Acid and linoleic acid?
linolenic = omega 3; linoleic = omega 6
what is the difference between Omega 6 and omega 3 fatty acids? What is their correlation with mortality from CVD?
omega 3 FA is less inflamatory then Omega 6. Because of this, the recommended ration of omega 6/ omega 3 is 1:1 to 4:1; LOWER RATIONS = LOWER MORTALITY FROM CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
what can deficiency of omega 3 cause? Why?
decrease in learning and memory, increased aggression and depression, alters auditory/olfactory senses to stimuli
why? several theories
omega 3 contribute to fluidity of cell membrane which affects protein membranes
omega 3 is a precurosr to resolvin which inhibits against oxidative-stress induced apoptosis and proinflammatory cells
omega 3 is crucial for neruon development and helps protect against apoptosis
Describe the pathway in which arachidonic acid is generated
stress factors (cytokines or atp from dead cells) activates GCPR
—> phospholipase C cleapves IP3—> DAG and Ca created
DAG with help of other lipases (diacylglycerol and monoacylclycerol lipase) creates AA
CA activates PKC—>MAPK—>PLA2—>phosphoatidylcholine—>AA
what three things stimulates PLA2? What inhibits PLA2? What can dysregulation of PLA2 cause?
stimluates: interleuken 1, angiotensen 2, thrombins
Inhibites: glucocorticoid (dexamethasone)
Dysregulation: alzheimers disease, multiple myeosis, epilepsy, ischemia
how is eicosanoids created? what is the difference between cox 1 and cox 2?
Created in one of two pathways
AA—>COX1,2—>PGH2, with help of PG synthases creates—>prostaglandins, thromboxanes , prostacyclins
AA —> LOX (lox 5,12,15); AKA lipoxygenases —> lipoxins (LX), leukotrienes (LT)
Cox-1 is constitutive, Cox-2 is inducible
Give examples in which PGE2 can have different effects depending on which receptor it binds on
PGE2 binds to neurons which illicit pain caused by inflamation
PGE2 binds (autocrine) to macrophages cells which leads to down regulation of TNF and upregulation of IL10 = less inflamation response
what are the three different precursor for prostraglandis?
AA
eicosatrienoic acid
eicopentaenoic acid
describe the synthesis of prostacycline and thromboxanes from AA. How do cell types affect this?
AA —> COX1,2 —> PGG2, with help of perixomes —> PGH2
Then, in endolethial cells: Prostacyclins (PGI2)
in platelets; thromboxanes (TXA2)
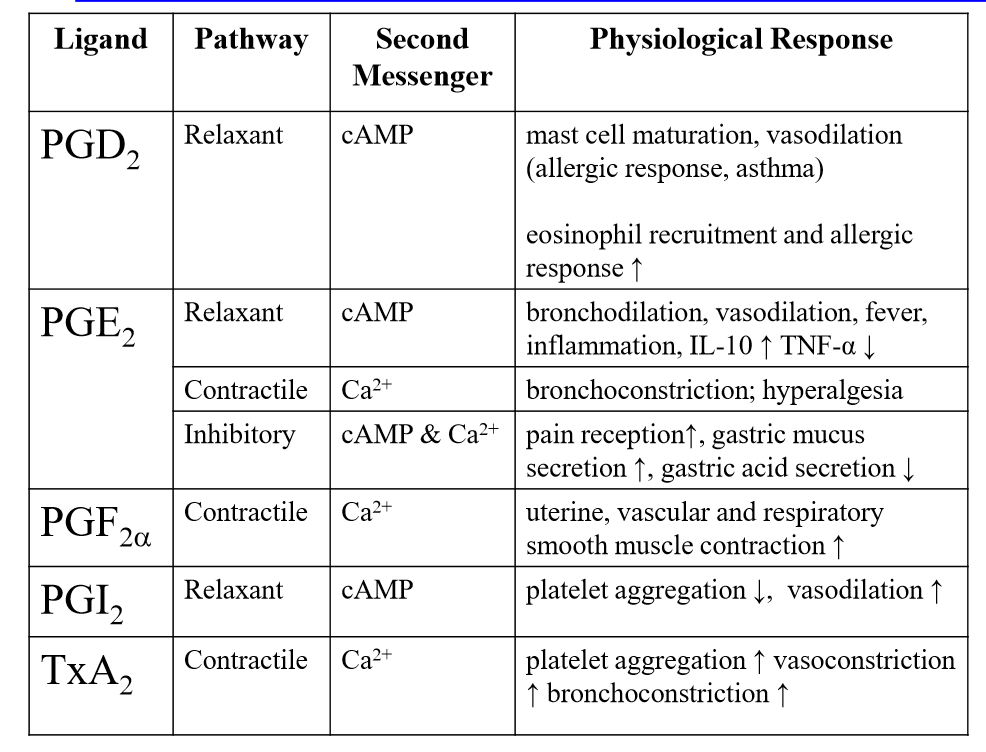
list the pathway, secondary messenger and physiological effects of:
PGD2
PGE2
PGF2a
PGI2
TxA2
Describe the effect of aspirin on Cox 1/ cox 2. Side effects?
irreversibly inhibits COX1; this reduces platelet aggregation (TXA2)
acetylates COX2; this causes production of 15R-HETE. 15R-HETE is converted into LIPOXINS by 5-lox in leukocytes; IF DHA or EPA comes into contact with COX2, converts into resolvins
Side effects: stomach iritation
what are resolvins made from? what does it do?
they are made from acetylated COX2 (via aspirin). They play an important role in the resolution stage in inflammation
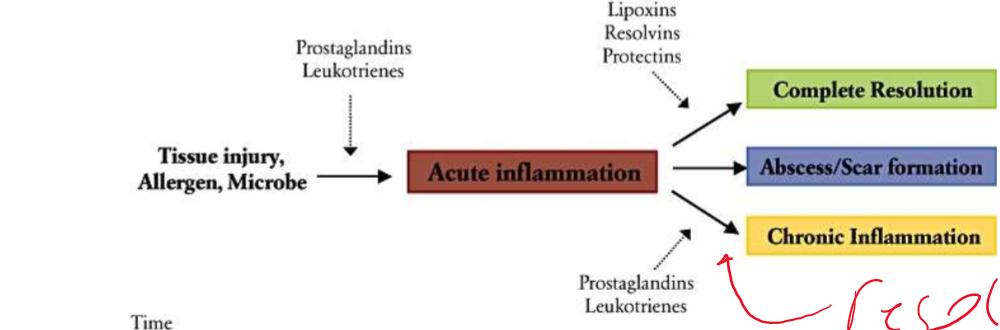
Fill out this chart
describe the effects of the four classic analgesics (pain reliever) on Cox1/2
Aspirin: cox1/2 irreversible inhibitor
tyenol: cox2 inhibitor in CNS
ibuproferin/naproxen = nonspecific cox1/2 inhibitor
compare and contrast ibuproferin/naproxen and celebrexx/vioxx
ibuproferin/naproxen = nonspecific Cox1/2 inhibitor, can lead to stomach ulcers due to lower pH
celebrexx/vioxx = specific cox 2 inhibitor, Targets inflammatory response; no side effects of advil bc does not touch Cox 1
list out the functions of these protaglandins/thronboxanes
PGI2, PGE2, PGD2,
PGF2a
TXA2

What is PGE2/PGF2 used for clinically? what is the name of the clinical drug that mimics this synthetically?
used to induce child birth or abortion; relaxing smooth muscles of passage ways. DINOPROSTONE
what is PGE1 used for clinically? what is the name of the clinical drug that mimics this synthetically?
Erectile dysfunction (aloprostadil), peptic ulcers, prevent closure of patent ductus arteriosus in newborns with particular cyanotic heart disease
what is PGI2 used for clinically? what is the name of the clinical drug that mimics this synthetically?
pulmonary hypertension (epoprostenol)
what is PGF2a used for clinically? what is the name of the clinical drug that mimics this synthetically?
induce labor through uterine muscle contraction (dinoprost) and in treatment of glaucoma (latanoprost)