Behavioral Neuroscience: Final Exam
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Clive Wearing
- both retrograde and anterograde amnesia
- amnesia caused by hippocampus/temporal lobe lobe encephalitis
- only conscious memory he had is his wife
- retained piano skills
Medial Temporal Lobe Amnesia
- primarily anterograde
- can't make new memories
- effects episodic memories more than semantic memories
Medial Temporal Lobectomy
- Removal of temporal lobes
- happened to H.M. to cure his epilepsy
- H.M.'s case taught us the STM/LTM distinction
Implicit Memory
- Memories we don't think about
- motor/procedural
Explicit Memory
- declarative
- conscious
- semantic v. episodic
Coma
pathological state of unconsciousness
Hebb's Theory
If something occurs that disrupts the consoldiation of memory, you likely won't remember what happened because the LTM was not formed
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
- Rat studies -- supports Hebb's theory
- Human studies -- doesn't support Hebb's theory
Hippocampus
Involved in memory formation and retrieval
Inferotemporal Cortex
Area of brain that lights up during learning also lights up during recall
Cerebellum
learning of associated motor tasks
Striatum
- basal ganglia: caudate, putamen, substantia nigra
- involved in habit formation and addiction
What is the penumbra in the context of neuronal death?
The vicinity of the injury where cells may die within a few days due to the effects of dying cells.
What causes neuronal death in the penumbra?
Excessive exposure to potassium and calcium, leading to overstimulation and release of glutamate.
What is edema?
Accumulation of fluid that creates pressure against cells, stimulating them to release glutamate.
What are three ways to prevent further cell loss after neuronal injury?
Block glutamate transmission, increase GABA transmission, and administer calcium channel blockers.
What characterizes cancer cells?
They grow out of control and invade other tissues due to DNA mutations.
What is a malignant tumor?
A cancerous tumor that can metastasize and spread to other tissues.
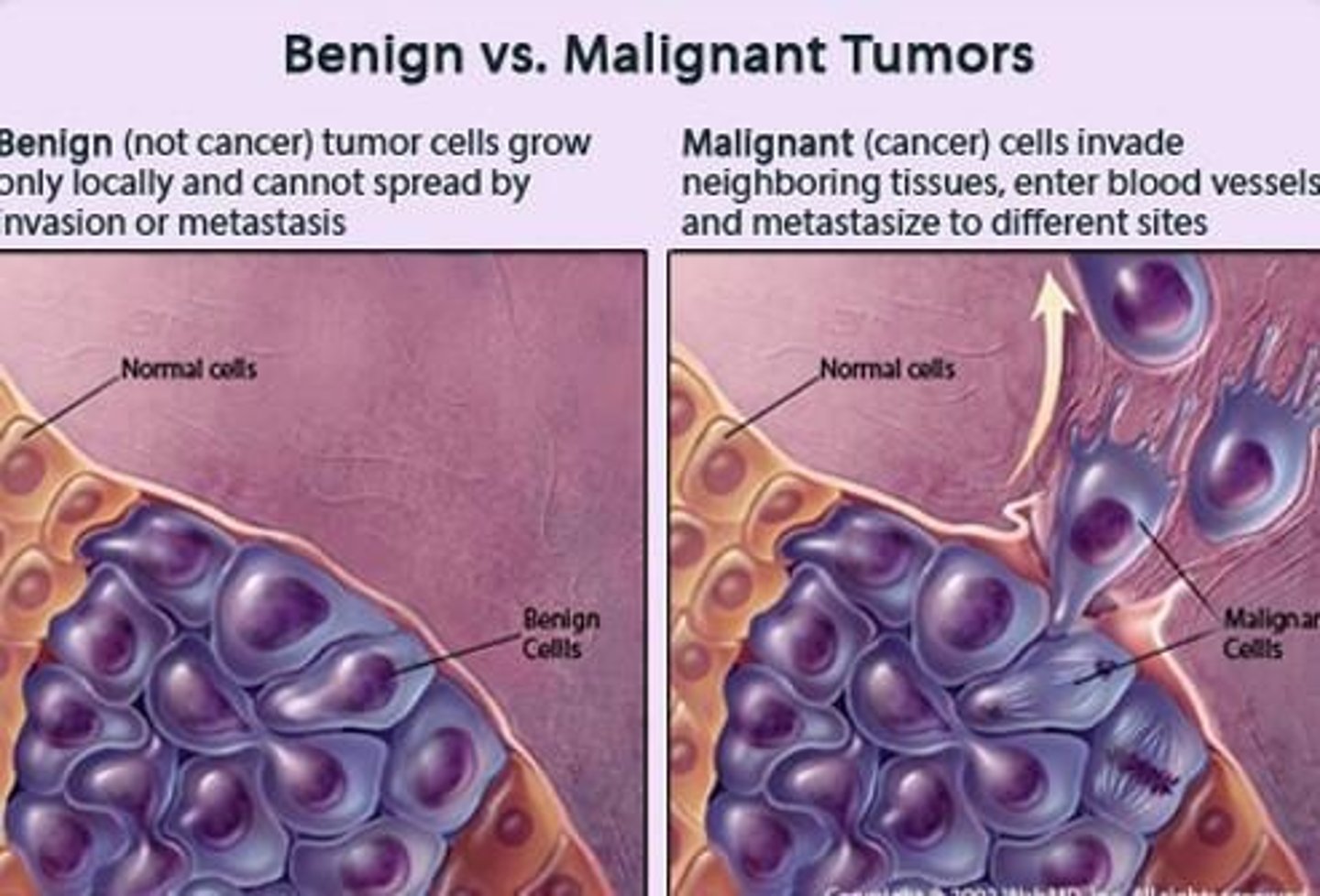
What is a benign tumor?
A noncancerous tumor with a distinct border that cannot metastasize.
What is metastasis?
The process by which cancer cells break off from a tumor, travel through the vascular system, and grow elsewhere in the body.
What is a glioma?
A cancerous brain tumor of glial cells.
What is a meningioma?
A benign tumor composed of the cells of the meninges.
What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
A stroke caused by the rupture of a cerebral blood vessel.
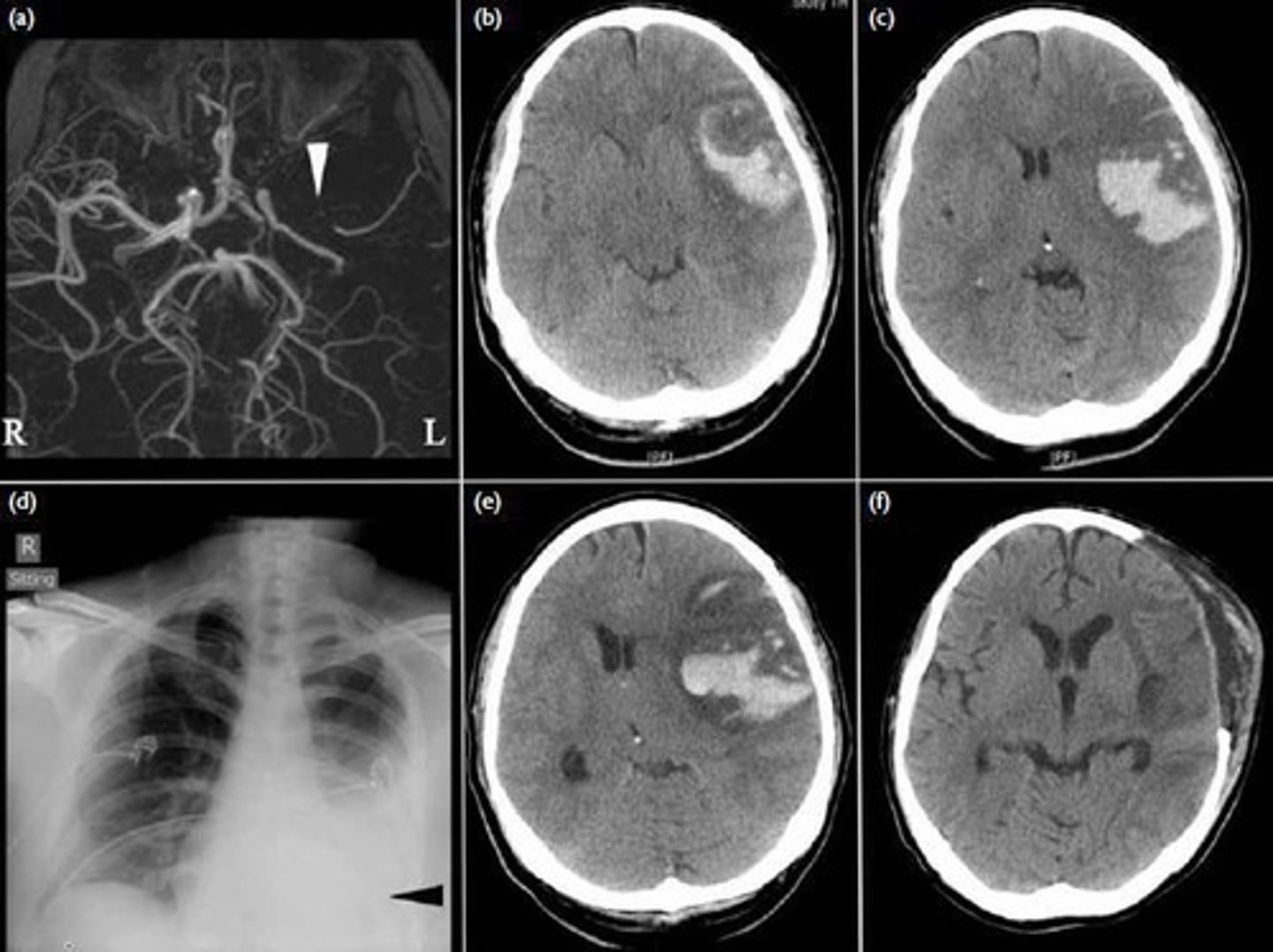
What is an obstructive stroke?
A stroke caused by the occlusion or blockage of a blood vessel.
What is a generalized seizure?
A seizure that involves most of the brain.
What is a Grand Mal seizure?
A tonic-clonic seizure resulting in convulsions and muscle contractions.
What is a Petite Mal seizure?
A type of seizure characterized by periods of inattention, often seen in children.
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)?
A birth defect caused by alcohol ingestion during pregnancy, leading to developmental issues.
What is Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
A hereditary disorder caused by the absence of an enzyme that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine, leading to brain damage.
What is Tay Sachs disease?
A fatal, heritable metabolic storage disorder causing brain cell swelling and cognitive decline.
What is Down syndrome?
A genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra twenty-first chromosome, leading to cognitive impairment and physical abnormalities.
What characterizes Parkinson's Disease?
Degeneration of dopamine cells in the basal ganglia, leading to muscle rigidity, slowness, and tremors.
What is Huntington's Disease?
An inherited disorder causing degeneration of the basal ganglia, leading to uncontrollable movements and dementia.
What is dementia?
A loss of cognitive abilities such as memory, perception, and judgment.
What is Locked-in Syndrome?
A neurological disorder with complete paralysis of voluntary muscles except for eye movement, while cognitive function remains intact.
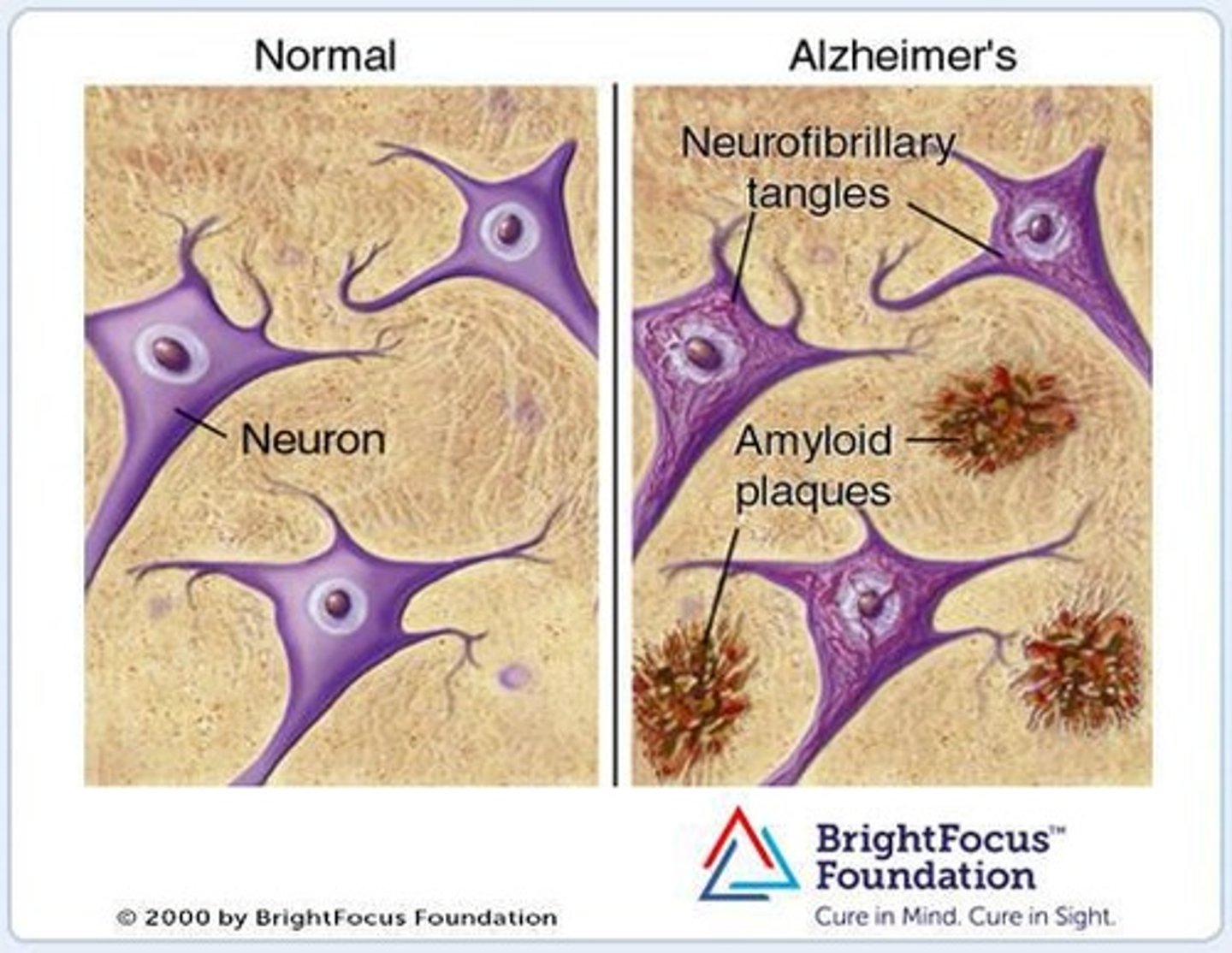
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease?
Impaired memory, confusion, changes in behavior, and difficulty with familiar tasks.
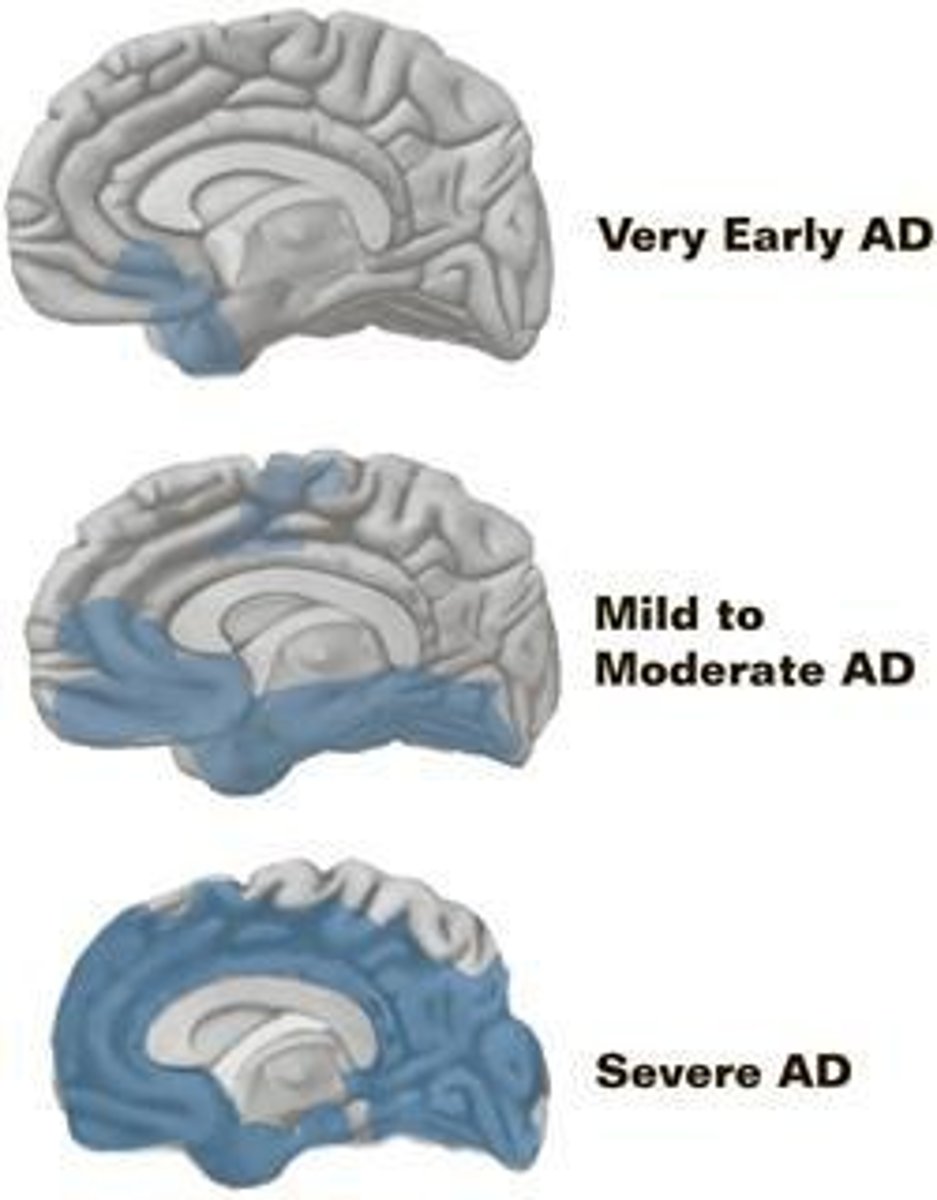
What is the difference between early-onset and late-onset Alzheimer's Disease?
Early-onset starts in the 40s and 50s, while late-onset is the most common form prevalent in 90% of cases.
What is ß-amyloid?
A protein found in excessive amounts in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, associated with plaque formation.
What is encephalitis?
An inflammation of the brain caused by bacteria, viruses, or toxic chemicals.
What is meningitis?
An inflammation of the meninges, which can be caused by viruses or bacteria.
What is transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE)?
A contagious brain disease that causes a sponge-like appearance in the brain due to misfolded prion proteins.
Lateralization
Specialization of the hemispheres
Aphasia
loss of language
Broca's Aphasia
- damage in the left Broca's area
- good comprehension
- pronunciation difficulty
- telegraphic speech
- naming difficulties
- still good with emotional words, especially swear words (emotional lang is right; damage is left)
- all deficits are true for sign language as well
telegraphic speech
use nouns and verbs only
Apraxia
difficulty in voluntary movement
Left Hemisphere
- used to be believed it was dominant
- damage is bilateral (but damage to the right is not bilateral)
Tests of Cerebral Lateralization
1. Sodium Amytal Tests
2. Dichotic Listening Tasks
3. Functional Brain Imaging
Sodium Amytal Test
- barbituate (NS depressant)
- makes you chatty and highly suggestible
- can be used to make one hemisphere fall asleep so you can be studied doing tasks with only one hemisphere available
Dichotic Listening Tasks
shows a right-ear advantage for language
Handedness
- Righties are left-lateralized for language
- 60% of lefties are left-lateralized, 20% are right-lateralized, and 20% aren't lateralized at all
- both righties and lefties have avg IQ of 100, but distribution is different
- lefties have twice the percentage at the high and low extremes
- left handedness probably adds genetic variability
Sex Differences in Lateralization
- women are less lateralized for language than men (tend to use both hemispheres more)
- not sure if this is due to neuroplastic reactions to socialization
human commissurotomy
surgical term for severing the corpus collosum
split brain
- occurs when the corpus collosum is severed
- usually done to cure epilepsy (generalized)
cross-cueing
when split-brain patients are provided an image to the right hemisphere, they have trouble verbally reporting what it is. When the right-hemisphere knows the answer, it can signal (shaking head) that the left-brain's guess was wrong
Myers and Sperry
- severed corpus collosum and optic chiasm in kittens and then covered one eye
- created scotomas in 1/2 of visual field
- when left eye was covered the right visual field went to the left hemisphere
- kittens learn to associate visual cue with a treat event when they didn't have any conscious awareness of the stimulus due to the scotoma
- when done on the other eye, the kittens had to relearn the task because the hemispheres could not communicate
hemispherectomy
- removal of a hemisphere of the brain, often to treat seizures
- cavity fills with cerebrospinal fluid
Lateralization of Function
Left-dominated:
- ipsilateral movement
- semantic memory
Right-dominated:
- spatial ability
- interpretation of emotion
- musical ability
- these aspects of language: emotion, intonation, interpretation of vowels
- emotional side of memory
Planum Temporale
- Wernicke's area
- language interpretation
- for most people, it's bigger on the left
- for 1/3 of people, it's bigger on the right
- located near auditory association areas
Wernicke's Aphasia
- fluent speech
- gramatically correct
- neologisms
- poor lang comprehension affections lang production because you cannot understand what you're saying
- high suicide rate
Neologisms
- meaningless words
- word salad
- Wernicke's aphasia
Heschl's Gyrus
- primary auditory cortex
- bigger on the right
Frontal Operculum
- Broca's area
- language production
- right: more surface area
- left: more volume, deeper
Theories of Asymmetry in Brain
1. Analytic-Synthetic Theory
2. Motor Theory
3. Linguistic Theory
Analytic-Synthetic Theory
- left specializes in analytics
- right specializes in synthesizing info
- this theory is untestable and not falsifiable
Motor Theory
- left specializes more than right for complex fine motor skills
- supported by apraxia
Linguistic Theory
- left evolved for linguistic specialization
- tools used by right hands = controlled by left hemisphere
- language is a symbolic tool
- however, lateralization and tool use are not exclusive to humans; developed long before humans
- there are analogues of Broca's area in animals, which probably led to animal vocalizations
Wernicke-Geshwind Model
- Broca's aphasia, Wernicke's aphasia, conduction aphasia
- arcuate fascicuous
- hugely influential
- outdate
- oversimplified
- no serial processing in the brain like this model predicts
Arcuate Fasciculus
- Subcortical fibers that connect broca's and wernicke's areas
Conduction aphasia
- damage to arcuate fasiculus
- fluent speech
- naming difficulties
- unable to repeat words
- subcortical damage, so it's less common
Monitoring Sleep
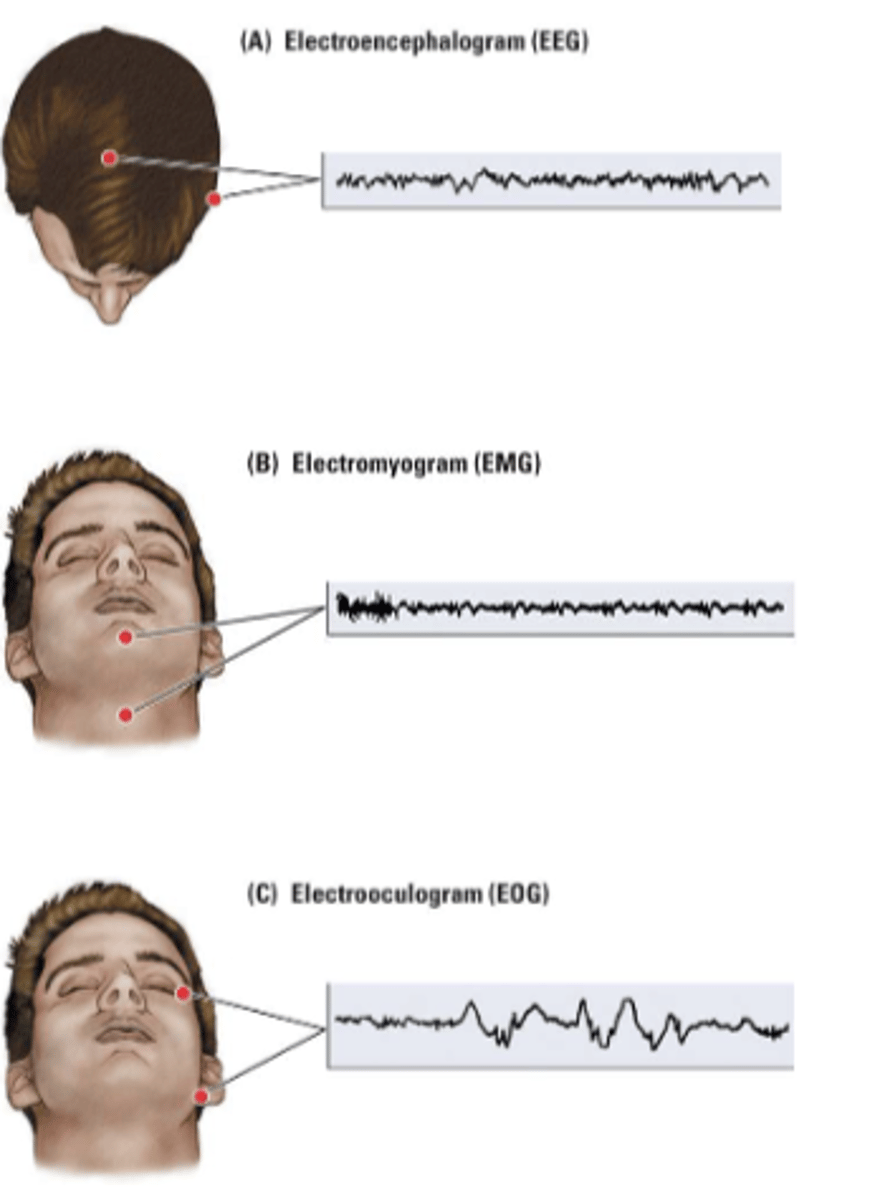
Brain wave, muscle tone, and eye movement can be monitored to determine stages of sleep cycles
Sleep Measures
-Electroencephalogram (EEG)
*Brain-wave activity
-Electromyogram (EMG)
*Muscle activity
-Electrooculogram (EOG)
*Eye movement
EEG Stages of A Sleep cycle
- A sleep cycle contains 4 stages
-EEG amplitude and frequency changes across the four stages
* Stage 1-4:
- non-REM (NREM) sleep
* Stage 3-4:
- Slow-wave (delta wave) sleep
- Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep occurs between sleep cycles
- In a sleep cycle, the sleep progresses to stage 4 sleep and the back to stages 3, 2, and REM
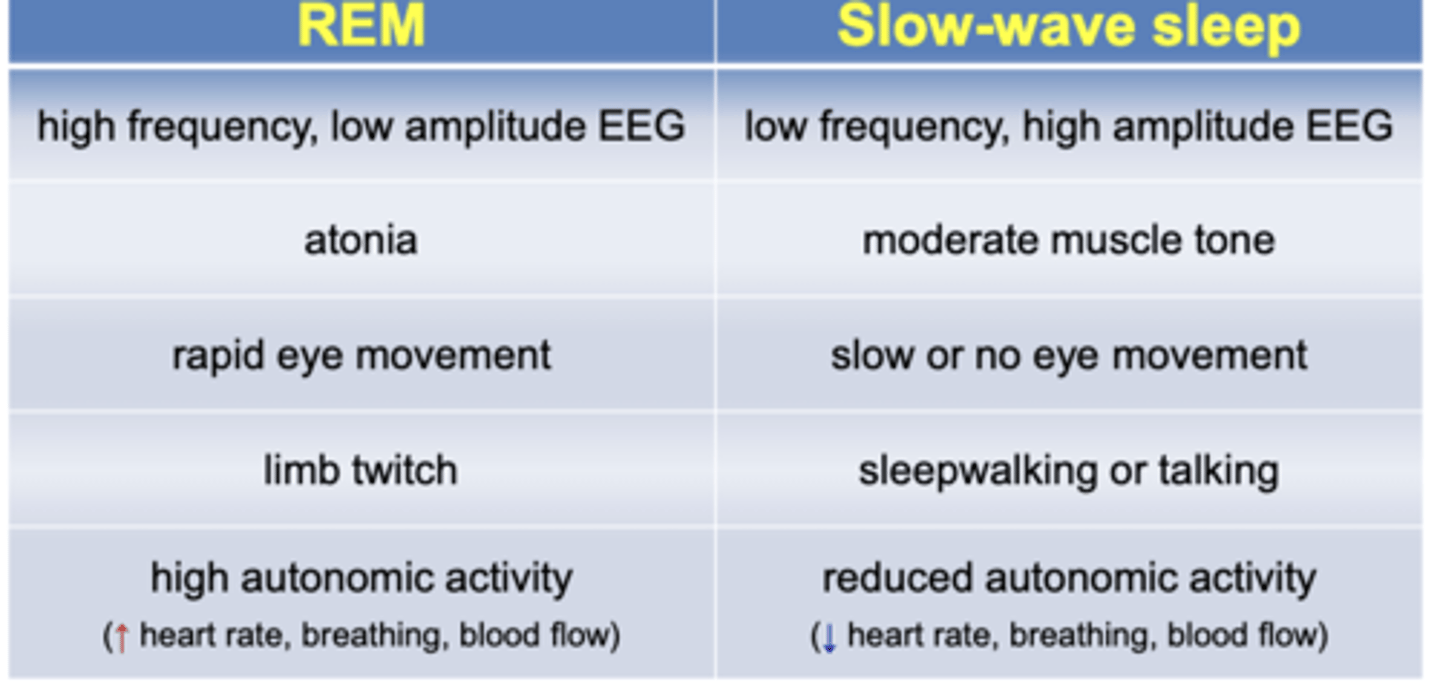
REM Sleep
-Characteristics of REM sleep
* Rapid eye movements
* Low amplitude, high frequency EEG
* Cerebral activity (EEG) increases to waking levels
* Atonia, loss of muscle tone
* Muscles of the extremities occasionally twitch
REM sleep pt 2
- Does dreaming only occur during REM sleep?
*NO. Dreaming occurs during non-REM sleep as wel. The types of dream during REM and non-REM differ
*Night terror during stage 3 is a sense of crushing feeling but not a vivid dream
REM vs. slow-wave sleep
Unilateral Sleep
Migratory birds and marine mammals such as dolphins and whale sleep one hemisphere at at a time
Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation impairs cognitive function and health
- Related to the development of cancer, obesity, type 2 diabetes etc.
Chronic sleep loss interferes with the activity of both neurons and glias
Sleep Deprivation- Microsleeps
- Brief sleep periods lasting up to a few seconds
- Occur during the day more frequently in sleep deprived subjects
Sleep Deprivation pt 2
- Percent of REM sleep decreases with aging
*may impact brain development
-After REMs deprivation
*increases tendency to go into REM
* REM rebound
Neural Mechanisms
-Reticular formation in the brain stem
*consists of multiple nuclei and nerve fiber tracts
*contains an arousal system and controls major events during REM sleep
Neural Mechanisms pt 2
- GABA neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic area (VLPOA) initiate sleep
*Anterior hypothalamic viral infection: disturbance during sleep
-Histaminergic, noradrenergic, and serotoninergic neurons are involved in wakefulness
*Posterior hypothalamus/midbrain viral infection: cannot stay awake, sleep too much
Sleep disorders
Insomnia: prolonged inability to sleep
- TOO little undisturbed sleep contributes to the perception of insomnia
Sleep apnea: breathing stops during sleep due to airway obstruction
*CPAP(continuous positive airway pressure) mask increases air flow and is used to improve sleep for people apnea
*periodic limb movement disorder/ restless legs syndrome
Insomnia treatments
1. Benzodiazepines (Valium & librium)
* Can develop drug tolerance
* sudden cessation after chronic use causes insomnia
* distort the patterns of sleep
* chronic use reduces life expectancy
1. Melatonin
* Slee- promoting effect, but there are individual differences
* Effective for melatonin-deficient insomniacs
* Can be used for blind people with sleep problems
Sleep Disorders pt 2
-Hypersomnia (Narcolepsy)
Sleep attack
uncontrollably falling asleep at inappropriate timing
- multiple sleep latency test measures the tendency to fall asleep under controlled condition during the day
cataplexy
sudden loss of muscle strength and collapse during awake phase of the awake-sleep cycle
Possible causes for hypersomnia (Narcolepsy)
1. loss of orexin neuron in the lateral hypothalamus
2. Genetic
3. infection
4. Autoimmune
REM sleep disorders
Cataplexy (a symptom of Narcolepsy)
* sudden collapse
fallen into REMs while remaining awake
sleep paralysis: inability to move while falling asleep or waking up
*Hypno(a)gogic hallucinations: dreamlike experience while awake)
Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: Advanced sleep phase syndrome
Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: Delayed sleep phase syndrome
Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: Non-24 hr sleep-wake syndrome
Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: irregular sleep-wake syndrome
Organizational Hormones
-influence anatomy, physiology, behavior at an early age
Activational Hormones
-influence sexual maturity
-pubertal changes
-The brain controls activational hormone release in adults via the hypothalamus and pituitary
Types of hormones
-Amino Acids
-Peptides and Proteins
-Steroid Hormones
Types of Glands: Exocrine
-release chemicals into ducts which carry them to their targets
ex: sweat glands, salivary glands
Types of Glands: Endocrine
-ductless
-release hormones directly into the circulatory system
-known as releasing hormones
-are located in the body as well as the brain
Amino Acid Hormones
-made of protein; not able to pass thru cell membrane
-bind to receptors
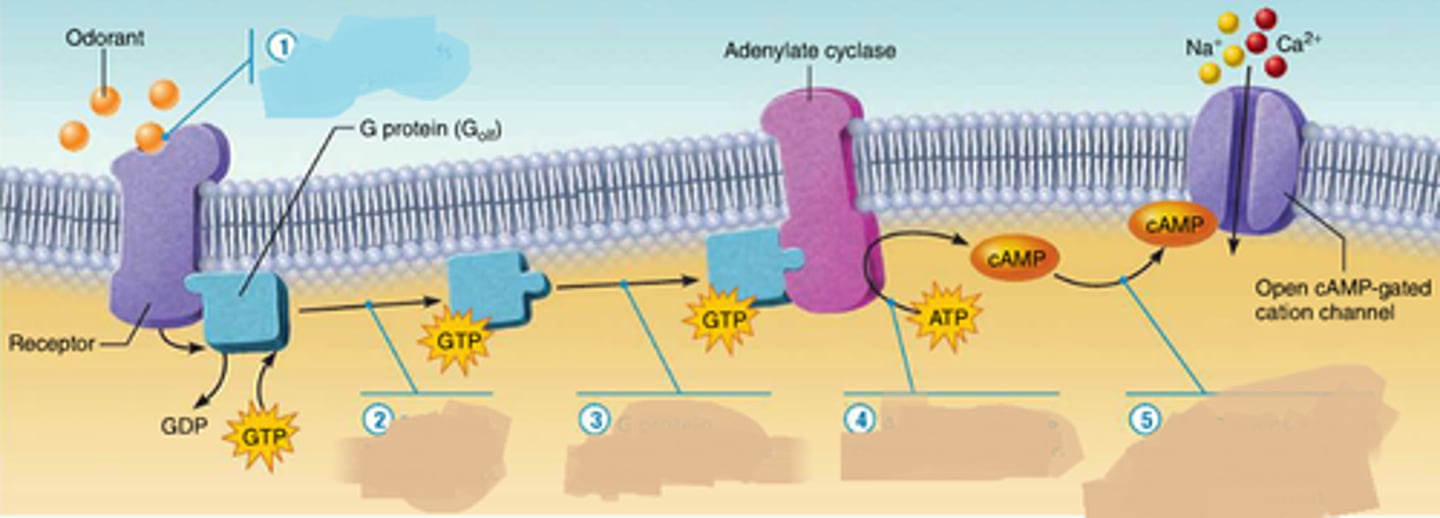
Peptide and protein hormones
-water-soluble and easily transported in blood; packaged in vesicles and released to blood by exocytosis; cannot cross cell membranes, so receptors are on the exterior of target cells.