chemistry final_ chapters 1-3
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
element
composed of one type of atom
compound
composed of two or more elements
homogenous mixture
a mixture with a uniform composition throughout
heterogenous mixture
a mixture with a non-uniform composition
physical properties
characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's identity. (phase changes, mixing, size changes, dissolving)
chemical properties
characteristics that are observed only after a chemical reaction has taken place (rusting, combustion, spoiling)
extensive properties
depend on amount of material used
intenstive properties
does not depend on the amount but the nature of element
density
mass/volume
law of mass conservation
matter can neither be destroyed or created, only changed in form
law of multiple proportions
when an element combines with a different element to form multiple compounds, the ratio of the masses of one element to a fixed amount of the second element is the ratio of small whole number
law of definite composition
a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it comes from
what did Dalton do
elements are made of tiny particles
atoms are indestructible
compounds always have the same relative numbers and types of atoms
all atoms of a given element are identical
what did thompson do
cathode rays tubes, discovered electron, plum pudding model
Millikan's oil drop experiment
found the charge of an electron
rutherford
discovered nucleus using gold foil experiment
atomic number
number of protons in an atom of an element
mass number
mass of atom (protons+neutrons)
average atomic mass
atomic mass= sum of (mass of isotope) (fractional abundance of isotope)
wavelength
distance between troughs
frequency
number of waves that pass a particular point in 1 second
speed of light
height of wave
photoelectric effect
a phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from the surface of metal when light strikes it
absorption
excitement
emisson
relaxation
energy of a photon
E=hv=hc/λ
energies and wavelengths of emitted photons
-2.179× 10^-18 (1/nf - 1/ni)
de brogiles wavelength
λ=h/vm
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know simultaneously both momentum and position of a particle with certainty
schrodinger’s equation
explains the wave-particle duality of the electron
principle quantum number (n)
corresponds to Bohrs energy level, shells or levels
angular momentum quantum number (l)
describes the shape of the orbital, referred to as subshells, equal to (n-1)
magnetic quantum number (ml)
orientation of space in orbital, possible values of -l to l
electron spin (ms)
½ or -1/2
pauli exclusion principle
if an orbital can only hold 2 electrons, then the maximum number of electrons allowed in any sublevel can be determined
hunds rule
the most stable arrangement of electron in a subshell is the one with the greatest number of unpaired e-s or parallel spins
aufbau principle
energy level and sublevels fill from lowest energy to high s p d f
Outer electrons or valence electrons
highest energy level (highest n level)
core electrons
non-valence electrons
diamagnetic
not attracted to a magnetic field
paramagnetic
attracted to a magnetic field
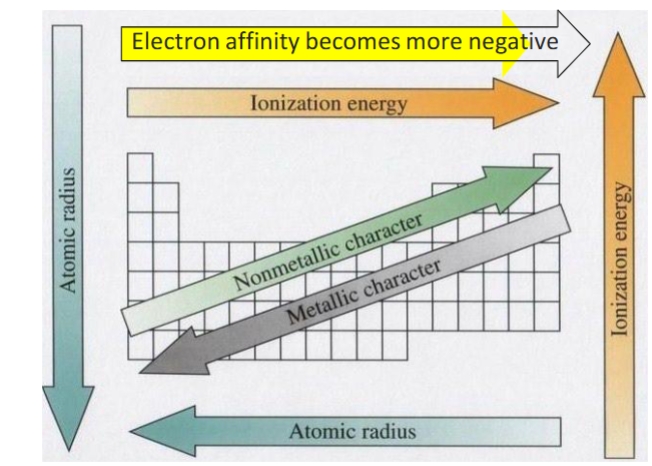
atomic radius
increases down a group, decreases across period (Rb is the biggest atom)
ionization energy
the minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion—> decreases down a period, increases as you move across a period (helium has the highest ionization energy)
exceptions to ionization energy pattern
boron and beryllium because it costs less energy to ionize
electron affinity
how likely an atom is to accept an electron- increases across a period
metallic character
metallic character increases down a group, decreases across a period (Fr is the most metallic)
periodic trends