wk 1 - intro to radiology and physics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
who uses dental radiographs
oral surgeons
orthodontists
general
periodontists
endodontists
TMJ
Legal
fistula
infection in the gum
purpose of dental radiographs
pt ed
diagnoses
localize lesions and foreign objects
provide info during tx
aid in concerns/thoughts
evaluation of periodontal bone
identify pathology, lesions, anomalies, etc
measure growth
every child should get an orthodontic evaluation by
8 yo to take sure everything is correct in the mouth
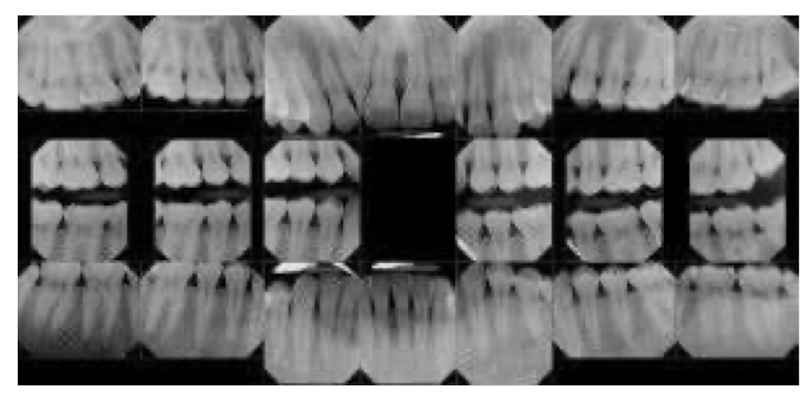
bite wings show
both arches
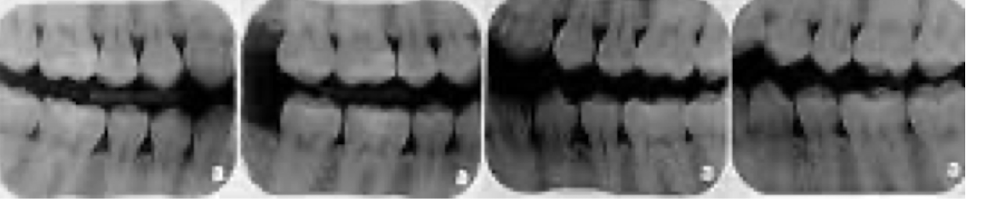
full mouth series shows
every tooth in the mouth and should ALWAYS start in anterior when exposing
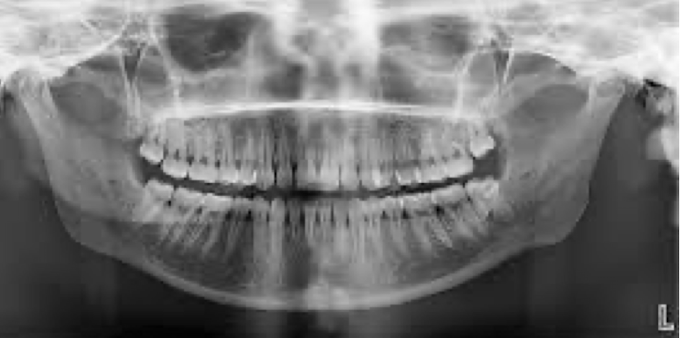
panoramic shows
mouth as a whole, less detailed
check up series consists of
2 top, 1 bottom,and bite wings
in a full mouth series, what tooth should ALWAYS be centered
second molar
a diagonostic radiograph shows
apices and a bit above
are DH in NYS allowed to diagnose
NO
Wilhelm Roentgen
discovered xrays, 1895, germany
Otto Walkoff
first dental radiograph, Germany
William Rollins
possible 1st US dental radiograph
focused on pt and operator safety and dangers of radiation
Edmund Kells
possible 1st US dental radiograph
discovered time and temp of developing
Kurks tube
tube with light and shadow
Coolidge tube
controlled ionization using heat filaments
Dental xrays are dangerous because
they are ionizing which can change cell structure
matter
anything that occupies space
energy
ability to over come resistance and do work
atom
made of proton, neutron, and electrons
molecule
group of atoms that retain properties
how many elements are there
118
smallest particle of an element is an
atom
atoms are usually _____ charged
neutrally
nucleus of an atom is made of
protons and neutrons
electrons
orbit nucleus and negatively charged
max # of shells an atom can have
7 shells, K - Q
K shell
closest to nucleus
strongest binding energy
binding energy
energy needed to remove the electron from shell
K shell max # of electrons
2
atomic number is
number of atoms
ONLY atom that is stable without neutrons
Hydrogen
ionization
production of ions or production of changing an atom into an ion
positively charged atom is a result of
a loss of an electron
negatively charged atom is a result of
a gain of an electron
ion pairs form when
electrons are removed from an atom during ionization
electromagnetic radiation
wavelike energy movement through space and matter
electromagnetic spectrum
radiations are arranged in an orderly manner according to their energies
properties of electromagnetic spectrum
travel at speed of light in a vacuum
have no electrical charge
have no mass
pass thru space as particles and in a wavelike motion
give off electrical field and magnetic field perpendicular to electric field
have energies that are measurable and different
distance - crest to crest (wavelength)
frequency - #of crests per second
x-rays on electromagnetic spectrum
short wavelength
high energy
high frequency
wavelength is measured
Angstroms (A)
dental radiographs are _____ Angstroms
.1-5A
frequency
number of crests passing a given point per second
frequency measured in
Hertz (Hz)
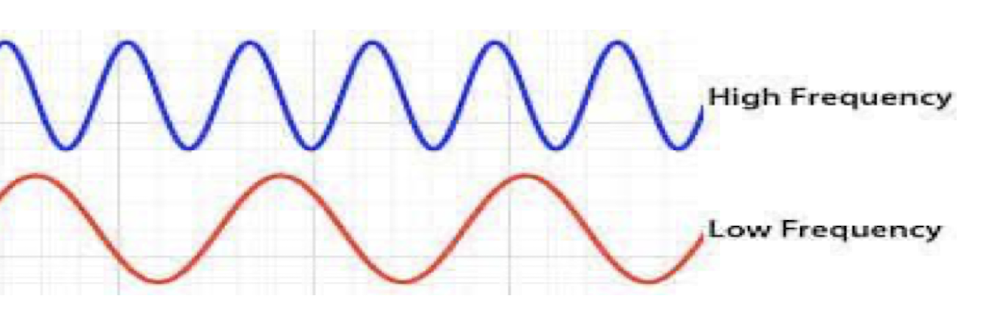
low frequency
long waves
low energy (Grenz rays)
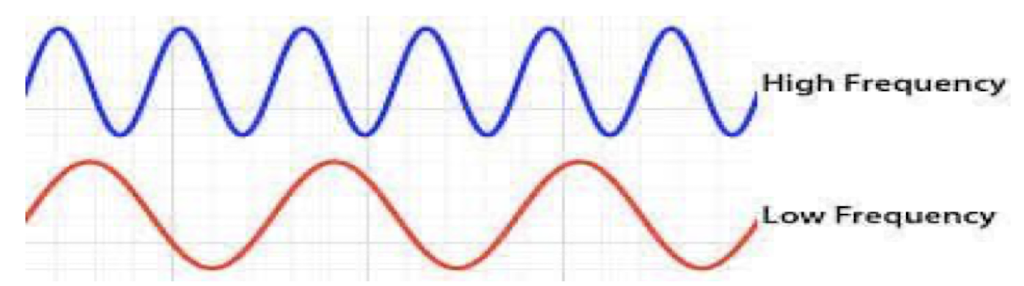
high frequency
short wavelength
high energy (penetrating power)
background radiation
all sources combined
cosmic - sun
terrestrial radiation - in ground
naturally occurring - unstable atoms that were ingested or inhaled
man made radiation exposure
48% of exposure and 2% consumer products
dental - xrays
medical - CT, xrays
consumer products - cigarettes, tv, smoke detectors