PSY100 - Midterm Exam Review
1/247
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
248 Terms
Structuralism contributor
Wilhelm Wundt & Edward Tichner
Wilhelm Wundt
Founded experimental psychology and created thought meter and voluntarism, and mental process hierarchy
Voluntarism
an approach that emphasizes the role of will and choice in determine thoughts, perceptions and behaviors
Structuralism
involves breaking down the mind into small sections, such as sensations, images, and feelings.
Edward Tichner
wundet’s student, believed in structuralism
Functionalism contributor
William James
William James
coined stream of consciousness, ideas people experience when awake + functionalism
Functionalism
views behavior as purposeful and contributing to survival.
Behaviourism contributor
John Waston, Edward Thorndike, B.F Skinner
Behaviorism
measurement of observable behaviors
John B. Watson
Tied psychology to the study of observable behaviors (brain images / reaction times) - little albert
Edward Thorndike
Law of effect: behavior with more pleasant outcomes are more likely to reoccur
B.F Skinner
extended thorndike’s idea in experimentation of how frequent behaviours performed with the Skinner box (reward/punishment)
Humanism Contributor
Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow
Humanism
people as inherently good and motivated to learn and improve.
Max Wertheimer
founded gestalt psychology and focused on the whole of behaviour
Gestalt Psychology
looks at the human mind and behavior as a whole focusing on principles such as proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, and simplicity.
demand characteristics
hints that influence particpants bejaviours
social desirable bias
survery responders answeing to beviewed favourably
hawthorne effect
change in subjects behaviour simply but the awareness of being observed
better than average effect
most people perceive themselves as bette than average
Objectivity
Conclusions based on facts without influence from emotion or biases.
Subjectivity
Conclusions that reflect personal point of view.
Theory
A set of facts and relationships that can explain and predict phenomena.
scientific method
a systematic procedure of observing and measuring phenomena, used to achieve the goals of description, prediction, and explanation
Scientific Theories must Consist of?
Testable, Falsifiable, Parsimonious
What are the examples of psychological theories?
intergroup contact, social comparison, social learning
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for a situation, often taking the form "if A happens, then B will result."
Variable
a characteristic or condition that changes or has different values for different individuals
Independent Variable
manipulated in an experiment to see its impact on the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
measured to see how it is affected by the independent variable.
What are the Definitions of Variables?
Conceptual (textbook definition) and Operational (definition of constructs)
Constructs
Internal attributes or characteristics that cannot be directly observed but are useful for describing and explaining behavior
Population
The group that researchers want to generalize their findings to.
Sample
The group of individuals from the population who are part of a study.
Descriptive Methods
concerned with a single variable of interest and may lead to claims regarding the frequency of a behavior.
Naturalistic observation
Passive observation
Observers do not change or alter ongoing behaviour
Participant observation
Active observation
Researcher actively involved in the situation
Labratory observation
Systematic observation
are made within a laboratory setting
what are the problems of descriptive methods?
Reactivity → demand characteristics
Observer/experimenter bias
Self-report bias → social desirable bias and better than average effect
Correlational Methods
associations between two or more variables; without manipulation
single group of participants
does not allow us to make causal claims
Correlation coefficient
shows the strength and the direction of the relationship between two variables (ranges from -1.00 to +1.00)
what are the problems with correlational methods?
Directionality → unsure which variable is influencing the other
Third variable problem → unsure whether another variable is also affecting the other two to change
Experimental Methods
examine cause and effect relationships between two variables
Experiments
Tightly controlled, Involve manipulating an independent variable to determine its impact on dependent variable
causal claims
only be made after a justified experiment
random assignment
an equal chance of being placed in any group in an experiment
random sample
equal chance of being chosen to participate
confound
anything that may unintentionally vary along with the independent variable
quasi experiement
no random assignment is possible
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
longitudinal study
search in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
descriptive statistics
organized data into meaningful patterns and summaries
normal distrubution/curve
a symmetrical probability function
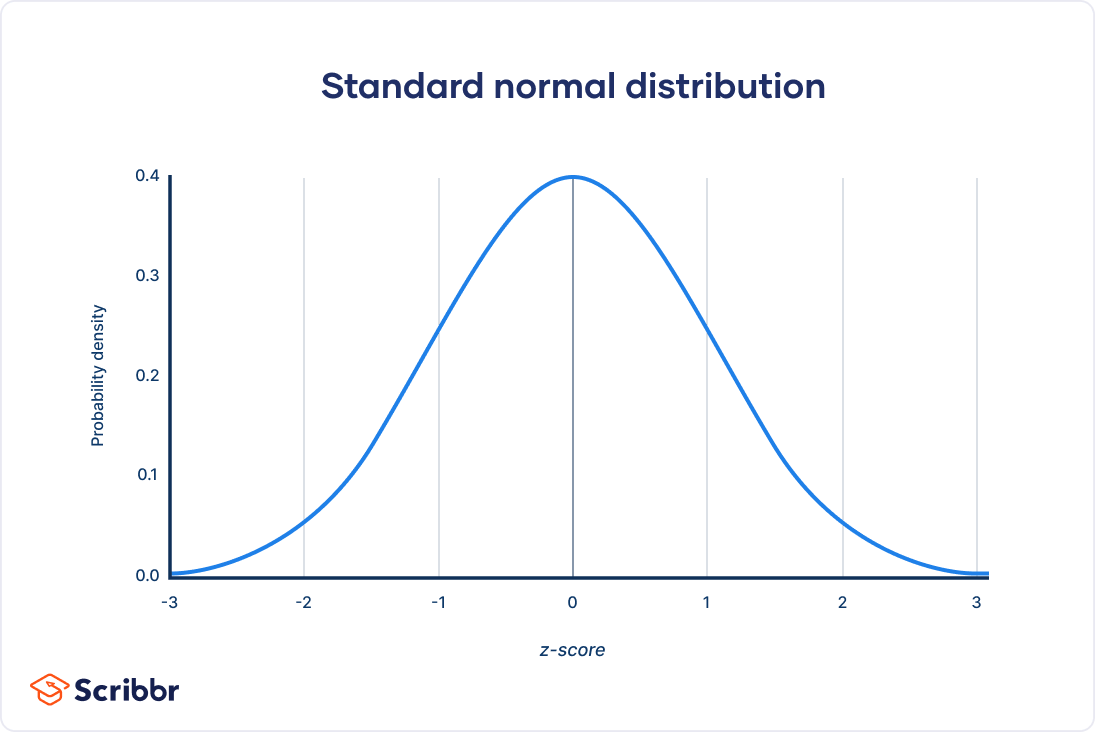
Standard deviation
measure of how tightly cluster around the mean and group of scores
inferential statistics
extends conclusions from a sample to a population
Statistical significance
deciding whether an observed result is due to chance
WEIRD Samples
the science over-relies on these types of participants: Western, Educated, Industrialised, Rich, and Democratic
validity
accuracy in results (must be reliable to be valid)
construct validity
how accurate are my operationalization?
external validity
extent to which we can generalize findings to real-world settings
internal validity
extent to which the study established a cause and effect relationship between variables
reliablity
consistency (doesn’t have to be valid)
interrater reliability
different judges agree in their assessment decisions
test/retest reliability
administering the same test twice over a period of time to a group of individuals
Epigenetics
changes in the gene expression that are due to non-genetic behaviour
Hereditary vs Heritability
genetic transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring
estimate of genetic proportion of variation in some specific trait (in a population, not individual)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord, which are responsible for processing and coordinating information.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The network of nerves that connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
neuron
basic units of the nervous system; operate through electrical impulses
axon
where action potiental travels down; transmit info to other neurons
dendrite
receives information from neurons
myelin sheath
insulator for axons; allow rapid transmission of signals
cell body
large central mass of neurons; contains nucleus
nodes of raniver
gaps in axon
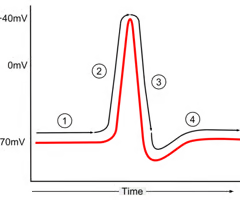
action potential labelling
1 - resting potential
2 - depolarization
3 - repolarization
4 - resting potential
action potential
neural impulse that travels along the axon causes release of chemicals from terminal buttons
resting potential
polarized state; negative INSID the cell. more sodium (Na+) OUTSIDE and more potassium (K+) INSIDE. (-70mV)
synapse
area between two neurons
receptor
part of a nerve that recieves and reads neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters
chemical signals that transmit signals to one neuron to another
motor neurons
send signals from the CNS to the skeletal muscles
sensory neuron
send information from sensory system, processes input from environment and senses
SAME
Sensory = Afferent, Motor = Efferent
Agonists
Drugs that enhance the actions of endogenous neurotransmitters by binding receptors and producing a response that mimics the effects.
Reuptake
neurotransmitters are recycled back into the neuron by transporters and stored for later use.
Antagonist
Drugs that inhibit the actions of endogenous neurotransmitters by blocking release of neurotransmitters, destroying neurotransmitters in the synapse, or mimicking a neurotransmitter to block neurotransmitter binding.
Neuroplasticity
The brain's ability to be changed or reorganized as a result of experience, drugs, or injury.
glutamate
primary excitatory transmitter
GABA
primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Serotonin
mood, impulsiveness, hunger, sleep
Dopamine
reward and motivation, voluntary movement
Acetylcholine
movement, memory, cognition, sleep
Epinephrine
(adrenaline) energy
Norepinephrine
arousal, alertness
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
Brainstem
Controls life-sustaining functions of the autonomic nervous system; breathing, digestion, and heartbeat.
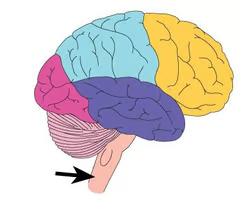
Cerebellum
coordinated movement and balance.
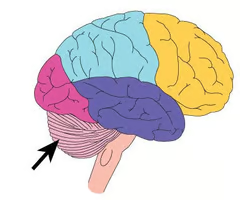
Hypothalamus
The brain's master regulatory structure that connects the nervous system to the endocrine system and controls functions related to homeostasis.
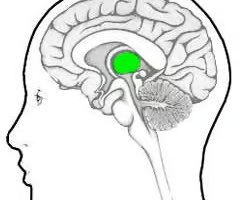
Thalamus
Acts as a relay station and handles all incoming sensory information except smell.